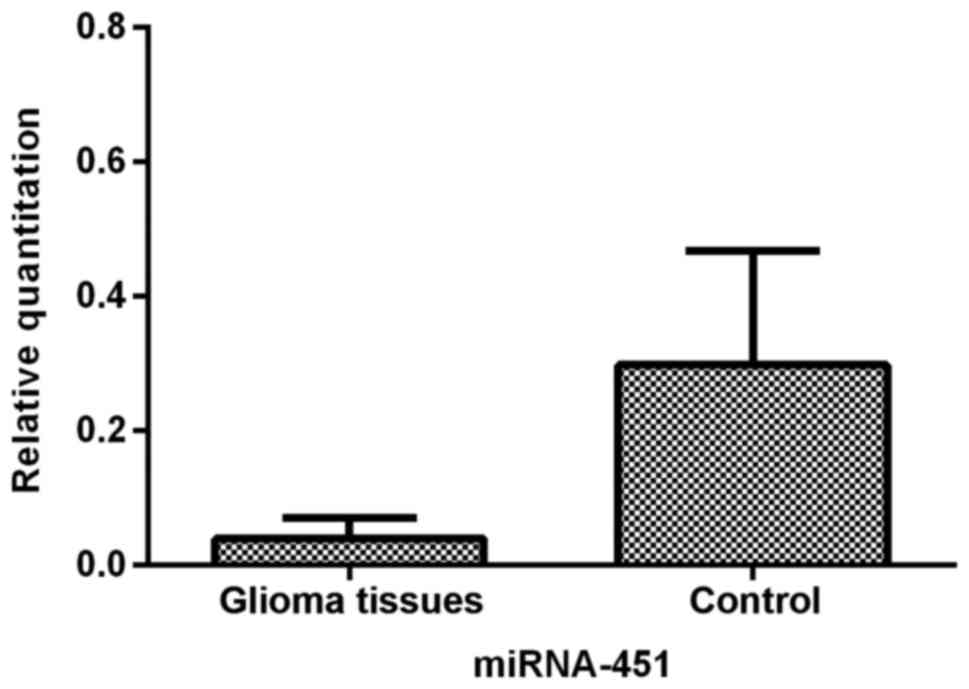
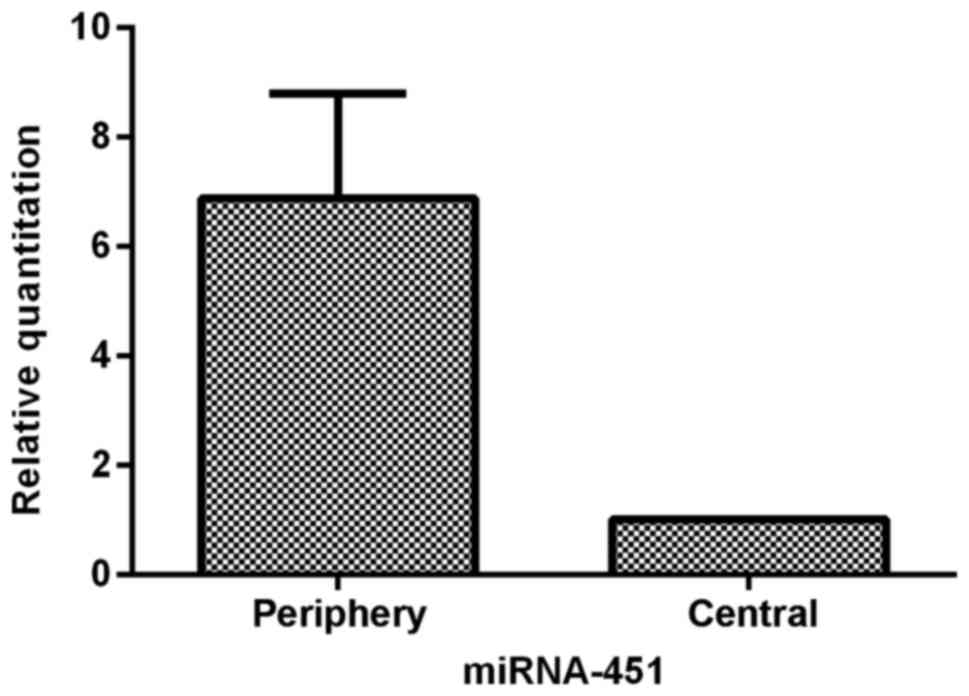
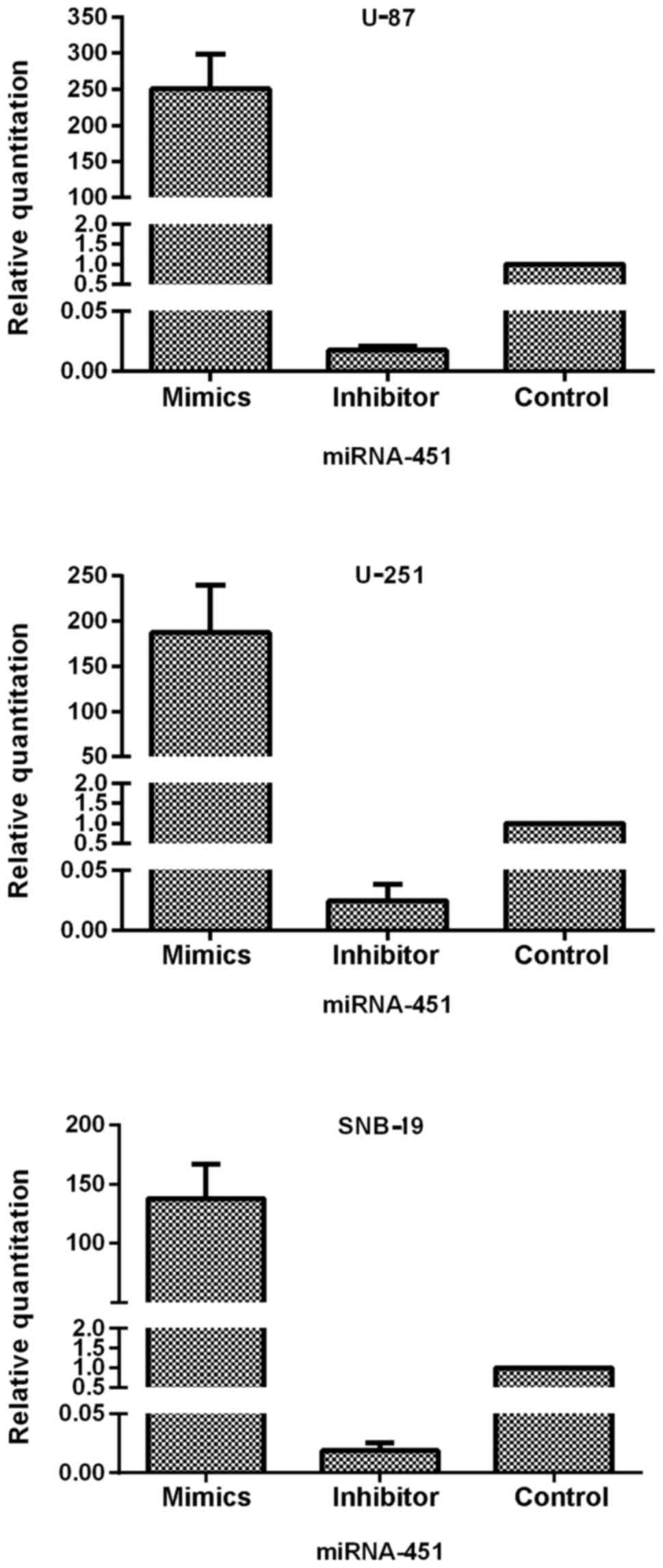
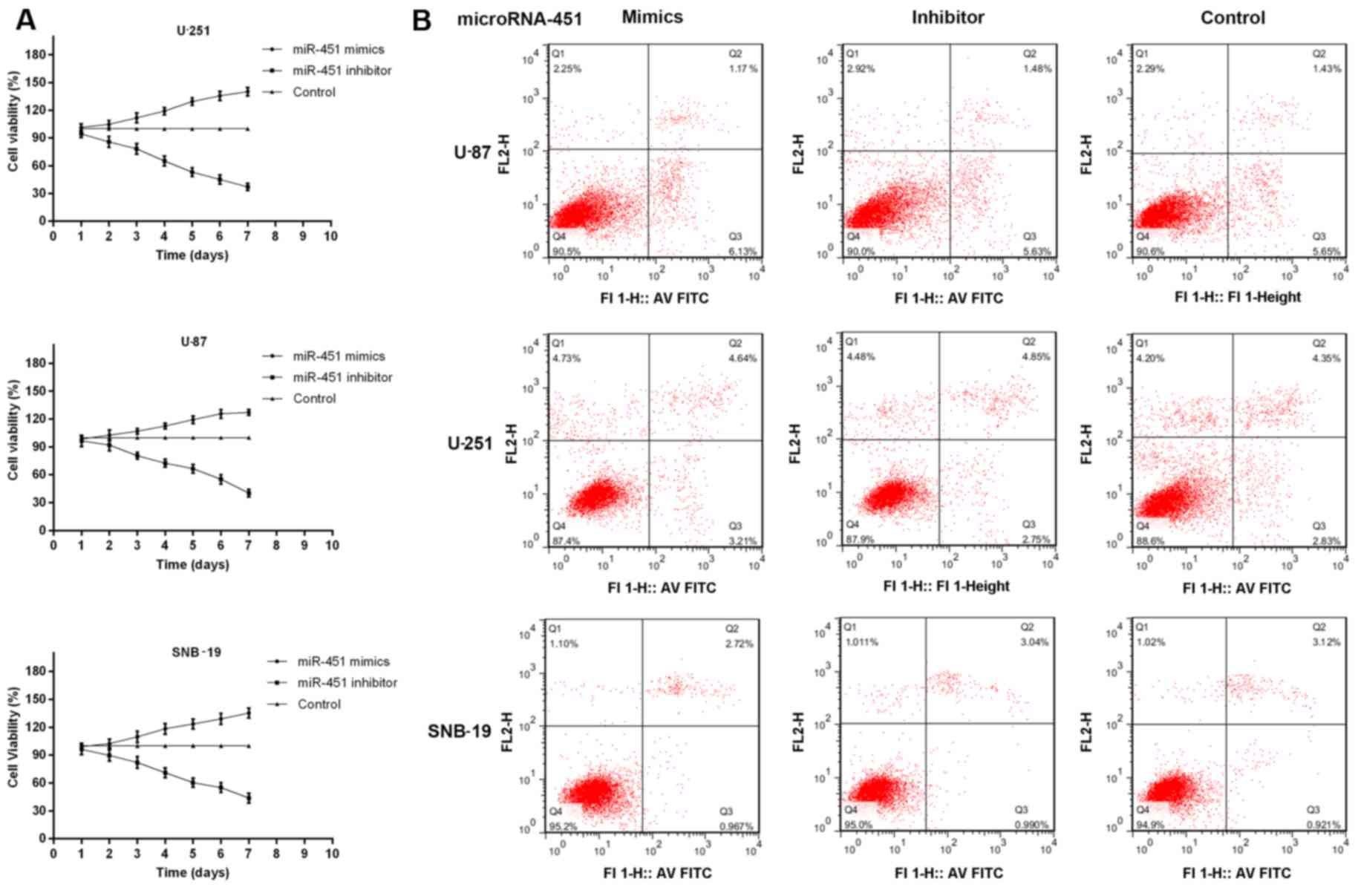
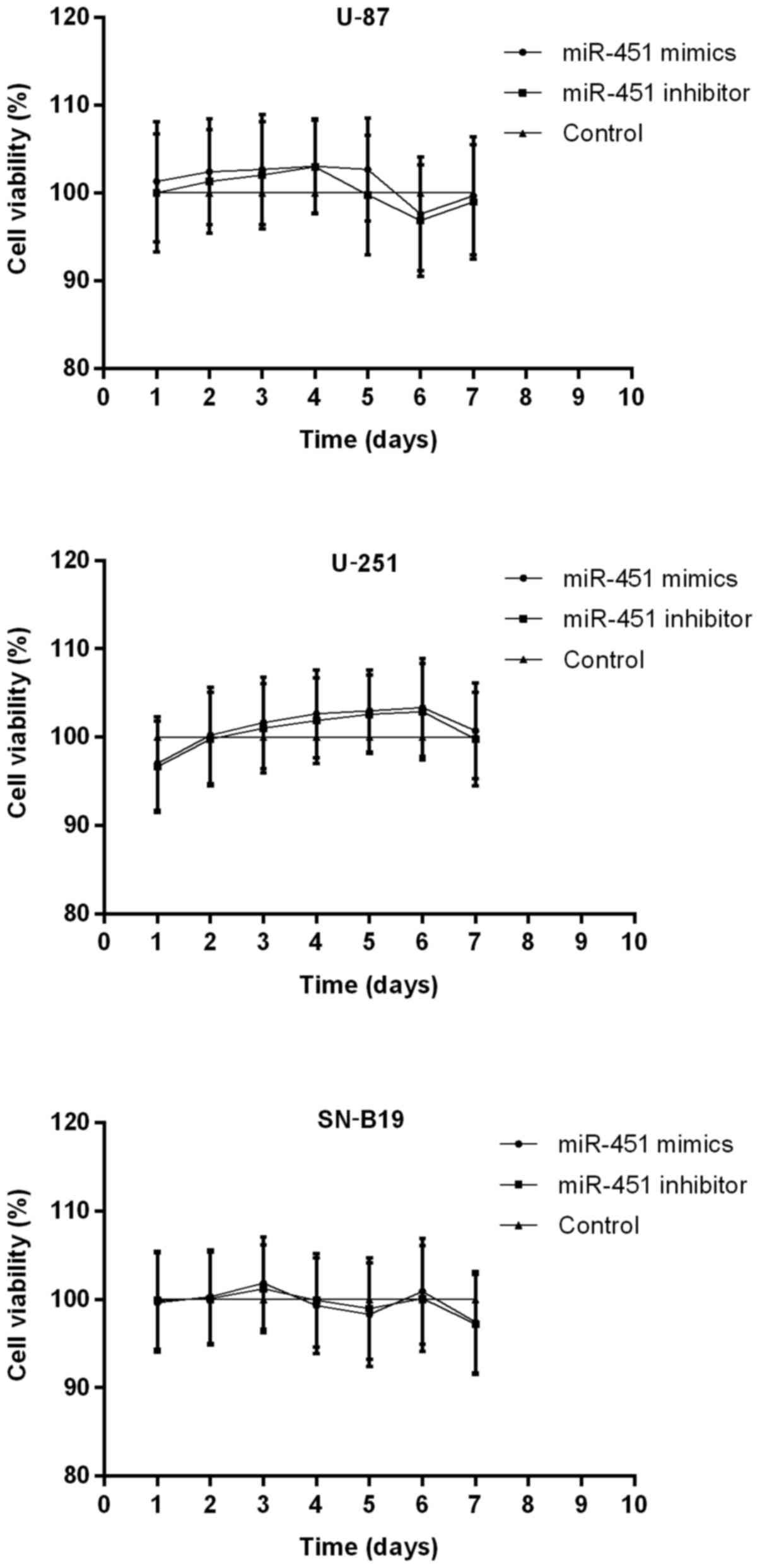
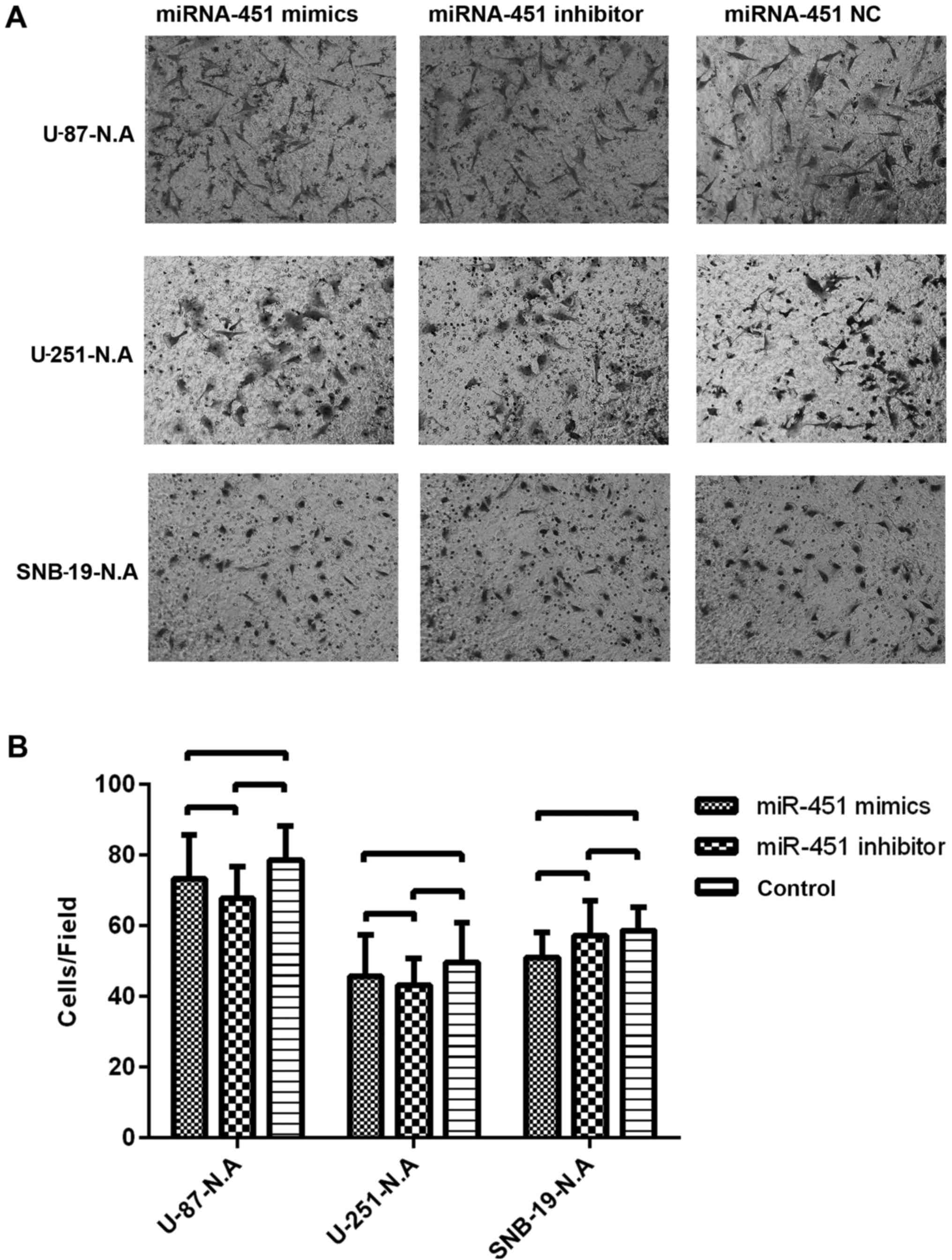
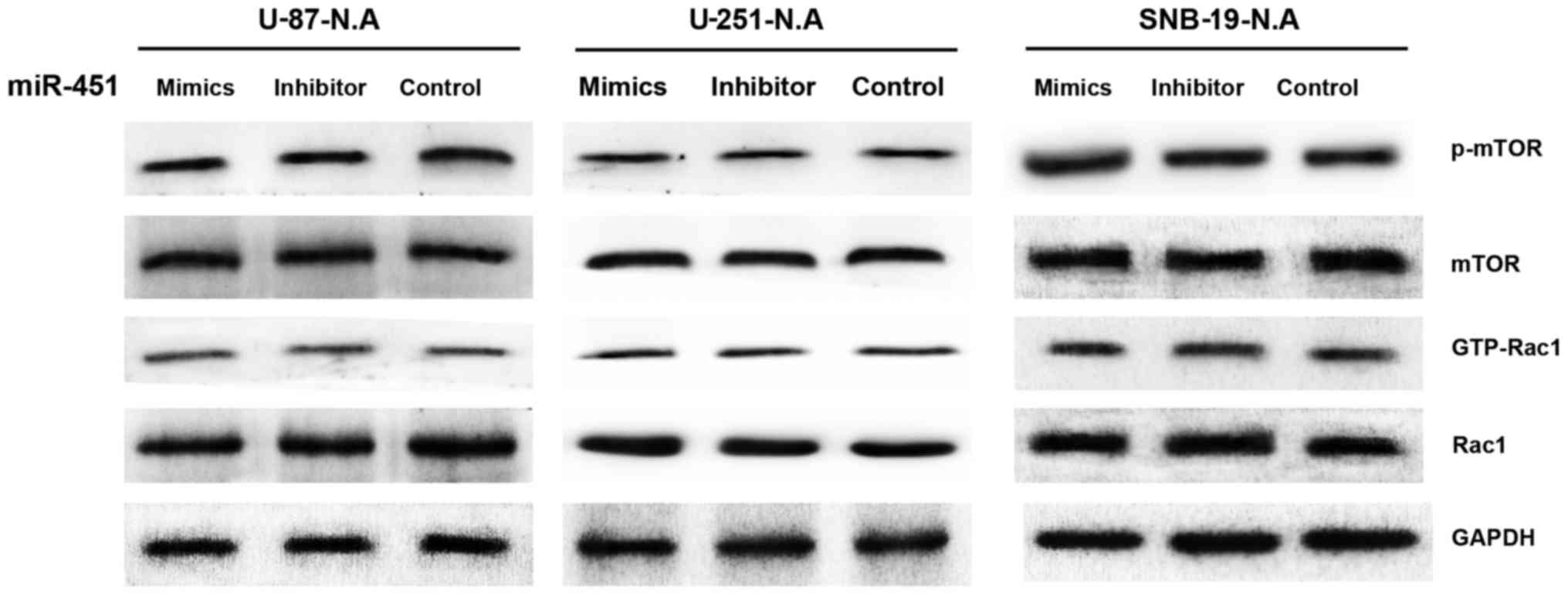
|
1
|
Furnari FB, Fenton T, Bachoo RM, Mukasa A,
Stommel JM, Stegh A, Hahn WC, Ligon KL, Louis DN, Brennan C, et al:
Malignant astrocytic glioma: Genetics, biology, and paths to
treatment. Genes Dev. 21:2683–2710. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen J, Li Y, Yu TS, McKay RM, Burns DK,
Kernie SG and Parada LF: A restricted cell population propagates
