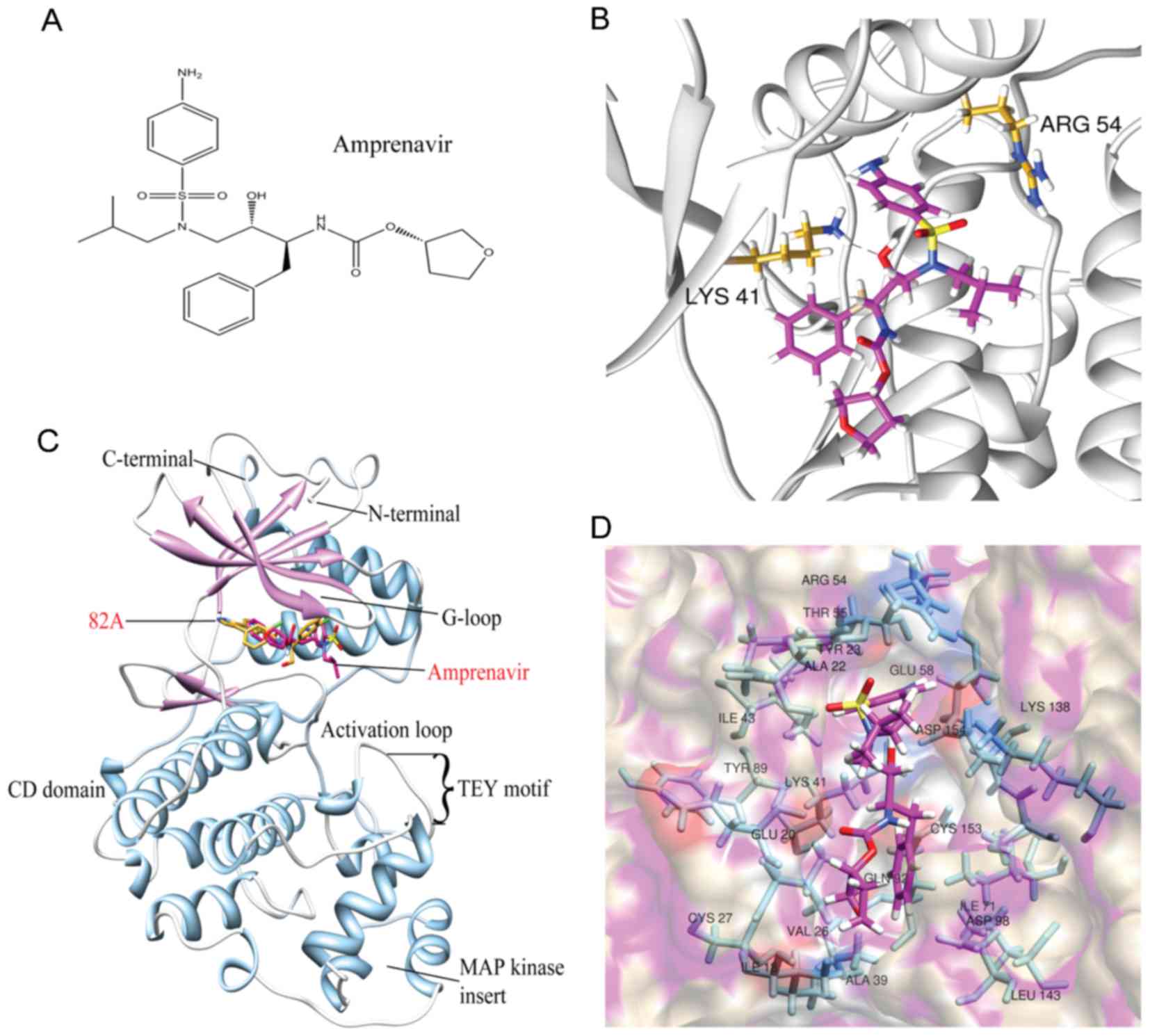
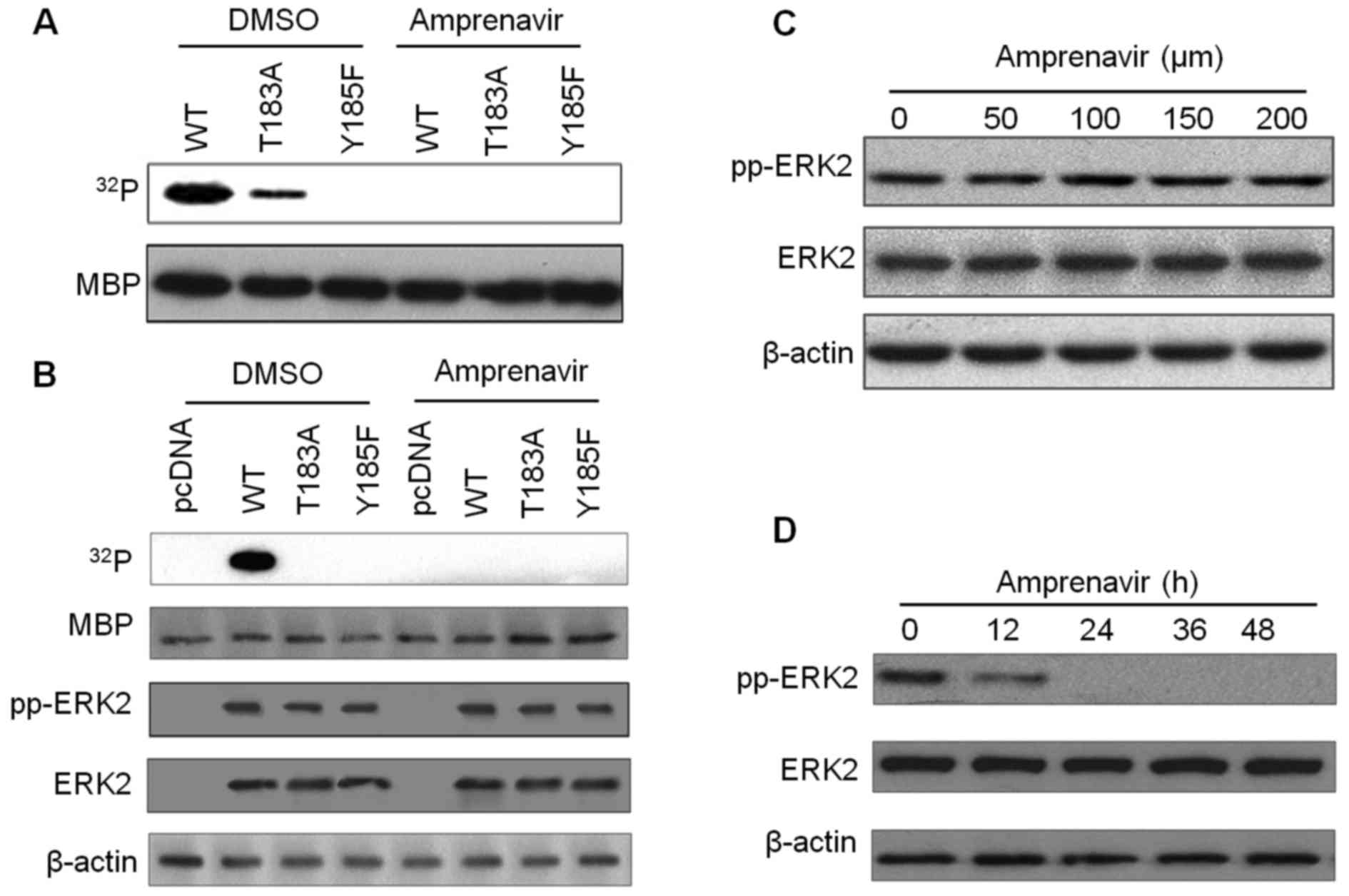
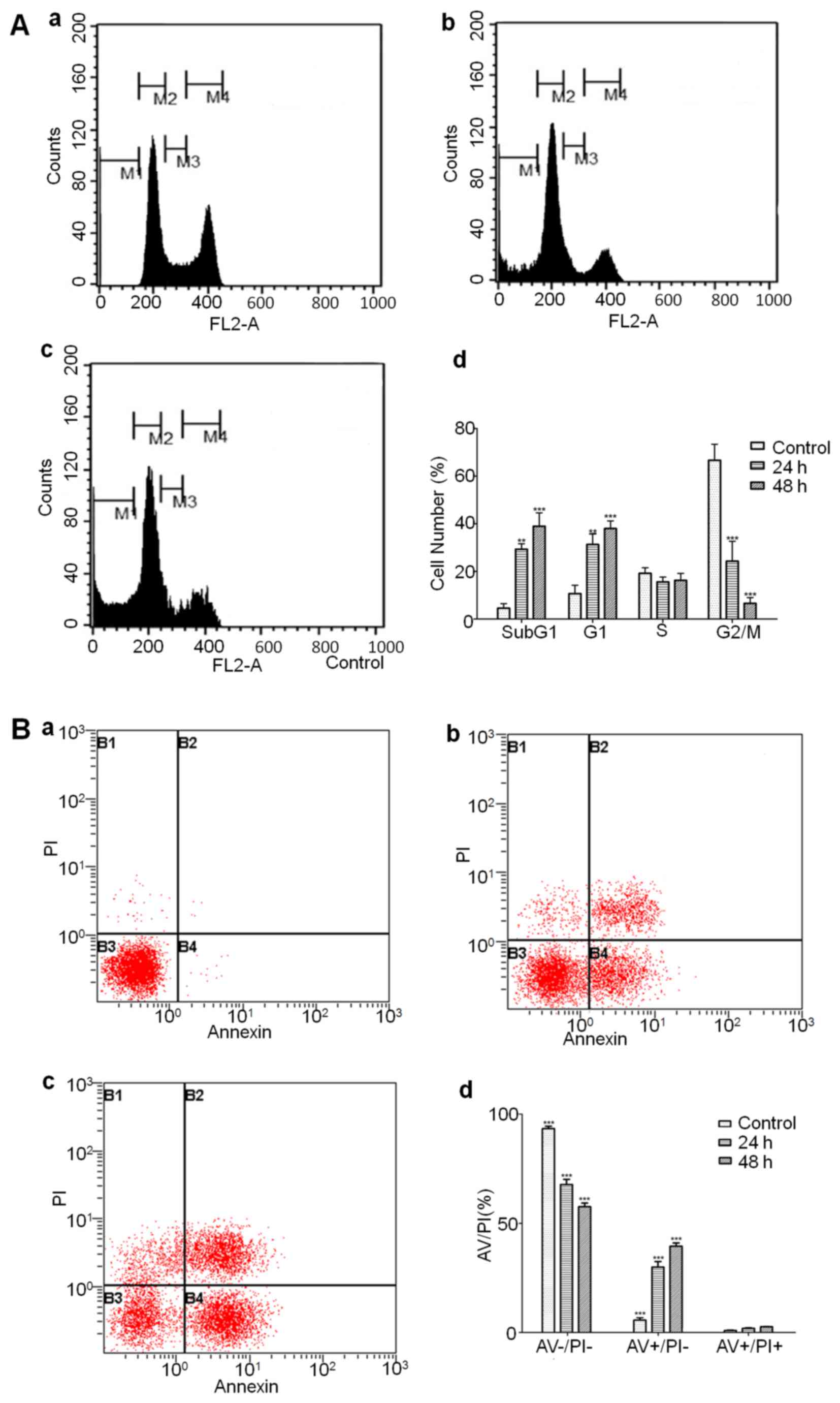
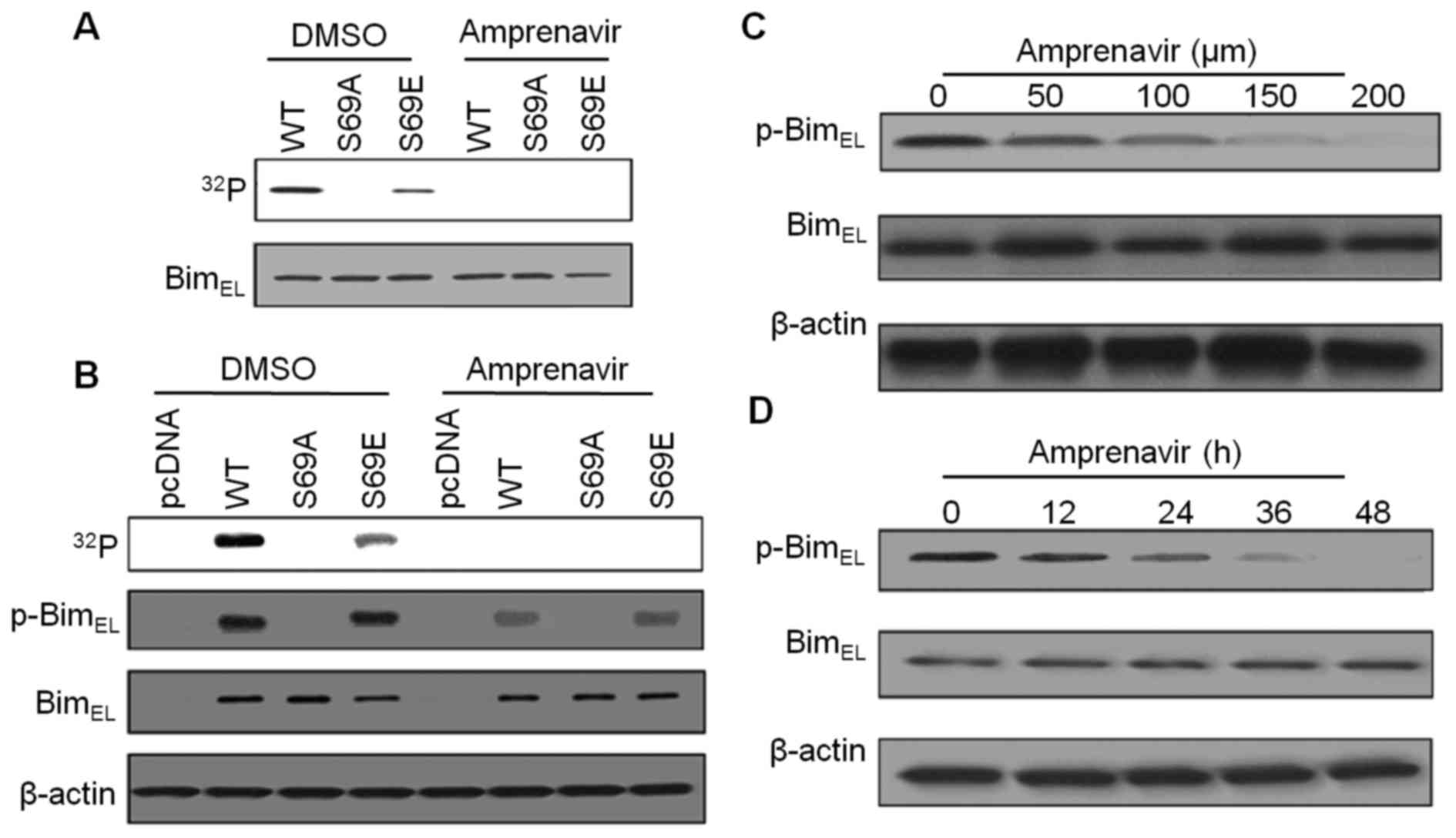
|
1
|
Giacinti L, Claudio PP, Lopez M and
Giordano A: Epigenetic information and estrogen receptor alpha
expression in breast cancer. Oncologist. 11:1–8. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
O'Connor L, Strasser A, O'Reilly LA,
Hausmann G, Adams JM, Cory S and Huang DC: Bim: A novel member of
the Bcl-2 family that promotes apoptosis. EMBO J. 17:384–395. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Akiyama T, Dass CR and Choong PF:
