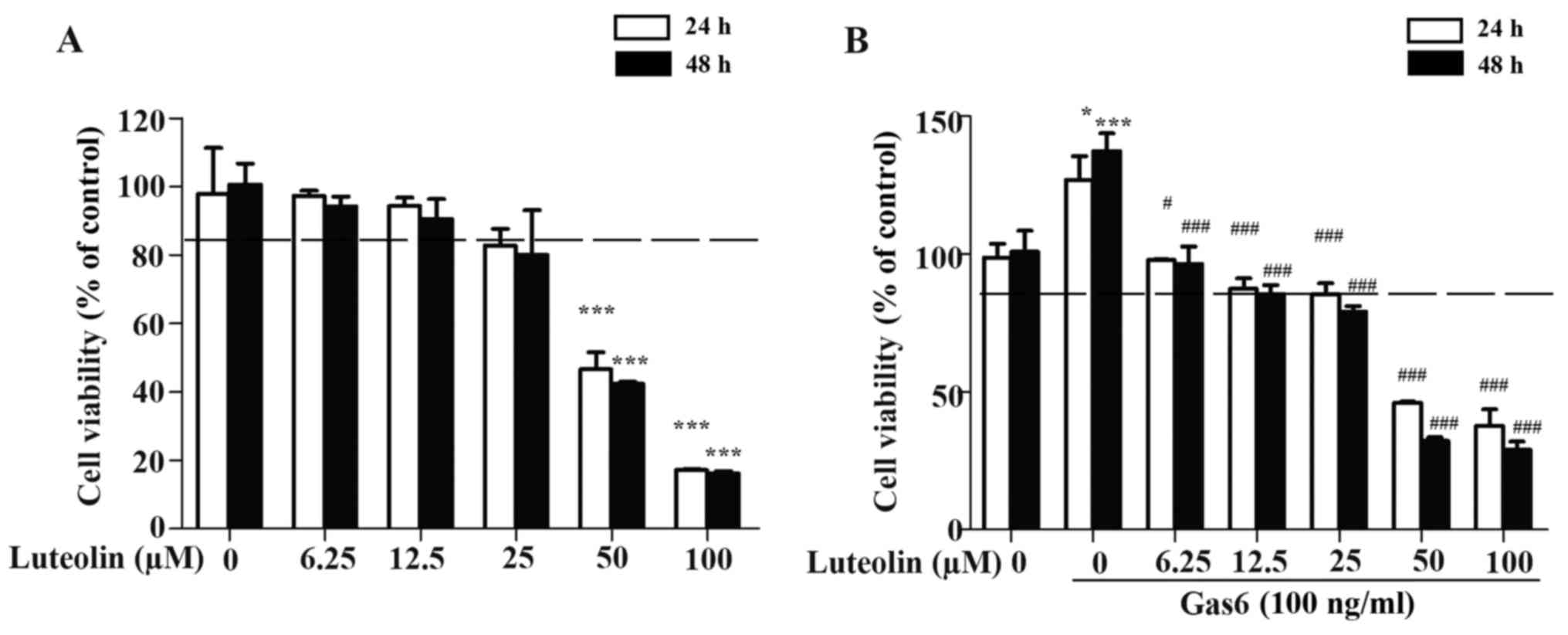
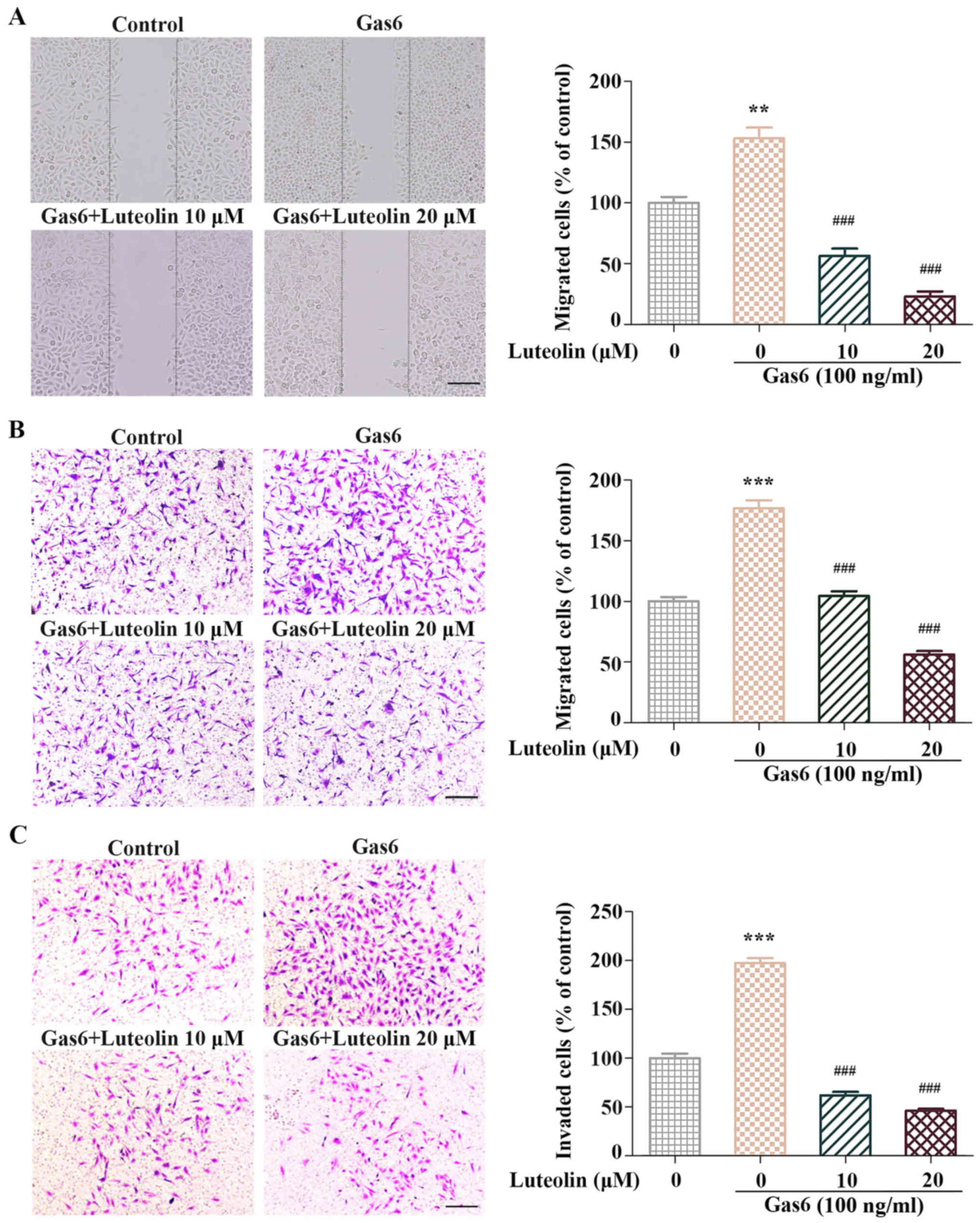
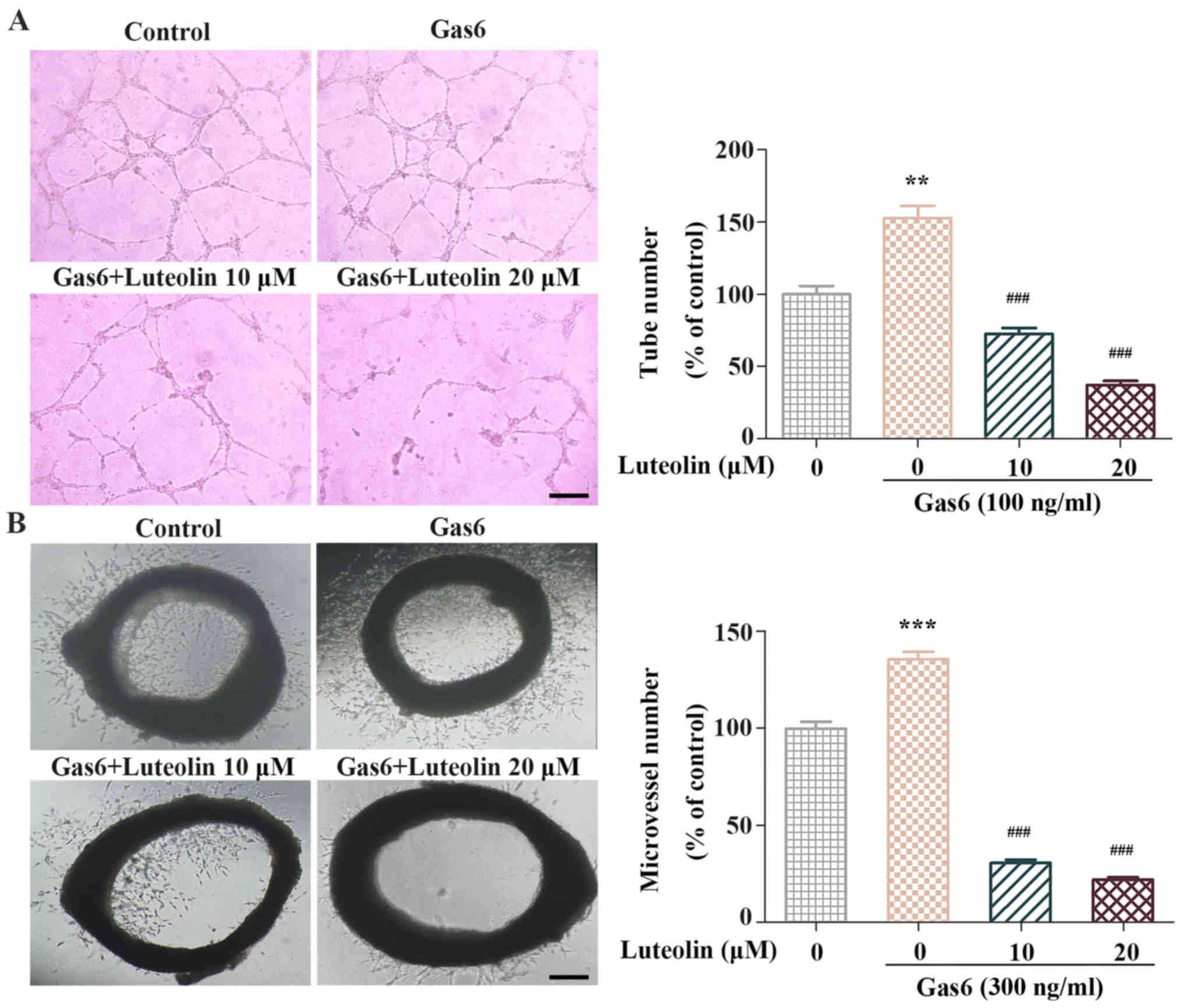
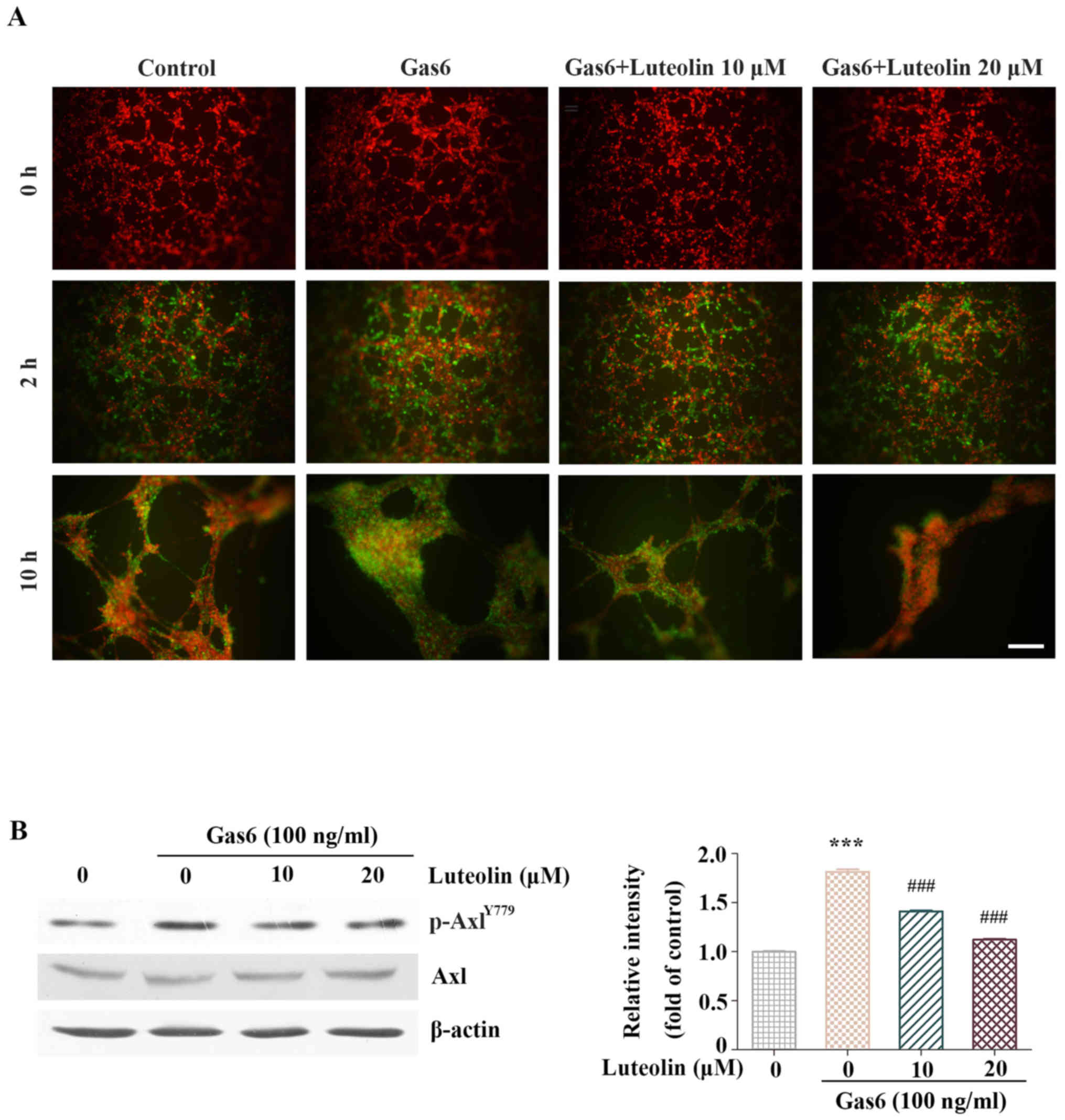
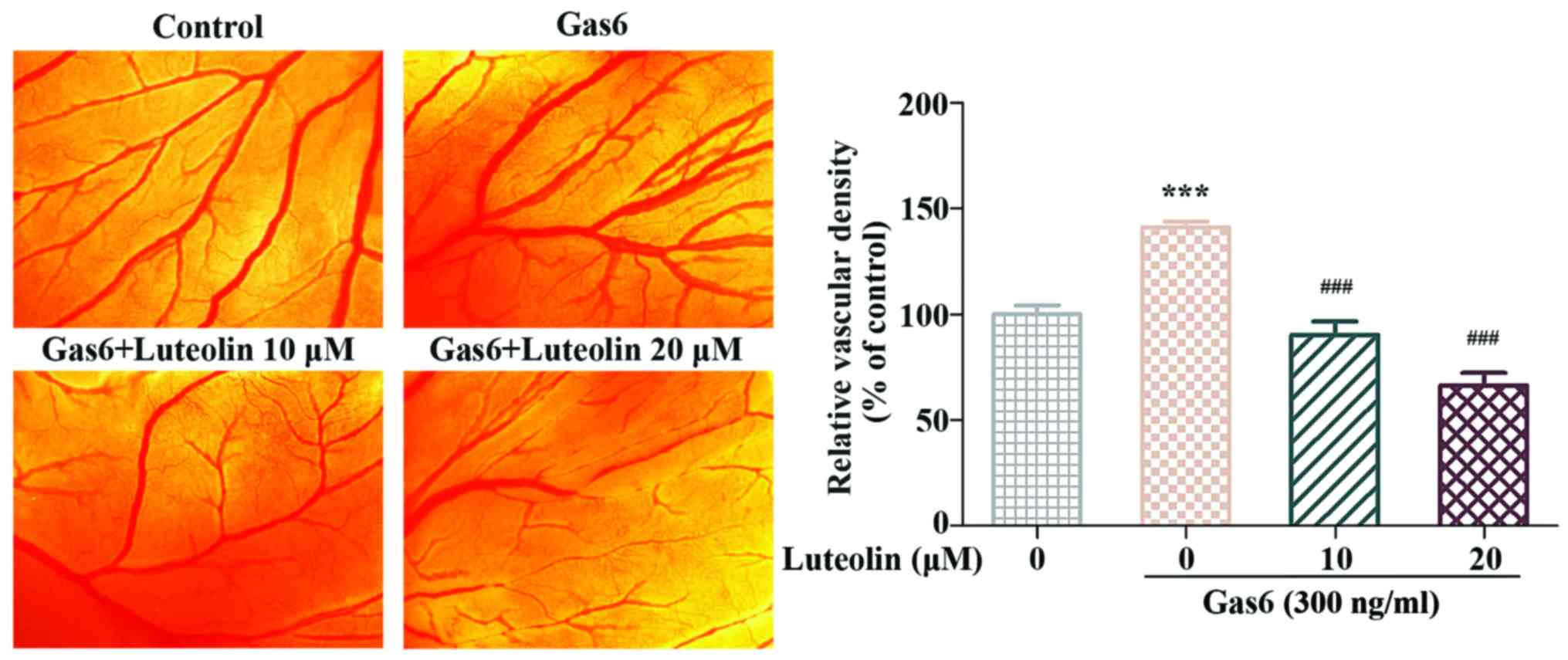
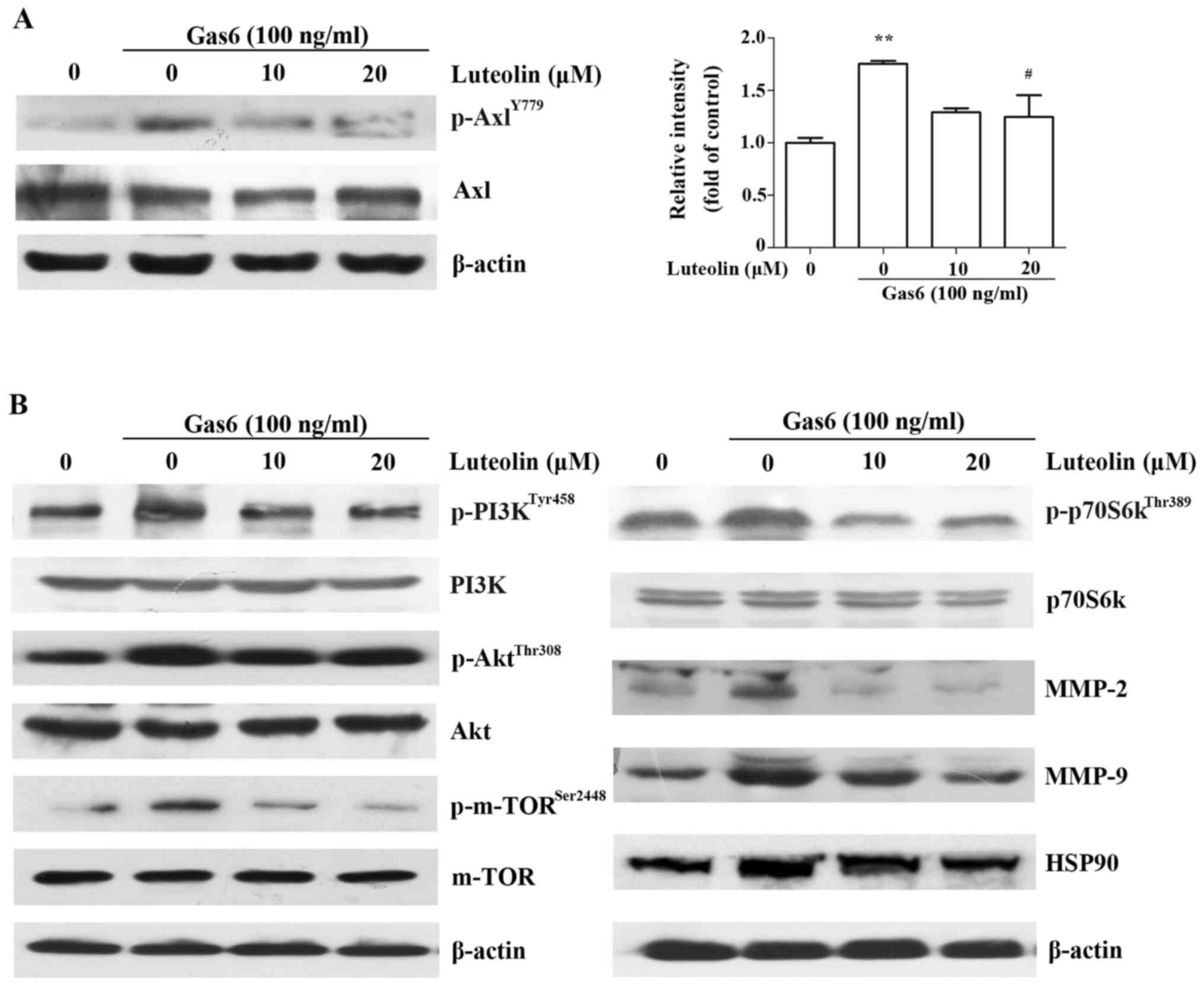
|
1
|
Dong R, Yang GD, Luo NA and Qu YQ: HuR: A
promising therapeutic target for angiogenesis. Gland Surg.
3:203–206. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Carmeliet P and Jain RK: Molecular
mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature.