glioblastoma growth after chemotherapy. Nature. 488:522–526. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Westermark B: Glioblastoma: a moving
target. Ups J Med Sci. 117:251–256. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Giese A, Bjerkvig R, Berens ME and
Westphal M: Cost of migration: Invasion of malignant gliomas and
implications for treatment. J Clin Oncol. 21:1624–1636. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wild-Bode C, Weller M, Rimner A, Dichgans
J and Wick W: Sublethal irradiation promotes migration and
invasiveness of glioma cells: Implications for radiotherapy of
human glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 61:2744–2750. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Di Nicolantonio F, Mercer SJ, Knight LA,
Gabriel FG, Whitehouse PA, Sharma S, Fernando A, Glaysher S, Di
Palma S, Johnson P, et al: Cancer cell adaptation to chemotherapy.
BMC Cancer. 5:782005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu Y and Zhou BP: New insights of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer metastasis. Acta
Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 40:643–650. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hatzikirou H, Basanta D, Simon M, Schaller
K and Deutsch A: 'Go or grow': the key to the emergence of invasion
in tumour progression? Math Med Biol. 29:49–65. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wullschleger S, Loewith R and Hall MN: TOR
signaling in growth and metabolism. Cell. 124:471–484. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu X, Zhang X, Xiang J, Lv Y and Shi J:
miR-451: Potential role as tumor suppressor of human hepatoma cell
growth and invasion. Int J Oncol. 45:739–745. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nan Y, Han L, Zhang A, Wang G, Jia Z, Yang
Y, Yue X, Pu P, Zhong Y and Kang C: MiRNA-451 plays a role as tumor
suppressor in human glioma cells. Brain Res. 1359:14–21. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Grimson A, Farh KK, Johnston WK,
Garrett-Engele P, Lim LP and Bartel DP: MicroRNA targeting
specificity in mammals: Determinants beyond seed pairing. Mol Cell.
27:91–105. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kloosterman WP and Plasterk RH: The
