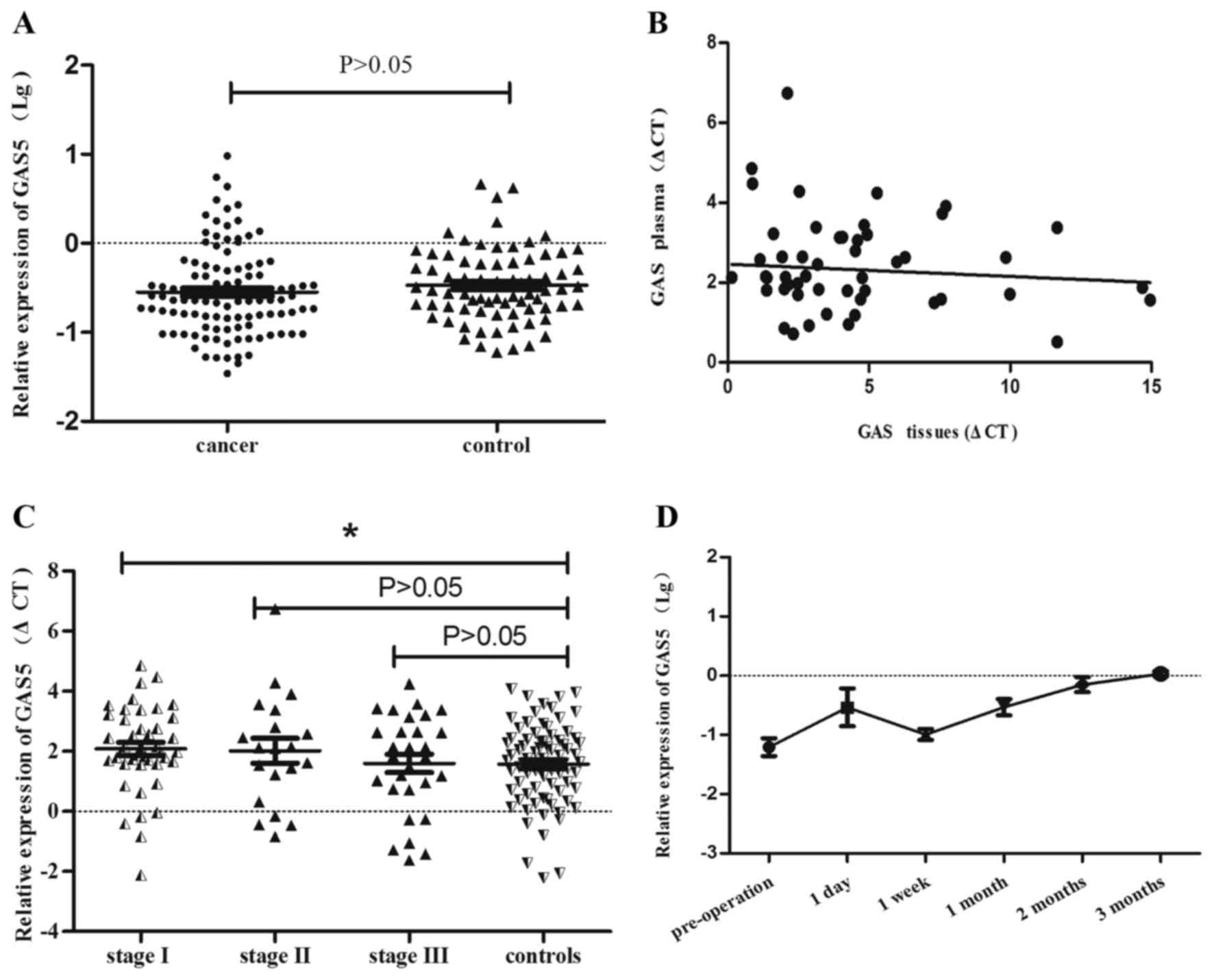
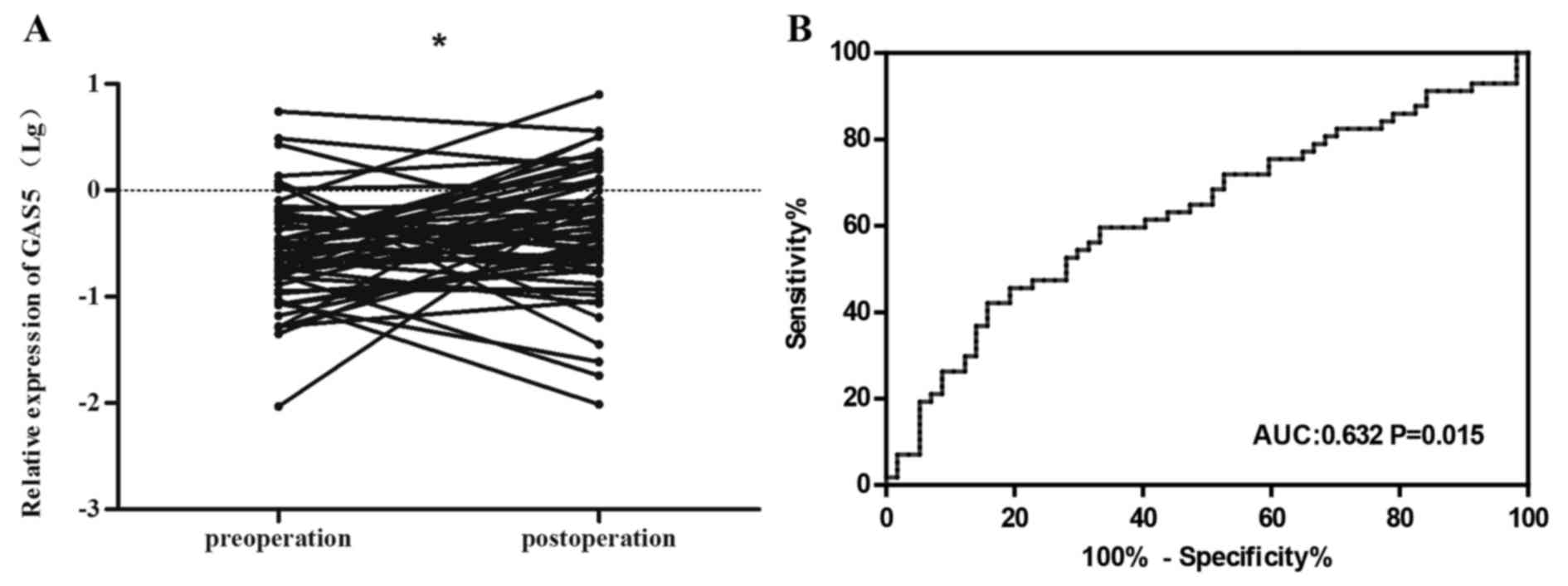
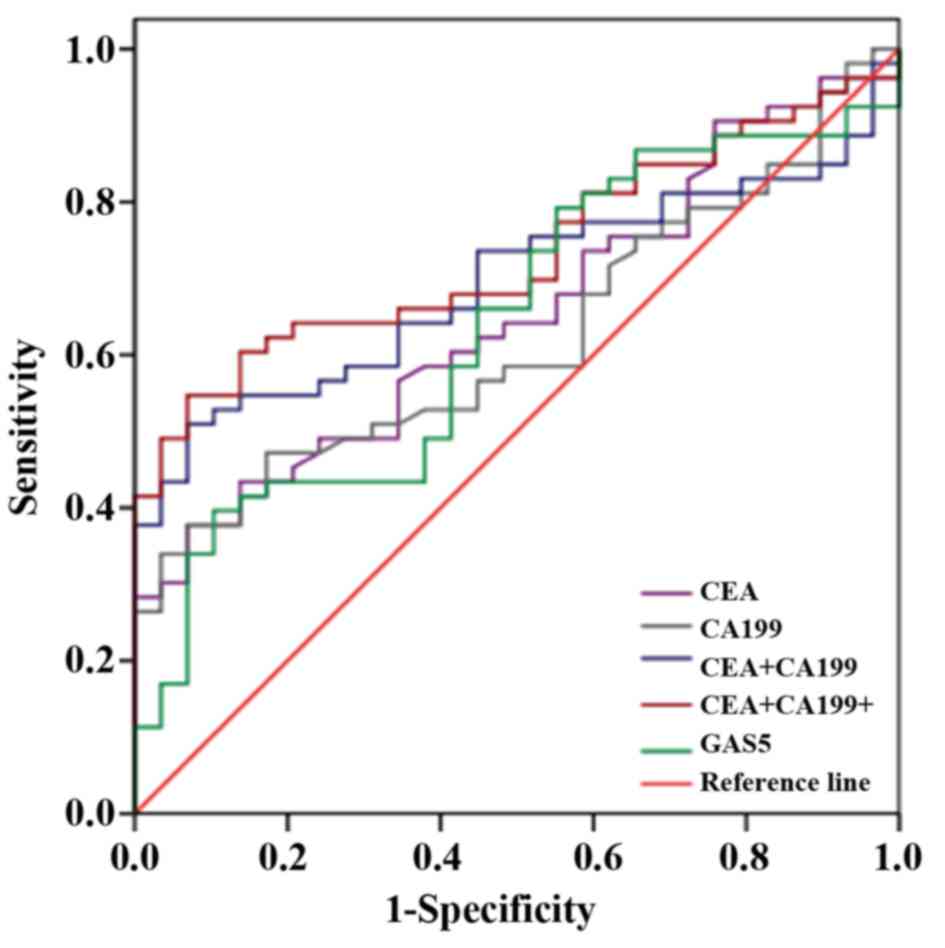
|
1
|
Haaland B, Tan PS, de Castro G Jr and
Lopes G: Meta-analysis of first-line therapies in advanced
non-small-cell lung cancer harboring EGFR-activating mutations. J
Thorac Oncol. 9:805–811. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ettinger DS, Akerley W, Bepler G, Blum MG,
Chang A, Cheney RT, Chirieac LR, D'Amico TA, Demmy TL, Ganti AK, et
al NCCN Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Panel Members: Non-small cell
lung cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 8:740–801. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wu Y, Liu H, Shi X, Yao Y, Yang W and Song
Y: The long non-coding RNA HNF1A-AS1 regulates proliferation and
metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:9160–9172. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Koudelakova V, Kneblova M, Trojanec R,
Drabek J and Hajduch M: Non-small cell lung cancer - genetic
predictors. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub.
157:125–136. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Han Li C and Chen Y: Small and long
non-coding RNAs: Novel targets in perspective cancer therapy. Curr
Genomics. 16:319–326. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Zhang A, Zhang J, Kaipainen A, Lucas JM
and Yang H: Long non-coding RNA: A newly deciphered 'code' in
prostate cancer. Cancer Lett. 375:323–330. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jin Z, Guan L, Song Y, Xiang GM, Chen SX
and Gao B: MicroRNA-138 regulates chemoresistance in human
