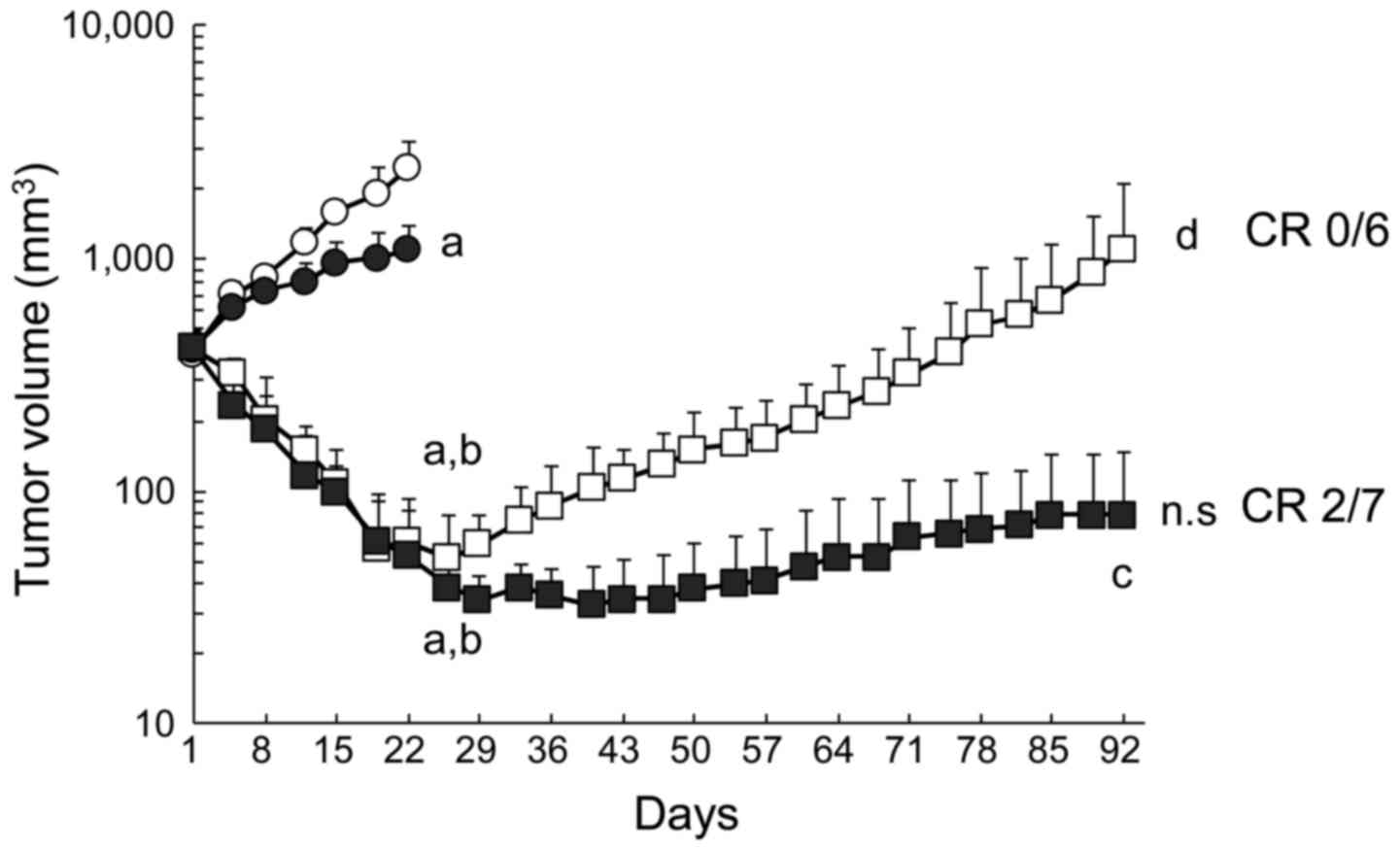
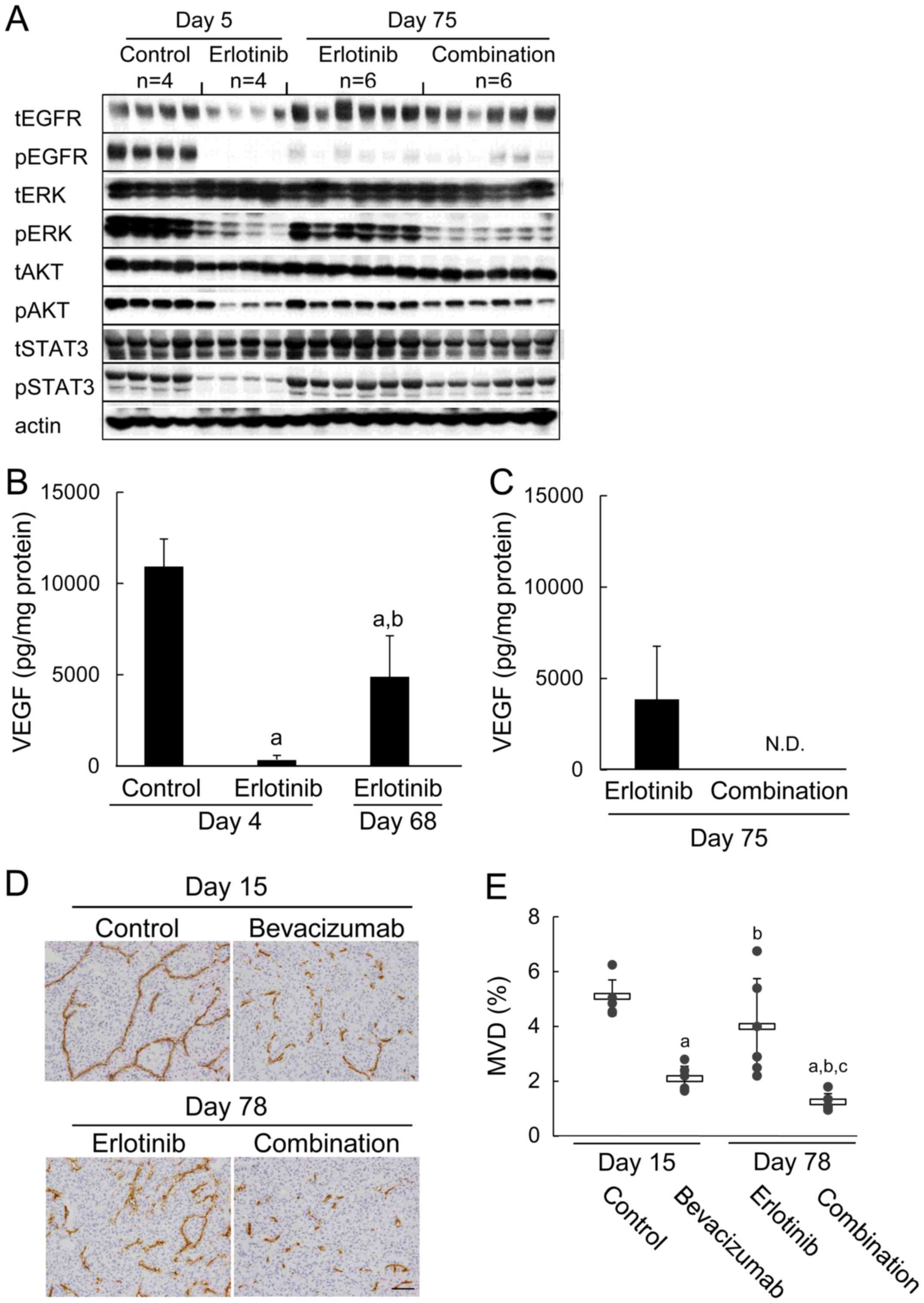
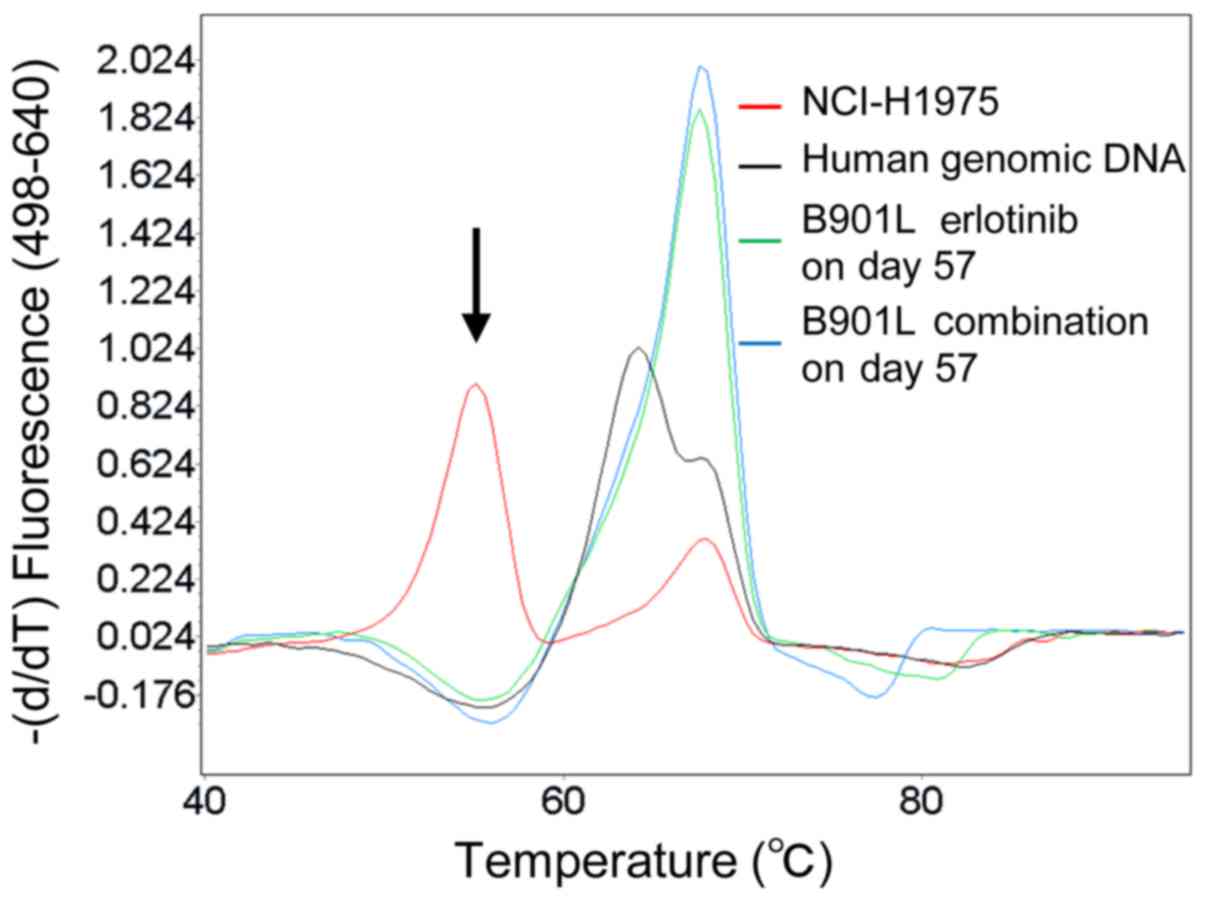
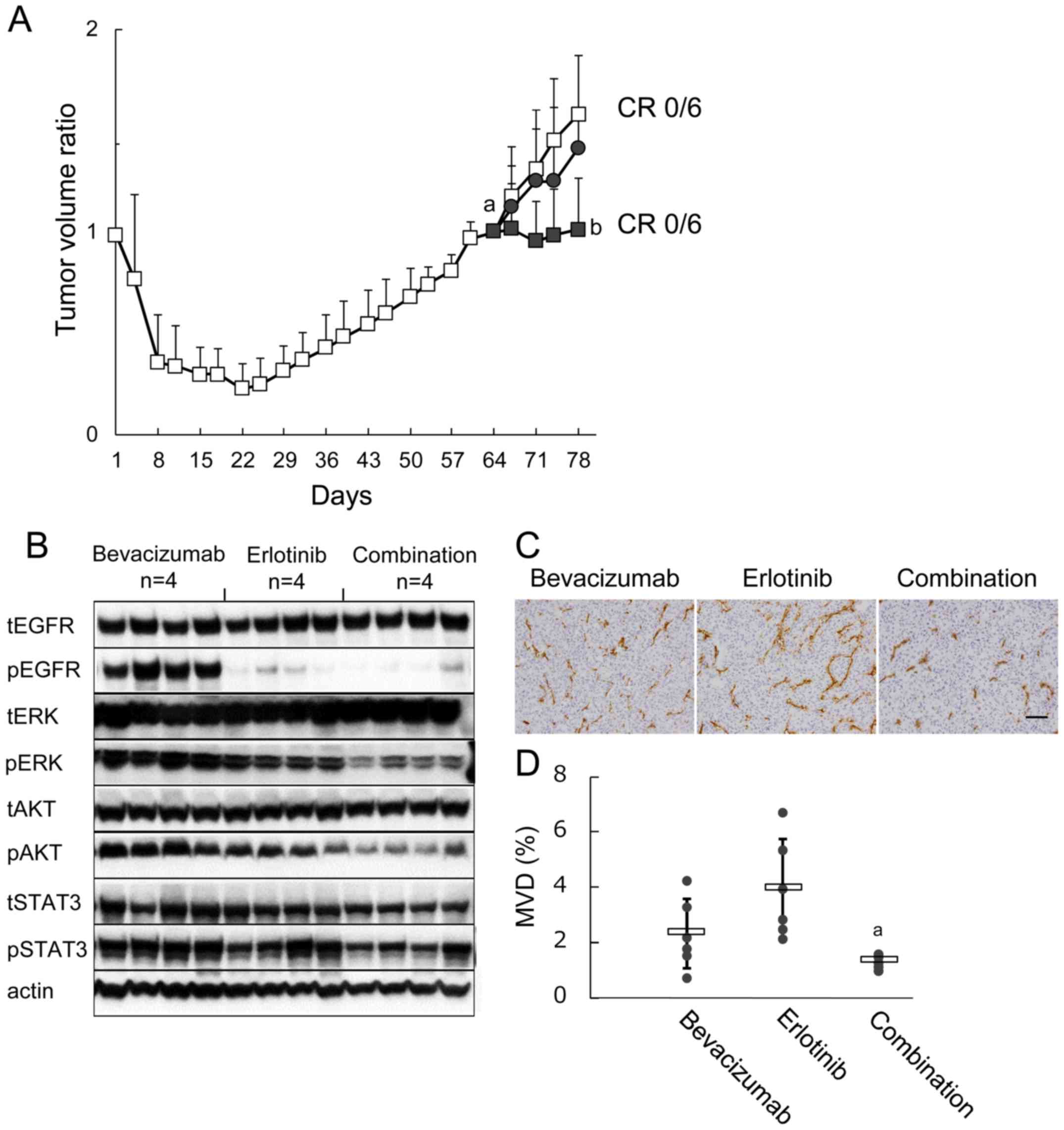
|
1
|
Shepherd FA, Rodrigues Pereira J, Ciuleanu
T, Tan EH, Hirsh V, Thongprasert S, Campos D, Maoleekoonpiroj S,
Smylie M, Martins R, et al National Cancer Institute of Canada
Clinical Trials Group: Erlotinib in previously treated
non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 353:123–132. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, Feng J, Liu XQ,
Wang C, Zhang S, Wang J, Zhou S, Ren S, et al: Erlotinib versus
chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced
EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL,
CTONG-0802): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study.