Bim-targeted cancer therapy: A link between drug action and
underlying molecular changes. Mol Cancer Ther. 8:3173–3180. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gogada R, Yadav N, Liu J, Tang S, Zhang D,
Schneider A, Seshadri A, Sun L, Aldaz CM, Tang DG, et al: Bim, a
proapoptotic protein, up-regulated via transcription factor
E2F1-dependent mechanism, functions as a prosurvival molecule in
cancer. J Biol Chem. 288:368–381. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Luciano F, Jacquel A, Colosetti P, Herrant
M, Cagnol S, Pages G and Auberger P: Phosphorylation of Bim-EL by
Erk1/2 on serine 69 promotes its degradation via the proteasome
pathway and regulates its proapoptotic function. Oncogene.
22:6785–6793. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ewings KE, Hadfield-Moorhouse K, Wiggins
CM, Wickenden JA, Balmanno K, Gilley R, Degenhardt K, White E and
Cook SJ: ERK1/2-dependent phosphorylation of BimEL promotes its
rapid dissociation from Mcl-1 and Bcl-xL. EMBO J. 26:2856–2867.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang H, Qian DZ, Tan YS, Lee K, Gao P,
Ren YR, Rey S, Hammers H, Chang D, Pili R, et al: Digoxin and other
cardiac glycosides inhibit HIF-1alpha synthesis and block tumor
growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:19579–19586. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Miller SC, Huang R, Sakamuru S, Shukla SJ,
Attene-Ramos MS, Shinn P, Van Leer D, Leister W, Austin CP and Xia
M: Identification of known drugs that act as inhibitors of
NF-kappaB signaling and their mechanism of action. Biochem
Pharmacol. 79:1272–1280. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Biechele TL, Camp ND, Fass DM, Kulikauskas
RM, Robin NC, White BD, Taraska CM, Moore EC, Muster J, Karmacharya
R, et al: Chemical-genetic screen identifies riluzole as an
enhancer of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in melanoma. Chem Biol.
