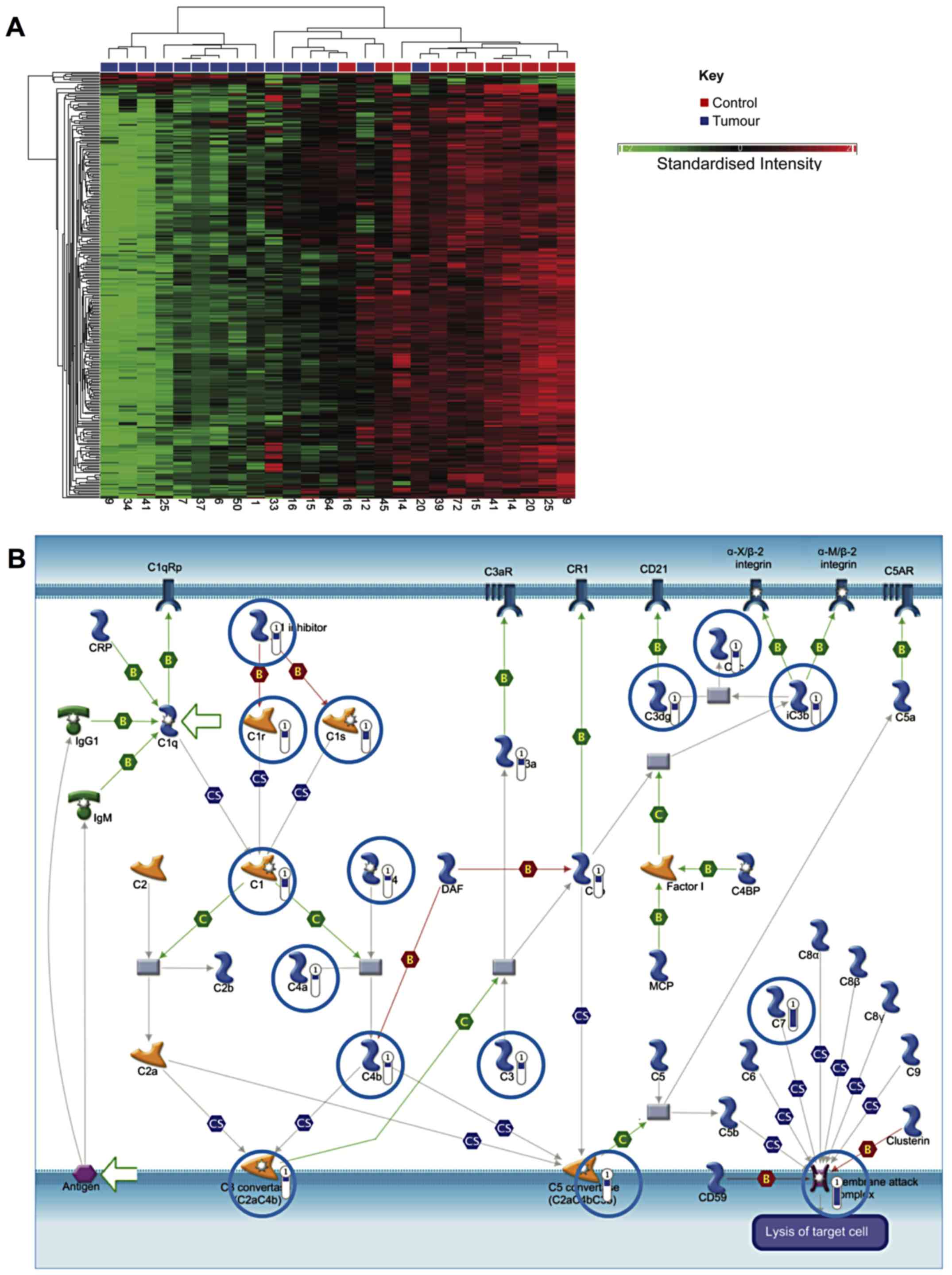
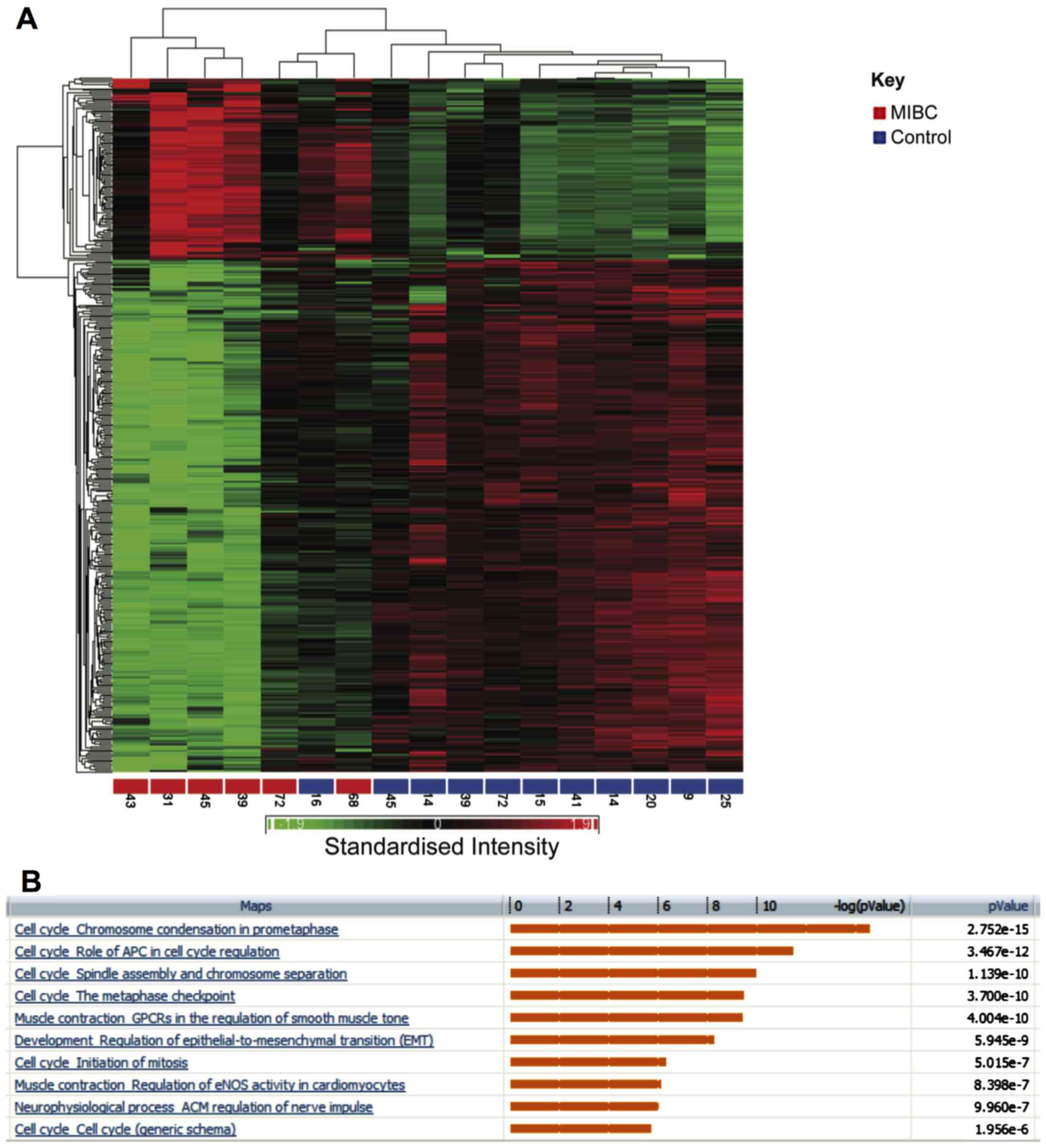
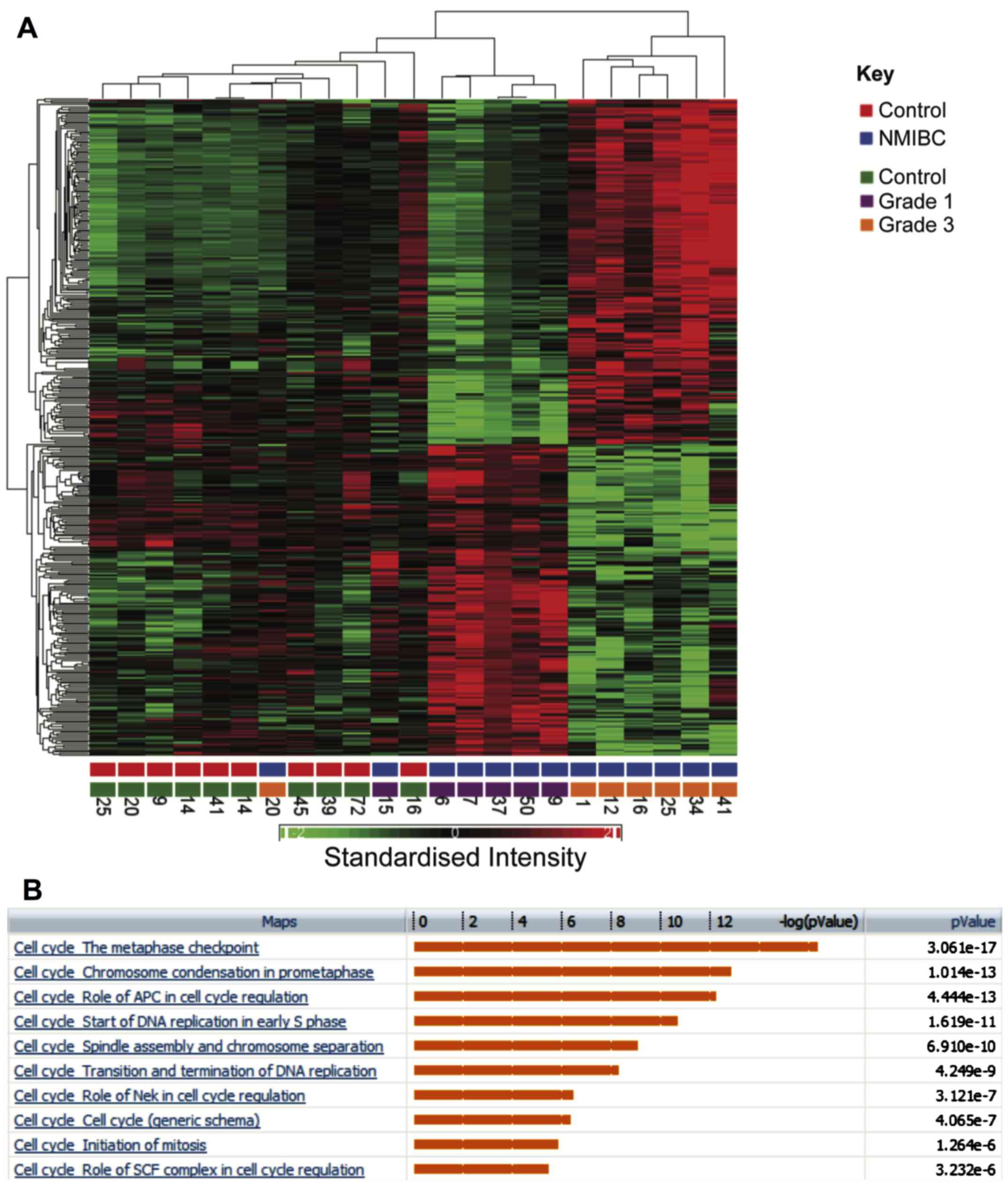
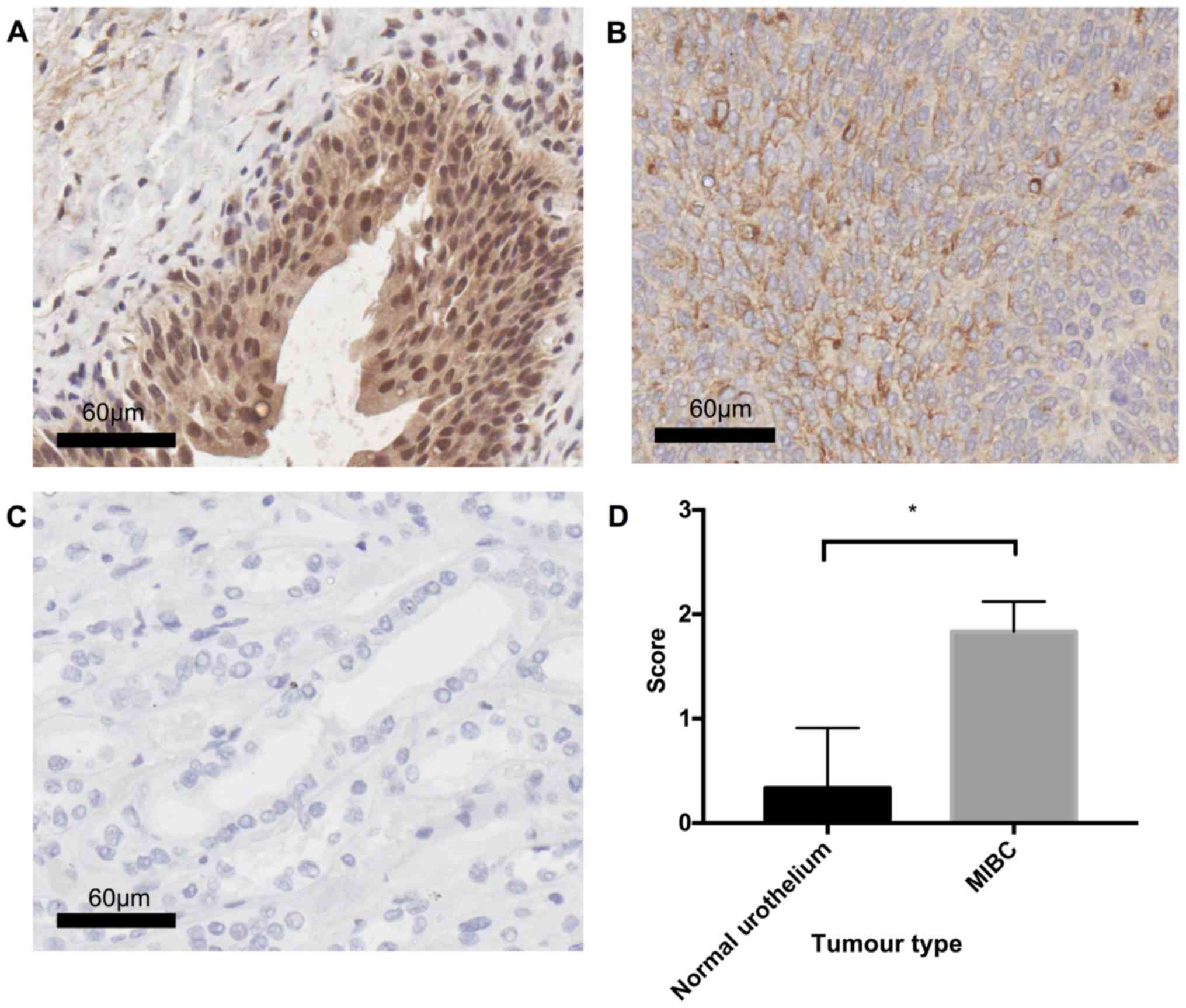
|
1
|
IARC: Cancer incidence and mortality
Worldwide. IARC CancerBase No. 10. Journal. 2015, http://globocan.iarc.fr.
|
|
2
|
Cancer Research UK: Bladder cancer
statistics. 2015, http://www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer-statistics/statistics-by-cancer-type/bladder-cancer.
|
|
3
|
Kaufman DS, Shipley WU and Feldman AS:
Bladder cancer. Lancet. 374:239–249. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sylvester RJ, van der Meijden AP,