473:298–307. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gavalas NG, Liontos M, Trachana SP,
Bagratuni T, Arapinis C, Liacos C, Dimopoulos MA and Bamias A:
Angiogenesis-related pathways in the pathogenesis of ovarian
cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 14:15885–15909. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Thanapprapasr D, Hu W, Sood AK and Coleman
RL: Moving beyond VEGF for anti-angiogenesis strategies in
gynecologic cancer. Curr Pharm Des. 18:2713–2719. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Alameddine RS, Yakan AS, Skouri H,
Mukherji D, Temraz S and Shamseddine A: Cardiac and vascular
toxicities of angiogenesis inhibitors: The other side of the coin.
Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 96:195–205. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kariolis MS, Miao YR, Jones DS II, Kapur
S, Mathews II, Giaccia AJ and Cochran JR: An engineered Axl 'decoy
receptor' effectively silences the Gas6-Axl signaling axis. Nat
Chem Biol. 10:977–983. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Avanzi GC, Gallicchio M, Bottarel F,
Gammaitoni L, Cavalloni G, Buonfiglio D, Bragardo M, Bellomo G,
Albano E, Fantozzi R, et al: GAS6 inhibits granulocyte adhesion to
endothelial cells. Blood. 91:2334–2340. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Manfioletti G, Brancolini C, Avanzi G and
Schneider C: The protein encoded by a growth arrest-specific gene
(gas6) is a new member of the vitamin K-dependent proteins related
to protein S, a negative coregulator in the blood coagulation
cascade. Mol Cell Biol. 13:4976–4985. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fotsis T, Pepper M, Adlercreutz H, Hase T,
Montesano R and Schweigerer L: Genistein, a dietary ingested
isoflavonoid, inhibits cell proliferation and in vitro
angiogenesis. J Nutr. 125(Suppl 3): 790S–797S. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zuo PY, Chen XL, Lei YH, Liu CY and Liu
YW: Growth arrest-specific gene 6 protein promotes the
proliferation and migration of endothelial progenitor cells through
the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 34:299–306.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Stenhoff J, Dahlbäck B and Hafizi S:
Vitamin K-dependent Gas6 activates ERK kinase and stimulates growth
of cardiac fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 319:871–878.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Son BK, Kozaki K, Iijima K, Eto M, Nakano
T, Akishita M and Ouchi Y: Gas6/Axl-PI3K/Akt pathway plays a
central role in the effect of statins on inorganic
phosphate-induced calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells.