Lancet Oncol. 12:735–742. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R,
Vergnenegre A, Massuti B, Felip E, Palmero R, Garcia-Gomez R,
Pallares C, Sanchez JM, et al Spanish Lung Cancer Group in
collaboration with Groupe Français de Pneumo-Cancérologie and
Associazione Italiana Oncologia Toracica: Erlotinib versus standard
chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with
advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer
(EURTAC): A multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial.
Lancet Oncol. 13:239–246. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pao W, Miller VA, Politi KA, Riely GJ,
Somwar R, Zakowski MF, Kris MG and Varmus H: Acquired resistance of
lung adenocarcinomas to gefitinib or erlotinib is associated with a
second mutation in the EGFR kinase domain. PLoS Med. 2:e732005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yu HA, Arcila ME, Rekhtman N, Sima CS,
Zakowski MF, Pao W, Kris MG, Miller VA, Ladanyi M and Riely GJ:
Analysis of tumor specimens at the time of acquired resistance to
EGFR-TKI therapy in 155 patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancers.
Clin Cancer Res. 19:2240–2247. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yuan F, Chen Y, Dellian M, Safabakhsh N,
Ferrara N and Jain RK: Time-dependent vascular regression and
permeability changes in established human tumor xenografts induced
by an anti-vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability
factor antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 93:14765–14770. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
O'Connor JP, Carano RA, Clamp AR, Ross J,
Ho CC, Jackson A, Parker GJ, Rose CJ, Peale FV, Friesenhahn M, et
al: Quantifying antivascular effects of monoclonal antibodies to
vascular endothelial growth factor: Insights from imaging. Clin
Cancer Res. 15:6674–6682. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gerber HP and Ferrara N: Pharmacology and
pharmacodynamics of bevacizumab as monotherapy or in combination
with cytotoxic therapy in preclinical studies. Cancer Res.
65:671–680. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yanagisawa M, Yorozu K, Kurasawa M, Nakano
K, Furugaki K, Yamashita Y, Mori K and Fujimoto-Ouchi K:
Bevacizumab improves the delivery and efficacy of paclitaxel.
