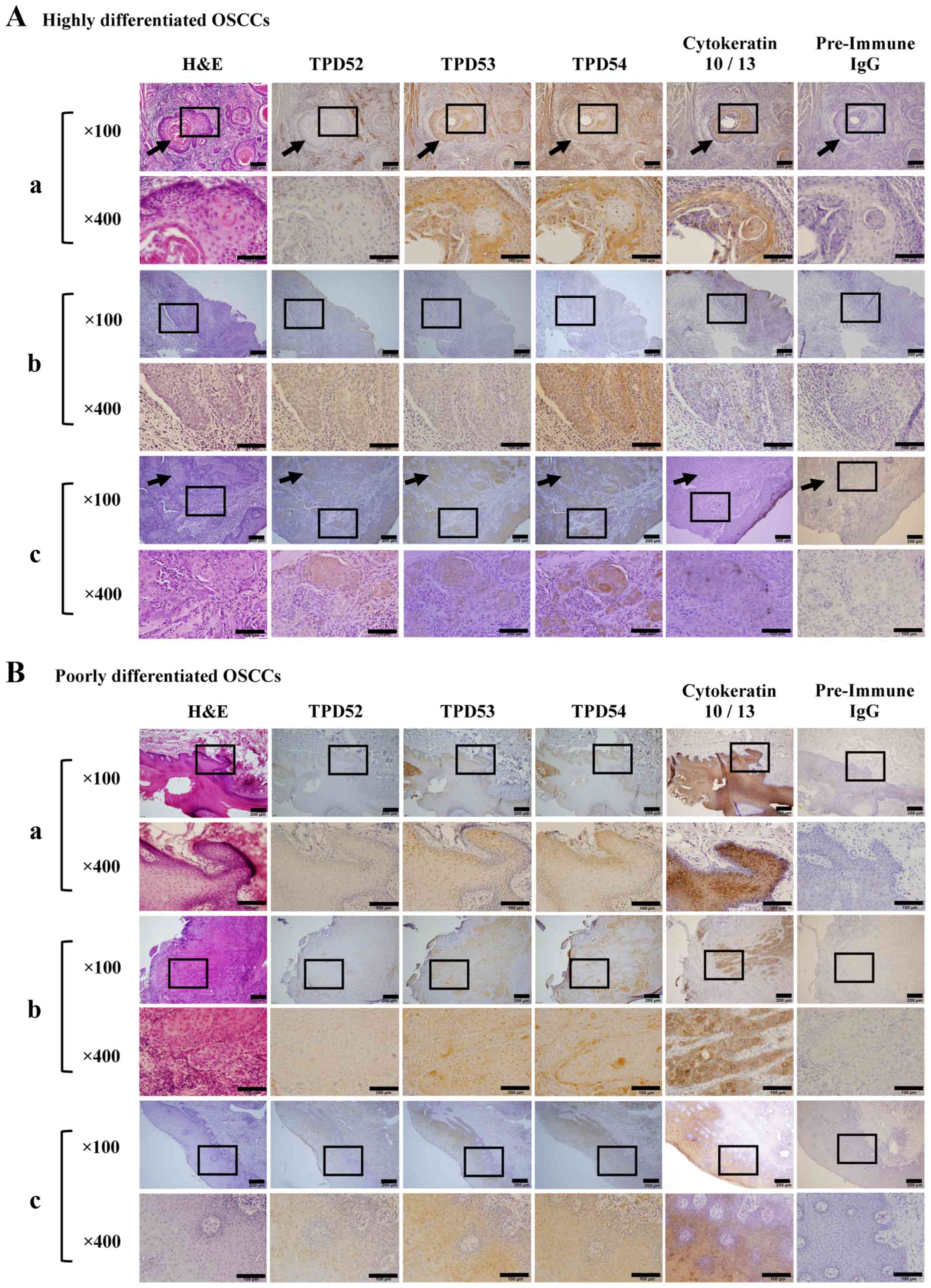
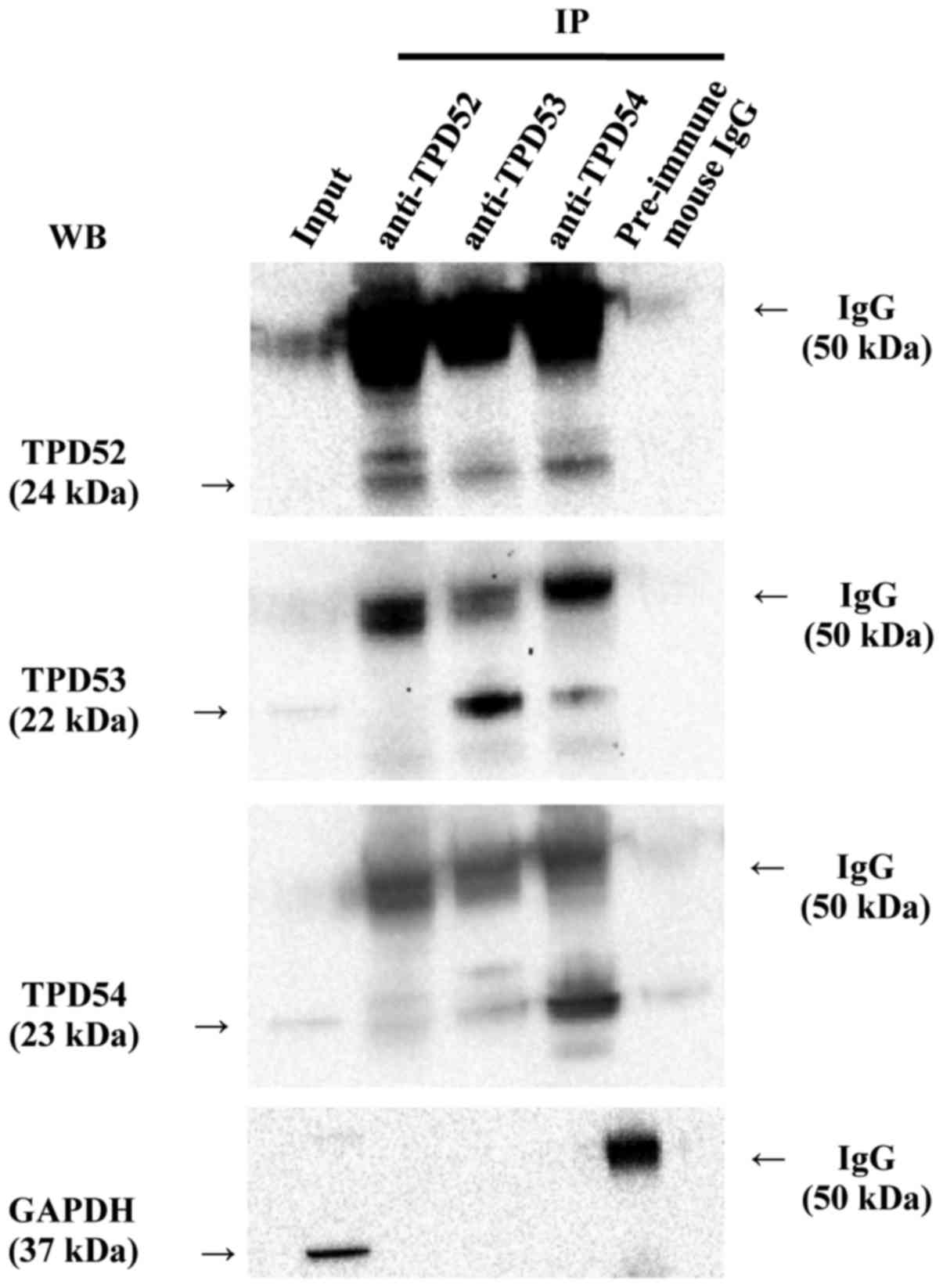
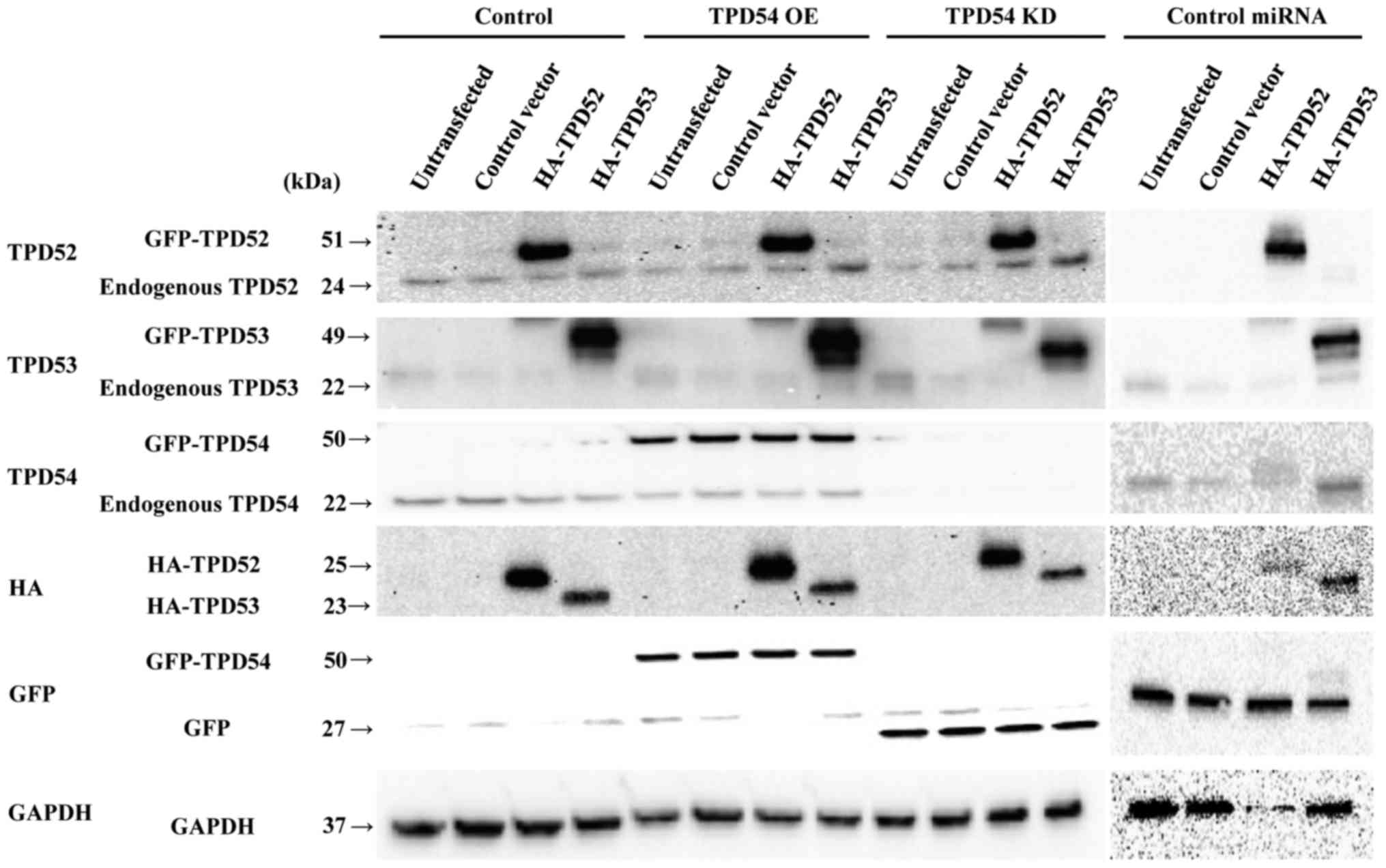
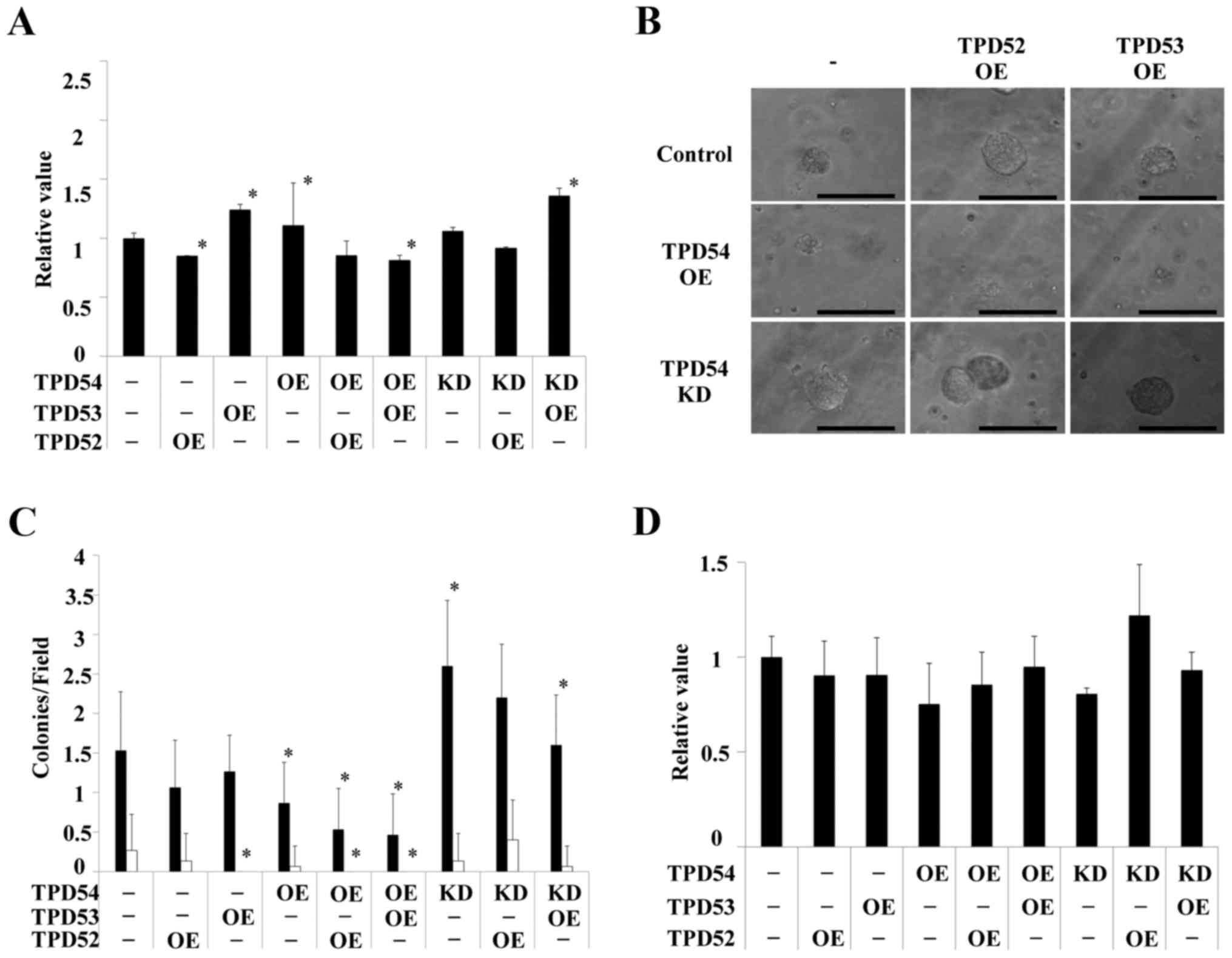
|
1
|
Byrne JA, Mattei MG and Basset P:
Definition of the tumor protein D52 (TPD52) gene family through
cloning of D52 homologues in human (hD53) and mouse (mD52).
Genomics. 35:523–532. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nourse CR, Mattei MG, Gunning P and Byrne
JA: Cloning of a third member of the D52 gene family indicates
alternative coding sequence usage in D52-like transcripts. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1443:155–168. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Byrne JA, Mattei MG, Basset P and Gunning
P: Identification and in situ hybridization mapping of a mouse
Tpd52l1 (D53) orthologue to chromosome 10A4-B2. Cytogenet Cell
Genet. 81:199–201. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Byrne JA, Nourse CR, Basset P and Gunning
P: Identification of homo- and heteromeric interactions between
members of the breast carcinoma-associated D52 protein family using
the yeast two-hybrid system. Oncogene. 16:873–881. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cao Q, Chen J, Zhu L, Liu Y, Zhou Z, Sha
J, Wang S and Li J: A testis-specific and testis developmentally
regulated tumor protein D52 (TPD52)-like protein TPD52L3/hD55
interacts with TPD52 family proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
344:798–806. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Byrne JA, Tomasetto C, Garnier JM, Rouyer
N, Mattei MG, Bellocq JP, Rio MC and Basset P: A screening method
to identify genes commonly overexpressed in carcinomas and the
identification of a novel complementary DNA sequence. Cancer Res.
