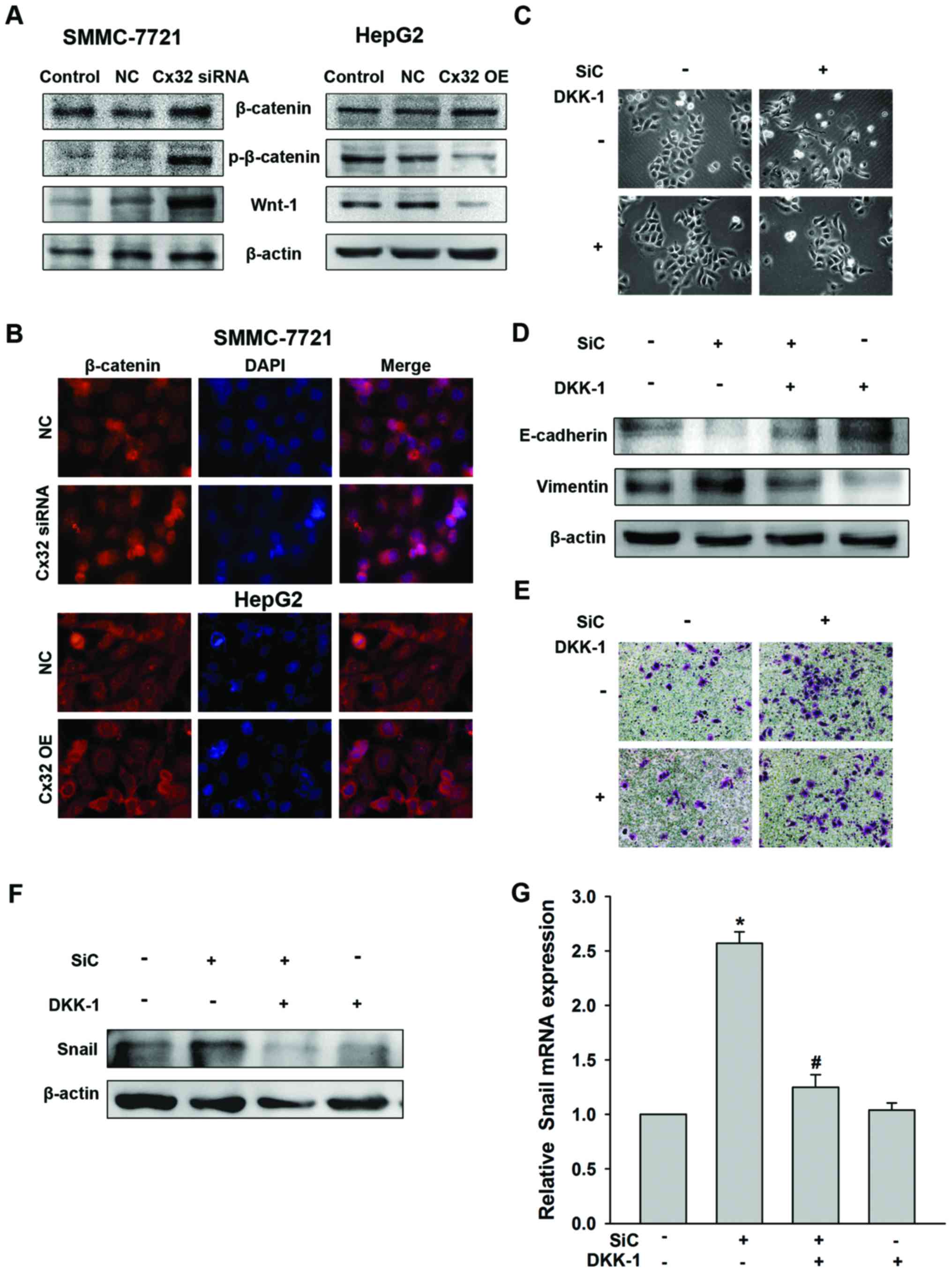
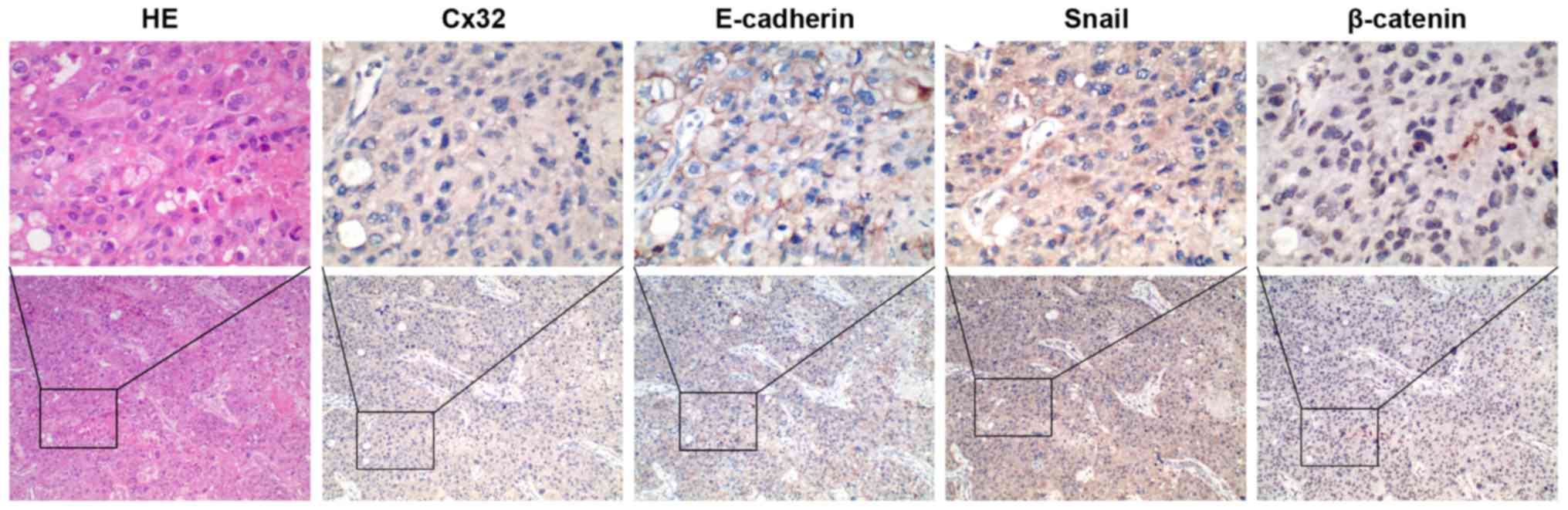
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rahbari NN, Mehrabi A, Mollberg NM, Müller
SA, Koch M, Büchler MW and Weitz J: Hepatocellular carcinoma:
Current management and perspectives for the future. Ann Surg.
253:453–469. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cauchy F, Soubrane O and Belghiti J: Liver
resection for HCC: Patient's selection and controversial scenarios.
Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 28:881–896. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cervantes-Arias A, Pang LY and Argyle DJ:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition as a fundamental mechanism
underlying the cancer phenotype. Vet Comp Oncol. 11:169–184. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zhou ZJ, Dai Z, Zhou SL, Hu ZQ, Chen Q,
Zhao YM, Shi YH, Gao Q, Wu WZ, Qiu SJ, et al: HNRNPAB induces
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes metastasis of
hepatocellular carcinoma by transcriptionally activating SNAIL.
Cancer Res. 74:2750–2762. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fu XT, Dai Z, Song K, Zhang ZJ, Zhou ZJ,
Zhou SL, Zhao YM, Xiao YS, Sun QM, Ding ZB, et al:
Macrophage-secreted IL-8 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition
in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by activating the
JAK2/STAT3/Snail pathway. Int J Oncol. 46:587–596. 2015.
|
|
7
|
Wu Y, Liu H, Weng H, Zhang X, Li P, Fan
CL, Li B, Dong PL, Li L, Dooley S, et al: Glypican-3 promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma cells