17:1177–1182. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dudley JT, Deshpande T and Butte AJ:
Exploiting drug-disease relationships for computational drug
repositioning. Brief Bioinform. 12:303–311. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Okimoto N, Futatsugi N, Fuji H, Suenaga A,
Morimoto G, Yanai R, Ohno Y, Narumi T and Taiji M: High-performance
drug discovery: Computational screening by combining docking and
molecular dynamics simulations. PLoS Comput Biol. 5:e10005282009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kinoshita T, Yoshida I, Nakae S, Okita K,
Gouda M, Matsubara M, Yokota K, Ishiguro H and Tada T: Crystal
structure of human mono-phosphorylated ERK1 at Tyr204. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 377:1123–1127. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Aronov AM, Baker C, Bemis GW, Cao J, Chen
G, Ford PJ, Germann UA, Green J, Hale MR, Jacobs M, et al: Flipped
out: Structure-guided design of selective pyrazolylpyrrole ERK
inhibitors. J Med Chem. 50:1280–1287. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rose PW, Bi C, Bluhm WF, Christie CH,
Dimitropoulos D, Dutta S, Green RK, Goodsell DS, Prlic A, Quesada
M, et al: The RCSB Protein Data Bank: New resources for research
and education. Nucleic Acids Res. 41:D475–D482. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch
GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC and Ferrin TE: UCSF Chimera - a
visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J
Comput Chem. 25:1605–1612. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kuntz ID, Blaney JM, Oatley SJ, Langridge
R and Ferrin TE: A geometric approach to macromolecule-ligand
interactions. J Mol Biol. 161:269–288. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Knox C, Law V, Jewison T, Liu P, Ly S,
Frolkis A, Pon A, Banco K, Mak C, Neveu V, et al: DrugBank 3.0: A
comprehensive resource for 'omics' research on drugs. Nucleic Acids
Res. 39:D1035–D1041. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
O'Boyle NM, Banck M, James CA, Morley C,
Vandermeersch T and Hutchison GR: Open Babel: An open chemical
toolbox. J Cheminform. 3:332011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Irwin JJ, Sterling T, Mysinger MM, Bolstad
ES and Coleman RG: ZINC: A free tool to discover chemistry for
biology. J Chem Inf Model. 52:1757–1768. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lang PT, Brozell SR, Mukherjee S,
Pettersen EF, Meng EC, Thomas V, Rizzo RC, Case DA, James TL and
Kuntz ID: DOCK 6: Combining techniques to model RNA-small molecule
complexes. RNA. 15:1219–1230. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Van Der Spoel D, Lindahl E, Hess B,
Groenhof G, Mark AE and Berendsen HJ: GROMACS: Fast, flexible, and
free. J Comput Chem. 26:1701–1718. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Schüttelkopf AW and van Aalten DM: PRODRG:
A tool for highthroughput crystallography of protein-ligand
complexes. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 60:1355–1363. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Li C, Chen J, Lu B, Shi Z, Wang H, Zhang
B, Zhao K, Qi W, Bao J and Wang Y: Molecular switch role of Akt in
Polygonatum odoratum lectin-induced apoptosis and autophagy in
human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. PLoS One.