non-small cell lung cancer via epithelial mesenchymal transition.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:1080–1086. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhu K, Ding H, Wang W, Liao Z, Fu Z, Hong
Y, Zhou Y, Zhang CY and Chen X: Tumor-suppressive miR-218-5p
inhibits cancer cell proliferation and migration via EGFR in
non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget. 7:28075–28085.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu H: MicroRNAs in breast cancer
initiation and progression. Cell Mol Life Sci. 69:3587–3599. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Schmitz SU, Grote P and Herrmann BG:
Mechanisms of long noncoding RNA function in development and
disease. Cell Mol Life Sci. 73:2491–2509. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tantai J, Hu D, Yang Y and Geng J:
Combined identification of long non-coding RNA XIST and HIF1A-AS1
in serum as an effective screening for non-small cell lung cancer.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:7887–7895. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Esteller M: Non-coding RNAs in human
disease. Nat Rev Genet. 12:861–874. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gibb EA, Brown CJ and Lam WL: The
functional role of long non-coding RNA in human carcinomas. Mol
Cancer. 10:382011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kaplan R, Luettich K, Heguy A, Hackett NR,
Harvey BG and Crystal RG: Monoallelic up-regulation of the
imprinted H19 gene in airway epithelium of phenotypically normal
cigarette smokers. Cancer Res. 63:1475–1482. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ricciuti B, Mencaroni C, Paglialunga L,