55:2896–2903. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen SL, Maroulakou IG, Green JE,
Romano-Spica V, Modi W, Lautenberger J and Bhat NK: Isolation and
characterization of a novel gene expressed in multiple cancers.
Oncogene. 12:741–751. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Malek RL, Irby RB, Guo QM, Lee K, Wong S,
He M, Tsai J, Frank B, Liu ET, Quackenbush J, et al: Identification
of Src transformation fingerprint in human colon cancer. Oncogene.
21:7256–7265. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Petrova DT, Asif AR, Armstrong VW, Dimova
I, Toshev S, Yaramov N, Oellerich M and Toncheva D: Expression of
chloride intracellular channel protein 1 (CLIC1) and tumor protein
D52 (TPD52) as potential biomarkers for colorectal cancer. Clin
Biochem. 41:1224–1236. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Byrne JA, Balleine RL, Schoenberg Fejzo M,
Mercieca J, Chiew YE, Livnat Y, St Heaps L, Peters GB, Byth K,
Karlan BY, et al: Tumor protein D52 (TPD52) is overexpressed and a
gene amplification target in ovarian cancer. Int J Cancer.
117:1049–1054. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Byrne JA, Maleki S, Hardy JR, Gloss BS,
Murali R, Scurry JP, Fanayan S, Emmanuel C, Hacker NF, Sutherland
RL, et al: MAL2 and tumor protein D52 (TPD52) are frequently
overexpressed in ovarian carcinoma, but differentially associated
with histological subtype and patient outcome. BMC Cancer.
10:4972010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fejzo MS, Dering J, Ginther C, Anderson L,
Ramos L, Walsh C, Karlan B and Slamon DJ: Comprehensive analysis of
20q13 genes in ovarian cancer identifies ADRM1 as amplification
target. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 47:873–883. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Willems A, De Gendt K, Allemeersch J,
Smith LB, Welsh M, Swinnen JV and Verhoeven G: Early effects of
Sertoli cell-selective androgen receptor ablation on testicular
gene expression. Int J Androl. 33:507–517. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Rubin MA, Varambally S, Beroukhim R,
Tomlins SA, Rhodes DR, Paris PL, Hofer MD, Storz-Schweizer M,
Kuefer R, Fletcher JA, et al: Overexpression, amplification, and
androgen regulation of TPD52 in prostate cancer. Cancer Res.
64:3814–3822. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen H, Pimienta G, Gu Y, Sun X, Hu J, Kim
MS, Chaerkady R, Gucek M, Cole RN, Sukumar S, et al: Proteomic
characterization of Her2/neu-overexpressing breast cancer cells.
Proteomics. 10:3800–3810. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Crugliano T, Quaresima B, Gaspari M,
Faniello MC, Romeo F, Baudi F, Cuda G, Costanzo F and Venuta S:
Specific changes in the proteomic pattern produced by the
BRCA1-Ser1841Asn missense mutation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
39:220–226. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Scanlan MJ, Gout I, Gordon CM, Williamson
B, Stockert E, Gure AO, Jäger D, Chen YT, Mackay A, O'Hare MJ, et
al: Humoral immunity to human breast cancer: Antigen definition and
quantitative analysis of mRNA expression. Cancer Immun.
1:42001.
