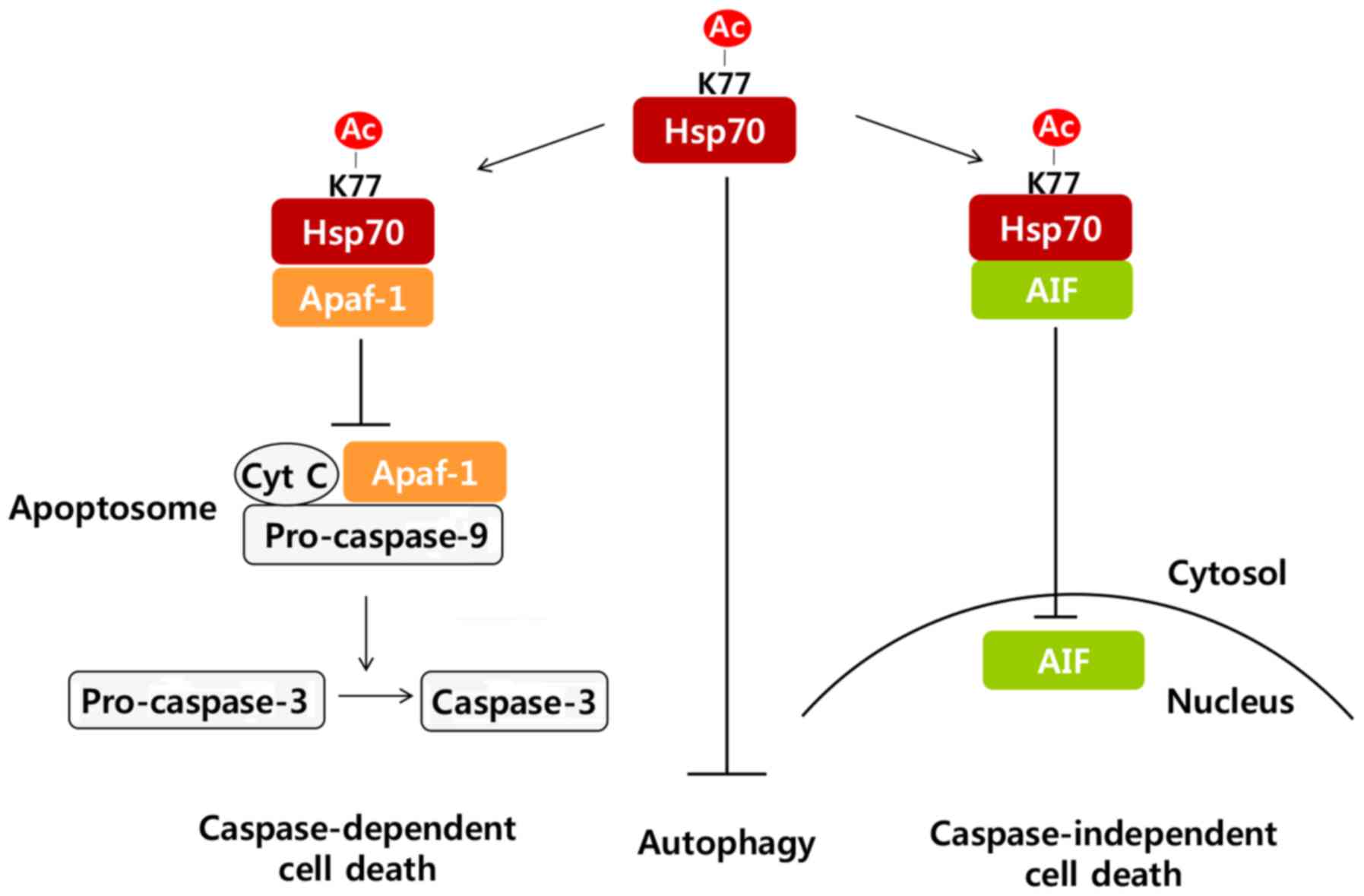
|
1
|
Wang M and Kaufman RJ: The impact of the
endoplasmic reticulum protein-folding environment on cancer
development. Nat Rev Cancer. 14:581–597. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jezierska-Drutel A, Rosenzweig SA and
Neumann CA: Role of oxidative stress and the microenvironment in
breast cancer development and progression. Adv Cancer Res.