Anticancer Drugs. 21:687–694. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Turley RS, Fontanella AN, Padussis JC,
Toshimitsu H, Tokuhisa Y, Cho EH, Hanna G, Beasley GM, Augustine
CK, Dewhirst MW, et al: Bevacizumab-induced alterations in vascular
permeability and drug delivery: A novel approach to augment
regional chemotherapy for in-transit melanoma. Clin Cancer Res.
18:3328–3339. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sandler A, Gray R, Perry MC, Brahmer J,
Schiller JH, Dowlati A, Lilenbaum R and Johnson DH:
Paclitaxel-carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non-small-cell
lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 355:2542–2550. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Herbst RS, Johnson DH, Mininberg E,
Carbone DP, Henderson T, Kim ES, Blumenschein G Jr, Lee JJ, Liu DD,
Truong MT, et al: Phase I/II trial evaluating the anti-vascular
endothelial growth factor monoclonal antibody bevacizumab in
combination with the HER-1/epidermal growth factor receptor
tyrosine kinase inhibitor erlotinib for patients with recurrent
non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 23:2544–2555. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Camp ER, Summy J, Bauer TW, Liu W, Gallick
GE and Ellis LM: Molecular mechanisms of resistance to therapies
targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor. Clin Cancer Res.
11:397–405. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Seto T, Kato T, Nishio M, Goto K, Atagi S,
Hosomi Y, Yamamoto N, Hida T, Maemondo M, Nakagawa K, et al:
Erlotinib alone or with bevacizumab as first-line therapy in
patients with advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer
harbouring EGFR mutations (JO25567): An open-label, randomised,
multicentre, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 15:1236–1244. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li H, Takayama K, Wang S, Shiraishi Y,
Gotanda K, Harada T, Furuyama K, Iwama E, Ieiri I, Okamoto I, et
al: Addition of bevacizumab enhances antitumor activity of
erlotinib against non-small cell lung cancer xenografts depending
on VEGF expression. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 74:1297–1305. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pore N, Jiang Z, Gupta A, Cerniglia G, Kao
GD and Maity A: EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors decrease VEGF
expression by both hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1-independent and
HIF-1-dependent mechanisms. Cancer Res. 66:3197–3204. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lee JG and Wu R: Erlotinib-cisplatin
combination inhibits growth and angiogenesis through c-MYC and
HIF-1α in EGFR-mutated lung cancer in vitro and in vivo. Neoplasia.
17:190–200. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tabernero J: The role of VEGF and EGFR
inhibition: Implications for combining anti-VEGF and anti-EGFR
agents. Mol Cancer Res. 5:203–220. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chatterjee S, Wieczorek C, Schöttle J,
Siobal M, Hinze Y, Franz T, Florin A, Adamczak J, Heukamp LC,
Neumaier B, et al: Transient antiangiogenic treatment improves
delivery of cytotoxic compounds and therapeutic outcome in lung
cancer. Cancer Res. 74:2816–2824. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Furugaki K, Yasuno H, Iwai T, Moriya Y,
Harada N and Fujimoto-Ouchi K: Melting curve analysis for mutations
of EGFR and KRAS. Anticancer Res. 34:613–621. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Furugaki K, Fukumura J, Iwai T, Yorozu K,
Kurasawa M, Yanagisawa M, Moriya Y, Yamamoto K, Suda K, Mizuuchi H,
et al: Impact of bevacizumab in combination with erlotinib on
EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer xenograft models with T790M
mutation or MET amplification. Int J Cancer. 138:1024–1032. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Nakade J, Takeuchi S, Nakagawa T, Ishikawa
D, Sano T, Nanjo S, Yamada T, Ebi H, Zhao L, Yasumoto K, et al:
Triple inhibition of EGFR, Met, and VEGF suppresses regrowth of
HGF-triggered, erlotinib-resistant lung cancer harboring an EGFR
mutation. J Thorac Oncol. 9:775–783. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Larsen AK, Ouaret D, El Ouadrani K and
Petitprez A: Targeting EGFR and VEGF(R) pathway cross-talk in tumor
survival and angiogenesis. Pharmacol Ther. 131:80–90. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Petit AM, Rak J, Hung MC, Rockwell P,
Goldstein N, Fendly B and Kerbel RS: Neutralizing antibodies
against epidermal growth factor and ErbB-2/neu receptor tyrosine
kinases down-regulate vascular endothelial growth factor production
by tumor cells in vitro and in vivo: Angiogenic implications for
signal transduction therapy of solid tumors. Am J Pathol.
