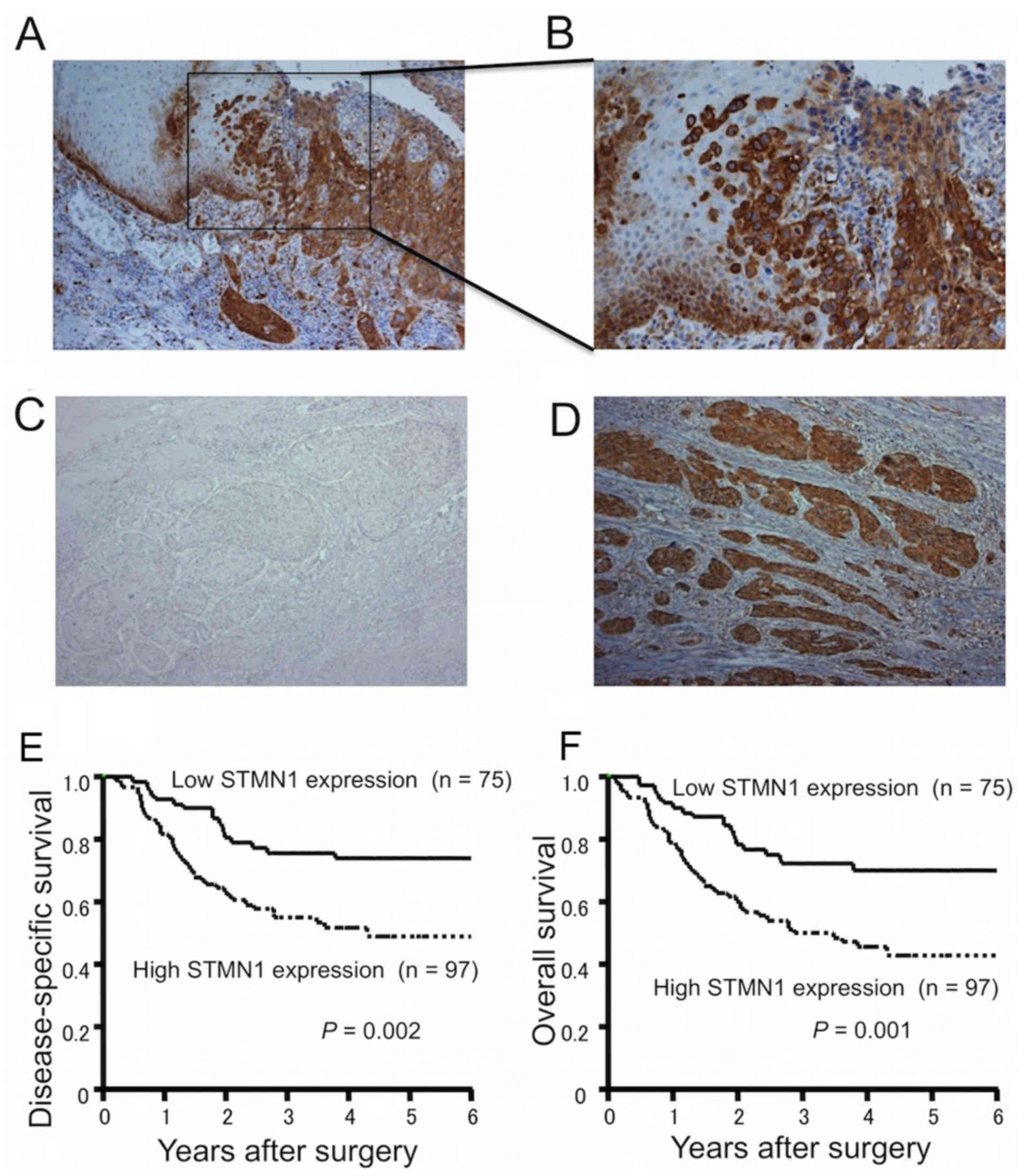
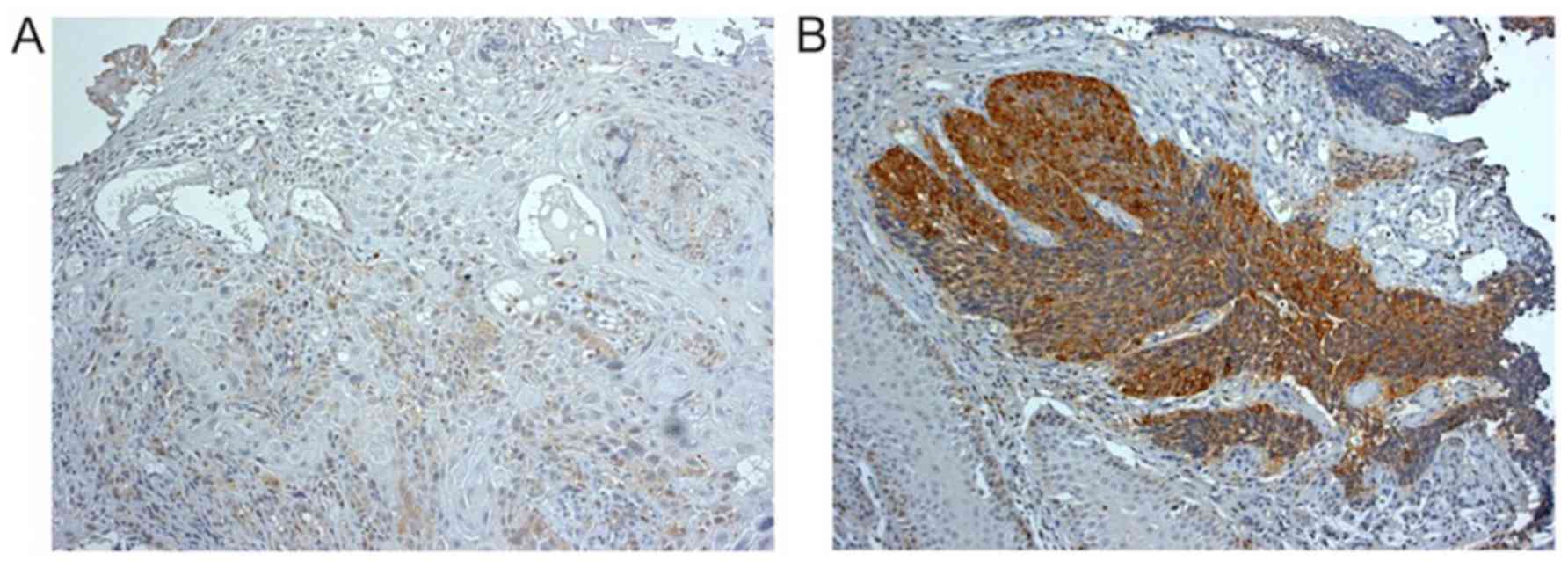
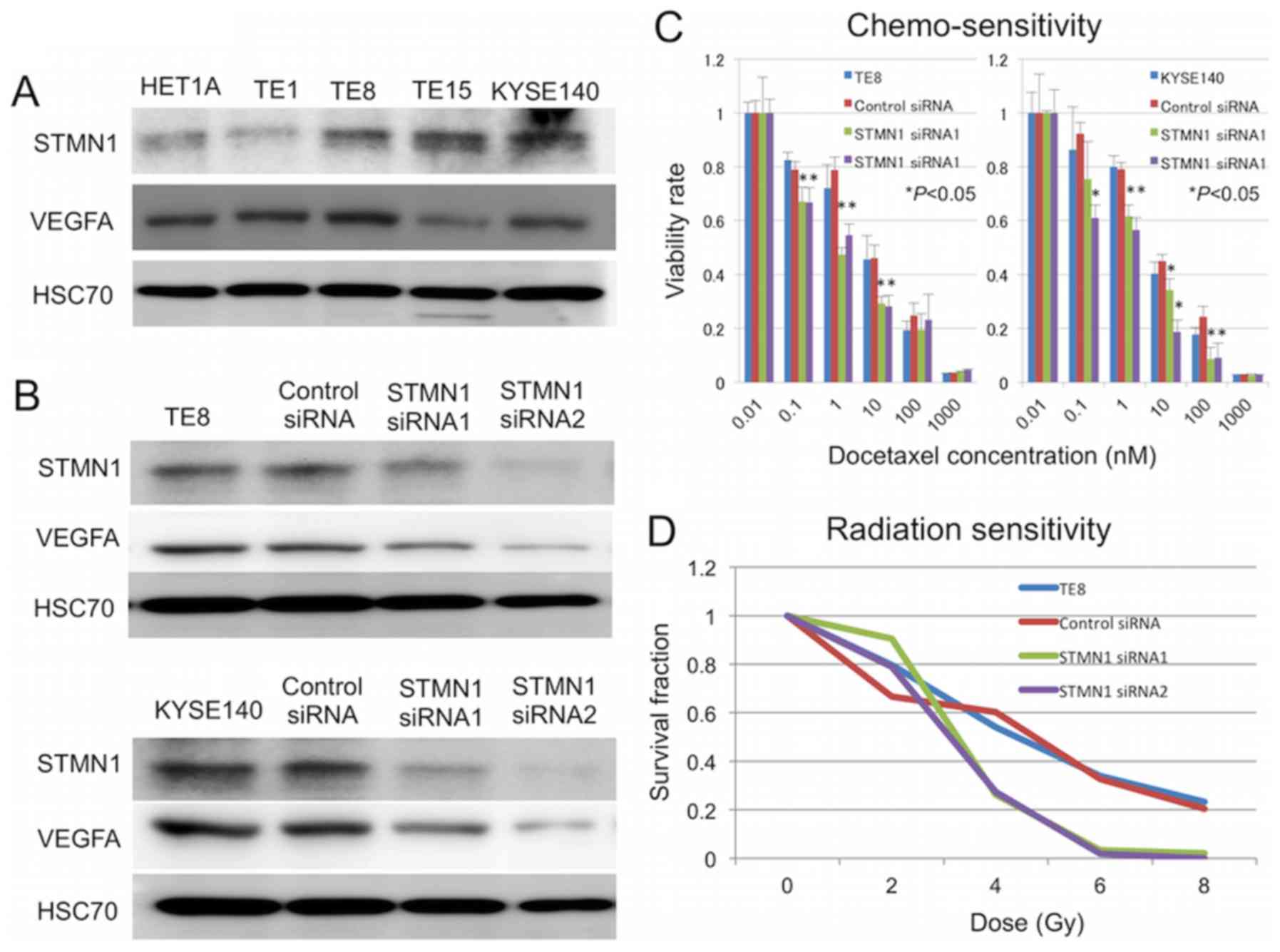
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Enzinger PC and Mayer RJ: Esophageal
cancer. N Engl J Med. 349:2241–2252. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gebski V, Burmeister B, Smithers BM, Foo
K, Zalcberg J and Simes J; Australasian Gastro-Intestinal Trials
group: Survival benefits from neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy or
chemotherapy in oesophageal carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Lancet
Oncol. 8:226–234. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mariette C, Piessen G and Triboulet JP:
Therapeutic strategies in oesophageal carcinoma: Role of surgery
and other modalities. Lancet Oncol. 8:545–553. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
van Hagen P, Hulshof MC, van Lanschot JJ,
Steyerberg EW, van Berge Henegouwen MI, Wijnhoven BP, Richel DJ,
Nieuwenhuijzen GA, Hospers GA, Bonenkamp JJ, et al CROSS group:
Preoperative chemoradiotherapy for esophageal or junctional cancer.
N Engl J Med. 366:2074–2084. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rubin CI and Atweh GF: The role of
stathmin in the regulation of the cell cycle. J Cell Biochem.
93:242–250. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Alli E, Yang JM, Ford JM and Hait WN:
Reversal of stathmin-mediated resistance to paclitaxel and
vinblastine in human breast carcinoma cells. Mol Pharmacol.
