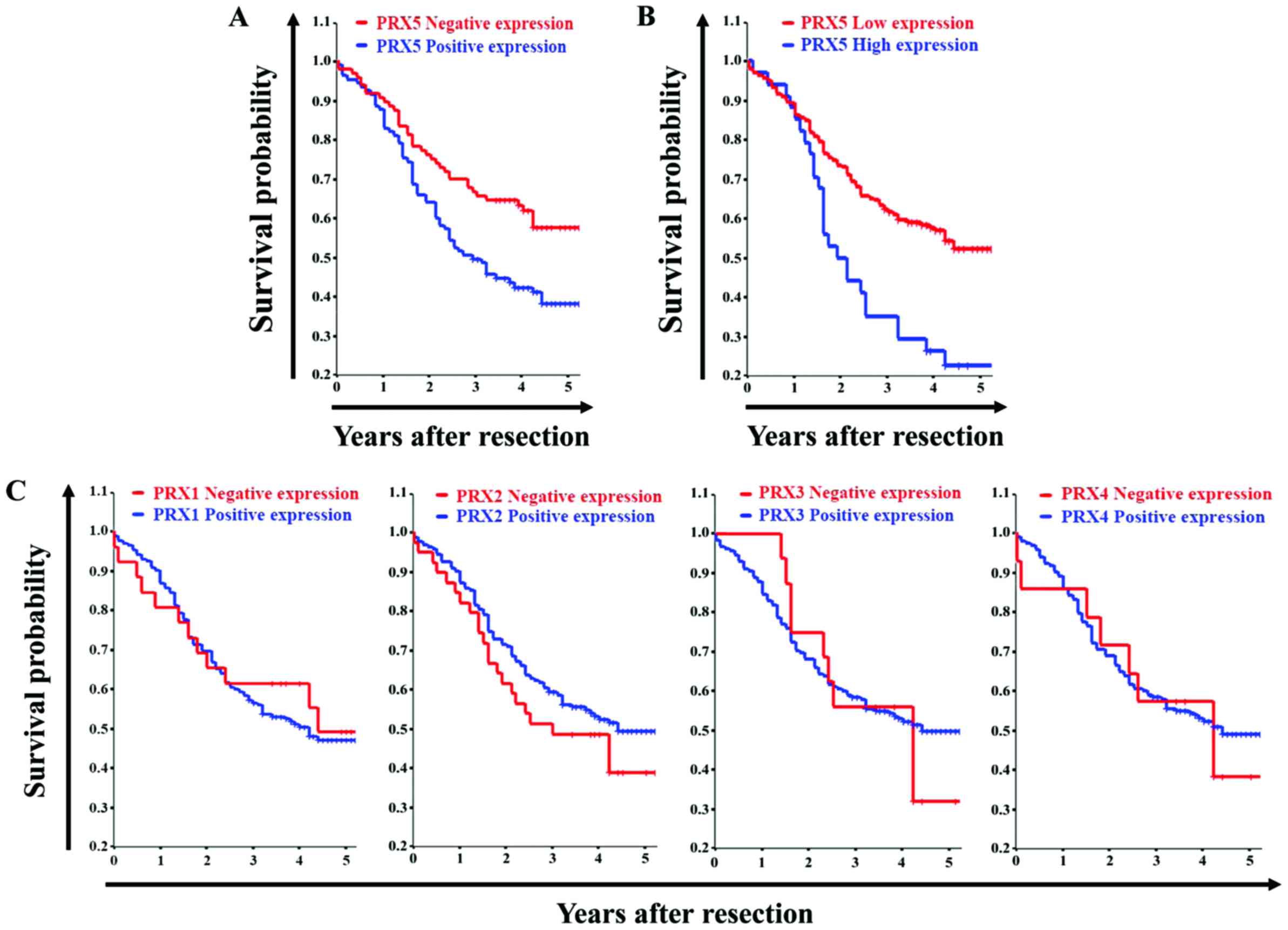
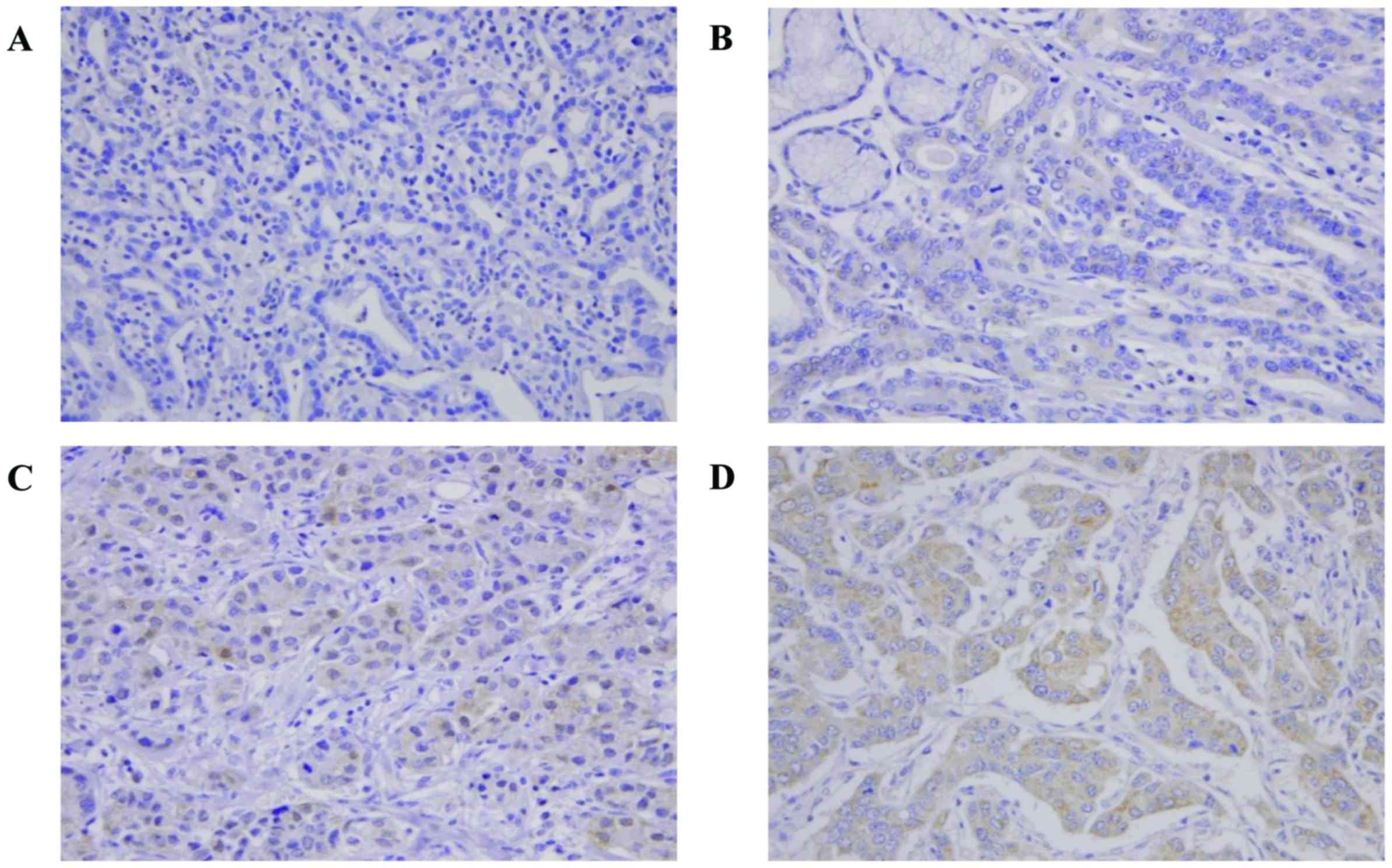
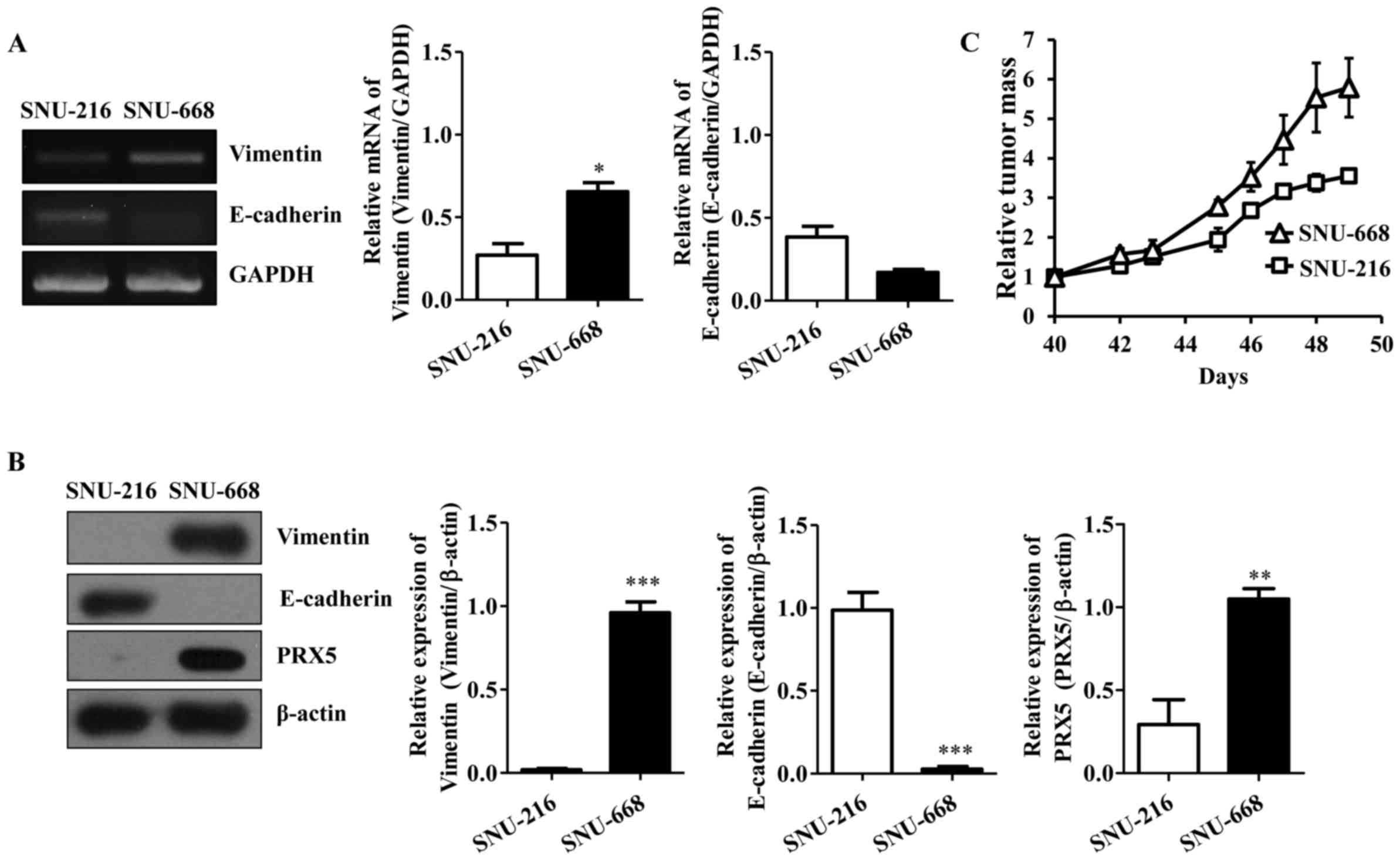
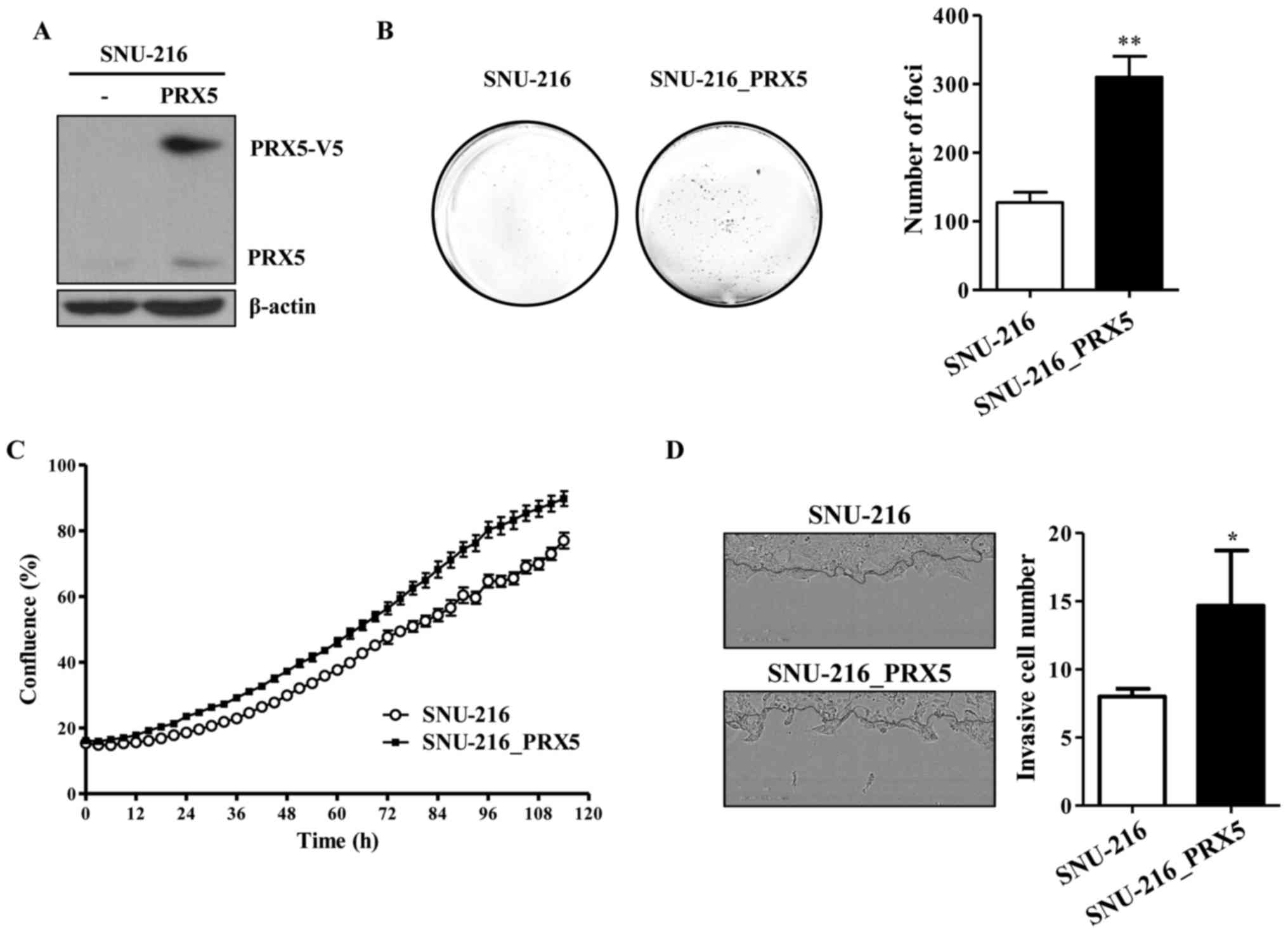
|
1
|
Yoon JH, Choi WS, Kim O, Choi BJ, Nam SW,
Lee JY and Park WS: Gastrokine 1 inhibits gastric cancer cell
migration and invasion by downregulating RhoA expression. Gastric
Cancer. 20:274–285. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Burlaka AP, Ganusevich II, Gafurov MR,
Lukin SM and Sidorik EP: Stomach Cancer: interconnection between
the redox state, activity of MMP-2, MMP-9 and stage of tumor