Paciullo F, Crinò L, Chiari R and Metro G: Long noncoding RNAs: New
insights into non-small cell lung cancer biology, diagnosis and
therapy. Med Oncol. 33:182016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Prensner JR and Chinnaiyan AM: The
emergence of lncRNAs in cancer biology. Cancer Discov. 1:391–407.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jin C, Peng X, Xie T, Lu X, Liu F, Wu H,
Yang Z, Wang J, Cheng L and Wu N: Detection of the long noncoding
RNAs nuclear-enriched autosomal transcript 1 (NEAT1) and metastasis
associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 in the peripheral blood
of HIV-1-infected patients. HIV Med. 17:68–72. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Yang Y, Cai Y, Wu G, Chen X, Liu Y, Wang
X, Yu J, Li C, Chen X, Jose PA, et al: Plasma long non-coding RNA,
CoroMarker, a novel biomarker for diagnosis of coronary artery
disease. Clin Sci. 129:675–685. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhou X, Yin C, Dang Y, Ye F and Zhang G:
Identification of the long non-coding RNA H19 in plasma as a novel
biomarker for diagnosis of gastric cancer. Sci Rep. 5:115162015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zheng K, Dou Y, He L, Li H, Zhang Z, Chen
Y, Ye A, Liu W and Kong L: Improved sensitivity and specificity for
prostate cancer diagnosis based on the urine PCA3/PSA ratio
acquired by sequence-specific RNA capture. Oncol Rep. 34:2439–2444.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sun M, Song J, Zhou Z, Zhu R, Jin H, Ji Y,
Lu Q and Ju H: Comparison of serum microRNA21 and tumor markers in
diagnosis of early non-small cell lung cancer. Dis Markers.