151:1523–1530. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yen L, You XL, Al Moustafa AE, Batist G,
Hynes NE, Mader S, Meloche S and Alaoui-Jamali MA: Heregulin
selectively up regulates vascular endothelial growth factor
secretion in cancer cells and stimulates angiogenesis. Oncogene.
19:3460–3469. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Viloria-Petit A, Crombet T, Jothy S,
Hicklin D, Bohlen P, Schlaeppi JM, Rak J and Kerbel RS: Acquired
resistance to the antitumor effect of epidermal growth factor
receptor-blocking antibodies in vivo: A role for altered tumor
angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 61:5090–5101. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Naumov GN, Nilsson MB, Cascone T, Briggs
A, Straume O, Akslen LA, Lifshits E, Byers LA, Xu L, Wu HK, et al:
Combined vascular endothelial growth factor receptor and epidermal
growth factor receptor (EGFR) blockade inhibits tumor growth in
xenograft models of EGFR inhibitor resistance. Clin Cancer Res.
15:3484–3494. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Schicher N, Paulitschke V, Swoboda A,
Kunstfeld R, Loewe R, Pilarski P, Pehamberger H and Hoeller C:
Erlotinib and bevacizumab have synergistic activity against
melanoma. Clin Cancer Res. 15:3495–3502. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Herbst RS and Sandler A: Bevacizumab and
erlotinib: A promising new approach to the treatment of advanced
NSCLC. Oncologist. 13:1166–1176. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhu AX, Duda DG, Sahani DV and Jain RK:
HCC and angiogenesis: Possible targets and future directions. Nat
Rev Clin Oncol. 8:292–301. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shojaei F, Wu X, Qu X, Kowanetz M, Yu L,
Tan M, Meng YG and Ferrara N: G-CSF-initiated myeloid cell
mobilization and angiogenesis mediate tumor refractoriness to
anti-VEGF therapy in mouse models. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
106:6742–6747. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Vandercappellen J, Van Damme J and Struyf
S: The role of CXC chemokines and their receptors in cancer. Cancer
Lett. 267:226–244. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Strieter RM, Burdick MD, Gomperts BN,
Belperio JA and Keane MP: CXC chemokines in angiogenesis. Cytokine
Growth Factor Rev. 16:593–609. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wei LH, Kuo ML, Chen CA, Chou CH, Lai KB,
Lee CN and Hsieh CY: Interleukin-6 promotes cervical tumor growth
by VEGF-dependent angiogenesis via a STAT3 pathway. Oncogene.
22:1517–1527. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nilsson MB, Langley RR and Fidler IJ:
Interleukin-6, secreted by human ovarian carcinoma cells, is a
potent proangiogenic cytokine. Cancer Res. 65:10794–10800. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Goel HL and Mercurio AM: VEGF targets the
tumour cell. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:871–882. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Barr MP, Gray SG, Gately K, Hams E, Fallon
PG, Davies AM, Richard DJ, Pidgeon GP and O'Byrne KJ: Vascular
endothelial growth factor is an autocrine growth factor, signaling
through neuropilin-1 in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer.
14:452015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Masood R, Cai J, Zheng T, Smith DL, Hinton
DR and Gill PS: Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is an
autocrine growth factor for VEGF receptor-positive human tumors.
Blood. 98:1904–1913. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Joyce JA and Pollard JW:
Microenvironmental regulation of metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer.
9:239–252. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Murdoch C, Muthana M, Coffelt SB and Lewis
CE: The role of myeloid cells in the promotion of tumour
angiogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:618–631. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Voron T, Marcheteau E, Pernot S, Colussi
O, Tartour E, Taieb J and Terme M: Control of the immune response
by pro-angiogenic factors. Front Oncol. 4:702014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Dineen SP, Lynn KD, Holloway SE, Miller
AF, Sullivan JP, Shames DS, Beck AW, Barnett CC, Fleming JB and
Brekken RA: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 mediates
macrophage infiltration into orthotopic pancreatic tumors in mice.
Cancer Res. 68:4340–4346. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ozao-Choy J, Ma G, Kao J, Wang GX, Meseck
M, Sung M, Schwartz M, Divino CM, Pan PY and Chen SH: The novel
role of tyrosine kinase inhibitor in the reversal of immune
suppression and modulation of tumor microenvironment for
immune-based cancer therapies. Cancer Res. 69:2514–2522. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|