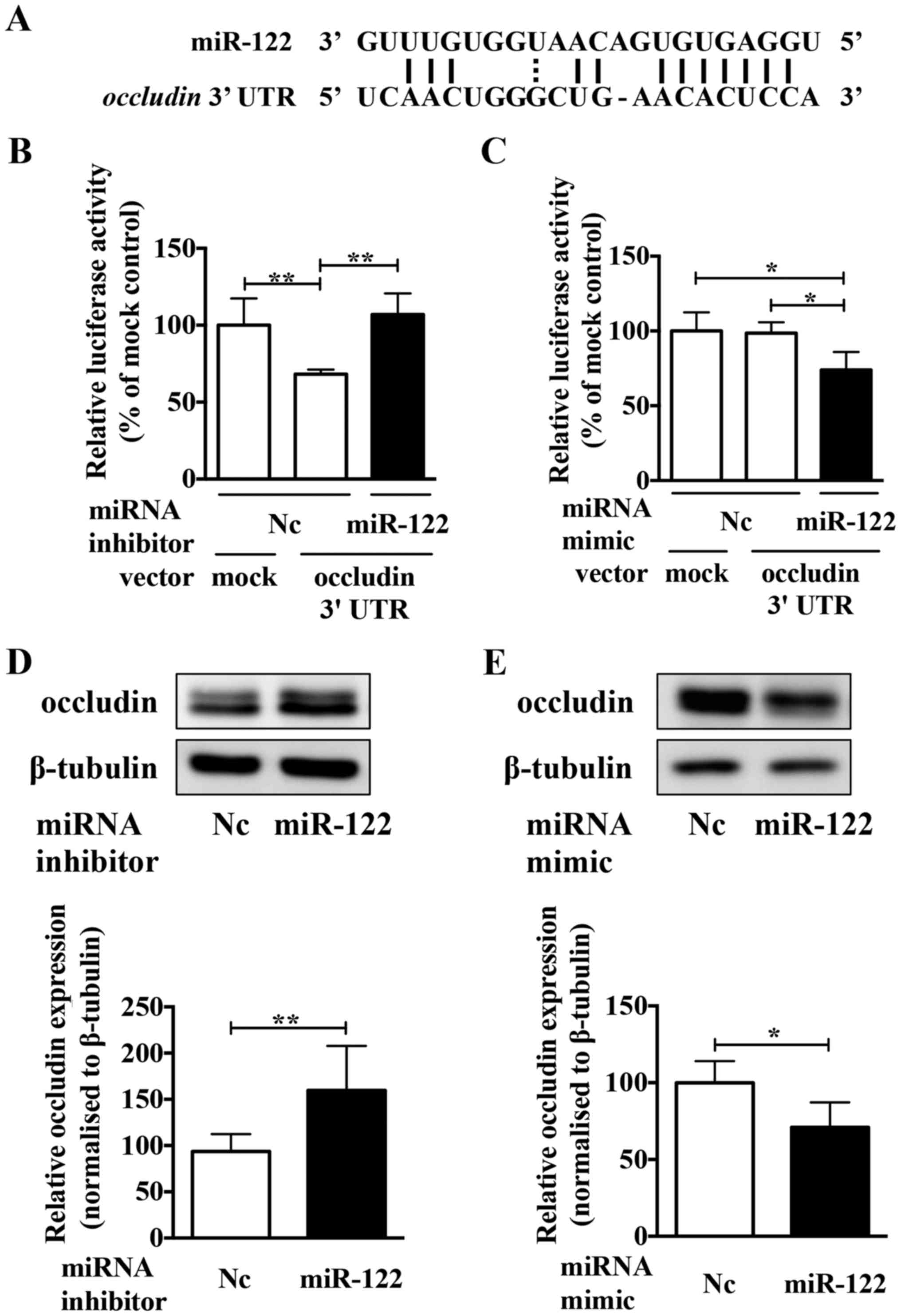
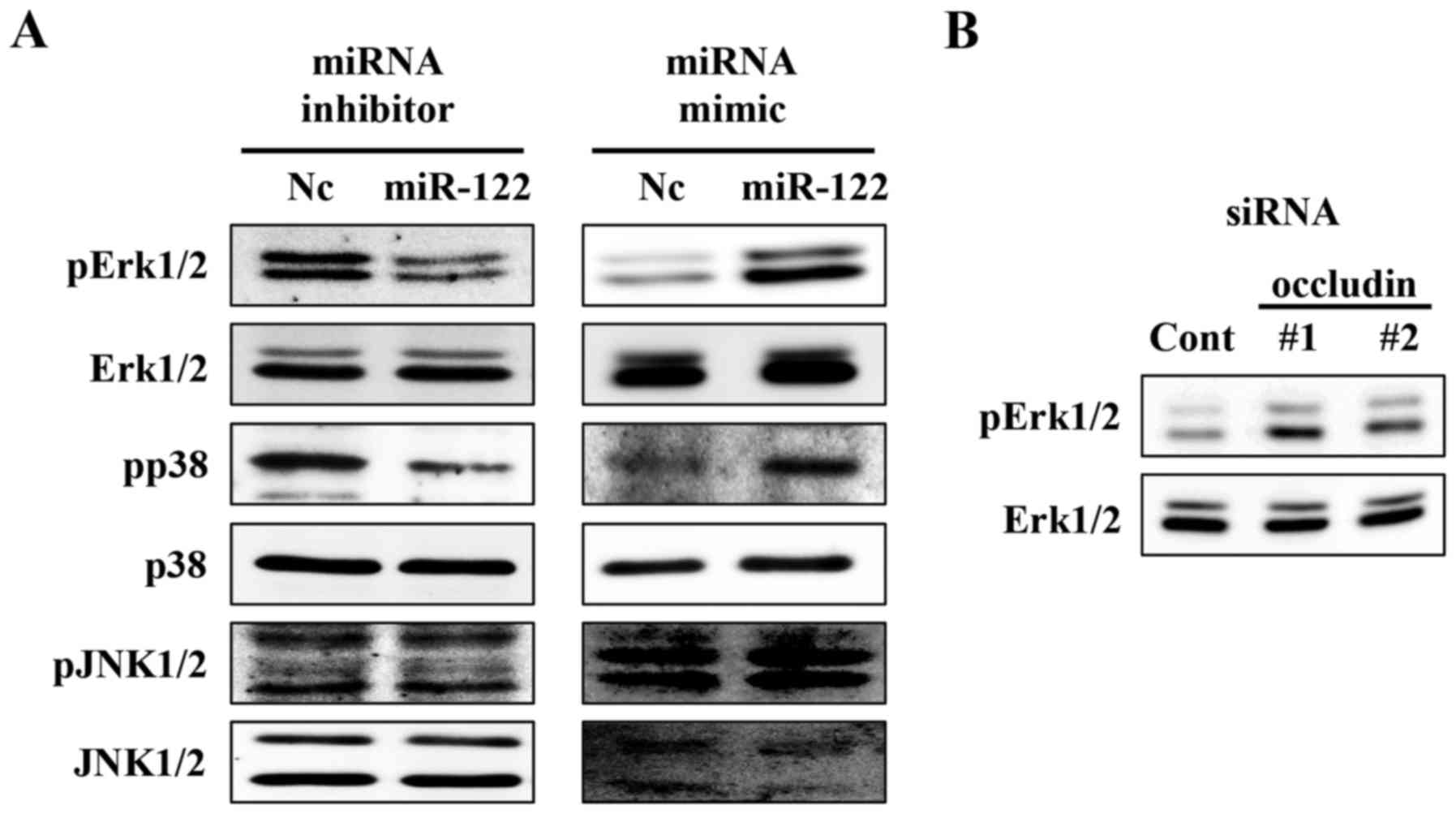
|
1
|
Jonasch E, Futreal PA, Davis IJ, Bailey
ST, Kim WY, Brugarolas J, Giaccia AJ, Kurban G, Pause A, Frydman J,
et al: State of the science: An update on renal cell carcinoma. Mol
Cancer Res. 10:859–880. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dutcher JP: Recent developments in the
treatment of renal cell carcinoma. Ther Adv Urol. 5:338–353. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ha M and Kim VN: Regulation of microRNA
biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:509–524. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jansson MD and Lund AH: MicroRNA and
cancer. Mol Oncol. 6:590–610. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lin S and Gregory RI: MicroRNA biogenesis
pathways in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 15:321–333. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li M, Wang Y, Song Y, Bu R, Yin B, Fei X,
Guo Q and Wu B: MicroRNAs in renal cell carcinoma: A systematic
review of clinical implications (Review). Oncol Rep. 33:1571–1578.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Weng L, Wu X, Gao H, Mu B, Li X, Wang JH,
Guo C, Jin JM, Chen Z, Covarrubias M, et al: MicroRNA profiling of
clear cell renal cell carcinoma by whole-genome small RNA deep
sequencing of paired frozen and formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded
tissue specimens. J Pathol. 222:41–51. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jingushi K, Ueda Y, Kitae K, Hase H, Egawa
H, Ohshio I, Kawakami R, Kashiwagi Y, Tsukada Y, Kobayashi T, et
al: miR-629 targets TRIM33 to promote TGFβ/Smad signaling and
metastatic phenotypes in ccRCC. Mol Cancer Res. 13:565–574. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Nakata W, Uemura M, Sato M, Fujita K,
Jingushi K, Ueda Y, Kitae K, Tsujikawa K and Nonomura N: Expression
of miR-27a-3p is an independent predictive factor for recurrence in
clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:21645–21654. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Osanto S, Qin Y, Buermans HP, Berkers J,
Lerut E, Goeman JJ and van Poppel H: Genome-wide microRNA
expression analysis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma by next
generation deep sequencing. PLoS One. 7:e382982012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tang K and Xu H: Prognostic value of
meta-signature miRNAs in renal cell carcinoma: An integrated miRNA
expression profiling analysis. Sci Rep. 5:102722015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gramantieri L, Ferracin M, Fornari F,
Veronese A, Sabbioni S, Liu CG, Calin GA, Giovannini C, Ferrazzi E,
Grazi GL, et al: Cyclin G1 is a target of miR-122a, a microRNA
frequently down-regulated in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer
Res. 67:6092–6099. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang F, Zhang L, Wang F, Wang Y, Huo XS,