Oosterlinck W, Witjes JA, Bouffioux C, Denis L, Newling DW and
Kurth K: Predicting recurrence and progression in individual
patients with stage Ta T1 bladder cancer using EORTC risk tables: a
combined analysis of 2596 patients from seven EORTC trials. Eur
Urol. 475–467. 2006.
|
|
5
|
Blaveri E, Simko JP, Korkola JE, Brewer
JL, Baehner F, Mehta K, Devries S, Koppie T, Pejavar S, Carroll P,
et al: Bladder cancer outcome and subtype classification by gene
expression. Clin Cancer Res. 11:4044–4055. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Elsamman E, Fukumori T, Ewis AA, Ali N,
Kajimoto K, Shinohara Y, Ishikawa M, Takahashi M, Nishitani MA,
Baba Y, et al: Differences in gene expression between noninvasive
and invasive transitional cell carcinoma of the human bladder using
complementary deoxyribonucleic acid microarray: Preliminary
results. Urol Oncol. 24:109–115. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Riester M, Taylor JM, Feifer A, Koppie T,
Rosenberg JE, Downey RJ, Bochner BH and Michor F: Combination of a
novel gene expression signature with a clinical nomogram improves
the prediction of survival in high-risk bladder cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 18:1323–1333. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sanchez-Carbayo M, Socci ND, Lozano J,
Saint F and Cordon-Cardo C: Defining molecular profiles of poor
outcome in patients with invasive bladder cancer using
oligonucleotide microarrays. J Clin Oncol. 24:778–789. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Irizarry RA, Hobbs B, Collin F,
Beazer-Barclay YD, Antonellis KJ, Scherf U and Speed TP:
Exploration, normalization, and summaries of high density
oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostatistics. 4:249–264.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu Z, Irizarry RA, Gentleman R,
Martinez-Murillo F and Spencer F: A Model-based background
adjustment for oligonucleotide expression arrays. J Am Stat Assoc.