119:107–125. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xu Y, Xia X and Pan H: Active autophagy in
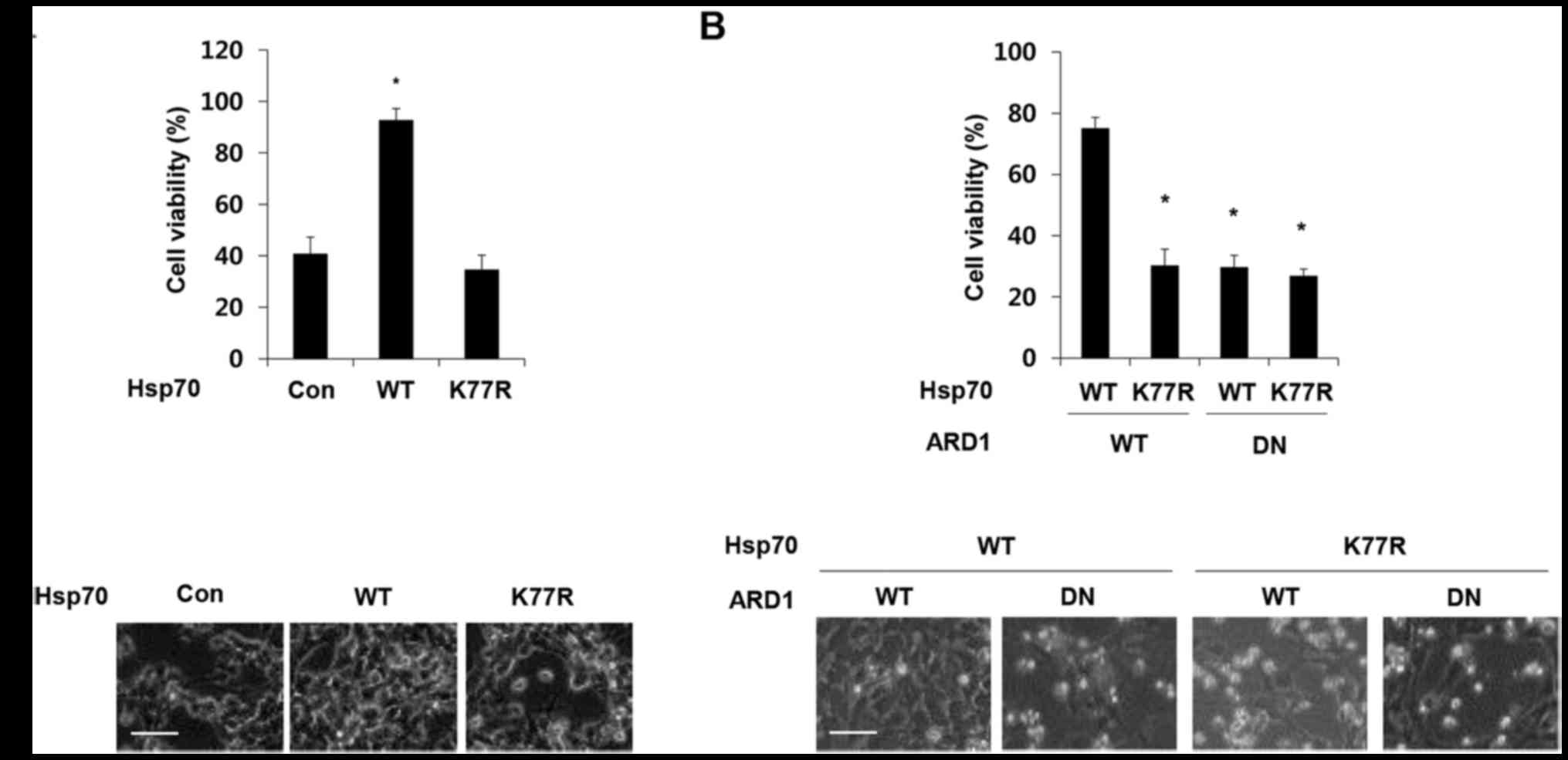
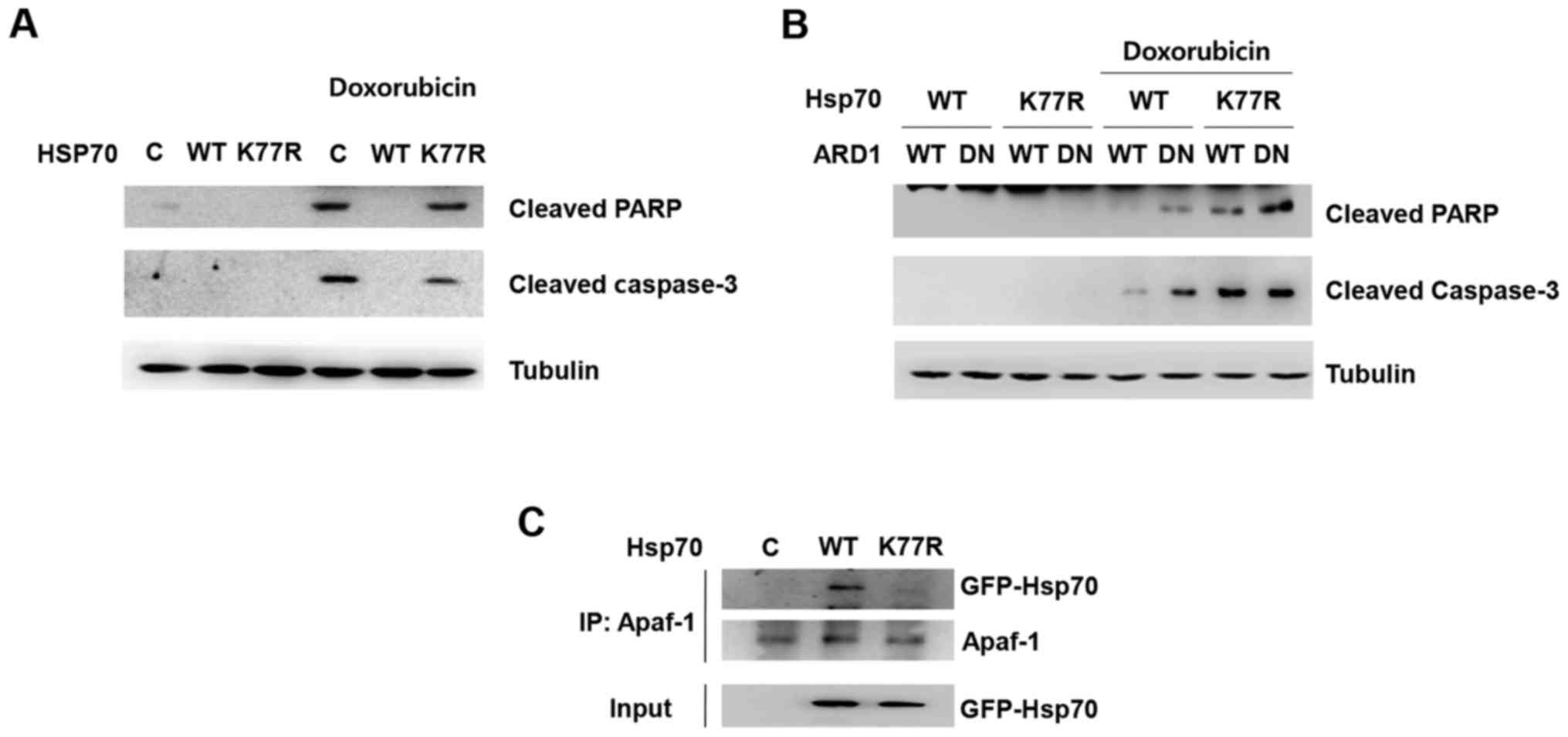
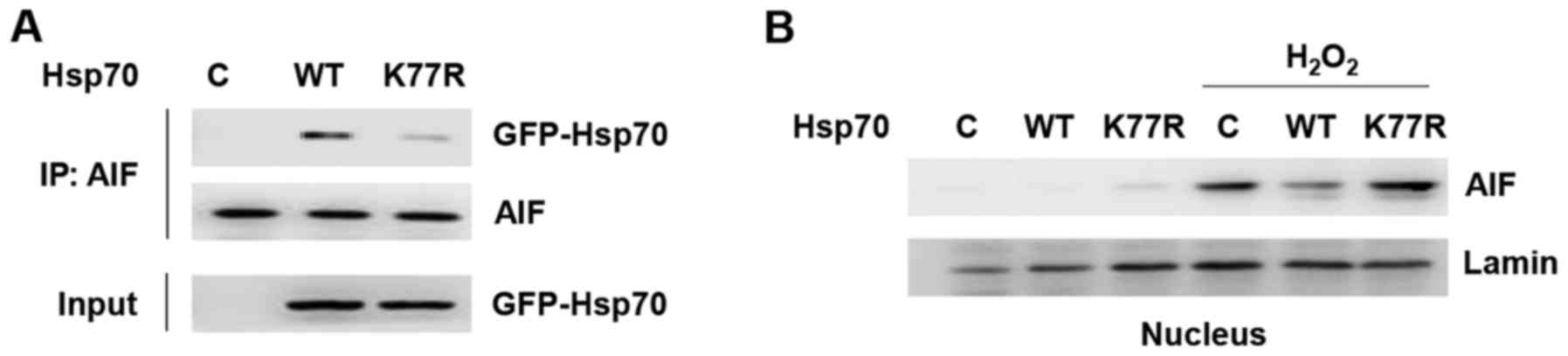
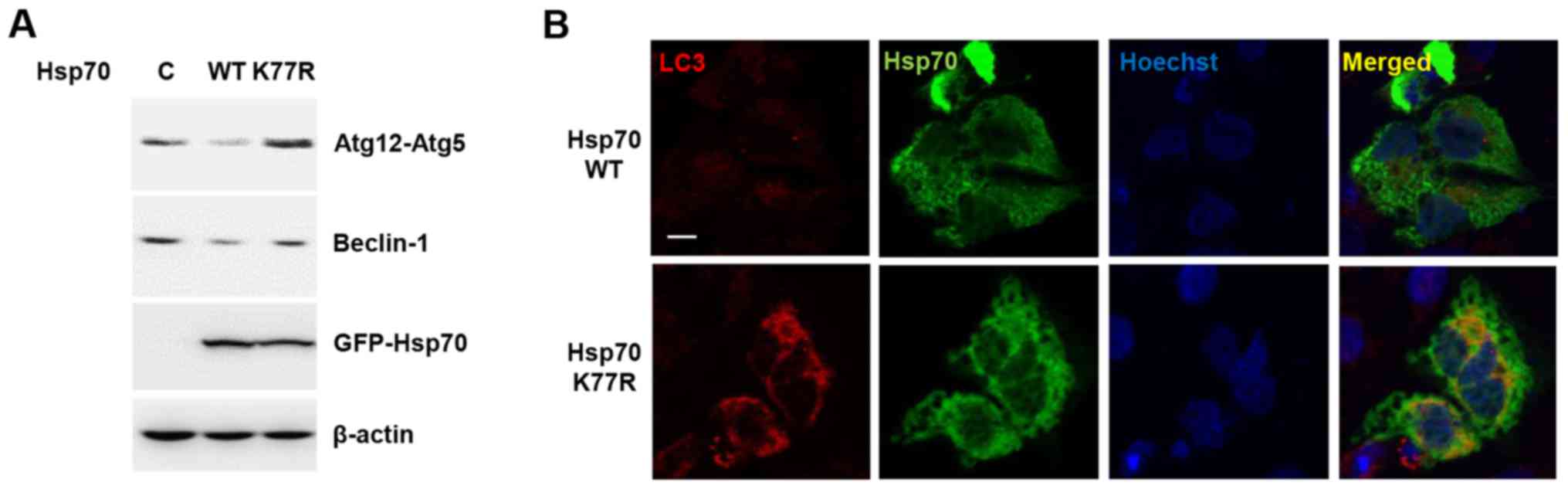
the tumor microenvironment: A novel mechanism for cancer
metastasis. Oncol Lett. 5:411–416. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vaughn AE and Deshmukh M: Glucose
metabolism inhibits apoptosis in neurons and cancer cells by redox
inactivation of cytochrome c. Nat Cell Biol. 10:1477–1483. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu Y, Borchert GL, Donald SP, Surazynski
A, Hu CA, Weydert CJ, Oberley LW and Phang JM: MnSOD inhibits
proline oxidase-induced apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells.
Carcinogenesis. 26:1335–1342. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fodale V, Pierobon M, Liotta L and
Petricoin E: Mechanism of cell adaptation: When and how do cancer
cells develop chemoresistance? Cancer J. 17:89–95. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Murphy ME: The HSP70 family and cancer.
Carcinogenesis. 34:1181–1188. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Goldberg AL: Protein degradation and
protection against misfolded or damaged proteins. Nature.
426:895–899. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hartl FU, Bracher A and Hayer-Hartl M:
Molecular chaperones in protein folding and proteostasis. Nature.
475:324–332. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Beere HM, Wolf BB, Cain K, Mosser DD,
Mahboubi A, Kuwana T, Tailor P, Morimoto RI, Cohen GM and Green DR:
Heat-shock protein 70 inhibits apoptosis by preventing recruitment
of procaspase-9 to the Apaf-1 apoptosome. Nat Cell Biol. 2:469–475.