Eur J Pharmacol. 556:1–8. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Melaragno MG, Fridell YW and Berk BC: The
Gas6/Axl system: A novel regulator of vascular cell function.
Trends Cardiovasc Med. 9:250–253. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Holland SJ, Pan A, Franci C, Hu Y, Chang
B, Li W, Duan M, Torneros A, Yu J, Heckrodt TJ, et al: R428, a
selective small molecule inhibitor of Axl kinase, blocks tumor
spread and prolongs survival in models of metastatic breast cancer.
Cancer Res. 70:1544–1554. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lei X, Chen M, Nie Q, Hu J, Zhuo Z, Yiu A,
Chen H, Xu N, Huang M, Ye K, et al: In vitro and in vivo
antiangiogenic activity of desacetylvinblastine monohydrazide
through inhibition of VEGFR2 and Axl pathways. Am J Cancer Res.
6:843–858. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ye X, Li Y, Stawicki S, Couto S,
Eastham-Anderson J, Kallop D, Weimer R, Wu Y and Pei L: An anti-Axl
monoclonal antibody attenuates xenograft tumor growth and enhances
the effect of multiple anticancer therapies. Oncogene.
29:5254–5264. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lin Y, Shi R, Wang X and Shen HM:
Luteolin, a flavonoid with potential for cancer prevention and
therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 8:634–646. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Seelinger G, Merfort I and Schempp CM:
Anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic activities of
luteolin. Planta Med. 74:1667–1677. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Clere N, Faure S, Martinez MC and
Andriantsitohaina R: Anticancer properties of flavonoids: Roles in
various stages of carcinogenesis. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med
Chem. 9:62–77. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pratheeshkumar P, Son YO, Budhraja A, Wang
X, Ding S, Wang L, Hitron A, Lee JC, Kim D, Divya SP, et al:
Luteolin inhibits human prostate tumor growth by suppressing
vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2-mediated
angiogenesis. PLoS One. 7:e522792012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhang DM, Liu JS, Tang MK, Yiu A, Cao HH,
Jiang L, Chan JY, Tian HY, Fung KP and Ye WC: Bufotalin from
Venenum Bufonis inhibits growth of multidrug resistant HepG2 cells
through G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Eur J Pharmacol.
692:19–28. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ming J, Zhou Y, Du J, Fan S, Pan B, Wang
Y, Fan L and Jiang J: Identification of miR-200a as a novel
suppressor of connexin 43 in breast cancer cells. Biosci Rep.
35:352015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Darland DC and D'Amore PA: TGF beta is
required for the formation of capillary-like structures in
three-dimensional cocultures of 10T1/2 and endothelial cells.
Angiogenesis. 4:11–20. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Staton CA, Stribbling SM, Tazzyman S,
Hughes R, Brown NJ and Lewis CE: Current methods for assaying
angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Int J Exp Pathol. 85:233–248.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shi JM, Bai LL, Zhang DM, Yiu A, Yin ZQ,
Han WL, Liu JS, Li Y, Fu DY and Ye WC: Saxifragifolin D induces the
interplay between apoptosis and autophagy in breast cancer cells
through ROS-dependent endoplasmic reticulum stress. Biochem
Pharmacol. 85:913–926. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Collett G, Wood A, Alexander MY, Varnum
BC, Boot-Handford RP, Ohanian V, Ohanian J, Fridell YW and Canfield
AE: Receptor tyrosine kinase Axl modulates the osteogenic
differentiation of pericytes. Circ Res. 92:1123–1129. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Stratman An, Malotte KM, Mahan RD, Davis
MJ and Davis GE: Pericyte recruitment during vasculogenic tube
assembly stimulates endothelial basement membrane matrix formation.