71:1233–1240. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Golouh R, Cufer T, Sadikov A, Nussdorfer
P, Usher PA, Brünner N, Schmitt M, Lesche R, Maier S, Timmermans M,
et al: The prognostic value of Stathmin-1, S100B2, and SYK proteins
in ER-positive primary breast cancer patients treated with adjuvant
tamoxifen monotherapy: an immunohistochemical study. Breast Cancer
Res Treat. 110:317–326. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ghosh R, Gu G, Tillman E, Yuan J, Wang Y,
Fazli L, Rennie PS and Kasper S: Increased expression and
differential phosphorylation of stathmin may promote prostate
cancer progression. Prostate. 67:1038–1052. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xi W, Rui W, Fang L, Ke D, Ping G and
Hui-Zhong Z: Expression of stathmin/op18 as a significant
prognostic factor for cervical carcinoma patients. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 135:837–846. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kim JY, Harvard C, You L, Xu Z,
Kuchenbecker K, Baehner R and Jablons D: Stathmin is overexpressed
in malignant mesothelioma. Anticancer Res. 27:39–44.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jeon TY, Han ME, Lee YW, Lee YS, Kim GH,
Song GA, Hur GY, Kim JY, Kim HJ, Yoon S, et al: Overexpression of
stathmin1 in the diffuse type of gastric cancer and its roles in
proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells. Br J Cancer.
102:710–718. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kang W, Tong JH, Chan AW, Lung RW, Chau
SL, Wong QW, Wong N, Yu J, Cheng AS and To KF: Stathmin1 plays
oncogenic role and is a target of microRNA-223 in gastric cancer.
PloS One. 7:e339192012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hsieh SY, Huang SF, Yu MC, Yeh TS, Chen
TC, Lin YJ, Chang CJ, Sung CM, Lee YL and Hsu CY: Stathmin1
overexpression associated with polyploidy, tumor-cell invasion,
early recurrence, and poor prognosis in human hepatoma. Mol
Carcinog. 49:476–487. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Trovik J, Wik E, Stefansson IM,
Marcickiewicz J, Tingulstad S, Staff AC, Njolstad TS; MoMaTec Study
Group; Vandenput I and Amant F: Stathmin overexpression identifies
high-risk patients and lymph node metastasis in endometrial cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 17:3368–3377. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zheng P, Liu YX, Chen L, Liu XH, Xiao ZQ,
Zhao L, Li GQ, Zhou J, Ding YQ and Li JM: Stathmin, a new target of
PRl-3 identified by proteomic methods, plays a key role in
progression and metastasis of colorectal cancer. J Proteome Res.
9:4897–4905. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lin WC, Chen SC, Hu FC, Chueh SC, Pu YS,
Yu HJ and Huang KH: Expression of stathmin in localized upper
urinary tract urothelial carcinoma: Correlations with prognosis.
Urology. 74:1264–1269. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Akhtar J, Wang Z, Yu C, Li CS, Shi YL and
Liu HJ: STMN-1 is a potential marker of lymph node metastasis in
distal esophageal adenocarcinomas and silencing its expression can
reverse malignant phenotype of tumor cells. BMC Cancer. 14:282014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang R, Dong K, Lin F, Wang X, Gao P, Wei
SH, Cheng SY and Zhang HZ: Inhibiting proliferation and enhancing
chemosensitivity to taxanes in osteosarcoma cells by RNA
interference-mediated downregulation of stathmin expression. Mol
Med. 13:567–575. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Feng W, Xiaoyan X, Xuan Y, Xiangke L,
Zichang Y, Ran Z, Liuxing W and Qingxia F: Silencing
stathmin-modulating efficiency of chemotherapy for esophageal
squamous cell cancer with paclitaxel. Cancer Gene Ther. 22:115–121.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Thallinger CM, Raderer M and Hejna M:
Esophageal cancer: A critical evaluation of systemic second-line
therapy. J Clin Oncol. 29:4709–4714. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pasini F, De Manzoni G, Pedrazzani C,
Grandinetti A, Durante E, Gabbani M, Tomezzoli A, Griso C,
Guglielmi A, Pelosi G, et al: High pathological response rate in
locally advanced esophageal cancer after neoadjuvant combined
modality therapy: Dose finding of a weekly chemotherapy schedule
with protracted venous infusion of 5-fluorouracil and dose