99:909–917. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Bolstad BM, Collin F, Simpson KM, Irizarry
RA and Speed TP: Experimental design and low-level analysis of
microarray data. Int Rev Neurobiol. 60:25–58. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pawitan Y, Michiels S, Koscielny S,
Gusnanto A and Ploner A: False discovery rate, sensitivity and
sample size for microarray studies. Bioinformatics. 21:3017–3024.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Edgar R, Domrachev M and Lash AE: Gene
Expression Omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array
data repository. Nucleic Acids Res. 30:207–210. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Dyrskjøt L, Kruhøffer M, Thykjaer T,
Marcussen N, Jensen JL, Møller K and Ørntoft TF: Gene expression in
the urinary bladder: A common carcinoma in situ gene expression
signature exists disregarding histopathological classification.
Cancer Res. 64:4040–4048. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Als AB, Dyrskjøt L, von der Maase H, Koed
K, Mansilla F, Toldbod HE, Jensen JL, Ulhøi BP, Sengeløv L, Jensen
KM, et al: Emmprin and survivin predict response and survival
following cisplatin-containing chemotherapy in patients with
advanced bladder cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 13:4407–4414. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhao WM and Fang G: Anillin is a substrate
of anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) that controls
spatial contractility of myosin during late cytokinesis. J Biol
Chem. 280:33516–33524. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Olakowski M, Tyszkiewicz T, Jarzab M, Krol
R, Oczko-Wojciechowska M, Kowalska M, Kowal M, Gala GM, Kajor M,
Lange D, et al: NBL1 and anillin (ANLN) genes over-expression in
pancreatic carcinoma. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 47:249–255. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gruss OJ and Vernos I: The mechanism of
spindle assembly: Functions of Ran and its target TPX2. J Cell
Biol. 166:949–955. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ronkainen H, Hirvikoski P, Kauppila S and
Vaarala MH: Anillin expression is a marker of favourable prognosis
in patients with renal cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 25:129–133.
2011.
|
|
21
|
Zaravinos A, Lambrou GI, Volanis D,
Delakas D and Spandidos DA: Spotlight on differentially expressed
genes in urinary bladder cancer. PLoS One. 6:e182552011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang Z, Zhang G and Kong C: High
expression of polo-like kinase 1 is associated with the metastasis
and recurrence in urothelial carcinoma of bladder. Urol Oncol.
31:1222–1230. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Stadler WM, Vaughn DJ, Sonpavde G,
Vogelzang NJ, Tagawa ST, Petrylak DP, Rosen P, Lin CC, Mahoney J,
Modi S, et al: An open-label, single-arm, phase 2 trial of the
Polo-like kinase inhibitor volasertib (BI 6727) in patients with
locally advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer. Cancer.
120:976–982. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ahmed M, Behera R, Chakraborty G, Jain S,
Kumar V, Sharma P, Bulbule A, Kale S, Kumar S, Mishra R, et al:
Osteopontin: A potentially important therapeutic target in cancer.
Expert. Opin Ther Targets. 15:1113–1126. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Xu ST, Guo C, Ding X, Fan WJ, Zhang FH, Xu
WL and Ma YC: Role of osteopontin in the regulation of human
bladder cancer proliferation and migration in T24 cells. Mol Med
Rep. 11:3701–3707. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Coppola D, Szabo M, Boulware D, Muraca P,
Alsarraj M, Chambers AF and Yeatman TJ: Correlation of osteopontin
protein expression and pathological stage across a wide variety of
tumor histologies. Clin Cancer Res. 10:184–190. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ke HL, Chang LL, Yang SF, Lin HH, Li CC,
Wu DC and Wu WJ: Osteopontin overexpression predicts poor prognosis
of upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma. Urol Oncol.