diverse functions of microRNAs in animal development and disease.
Dev Cell. 11:441–450. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hatziapostolou M and Iliopoulos D:
Epigenetic aberrations during oncogenesis. Cell Mol Life Sci.
68:1681–1702. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Iorio MV and Croce CM: microRNA
involvement in human cancer. Carcinogenesis. 33:1126–1133. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang Y, Dutta A and Abounader R: The role
of microRNAs in glioma initiation and progression. Front Biosci
(Landmark Ed). 17:700–712. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Gits CM, van Kuijk PF, Jonkers MB, Boersma
AW, Smid M, van Ijcken WF, Coindre JM, Chibon F, Verhoef C,
Mathijssen RH, et al: MicroRNA expression profiles distinguish
liposarcoma subtypes and implicate miR-145 and miR-451 as tumor
suppressors. Int J Cancer. 135:348–361. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu D, Liu C, Wang X, Ingvarsson S and
Chen H: MicroRNA-451 suppresses tumor cell growth by
down-regulating IL6R gene expression. Cancer Epidemiol. 38:85–92.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Godlewski J, Nowicki MO, Bronisz A, Nuovo
G, Palatini J, De Lay M, Van Brocklyn J, Ostrowski MC, Chiocca EA
and Lawler SE: MicroRNA-451 regulates LKB1/AMPK signaling and
allows adaptation to metabolic stress in glioma cells. Mol Cell.