through ERK signaling pathway. Int J Oncol. 46:1275–1285.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yu M, Zhang C, Li L, Dong S, Zhang N and
Tong X: Cx43 reverses the resistance of A549 lung adenocarcinoma
cells to cisplatin by inhibiting EMT. Oncol Rep. 31:2751–2758.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mao XY, Li QQ, Gao YF, Zhou HH, Liu ZQ and
Jin WL: Gap junction as an intercellular glue: Emerging roles in
cancer EMT and metastasis. Cancer Lett. 381:133–137. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Naus CC and Laird DW: Implications and
challenges of connexin connections to cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
10:435–441. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vinken M, Henkens T, De Rop E, Fraczek J,
Vanhaecke T and Rogiers V: Biology and pathobiology of gap
junctional channels in hepatocytes. Hepatology. 47:1077–1088. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Mesnil M, Crespin S, Avanzo JL and
Zaidan-Dagli ML: Defective gap junctional intercellular
communication in the carcinogenic process. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1719:125–145. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fujimoto E, Sato H, Shirai S, Nagashima Y,
Fukumoto K, Hagiwara H, Negishi E, Ueno K, Omori Y, Yamasaki H, et
al: Connexin32 as a tumor suppressor gene in a metastatic renal
cell carcinoma cell line. Oncogene. 24:3684–3690. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
King TJ and Lampe PD: The gap junction
protein connexin32 is a mouse lung tumor suppressor. Cancer Res.