Yin YX, Wang YQ, Zhang L and Sun SH: Modulation of the unfolded
protein response is the core of microRNA-122-involved sensitivity
to chemotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Neoplasia. 13:590–600.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nassirpour R, Mehta PP and Yin MJ: miR-122
regulates tumorigenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting
AKT3. PLoS One. 8:e796552013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chow TF, Youssef YM, Lianidou E, Romaschin
AD, Honey RJ, Stewart R, Pace KT and Yousef GM: Differential
expression profiling of microRNAs and their potential involvement
in renal cell carcinoma pathogenesis. Clin Biochem. 43:150–158.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chen J, Zhang D, Zhang W, Tang Y, Yan W,
Guo L and Shen B: Clear cell renal cell carcinoma associated
microRNA expression signatures identified by an integrated
bioinformatics analysis. J Transl Med. 11:1692013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lian JH, Wang WH, Wang JQ, Zhang YH and Li
Y: MicroRNA-122 promotes proliferation, invasion and migration of
renal cell carcinoma cells through the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:5017–5021. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fong MY, Zhou W, Liu L, Alontaga AY,
Chandra M, Ashby J, Chow A, O'Connor ST, Li S, Chin AR, et al:
Breast-cancer-secreted miR-122 reprograms glucose metabolism in
premetastatic niche to promote metastasis. Nat Cell Biol.