29:703–709. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zaravinos A, Volanis D, Lambrou GI,
Delakas D and Spandidos DA: Role of the angiogenic components,
VEGFA, FGF2, OPN and RHOC, in urothelial cell carcinoma of the
urinary bladder. Oncol Rep. 28:1159–1166. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fang ZQ, Zang WD, Chen R, Ye BW, Wang XW,
Yi SH, Chen W, He F and Ye G: Gene expression profile and
enrichment pathways in different stages of bladder cancer. Genet
Mol Res. 12:1479–1489. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Imano M, Satou T, Itoh T, Sakai K,
Ishimaru E, Yasuda A, Peng YF, Shinkai M, Akai F, Yasuda T, et al:
Immunohistochemical expression of osteopontin in gastric cancer. JJ
Gastrointest Surg. 13:1577–1582. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kita Y, Natsugoe S, Okumura H, Matsumoto
M, Uchikado Y, Setoyama T, Owaki T, Ishigami S and Aikou T:
Expression of osteopontin in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Br J Cancer. 95:634–638. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Song JY, Lee JK, Lee NW, Yeom BW, Kim SH
and Lee KW: Osteopontin expression correlates with invasiveness in
cervical cancer. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 49:434–438. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Forootan SS, Foster CS, Aachi VR, Adamson
J, Smith PH, Lin K and Ke Y: Prognostic significance of osteopontin
expression in human prostate cancer. Int J Cancer. 118:2255–2261.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Weber GF, Lett GS and Haubein NC:
Osteopontin is a marker for cancer aggressiveness and patient
survival. Br J Cancer. 103:861–869. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Collins AL, Rock J, Malhotra L, Frankel WL
and Bloomston M: Osteopontin expression is associated with improved
survival in patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg
Oncol. 19:2673–2678. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhao L, Wang Y, Qu N, Huang C and Chen L:
Significance of plasma osteopontin levels in patients with bladder
urothelial carcinomas. Mol Diagn Ther. 16:311–316. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Naor D, Sionov RV and Ish-Shalom D: CD44:
Structure, function, and association with the malignant process.
Adv Cancer Res. 71:241–319. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ang C, Chambers AF, Tuck AB, Winquist E
and Izawa JI: Plasma osteopontin levels are predictive of disease
stage in patients with transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder.
BJU Int. 96:803–805. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lim J and Thiery JP:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions: Insights from development.
Development. 139:3471–3486. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Baumgart E, Cohen MS, Silva Neto B, Jacobs
MA, Wotkowicz C, Rieger-Christ KM, Biolo A, Zeheb R, Loda M,
Libertino JA, et al: Identification and prognostic significance of
an epithelialmesenchymal transition expression profile in human
bladder tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 13:1685–1694. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Varela JC, Atkinson C, Woolson R, Keane TE
and Tomlinson S: Upregulated expression of complement inhibitory
proteins on bladder cancer cells and anti-MUC1 antibody immune
selection. Int J Cancer. 123:1357–1363. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Babjuk M, Soukup V, Pesl M, Kostirova M,
Drncova E, Smolova H, Szakacsova M, Getzenberg R, Pavlik I and
Dvoracek J: Urinary cytology and quantitative BTA and UBC tests in
surveillance of patients with pTapT1 bladder urothelial carcinoma.
Urology. 71:718–722. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Cheng ZZ, Corey MJ, Pärepalo M, Majno S,
Hellwage J, Zipfel PF, Kinders RJ, Raitanen M, Meri S and Jokiranta
TS: Complement factor H as a marker for detection of bladder
cancer. Clin Chem. 51:856–863. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Warzecha CC, Sato TK, Nabet B, Hogenesch
JB and Carstens RP: ESRP1 and ESRP2 are epithelial
cell-type-specific regulators of FGFR2 splicing. Mol Cell.
33:591–601. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Diez de Medina SG, Chopin D, El Marjou A,
Delouvee A, LaRochelle WJ, Hoznek A, Abbou C, Aaronson SA, Thiery
JP and Radvanyi F: Decreased expression of keratinocyte growth
factor receptor in a subset of human transitional cell bladder
carcinomas. Oncogene. 14:323–330. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chaffer CL, Brennan JP, Slavin JL, Blick
T, Thompson EW and Williams ED: Mesenchymal-to-epithelial
transition facilitates bladder cancer metastasis: Role of
fibroblast growth factor receptor-2. Cancer Res. 66:11271–11278.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network:
Comprehensive molecular characterization of urothelial bladder
carcinoma. Nature. 507:315–322. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|