9:e1015262014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shi W, Deng J, Tong R, Yang Y, He X, Lv J,
Wang H, Deng S, Qi P, Zhang D, et al: Molecular mechanisms
underlying mangiferininduced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in
A549 human lung carcinoma cells. Mol Med Rep. 13:3423–3432.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang Y, Liu Y, Wang H, Li C, Qi P and Bao
J: Agaricus bisporus lectins mediates islet β-cell proliferation
through regulation of cell cycle proteins. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
237:287–296. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Jiagang D, Li C, Wang H, Hao E, Du Z, Bao
C, Lv J and Wang Y: Amygdalin mediates relieved atherosclerosis in
apolipoprotein E deficient mice through the induction of regulatory
T cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 411:523–529. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang W, Zheng Y, Xia Y, Ji H, Chen X, Guo
F, Lyssiotis CA, Aldape K, Cantley LC and Lu Z: ERK1/2-dependent
phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of PKM2 promotes the
Warburg effect. Nat Cell Biol. 14:1295–1304. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang Y, Wang H, Liu Y, Li C, Qi P and Bao
J: Antihyperglycemic effect of ginsenoside Rh2 by inducing islet
beta-cell regeneration in mice. Horm Metab Res. 44:33–40. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Yun J, Lv YG, Yao Q, Wang L, Li YP and Yi
J: Wortmannin inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of MCF-7
breast cancer cells. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 33:367–369.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
He JC, Husain M, Sunamoto M, D'Agati VD,
Klotman ME, Iyengar R and Klotman PE: Nef stimulates proliferation
of glomerular podocytes through activation of Src-dependent Stat3
and MAPK1,2 pathways. J Clin Invest. 114:643–651. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Biggs TE, Cooke SJ, Barton CH, Harris MP,
Saksela K and Mann DA: Induction of activator protein 1 (AP-1) in
macrophages by human immunodeficiency virus type-1 NEF is a
cell-typespecific response that requires both hck and MAPK
signaling events. J Mol Biol. 290:21–35. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Schrager JA, Der Minassian V and Marsh JW:
HIV Nef increases T cell ERK MAP kinase activity. J Biol Chem.
277:6137–6142. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kinoshita T, Warizaya M, Ohori M, Sato K,
Neya M and Fujii T: Crystal structure of human ERK2 complexed with
a pyrazolo[3,4-c]pyridazine derivative. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
16:55–58. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Park H, Bahn YJ, Jeong DG, Woo EJ, Kwon JS
and Ryu SE: Identification of novel inhibitors of extracellular
signal-regulated kinase 2 based on the structure-based virtual
screening. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 18:5372–5376. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ohori M, Kinoshita T, Okubo M, Sato K,
Yamazaki A, Arakawa H, Nishimura S, Inamura N, Nakajima H, Neya M,
et al: Identification of a selective ERK inhibitor and structural
determination of the inhibitor-ERK2 complex. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 336:357–363. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Aronov AM, Tang Q, Martinez-Botella G,
Bemis GW, Cao J, Chen G, Ewing NP, Ford PJ, Germann UA, Green J, et
al: Structure-guided design of potent and selective
pyrimidylpyrrole inhibitors of extracellular signal-regulated
kinase (ERK) using conformational control. J Med Chem.
52:6362–6368. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang Z, Canagarajah BJ, Boehm JC, Kassisà
S, Cobb MH, Young PR, Abdel-Meguid S, Adams JL and Goldsmith EJ:
Structural basis of inhibitor selectivity in MAP kinases.
Structure. 6:1117–1128. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ikezoe T, Saito T, Bandobashi K, Yang Y,
Koeffler HP and Taguchi H: HIV-1 protease inhibitor induces growth
arrest and apoptosis of human multiple myeloma cells via
inactivation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2. Mol Cancer Ther.
3:473–479. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Pyrko P, Kardosh A, Wang W, Xiong W,
Schönthal AH and Chen TC: HIV-1 protease inhibitors nelfinavir and
atazanavir induce malignant glioma death by triggering endoplasmic
reticulum stress. Cancer Res. 67:10920–10928. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Pajonk F, Himmelsbach J, Riess K, Sommer A
and McBride WH: The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-1 protease
inhibitor saquinavir inhibits proteasome function and causes
apoptosis and radiosensitization in non-HIV-associated human cancer
cells. Cancer Res. 62:5230–5235. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gills JJ1, Lopiccolo J, Tsurutani J,
Shoemaker RH, Best CJ, Abu-Asab MS, Borojerdi J, Warfel NA, Gardner
ER, Danish M, et al: Nelfinavir, A lead HIV protease inhibitor, is
a broadspectrum, anticancer agent that induces endoplasmic
reticulum stress, autophagy, and apoptosis in vitro and in vivo.
Clin Cancer Res. 13:5183–5194. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Esposito V, Verdina A, Manente L, Spugnini
EP, Viglietti R, Parrella R, Pagliano P, Parrella G, Galati R, De
Luca A, et al: Amprenavir inhibits the migration in human
hepatocarcinoma cell and the growth of xenografts. J Cell Physiol.
228:640–645. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|