17:183–194. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tsukita S and Furuse M: Occludin and
claudins in tight-junction strands: Leading or supporting players?
Trends Cell Biol. 9:268–273. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jiang WG, Martin TA, Matsumoto K, Nakamura
T and Mansel RE: Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor decreases
the expression of occludin and transendothelial resistance (TER)
and increases paracellular permeability in human vascular
endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 181:319–329. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jiang WG, Bryce RP, Horrobin DF and Mansel
RE: Regulation of tight junction permeability and occludin
expression by polyunsaturated fatty acids. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 244:414–420. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gopalakrishnan S, Raman N, Atkinson SJ and
Marrs JA: Rho GTPase signaling regulates tight junction assembly
and protects tight junctions during ATP depletion. Am J Physiol.
275:C798–C809. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
van ZF: Krupitza G and Mikulits W: Initial
steps of metastasis: Cell invasion and endothelial transmigration.
Mutat Res. 728:23–34. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Stoletov K, Kato H, Zardouzian E, Kelber
J, Yang J, Shattil S and Klemke R: Visualizing extravasation
dynamics of metastatic tumor cells. J Cell Sci. 123:2332–2341.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shin K, Fogg VC and Margolis B: Tight
junctions and cell polarity. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 22:207–235.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rao R: Occludin phosphorylation in
regulation of epithelial tight junctions. Ann NY Acad Sci.
1165:62–68. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Van Itallie CM, Fanning AS, Holmes J and
Anderson JM: Occludin is required for cytokine-induced regulation
of tight junction barriers. J Cell Sci. 123:2844–2852. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Raleigh DR, Boe DM, Yu D, Weber CR,
Marchiando AM, Bradford EM, Wang Y, Wu L, Schneeberger EE, Shen L,
et al: Occludin S408 phosphorylation regulates tight junction
protein interactions and barrier function. J Cell Biol.
193:565–582. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li D and Mrsny RJ: Oncogenic Raf-1
disrupts epithelial tight junctions via downregulation of occludin.
J Cell Biol. 148:791–800. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Runkle EA, Rice SJ, Qi J, Masser D,
Antonetti DA, Winslow MM and Mu D: Occludin is a direct target of
thyroid transcription factor-1 (TTF-1/NKX2-1). J Biol Chem.
287:28790–28801. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Osanai M, Murata M, Nishikiori N, Chiba H,
Kojima T and Sawada N: Epigenetic silencing of occludin promotes
tumorigenic and metastatic properties of cancer cells via
modulations of unique sets of apoptosis-associated genes. Cancer
Res. 66:9125–9133. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Osanai M, Murata M, Nishikiori N, Chiba H,
Kojima T and Sawada N: Occludin-mediated premature senescence is a
fail-safe mechanism against tumorigenesis in breast carcinoma
cells. Cancer Sci. 98:1027–1034. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Long H, Crean CD, Lee WH, Cummings OW and
Gabig TG: Expression of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin
receptors claudin-3 and claudin-4 in prostate cancer epithelium.
Cancer Res. 61:7878–7881. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tzelepi VN, Tsamandas AC, Vlotinou HD,
Vagianos CE and Scopa CD: Tight junctions in thyroid
carcinogenesis: Diverse expression of claudin-1, claudin-4,
claudin-7 and occludin in thyroid neoplasms. Mod Pathol. 21:22–30.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Harten SK, Shukla D, Barod R, Hergovich A,
Balda MS, Matter K, Esteban MA and Maxwell PH: Regulation of renal
epithelial tight junctions by the von Hippel-Lindau tumor
suppressor gene involves occludin and claudin 1 and is independent
of E-cadherin. Mol Biol Cell. 20:1089–1101. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
36
|
Blain SW, Scher HI, Cordon-Cardo C and
Koff A: p27 as a target for cancer therapeutics. Cancer Cell.