growth. Cancer Microenviron. 9:27–32. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kim KH, Lee KW, Baek SK, Chang HJ, Kim YJ,
Park DJ, Kim JH, Kim HH and Lee JS: Survival benefit of gastrectomy
± metastasectomy in patients with metastatic gastric cancer
receiving chemotherapy. Gastric Cancer. 14:130–138. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cheon SH, Rha SY, Jeung HC, Im CK, Kim SH,
Kim HR, Ahn JB, Roh JK, Noh SH and Chung HC: Survival benefit of
combined curative resection of the stomach (D2 resection) and liver
in gastric cancer patients with liver metastases. Ann Oncol.
19:1146–1153. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Otsuki S, Inokuchi M, Enjoji M, Ishikawa
T, Takagi Y, Kato K, Yamada H, Kojima K and Sugihara K: Vimentin
expression is associated with decreased survival in gastric cancer.
Oncol Rep. 25:1235–1242. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rosivatz E, Becker KF, Kremmer E, Schott
C, Blechschmidt K, Höfler H and Sarbia M: Expression and nuclear
localization of Snail, an E-cadherin repressor, in adenocarcinomas
of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Virchows Arch. 448:277–287.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JM and Cross CE:
Free radicals, antioxidants, and human disease: Where are we now? J
Lab Clin Med. 119:598–620. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Finkel T and Holbrook NJ: Oxidants,
oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature. 408:239–247.
2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Finkel T: Oxidant signals and oxidative
stress. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 15:247–254. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Grek CL and Tew KD: Redox metabolism and
malignancy. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 10:362–368. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Poli G, Leonarduzzi G, Biasi F and
Chiarpotto E: Oxidative stress and cell signalling. Curr Med Chem.