|
|
18
|
Lewis JD, Payton LA, Whitford JG, Byrne
JA, Smith DI, Yang L and Bright RK: Induction of tumorigenesis and
metastasis by the murine orthologue of tumor protein D52. Mol
Cancer Res. 5:133–144. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shehata M, Bièche I, Boutros R,
Weidenhofer J, Fanayan S, Spalding L, Zeps N, Byth K, Bright RK,
Lidereau R, et al: Nonredundant functions for tumor protein
D52-like proteins support specific targeting of TPD52. Clin Cancer
Res. 14:5050–5060. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ummanni R, Teller S, Junker H, Zimmermann
U, Venz S, Scharf C, Giebel J and Walther R: Altered expression of
tumor protein D52 regulates apoptosis and migration of prostate
cancer cells. FEBS J. 275:5703–5713. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang D, He D, Xue Y, Wang R, Wu K, Xie H,
Zeng J, Wang X, Zhau HE, Chung LW, et al: PrLZ protects prostate
cancer cells from apoptosis induced by androgen deprivation via the
activation of Stat3/Bcl-2 pathway. Cancer Res. 71:2193–2202. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang H, Wang J, Pang B, Liang RX, Li S,
Huang PT, Wang R, Chung LW, Zhau HE, Huang C, et al: PC-1/PrLZ
contributes to malignant progression in prostate cancer. Cancer
Res. 67:8906–8913. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhao P, Zhong W, Ying X, Yao B, Yuan Z, Fu
J and Zhou Z: Comparative proteomic analysis of
anti-benzo(a)pyrene-7,8-dihydrodiol-9,10-epoxide-transformed and
normal human bronchial epithelial G0/G1 cells. Chem Biol Interact.
186:166–173. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sims AH, Finnon P, Miller CJ, Bouffler SD,
Howell A, Scott D and Clarke RB: TPD52 and NFKB1 gene expression
levels correlate with G2 chromosomal radiosensitivity in
lymphocytes of women with and at risk of hereditary breast cancer.
Int J Radiat Biol. 83:409–420. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Boutros R, Fanayan S, Shehata M and Byrne
JA: The tumor protein D52 family: Many pieces, many puzzles.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 325:1115–1121. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wilson SH, Bailey AM, Nourse CR, Mattei MG
and Byrne JA: Identification of MAL2, a novel member of the mal
proteolipid family, though interactions with TPD52-like proteins in
the yeast two-hybrid system. Genomics. 76:81–88. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Thomas DD, Kaspar KM, Taft WB, Weng N,
Rodenkirch LA and Groblewski GE: Identification of Annexin VI as a
Ca2+-sensitive CRHSP-28-binding protein in pancreatic
acinar cells. J Biol Chem. 277:35496–35502. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Proux-Gillardeaux V, Galli T, Callebaut I,
Mikhailik A, Calothy G and Marx M: D53 is a novel endosomal
SNARE-binding protein that enhances interaction of syntaxin 1 with
the synaptobrevin 2 complex in vitro. Biochem J. 370:213–221. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Boutros R, Bailey AM, Wilson SHD and Byrne
JA: Alternative splicing as a mechanism for regulating 14-3-3
binding: Interactions between hD53 (TPD52L1) and 14-3-3 proteins. J
Mol Biol. 332:675–687. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kamili A, Roslan N, Frost S, Cantrill LC,
Wang D, Della-Franca A, Bright RK, Groblewski GE, Straub BK, Hoy
AJ, et al: TPD52 expression increases neutral lipid storage within
cultured cells. J Cell Sci. 128:3223–3238. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Byrne JA, Frost S, Chen Y and Bright RK:
Tumor protein D52 (TPD52) and cancer-oncogene understudy or
understudied oncogene? Tumour Biol. 35:7369–7382. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang W and Liu HT: MAPK signal pathways
in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell
Res. 12:9–18. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Manning BD and Cantley LC: AKT/PKB
signaling: Navigating downstream. Cell. 129:1261–1274. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fornaro M, Manes T and Languino LR:
Integrins and prostate cancer metastases. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
20:321–331. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Wu WS: The signaling mechanism of ROS in
tumor progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 25:695–705. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bhaskar PT and Hay N: The two TORCs and
Akt. Dev Cell. 12:487–502. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Legate KR, Wickström SA and Fässler R:
Genetic and cell biological analysis of integrin outside-in
signaling. Genes Dev. 23:397–418. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fujita A and Kondo S: Identification of
TPD54 as a candidate marker of oral epithelial carcinogenesis. J
Oral Maxillofac Surg Med Pathol. 27:770–774. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Mukudai Y, Kondo S, Fujita A, Yoshihama Y,
Shirota T and Shintani S: Tumor protein D54 is a negative regulator
of extracellular matrix-dependent migration and attachment in oral
squamous cell carcinoma-derived cell lines. Cell Oncol (Dordr).