2016:38231212016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen F, Li WM, Wang DM, Gao SS, Bao Y,
Chen WB and Liu D: Clinical value of combined detection of serum
tumor markers in lung cancer diagnosis. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi
Xue Ban. 39:832–835. 2008.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shi X, Sun M, Liu H, Yao Y, Kong R, Chen F
and Song Y: A critical role for the long non-coding RNA GAS5 in
proliferation and apoptosis in non-small-cell lung cancer. Mol
Carcinog. 54(Suppl 1): E1–E12. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Tong YS, Wang XW, Zhou XL, Liu ZH, Yang
TX, Shi WH, Xie HW, Lv J, Wu QQ and Cao XF: Identification of the
long non-coding RNA POU3F3 in plasma as a novel biomarker for
diagnosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Cancer.
14:32015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shao Y, Ye M, Jiang X, Sun W, Ding X, Liu
Z, Ye G, Zhang X, Xiao B and Guo J: Gastric juice long noncoding
RNA used as a tumor marker for screening gastric cancer. Cancer.
120:3320–3328. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang-Chun F, Min F, Di Z and Yan-Chun H:
Retrospective study to determine diagnostic utility of 6 commonly
used lung cancer biomarkers among Han and Uygur population in
Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region of People's Republic of China.
Medicine (Baltimore). 95:e35682016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ma L, Bajic VB and Zhang Z: On the
classification of long non-coding RNAs. RNA Biol. 10:925–933. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Malih S, Saidijam M and Malih N: A brief
review on long noncoding RNAs: a new paradigm in breast cancer
pathogenesis, diagnosis and therapy. Tumour Biol. 37:1479–1485.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Peng L, Yuan X, Jiang B, Tang Z and Li GC:
LncRNAs: key players and novel insights into cervical cancer.
Tumour Biol. 37:2779–2788. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Yang Q, Zhang RW, Sui PC, He HT and Ding
L: Dysregulation of non-coding RNAs in gastric cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 21:10956–10981. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Roberts TC, Morris KV and Wood MJ: The
role of long non-coding RNAs in neurodevelopment, brain function
and neurological disease. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci.
369:3692014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Lorenzen JM and Thum T: Long noncoding
RNAs in kidney and cardiovascular diseases. Nat Rev Nephrol.
12:360–373. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ferreira LB, Palumbo A, de Mello KD,
Sternberg C, Caetano MS, de Oliveira FL, Neves AF, Nasciutti LE,
Goulart LR and Gimba ER: PCA3 noncoding RNA is involved in the
control of prostate-cancer cell survival and modulates androgen
receptor signaling. BMC Cancer. 12:5072012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cui Y, Cao W, Li Q, Shen H, Liu C, Deng J,
Xu J and Shao Q: Evaluation of prostate cancer antigen 3 for
detecting prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Sci Rep. 6:257762016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Konishi H, Ichikawa D, Yamamoto Y, Arita
T, Shoda K, Hiramoto H, Hamada J, Itoh H, Fujita Y, Komatsu S, et
al: Plasma level of metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma
transcript 1 is associated with liver damage and predicts
development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 107:149–154.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
38
|
Li Q, Shao Y, Zhang X, Zheng T, Miao M,
Qin L, Wang B, Ye G, Xiao B and Guo J: Plasma long noncoding RNA
protected by exosomes as a potential stable biomarker for gastric
cancer. Tumour Biol. 36:2007–2012. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Schneider C, King RM and Philipson L:
Genes specifically expressed at growth arrest of mammalian cells.
