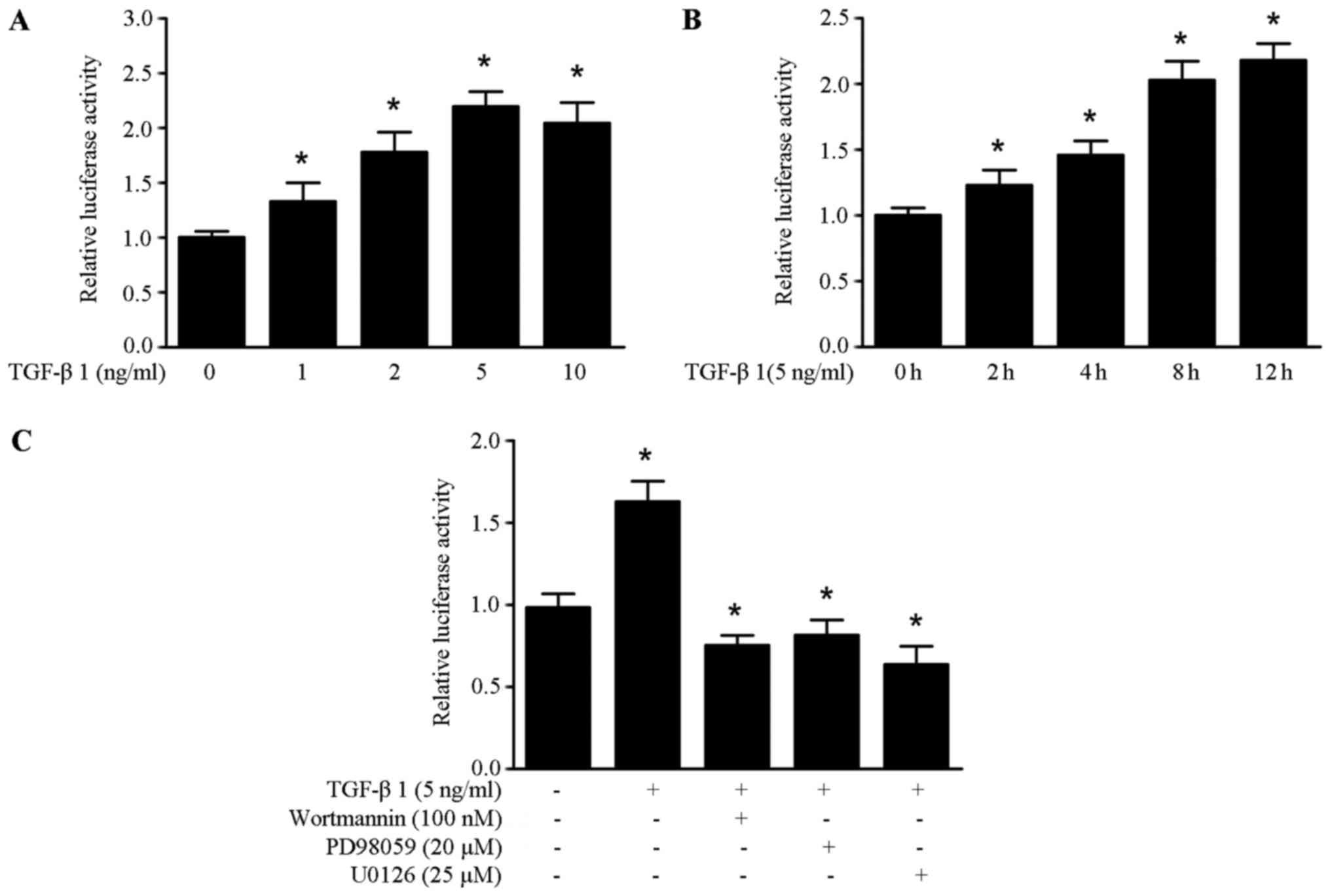
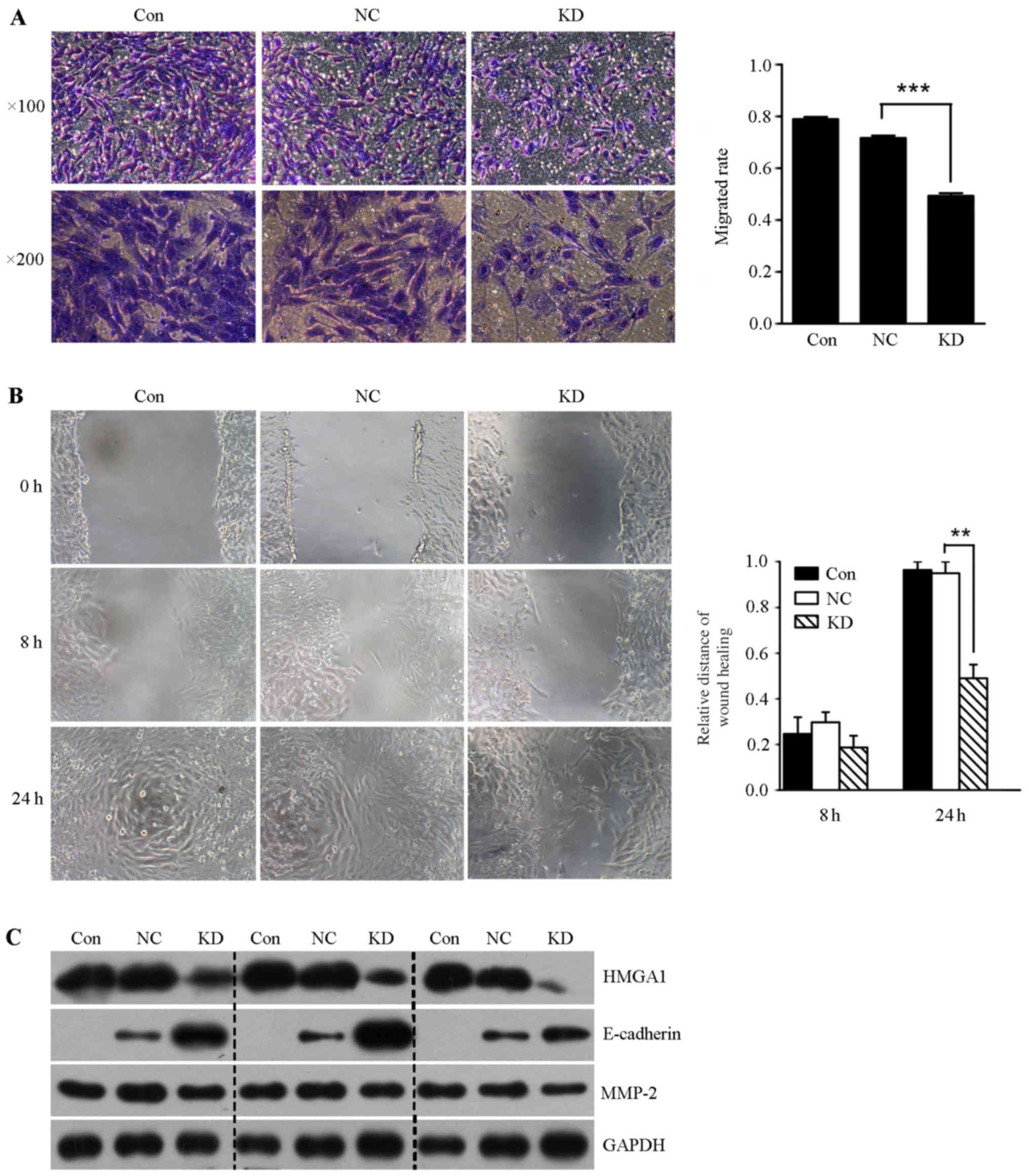
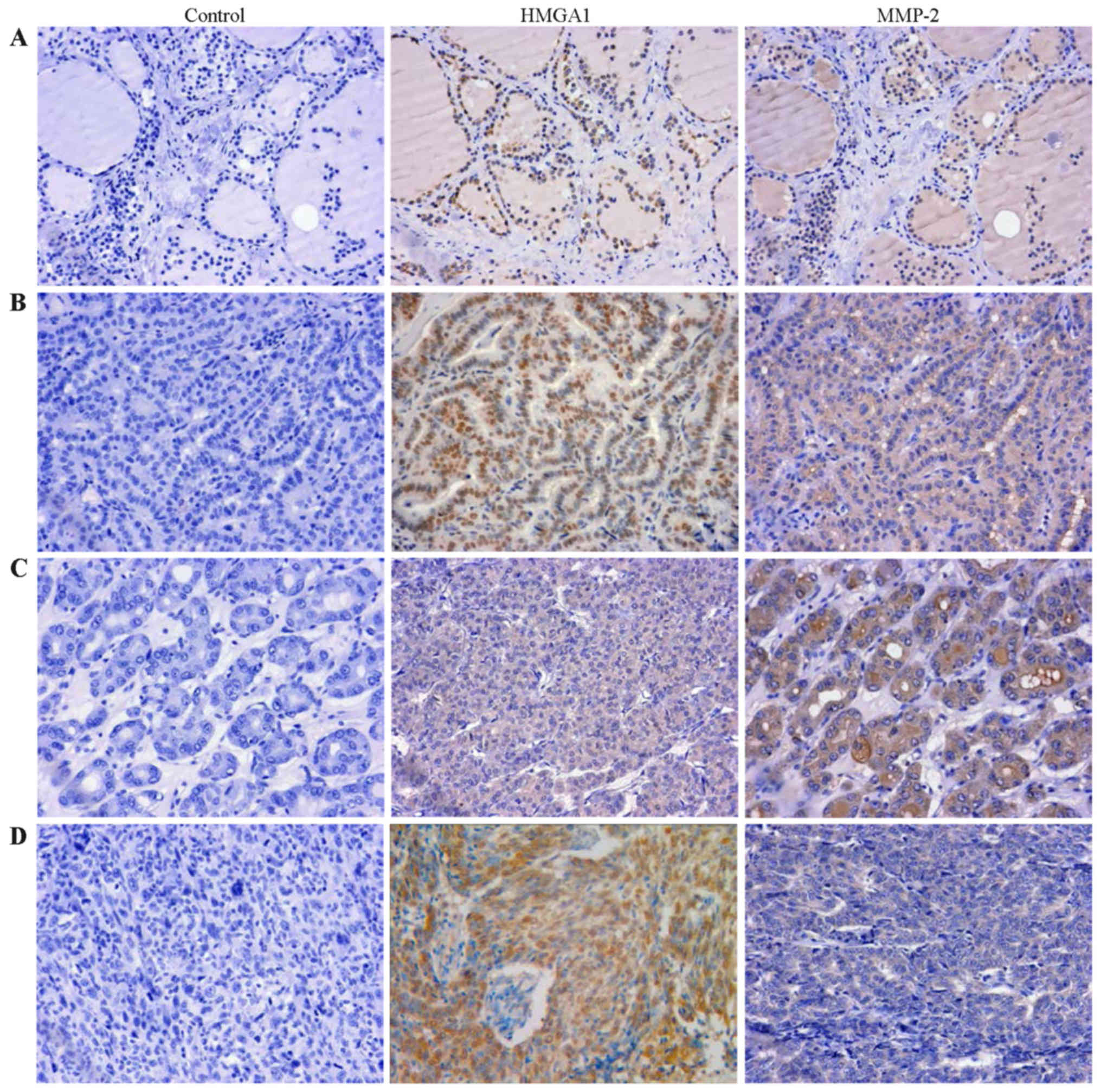
|
1
|
Fusco A and Fedele M: Roles of HMGA
proteins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:899–910. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Reeves R: Nuclear functions of the HMG
proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1799:3–14. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Resar LM: The high mobility group A1 gene:
Transforming inflammatory signals into cancer? Cancer Res.
70:436–439. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shah SN, Cope L, Poh W, Belton A, Roy S,
Talbot CC Jr, Sukumar S, Huso DL and Resar LM: HMGA1: A master
regulator of tumor progression in triple-negative breast cancer
cells. PLoS One. 8:e634192013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Abe N, Watanabe T, Masaki T, Mori T,
Sugiyama M, Uchimura H, Fujioka Y, Chiappetta G, Fusco A and Atomi
Y: Pancreatic duct cell carcinomas express high levels of high
mobility group I(Y) proteins. Cancer Res. 60:3117–3122.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Meyer B, Loeschke S, Schultze A, Weigel T,
Sandkamp M, Goldmann T, Vollmer E and Bullerdiek J: HMGA2
overexpression in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Carcinog.