Blood. 114:5091–5101. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
García-Caballero M, Cañedo L,
Fernández-Medarde A, Medina MA and Quesada AR: The marine fungal
metabolite, AD0157, inhibits angiogenesis by targeting the Akt
signaling pathway. Mar Drugs. 12:279–299. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Davidson B, Goldberg I, Gotlieb WH,
Kopolovic J, Risberg B, Ben-Baruch G and Reich R: Coordinated
expression of integrin subunits, matrix metalloproteinases (MMP),
angiogenic genes and Ets transcription factors in advanced-stage
ovarian carcinoma: A possible activation pathway? Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 22:103–115. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chang DJ, An H, Kim KS, Kim HH, Jung J,
Lee JM, Kim NJ, Han YT, Yun H, Lee S, et al: Design, synthesis, and
biological evaluation of novel deguelin-based heat shock protein 90
(HSP90) inhibitors targeting proliferation and angiogenesis. J Med
Chem. 55:10863–10884. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Negrão R, Costa R, Duarte D, Gomes TT,
Coelho P, Guimarães JT, Guardão L, Azevedo I and Soares R:
Xanthohumol-supplemented beer modulates angiogenesis and
inflammation in a skin wound healing model. Involvement of local
adipocytes. J Cell Biochem. 113:100–109. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Sreelakshmi V, Sasikala V and Abraham A:
Luteolin supplementation prevents selenite-induced cataractogenesis
in Sprague Dawley rat pups. Chem Biodivers. 12:1881–1890. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li Y, Ye X, Tan C, Hongo JA, Zha J, Liu J,
Kallop D, Ludlam MJ and Pei L: Axl as a potential therapeutic
target in cancer: Role of Axl in tumor growth, metastasis and
angiogenesis. Oncogene. 28:3442–3455. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kim YS, Jung SH, Jung DH, Choi SJ, Lee YR
and Kim JS: Gas6 stimulates angiogenesis of human retinal
endothelial cells and of zebrafish embryos via ERK1/2 signaling.
PLoS One. 9:e839012014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang C, Jin H, Wang N, Fan S, Wang Y,
Zhang Y, Wei L, Tao X, Gu D, Zhao F, et al: Gas6/Axl axis
contributes to chemoresistance and metastasis in breast cancer
through Akt/GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling. Theranostics. 6:1205–1219.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
36
|
Roberts CM, Tran MA, Pitruzzello MC, Wen
W, Loeza J, Dellinger TH, Mor G and Glackin CA: TWIST1 drives
cisplatin resistance and cell survival in an ovarian cancer model,
via upregulation of GAS6, L1CAM, and Akt signalling. Sci Rep.
6:376522016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lee YJ, Lim T, Han MS, Lee SH, Baek SH,
Nan HY and Lee C: Anticancer effect of luteolin is mediated by
downregulation of TAM receptor tyrosine kinases, but not
interleukin-8, in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncol Rep.
37:1219–1226. 2017.
|
|
38
|
Bagli E, Stefaniotou M, Morbidelli L,
Ziche M, Psillas K, Murphy C and Fotsis T: Luteolin inhibits
vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis; inhibition
of endothelial cell survival and proliferation by targeting
phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase activity. Cancer Res. 64:7936–7946.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yadav L, Puri N, Rastogi V, Satpute P and
Sharma V: Tumour angiogenesis and angiogenic inhibitors: A review.
J Clin Diagn Res. 9:XE01–XE05. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Keating GM: Bevacizumab: A review of its
use in advanced cancer. Drugs. 74:1891–1925. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|