Cell. 54:787–793. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mourtada-Maarabouni M, Hasan AM, Farzaneh
F and Williams GT: Inhibition of human T-cell proliferation by
mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) antagonists requires noncoding
RNA growth-arrest-specific transcript 5 (GAS5). Mol Pharmacol.
78:19–28. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tani H, Torimura M and Akimitsu N: The RNA
degradation pathway regulates the function of GAS5 a non-coding RNA
in mammalian cells. PLoS One. 8:e556842013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mourtada-Maarabouni M, Hedge VL, Kirkham
L, Farzaneh F and Williams GT: Growth arrest in human T-cells is
controlled by the non-coding RNA growth-arrest-specific transcript
5 (GAS5). J Cell Sci. 121:939–946. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ren S, Wang F, Shen J, Sun Y, Xu W, Lu J,
Wei M, Xu C, Wu C, 'Zhang Z, et al: Long non-coding RNA metastasis
associated in lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 derived miniRNA as a
novel plasma-based biomarker for diagnosing prostate cancer. Eur J
Cancer (Oxford). 49:2949–2959. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Han L, Ma P, Liu SM and Zhou X:
Circulating long noncoding RNA GAS5 as a potential biomarker in
breast cancer for assessing the surgical effects. Tumour Biol.
37:6847–6854. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Schwarzenbach H, Hoon DS and Pantel K:
Cell-free nucleic acids as biomarkers in cancer patients. Nat Rev
Cancer. 11:426–437. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Stroun M, Maurice P, Vasioukhin V, Lyautey
J, Lederrey C, Lefort F, Rossier A, Chen XQ and Anker P: The origin
and mechanism of circulating DNA. Ann NY Acad Sci. 906:161–168.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yang Y, Shao Y, Zhu M, L Q, Yang F, Lu X,
Xu C, Xiao B, Sun Y and Guo J: Using gastric juice
lncRNA-ABHD11-AS1 as a novel type of biomarker in the
screening of gastric cancer. Tumour Biol. 37:1183–1188. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Chen G, Wang J and Cui Q: Could
circulating miRNAs contribute to cancer therapy? Trends Mol Med.
19:71–73. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Yang T, Zeng H, Chen W, Zheng R, Zhang Y,
Li Z, Qi J, Wang M, Chen T, Lou J, et al: Helicobacter pylori
infection, H19 and LINC00152 expression in serum and risk of
gastric cancer in a Chinese population. Cancer Epidemiol.
44:147–153. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhang K, Luo Z, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Wu L,
Liu L, Yang J, Song X and Liu J: Circulating lncRNA H19 in plasma
as a novel biomarker for breast cancer. Cancer Biomark. 17:187–194.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhang M, Guo H, Zhao S and Wang Y, Yang M,
Yu J, Yan Y and Wang Y: Efficacy of epidermal growth factor
receptor inhibitors in combination with chemotherapy in advanced
non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis of randomized
controlled trials. Oncotarget. 7:39823–39833. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Greenhalgh J, Dwan K, Boland A, Bates V,
Vecchio F, Dundar Y, Jain P and Green JA: First-line treatment of
advanced epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation positive
non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer. Cochrane Database Syst
Rev. 5:CD0103832016.
|
|
53
|
Cheng N, Li X, Zhao C, Ren S, Chen X, Cai
W, Zhao M, Zhang Y, Li J, Wang Q, et al: Microarray expression
profile of long non-coding RNAs in EGFR-TKIs resistance of human
non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Rep. 33:833–839. 2015.
|
|
54
|
Wang Y, Chen W, Chen J, Pan Q and Pan J:
LncRNA expression profiles of EGFR exon 19 deletions in lung
adenocarcinoma ascertained by using microarray analysis. Med Oncol.
31:1372014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Dong S, Qu X, Li W, Zhong X, Li P, Yang S,
Chen X, Shao M and Zhang L: The long non-coding RNA, GAS5, enhances
gefitinib-induced cell death in innate EGFR tyrosine kinase
inhibitor-resistant lung adenocarcinoma cells with wide-type EGFR
via downregulation of the IGF-1R expression. J Hematol Oncol.
8:432015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|