46:503–511. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Masciullo V, Baldassarre G, Pentimalli F,
Berlingieri MT, Boccia A, Chiappetta G, Palazzo J, Manfioletti G,
Giancotti V, Viglietto G, et al: HMGA1 protein over-expression is a
frequent feature of epithelial ovarian carcinomas. Carcinogenesis.
24:1191–1198. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Belton A, Gabrovsky A, Bae YK, Reeves R,
Iacobuzio Donahue C, Huso DL and Resar LM: HMGA1 induces intestinal
polyposis in transgenic mice and drives tumor progression and stem
cell properties in colon cancer cells. PLoS One. 7:e300342012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chiappetta G, Tallini G, De Biasio MC,
Manfioletti G, Martinez-Tello FJ, Pentimalli F, de Nigris F, Mastro
A, Botti G, Fedele M, et al: Detection of high mobility group I
HMGI(Y) protein in the diagnosis of thyroid tumors: HMGI(Y)
expression represents a potential diagnostic indicator of
carcinoma. Cancer Res. 58:4193–4198. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Huang R, Huang D, Dai W and Yang F:
Overexpression of HMGA1 correlates with the malignant status and
prognosis of breast cancer. Mol Cell Biochem. 404:251–257. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Heldin CH, Landström M and Moustakas A:
Mechanism of TGF beta signaling to growth arrest, apoptosis, and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 21:166–176.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ikushima H and Miyazono K: TGFbeta
signalling: A complex web in cancer progression. Nat Rev Cancer.
10:415–424. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Massagué J: TGFbeta in cancer. Cell.
134:215–230. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang L, Pang Y and Moses HL: TGF beta and
immune cells: An important regulatory axis in the tumor
microenvironment and progression. Trends Immunol. 31:220–227. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Inman GJ: Switching TGFβ from a tumor
suppressor to a tumor promoter. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 21:93–99.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Joshi A and Cao D: TGF beta signaling,
tumor microenvironment and tumor progression: The butterfly effect.
Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 15:180–194. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Meulmeester E and Ten Dijke P: The dynamic
roles of TGF-β in cancer. J Pathol. 223:205–218. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Smith AL, Robin TP and Ford HL: Molecular
pathways: Targeting the TGF-β pathway for cancer therapy. Clin
Cancer Res. 18:4514–4521. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Derynck R, Akhurst RJ and Balmain A:
TGF-beta signaling in tumor suppression and cancer progression. Nat
Genet. 29:117–129. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lenferink AE, Cantin C, Nantel A, Wang E,
Durocher Y, Banville M, Paul Roc B, Marcil A, Wilson MR and
O'Connor-McCourt MD: Transcriptome profiling of a TGF-beta-induced
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition reveals extracellular
clusterin as a target for therapeutic antibodies. Oncogene.
29:831–844. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Vincent T, Neve EP, Johnson JR, Kukalev A,
Rojo F, Albanell J, Pietras K, Virtanen I, Philipson L, Leopold PL,
et al: A SNAIL1-SMAD3/4 transcriptional repressor complex promotes
TGF-beta mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Cell Biol.
11:943–950. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Voulgari A and Pintzas A:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer metastasis: Mechanisms,
markers and strategies to overcome drug resistance in the clinic.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1796:75–90. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wendt MK, Allington TM and Schiemann WP:
Mechanisms of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition by TGF-beta.
Future Oncol. 5:1145–1168. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhong J, Cao RX, Zu XY, Hong T, Yang J,
Liu L, Xiao XH, Ding WJ, Zhao Q, Liu JH, et al: Identification and
characterization of novel spliced variants of PRMT2 in breast
carcinoma. FEBS J. 279:316–335. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Lois C, Hong EJ, Pease S, Brown EJ and
Baltimore D: Germline transmission and tissue-specific expression
of transgenes delivered by lentiviral vectors. Science.
295:868–872. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhong J, Cao RX, Liu JH, Liu YB, Wang J,
Liu LP, Chen YJ, Yang J, Zhang QH, Wu Y, et al: Nuclear loss of
protein arginine N-methyltransferase 2 in breast carcinoma is
associated with tumor grade and overexpression of cyclin D1
protein. Oncogene. 33:5546–5558. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Welch DR, Fabra A and Nakajima M:
Transforming growth factor beta stimulates mammary adenocarcinoma
cell invasion and metastatic potential. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
87:7678–7682. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Derynck R and Zhang YE: Smad-dependent and
Smad-independent pathways in TGF-beta family signalling. Nature.