3:111–115. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Henze AT, Garvalov BK, Seidel S, Cuesta
AM, Ritter M, Filatova A, Foss F, Dopeso H, Essmann CL, Maxwell PH,
et al: Loss of PHD3 allows tumours to overcome hypoxic growth
inhibition and sustain proliferation through EGFR. Nat Commun.
5:55822014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Garvalov BK, Foss F, Henze AT, Bethani I,
Gräf-Höchst S, Singh D, Filatova A, Dopeso H, Seidel S, Damm M, et
al: PHD3 regulates EGFR internalization and signalling in tumours.
Nat Commun. 5:55772014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lin SC, Chien CW, Lee JC, Yeh YC, Hsu KF,
Lai YY, Lin SC and Tsai SJ: Suppression of dual-specificity
phosphatase-2 by hypoxia increases chemoresistance and malignancy
in human cancer cells. J Clin Invest. 121:1905–1916. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Nagaoka K, Fujii K, Zhang H, Usuda K,
Watanabe G, Ivshina M and Richter JD: CPEB1 mediates
epithelial-to-mesenchyme transition and breast cancer metastasis.
Oncogene. 35:2893–2901. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
41
|
Yan X, Zhou H and Zhang T, Xu P, Zhang S,
Huang W, Yang L, Gu X, Ni R and Zhang T: Downregulation of FOXP2
promoter human hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion. Tumour Biol.
36:9611–9619. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kuo IY, Wu CC, Chang JM, Huang YL, Lin CH,
Yan JJ, Sheu BS, Lu PJ, Chang WL, Lai WW, et al: Low SOX17
expression is a prognostic factor and drives transcriptional
dysregulation and esophageal cancer progression. Int J Cancer.
135:563–573. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Günzel D and Yu AS: Claudins and the
modulation of tight junction permeability. Physiol Rev. 93:525–569.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Takai Y and Nakanishi H: Nectin and
afadin: Novel organizers of intercellular junctions. J Cell Sci.
116:17–27. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Cheng L, Montironi R, Davidson DD and
Lopez-Beltran A: Staging and reporting of urothelial carcinoma of
the urinary bladder. Mod Pathol. 22(Suppl 2): S70–S95. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lim SB, Yu CS, Jang SJ, Kim TW, Kim JH and
Kim JC: Prognostic significance of lymphovascular invasion in
sporadic colorectal cancer. Dis Colon Rectum. 53:377–384. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Cheng L, Jones TD, Lin H, Eble JN, Zeng G,
Carr MD and Koch MO: Lymphovascular invasion is an independent
prognostic factor in prostatic adenocarcinoma. J Urol.
174:2181–2185. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Katz MD, Serrano MF, Humphrey PA, Grubb RL
III, Skolarus TA, Gao F and Kibel AS: The role of lymphovascular
space invasion in renal cell carcinoma as a prognostic marker of
survival after curative resection. Urol Oncol. 29:738–744. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Belsante M, Darwish O, Youssef R, Bagrodia
A, Kapur P, Sagalowsky AI, Lotan Y and Margulis V: Lymphovascular
invasion in clear cell renal cell carcinoma - association with
disease-free and cancer-specific survival. Urol Oncol.
32:30.e23–30.e28. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Wang B, Wang H and Yang Z: MiR-122
inhibits cell proliferation and tumorigenesis of breast cancer by
targeting IGF1R. PLoS One. 7:e470532012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Janssen HL, Reesink HW, Lawitz EJ, Zeuzem
S, Rodriguez-Torres M, Patel K, van der Meer AJ, Patick AK, Chen A,
Zhou Y, et al: Treatment of HCV infection by targeting microRNA. N
Engl J Med. 368:1685–1694. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|