escalation of cisplatin, docetaxel and concurrent radiotherapy. Ann
Oncol. 16:1133–1139. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Okumura H, Uchikado Y, Setoyama T,
Matsumoto M, Owaki T, Ishigami S and Natsugoe S: Biomarkers for
predicting the response of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma to
neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy. Surg Today. 44:421–428. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhang X, Ji J, Yang Y, Zhang J and Shen L:
Stathmin1 increases radioresistance by enhancing autophagy in
non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Onco Targets Ther. 9:2565–2574.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sobin LH and Wittekind CW: TNM
Classification of Malignant Tumours. 6th edition. John Wiley &
Sons; Hoboken, NJ: 2002
|
|
26
|
Fukuchi M, Fukai Y, Sohda M, Miyazaki T,
Nakajima M, Inose T, Tanaka N, Tsukada K, Kato H and Kuwano H:
Expression of the prolyl isomerase Pin1 is a useful indicator of
sensitivity to chemoradiotherapy in advanced esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 21:853–859. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Suzuki S, Miyazaki T, Tanaka N, Sakai M,
Sano A, Inose T, Sohda M, Nakajima M, Kato H and Kuwano H:
Prognostic significance of CD151 expression in esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma with aggressive cell proliferation and invasiveness.
Ann Surg Oncol. 18:888–893. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Singer S, Ehemann V, Brauckhoff A, Keith
M, Vreden S, Schirmacher P and Breuhahn K: Protumorigenic
overexpression of stathmin/op18 by gain-of-function mutation in p53
in human hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatology. 46:759–768. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Japanese Society for Esophageal Diseases:
Guidelines for the Clinical and Pathological Studies on Carcinoma
of the Esophagus. 10th edition. Kanehara; 2007
|
|
30
|
Watanabe A, Suzuki H, Yokobori T, Altan B,
Kubo N, Araki K, Wada S, Mochida Y, Sasaki S, Kashiwabara K, et al:
Forkhead box protein C2 contributes to invasion and metastasis of
extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, resulting in a poor prognosis.
Cancer Sci. 104:1427–1432. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Belletti B, Nicoloso MS, Schiappacassi M,
Berton S, Lovat F, Wolf K, Canzonieri V, D'andrea S, Zucchetto A,
Friedl P, et al: Stathmin activity influences sarcoma cell shape,
motility, and metastatic potential. Mol Biol Cell. 19:2003–2013.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li N, Jiang P, Du W, Wu Z, Li C, Qiao M,
Yang X and Wu M: Siva1 suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition
and metastasis of tumor cells by inhibiting stathmin and
stabilizing microtubules. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:12851–12856.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yokobori T, Suzuki S, Tanaka N, Inose T,
Sohda M, Sano A, Sakai M, Nakajima M, Miyazaki T, Kato H, et al:
MiR-150 is associated with poor prognosis in esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma via targeting the EMT inducer ZEB1. Cancer Sci.
104:48–54. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Salvesen HB, Carter SL, Mannelqvist M,
Dutt A, Getz G, Stefansson IM, Raeder MB, Sos ML, Engelsen IB,
Trovik J, et al: Integrated genomic profiling of endometrial
carcinoma associates aggressive tumors with indicators of PI3
kinase activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:4834–4839. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim BM and Hong Y, Lee S, Liu P, Lim JH,
Lee YH, Lee TH, Chang KT and Hong Y: Therapeutic implications for
overcoming radiation resistance in cancer therapy. Int J Mol Sci.
16:26880–26913. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Vaupel P, Thews O and Hoeckel M: Treatment
resistance of solid tumors: Role of hypoxia and anemia. Med Oncol.
18:243–259. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Yoshie M, Miyajima E, Kyo S and Tamura K:
Stathmin, a micro-tubule regulatory protein, is associated with
hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha levels in human endometrial and
endothelial cells. Endocrinology. 150:2413–2418. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|