37:620–632. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Azab AK, Azab F, Blotta S, Pitsillides CM,
Thompson B, Runnels JM, Roccaro AM, Ngo HT, Melhem MR, Sacco A, et
al: RhoA and Rac1 GTPases play major and differential roles in
stromal cell-derived factor-1-induced cell adhesion and chemo-taxis
in multiple myeloma. Blood. 114:619–629. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Giese A, Loo MA, Tran N, Haskett D, Coons
SW and Berens ME: Dichotomy of astrocytoma migration and
proliferation. Int J Cancer. 67:275–282. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tamaki M, McDonald W, Amberger VR, Moore E
and Del Maestro RF: Implantation of C6 astrocytoma spheroid into
collagen type I gels: Invasive, proliferative, and enzymatic
char-acterizations. J Neurosurg. 87:602–609. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yu SP, Yang XJ, Zhang B, Ming HL, Chen C,
Ren BC, Liu ZF and Liu B: Enhanced invasion in vitro and the
distribution patterns in vivo of CD133+ glioma stem
cells. Chin Med J (Engl). 124:2599–2604. 2011.
|
|
26
|
de Groot JF, Fuller G, Kumar AJ, Piao Y,
Eterovic K, Ji Y and Conrad CA: Tumor invasion after treatment of
glioblastoma with bevacizumab: Radiographic and pathologic
correlation in humans and mice. Neuro Oncol. 12:233–242. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hardie DG: AMP-activated/SNF1 protein
kinases: Conserved guardians of cellular energy. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 8:774–785. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hardie DG and Carling D: The AMP-activated
protein kinase: Fuel gauge of the mammalian cell? Eur J Biochem.
246:259–273. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hardie DG, Scott JW, Pan DA and Hudson ER:
Management of cellular energy by the AMP-activated protein kinase
system. FEBS Lett. 546:113–120. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Carling D: The AMP-activated protein
kinase cascade - a unifying system for energy control. Trends
Biochem Sci. 29:18–24. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hardie DG: The AMP-activated protein
kinase pathway - new players upstream and downstream. J Cell Sci.
117:5479–5487. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kahn BB, Alquier T, Carling D and Hardie
DG: AMP-activated protein kinase: Ancient energy gauge provides
clues to modern understanding of metabolism. Cell Metab. 1:15–25.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hawley SA, Pan DA, Mustard KJ, Ross L,
Bain J, Edelman AM, Frenguelli BG and Hardie DG:
Calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase-beta is an alternative
upstream kinase for AMP-activated protein kinase. Cell Metab.
2:9–19. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hurley RL, Anderson KA, Franzone JM, Kemp
BE, Means AR and Witters LA: The
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinases are
AMP-activated protein kinase kinases. J Biol Chem. 280:29060–29066.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Woods A, Dickerson K, Heath R, Hong SP,
Momcilovic M, Johnstone SR, Carlson M and Carling D:
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase-beta
acts upstream of AMP-activated protein kinase in mammalian cells.
Cell Metab. 2:21–33. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Fan QW, Cheng C, Knight ZA, Haas-Kogan D,
Stokoe D, James CD, McCormick F, Shokat KM and Weiss WA: EGFR
signals to mTOR through PKC and independently of Akt in glioma. Sci
Signal. 2:ra42009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Horwitz AR and Parsons JT: Cell migration:
'movin' on. Science. 286:1102–1103. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Forget MA, Desrosiers RR, Gingras D and
Béliveau R: Phosphorylation states of Cdc42 and RhoA regulate their
interactions with Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor and their
extraction from biological membranes. Biochem J. 361:243–254. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang B, Sun J, Yu SP, Chen C, Liu B, Liu
ZF, Ren BC, Ming HL and Yang XJ: Rac1 cells distributed in
accordance with CD 133 cells in glioblastomas and the elevated
invasiveness of CD 133 glioma cells with higher Rac1 activity. Chin
Med J. 125:4344–4348. 2012.
|