2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Saleh A, Srinivasula SM, Balkir L, Robbins
PD and Alnemri ES: Negative regulation of the Apaf-1 apoptosome by
Hsp70. Nat Cell Biol. 2:476–483. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ravagnan L, Gurbuxani S, Susin SA, Maisse
C, Daugas E, Zamzami N, Mak T, Jäättelä M, Penninger JM, Garrido C,
et al: Heat-shock protein 70 antagonizes apoptosis-inducing factor.
Nat Cell Biol. 3:839–843. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Candé C, Cohen I, Daugas E, Ravagnan L,
Larochette N, Zamzami N and Kroemer G: Apoptosis-inducing factor
(AIF): A novel caspase-independent death effector released from
mitochondria. Biochimie. 84:215–222. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Daugas E, Susin SA, Zamzami N, Ferri KF,
Irinopoulou T, Larochette N, Prévost MC, Leber B, Andrews D,
Penninger J, et al: Mitochondrio-nuclear translocation of AIF in
apoptosis and necrosis. FASEB J. 14:729–739. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu Y and Levine B: Autosis and autophagic
cell death: The dark side of autophagy. Cell Death Differ.
22:367–376. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Tsujimoto Y and Shimizu S: Another way to
die: Autophagic programmed cell death. Cell Death Differ. 12(Suppl
2): 1528–1534. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Glick D, Barth S and Macleod KF:
Autophagy: Cellular and molecular mechanisms. J Pathol. 221:3–12.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dokladny K, Zuhl MN, Mandell M,
Bhattacharya D, Schneider S, Deretic V and Moseley PL: Regulatory
coordination between two major intracellular homeostatic systems:
Heat shock response and autophagy. J Biol Chem. 288:14959–14972.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Seo JH, Park JH, Lee EJ, Vo TT, Choi H,
Kim JY, Jang JK, Wee HJ, Lee HS, Jang SH, et al: ARD1-mediated
Hsp70 acetylation balances stress-induced protein refolding and
degradation. Nat Commun. 7:128822016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cha JH, Wee HJ, Seo JH, Ahn BJ, Park JH,
Yang JM, Lee SW, Lee OH, Lee HJ, Gelman IH, et al: Prompt meningeal
reconstruction mediated by oxygen-sensitive AKAP12 scaffolding
protein after central nervous system injury. Nat Commun.
5:49522014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Seo JH, Park JH, Lee EJ, Vo TT, Choi H,
Jang JK, Wee HJ, Ahn BJ, Cha JH, Shin MW, et al: Autoacetylation
regulates differentially the roles of ARD1 variants in
tumorigenesis. Int J Oncol. 46:99–106. 2015.
|
|
22
|
Yang Y, Fiskus W, Yong B, Atadja P,
Takahashi Y, Pandita TK, Wang HG and Bhalla KN: Acetylated hsp70
and KAP1-mediated Vps34 SUMOylation is required for autophagosome
creation in autophagy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:6841–6846. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lamb CA, Yoshimori T and Tooze SA: The
autophagosome: Origins unknown, biogenesis complex. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 14:759–774. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kang R, Zeh HJ, Lotze MT and Tang D: The
Beclin 1 network regulates autophagy and apoptosis. Cell Death
Differ. 18:571–580. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hanada T, Noda NN, Satomi Y, Ichimura Y,
Fujioka Y, Takao T, Inagaki F and Ohsumi Y: The Atg12-Atg5
conjugate has a novel E3-like activity for protein lipidation in
autophagy. J Biol Chem. 282:37298–37302. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tanida I, Ueno T and Kominami E: LC3
conjugation system in mammalian autophagy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
36:2503–2518. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lamoureux F, Thomas C, Crafter C, Kumano
M, Zhang F, Davies BR, Gleave ME and Zoubeidi A: Blocked autophagy
using lysosomotropic agents sensitizes resistant prostate tumor
cells to the novel Akt inhibitor AZD5363. Clin Cancer Res.
19:833–844. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Yonekawa T and Thorburn A: Autophagy and
cell death. Essays Biochem. 55:105–117. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shimizu S, Kanaseki T, Mizushima N, Mizuta
T, Arakawa-Kobayashi S, Thompson CB and Tsujimoto Y: Role of Bcl-2
family proteins in a non-apoptotic programmed cell death dependent
on autophagy genes. Nat Cell Biol. 6:1221–1228. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yu L, Alva A, Su H, Dutt P, Freundt E,
Welsh S, Baehrecke EH and Lenardo MJ: Regulation of an ATG7-beclin
1 program of autophagic cell death by caspase-8. Science.
304:1500–1502. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|