425:577–584. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Moustakas A and Heldin CH: Non-Smad
TGF-beta signals. J Cell Sci. 118:3573–3584. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhong J, Liu C, Chen YJ, Zhang QH, Yang J,
Kang X, Chen SR, Wen GB, Zu XY and Cao RX: The association between
S100A13 and HMGA1 in the modulation of thyroid cancer proliferation
and invasion. J Transl Med. 14:802016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liau SS, Jazag A, Ito K and Whang EE:
Overexpression of HMGA1 promotes anoikis resistance and
constitutive Akt activation in pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. Br
J Cancer. 96:993–1000. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Di Cello F, Shin J, Harbom K and Brayton
C: Knockdown of HMGA1 inhibits human breast cancer cell growth and
metastasis in immunodeficient mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
434:70–74. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pegoraro S, Ros G, Piazza S, Sommaggio R,
Ciani Y, Rosato A, Sgarra R, Del Sal G and Manfioletti G: HMGA1
promotes metastatic processes in basal-like breast cancer
regulating EMT and stemness. Oncotarget. 4:1293–1308. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Puca F, Colamaio M, Federico A, Gemei M,
Tosti N, Bastos AU, Del Vecchio L, Pece S, Battista S and Fusco A:
HMGA1 silencing restores normal stem cell characteristics in colon
cancer stem cells by increasing p53 levels. Oncotarget.
5:3234–3245. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Qu Y, Wang Y, Ma J, Zhang Y, Meng N, Li H,
Wang Y and Wei W: Overexpression of high mobility group A1 protein
in human uveal melanomas: Implication for prognosis. PLoS One.
8:e687242013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
D'Angelo D, Mussnich P, Rosa R, Bianco R,
Tortora G and Fusco A: High mobility group A1 protein expression
reduces the sensitivity of colon and thyroid cancer cells to
antineoplastic drugs. BMC Cancer. 14:8512014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Frasca F, Rustighi A, Malaguarnera R,
Altamura S, Vigneri P, Del Sal G, Giancotti V, Pezzino V, Vigneri R
and Manfioletti G: HMGA1 inhibits the function of P53 family
members in thyroid cancer cells. Cancer Res. 66:2980–2989. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Martinez Hoyos J, Ferraro A, Sacchetti S,
Keller S, De Martino I, Borbone E, Pallante P, Fedele M, Montanaro
D, Esposito F, et al: HAND1 gene expression is negatively regulated
by the High Mobility Group A1 proteins and is drastically reduced
in human thyroid carcinomas. Oncogene. 28:876–885. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Zu X, Zhong J, Tan J, Tan L, Yang D, Zhang
Q, Ding W, Liu W, Wen G, Liu J, et al: TGF-β1 induces HMGA1
expression in human breast cancer cells: Implications of the
involvement of HMGA1 in TGF-β signaling. Int J Mol Med. 35:693–701.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hillion J, Roy S, Heydarian M, Cope L,
Xian L, Koo M, Luo LZ, Kellyn K, Ronnett BM, Huso T, et al: The
high mobility group A1 (HMGA1) gene is highly overexpressed in
human uterine serous carcinomas and carcinosarcomas and drives
matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) in a subset of tumors. Gynecol
Oncol. 141:580–587. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hillion J, Wood LJ, Mukherjee M,
Bhattacharya R, Di Cello F, Kowalski J, Elbahloul O, Segal J,
Poirier J, Rudin CM, et al: Upregulation of MMP-2 by HMGA1 promotes
transformation in undifferentiated, large cell lung cancer. Mol
Cancer Res. 7:1803–1812. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Takaha N, Resar LM, Vindivich D and Coffey
DS: High mobility group protein HMGI(Y) enhances tumor cell growth,
invasion, and matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression in prostate
cancer cells. Prostate. 60:160–167. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liau SS, Jazag A and Whang EE: HMGA1 is a
determinant of cellular invasiveness and in vivo metastatic
potential in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 66:11613–11622.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Reeves R, Edberg DD and Li Y:
Architectural transcription factor HMGI(Y) promotes tumor
progression and mesenchymal transition of human epithelial cells.
Mol Cell Biol. 21:575–594. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|