11:1163–1182. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tehan L, Taparra K and Phelan S:
Peroxiredoxin overexpression in MCF-7 breast cancer cells and
regulation by cell proliferation and oxidative stress. Cancer
Invest. 31:374–384. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kropotov A, Gogvadze V, Shupliakov O,
Tomilin N, Serikov VB, Tomilin NV and Zhivotovsky B: Peroxiredoxin
V is essential for protection against apoptosis in human lung
carcinoma cells. Exp Cell Res. 312:2806–2815. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Caldeira J, Figueiredo J, Brás-Pereira C,
Carneiro P, Moreira AM, Pinto MT, Relvas JB, Carneiro F, Barbosa M,
Casares F, et al: E-cadherin-defective gastric cancer cells depend
on Laminin to survive and invade. Hum Mol Genet. 24:5891–5900.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen HC, Chu RY, Hsu PN, Hsu PI, Lu JY,
Lai KH, Tseng HH, Chou NH, Huang MS, Tseng CJ, et al: Loss of
E-cadherin expression correlates with poor differentiation and
invasion into adjacent organs in gastric adenocarcinomas. Cancer
Lett. 201:97–106. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tölle A, Schlame M, Charlier N, Guthmann F
and Rüstow B: Vitamin E differentially regulates the expression of
peroxire-doxin-1 and -6 in alveolar type II cells. Free Radic Biol
Med. 38:1401–1408. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kim B, Park J, Chang KT and Lee DS:
Peroxiredoxin 5 prevents amyloid-beta oligomer-induced neuronal
cell death by inhibiting ERK-Drp1-mediated mitochondrial
fragmentation. Free Radic Biol Med. 90:184–194. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Knoops B, Goemaere J, Van der Eecken V and
Declercq JP: Peroxiredoxin 5: Structure, mechanism, and function of
the mammalian atypical 2-Cys peroxiredoxin. Antioxid Redox Signal.
15:817–829. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Li L, Zhang YG and Chen CL: Anti-apoptotic
role of peroxiredoxin III in cervical cancer cells. FEBS Open Bio.
3:51–54. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Whitaker HC, Patel D, Howat WJ, Warren AY,
Kay JD, Sangan T, Marioni JC, Mitchell J, Aldridge S, Luxton HJ, et
al: Peroxiredoxin-3 is overexpressed in prostate cancer and
promotes cancer cell survival by protecting cells from oxidative
stress. Br J Cancer. 109:983–993. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Choi H, Chang JW and Jung YK:
Peroxiredoxin 6 interferes with TRAIL-induced death-inducing
signaling complex formation by binding to death effector domain
caspase. Cell Death Differ. 18:405–414. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Japanese Gastric Cancer Association:
Japanese classification of gastric carcinoma. 2nd English edition.
Gastric Cancer. 1:10–24. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Han G, Lu SL, Li AG, He W, Corless CL,
Kulesz-Martin M and Wang XJ: Distinct mechanisms of
TGF-beta1-mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and
metastasis during skin carcinogenesis. J Clin Invest.
115:1714–1723. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee JM, Dedhar S, Kalluri R and Thompson
EW: The epithelial-mesenchymal transition: New insights in
signaling, development, and disease. J Cell Biol. 172:973–981.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shih JY and Yang PC: The EMT regulator
slug and lung carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 32:1299–1304. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Iwatsuki M, Mimori K, Yokobori T, Ishi H,
Beppu T, Nakamori S, Baba H and Mori M: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in cancer development and its clinical significance.
Cancer Sci. 101:293–299. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Sung WJ, Park KS, Kwak SG, Hyun DS, Jang
JS and Park KK: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in patients of
pulmonary adenocarcinoma: Correlation with cancer stem cell markers
and prognosis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:8997–9009. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhai X, Zhu H, Wang W, Zhang S, Zhang Y
and Mao G: Abnormal expression of EMT-related proteins, S100A4,
vimentin and E-cadherin, is correlated with clinicopathological
features and prognosis in HCC. Med Oncol. 31:9702014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Han MW, Lee JC, Kim YM, Cha HJ, Roh JL,
Choi SH, Nam SY, Cho KJ, Kim SW and Kim SY: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition: Clinical implications for nodal metastasis and
prognosis of tongue cancer. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 152:80–86.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|