36:233–245. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Takahashi K: Establishment and
characterization of a cell line(SAS) from poorly differentiated
human squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue. Jpn Stomatological
Soc. 38:20–28. 1989.
|
|
41
|
Momose F, Araida T, Negishi A, Ichijo H,
Shioda S and Sasaki S: Variant sublines with different metastatic
potentials selected in nude mice from human oral squamous cell
carcinomas. J Oral Pathol Med. 18:391–395. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Tsukamoto H, Kondo S, Mukudai Y, Nagumo T,
Yasuda A, Kurihara Y, Kamatani T and Shintani S: Evaluation of
anticancer activities of benzo[c]phenanthridine alkaloid
sanguinarine in oral squamous cell carcinoma cell line. Anticancer
Res. 31:2841–2846. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Enomoto-Iwamoto M, Iwamoto M, Mukudai Y,
Kawakami Y, Nohno T, Higuchi Y, Takemoto S, Ohuchi H, Noji S and
Kurisu K: Bone morphogenetic protein signaling is required for
maintenance of differentiated phenotype, control of proliferation,
and hypertrophy in chondrocytes. J Cell Biol. 140:409–418. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chen Y, Lu B, Yang Q, Fearns C, Yates JR
III and Lee JD: Combined integrin phosphoproteomic analyses and
small interfering RNA - based functional screening identify key
regulators for cancer cell adhesion and migration. Cancer Res.
69:3713–3720. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yasuda A, Kondo S, Nagumo T, Tsukamoto H,
Mukudai Y, Umezawa K and Shintani S: Anti-tumor activity of
dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin against human oral squamous cell
carcinoma cell lines in vitro and in vivo. Oral Oncol. 47:334–339.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Shiogama S, Yoshiba S, Soga D, Motohashi H
and Shintani S: Aberrant expression of EZH2 is associated with
pathological findings and P53 alteration. Anticancer Res.
33:4309–4317. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Mukudai Y, Zhang M, Shiogama S, Kondo S,
Ito C, Motohashi H, Kato K, Fujii M, Shintani S, Shigemori H, et
al: Methanol and butanol extracts of Paeonia lutea leaves repress
metastasis of squamous cell carcinoma. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2016:60872132016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wang R, Xu J, Mabjeesh N, Zhu G, Zhou J,
Amin M, He D, Marshall FF, Zhau HE and Chung LW: PrLZ is expressed
in normal prostate development and in human prostate cancer
progression. Clin Cancer Res. 13:6040–6048. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Cifone MA and Fidler IJ: Correlation of
patterns of anchorage-independent growth with in vivo behavior of
cells from a murine fibrosarcoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
77:1039–1043. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hahn WC, Counter CM, Lundberg AS,
Beijersbergen RL, Brooks MW and Weinberg RA: Creation of human
tumour cells with defined genetic elements. Nature. 400:464–468.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chen SL, Zhang XK, Halverson DO, Byeon MK,
Schweinfest CW, Ferris DK and Bhat NK: Characterization of human N8
protein. Oncogene. 15:2577–2588. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Proux V, Provot S, Felder-Schmittbuhl MP,
Laugier D, Calothy G and Marx M: Characterization of a leucine
zipper-containing protein identified by retroviral insertion in
avian neuroretina cells. J Biol Chem. 271:30790–30797. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Sathasivam P, Bailey AM, Crossley M and
Byrne JA: The role of the coiled-coil motif in interactions
mediated by TPD52. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 288:56–61. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Li L, Xie H, Liang L, Gao Y, Zhang D, Fang
L, Lee SO, Luo J, Chen X, Wang X, et al: Increased PrLZ-mediated
androgen receptor transactivation promotes prostate cancer growth
at castration-resistant stage. Carcinogenesis. 34:257–267. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
55
|
He Y, Chen F, Cai Y and Chen S: Knockdown
of tumor protein D52-like 2 induces cell growth inhibition and
apoptosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Biol Int.
39:264–271. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Jiang L, Ji N, Zhou Y, Li J, Liu X, Wang
Z, Chen Q and Zeng X: CAL 27 is an oral adenosquamous carcinoma
cell line. Oral Oncol. 45:e204–e207. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Eagle H: Propagation in a fluid medium of
a human epidermoid carcinoma, strain KB. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med.
89:362–364. 1955. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|