64:7191–7196. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ito A, Koma Y, Uchino K, Okada T,
Ohbayashi C, Tsubota N and Okada M: Increased expression of
connexin 26 in the invasive component of lung squamous cell
carcinoma: Significant correlation with poor prognosis. Cancer
Lett. 234:239–248. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kanczuga-Koda L, Sulkowska M, Koda M,
Rutkowski R and Sulkowski S: Increased expression of gap junction
protein-connexin 32 in lymph node metastases of human ductal breast
cancer. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 45(Suppl 1): S175–S180. 2007.
|
|
17
|
Stoletov K, Strnadel J, Zardouzian E,
Momiyama M, Park FD, Kelber JA, Pizzo DP, Hoffman R, VandenBerg SR
and Klemke RL: Role of connexins in metastatic breast cancer and
melanoma brain colonization. J Cell Sci. 126:904–913. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang Y, Zhu J, Zhang N, Zhao Y, Li WY,
Zhao FY, Ou YR, Qin SK and Wu Q: Impaired gap junctions in human
hepatocellular carcinoma limit intrinsic oxaliplatin
chemosensitivity: A key role of connexin 26. Int J Oncol.
48:703–713. 2016.
|
|
19
|
Regidor PA, Regidor M, Schindler AE and
Winterhager E: Aberrant expression pattern of gap junction
connexins in endometriotic tissues. Mol Hum Reprod. 3:375–381.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sugimachi K, Tanaka S, Kameyama T, Taguchi
K, Aishima S, Shimada M, Sugimachi K and Tsuneyoshi M:
Transcriptional repressor snail and progression of human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 9:2657–2664.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wu Q, Wang R, Yang Q, Hou X, Chen S, Hou
Y, Chen C, Yang Y, Miele L, Sarkar FH, et al: Chemoresistance to
gemcitabine in hepatoma cells induces epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and involves activation of PDGF-D pathway. Oncotarget.
4:1999–2009. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Edwards GO, Jondhale S, Chen T and Chipman
JK: A quantitative inverse relationship between connexin32
expression and cell proliferation in a rat hepatoma cell line.
Toxicology. 253:46–52. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhao B, Zhao W, Wang Y, Xu Y, Xu J, Tang
K, Zhang S, Yin Z, Wu Q and Wang X: Connexin32 regulates hepatoma
cell metastasis and proliferation via the p53 and Akt pathways.
Oncotarget. 6:10116–10133. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Heuberger J and Birchmeier W: Interplay of
cadherin-mediated cell adhesion and canonical Wnt signaling. Cold
Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2:–a002915. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
van Veelen W, Le NH, Helvensteijn W,
Blonden L, Theeuwes M, Bakker ER, Franken PF, van Gurp L, Meijlink
F, van der Valk MA, et al: β-catenin tyrosine 654 phosphorylation
increases Wnt signalling and intestinal tumorigenesis. Gut.
60:1204–1212. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Aguilera O, Fraga MF, Ballestar E, Paz MF,
Herranz M, Espada J, García JM, Muñoz A, Esteller M and
González-Sancho JM: Epigenetic inactivation of the Wnt antagonist
DICKKOPF-1 (DKK-1) gene in human colorectal cancer. Oncogene.
25:4116–4121. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li Q, Omori Y, Nishikawa Y, Yoshioka T,
Yamamoto Y and Enomoto K: Cytoplasmic accumulation of connexin32
protein enhances motility and metastatic ability of human hepatoma
cells in vitro and in vivo. Int J Cancer. 121:536–546. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Moreno-Bueno G, Portillo F and Cano A:
Transcriptional regulation of cell polarity in EMT and cancer.
Oncogene. 27:6958–6969. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang Y, Shi J, Chai K, Ying X and Zhou BP:
The role of Snail in EMT and tumorigenesis. Curr Cancer Drug
Targets. 13:963–972. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yook JI, Li XY, Ota I, Hu C, Kim HS, Kim
NH, Cha SY, Ryu JK, Choi YJ, Kim J, et al: A Wnt-Axin2-GSK3beta
cascade regulates Snail1 activity in breast cancer cells. Nat Cell
Biol. 8:1398–1406. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bachelder RE, Yoon SO, Franci C, de
Herreros AG and Mercurio AM: Glycogen synthase kinase-3 is an
endogenous inhibitor of Snail transcription: Implications for the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Cell Biol. 168:29–33. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim M, Lee HC, Tsedensodnom O, Hartley R,
Lim YS, Yu E, Merle P and Wands JR: Functional interaction between
Wnt3 and Frizzled-7 leads to activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin
signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Hepatol.
48:780–791. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Plante I, Charbonneau M and Cyr DG:
Activation of the integrin-linked kinase pathway downregulates
hepatic connexin32 via nuclear Akt. Carcinogenesis. 27:1923–1929.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|