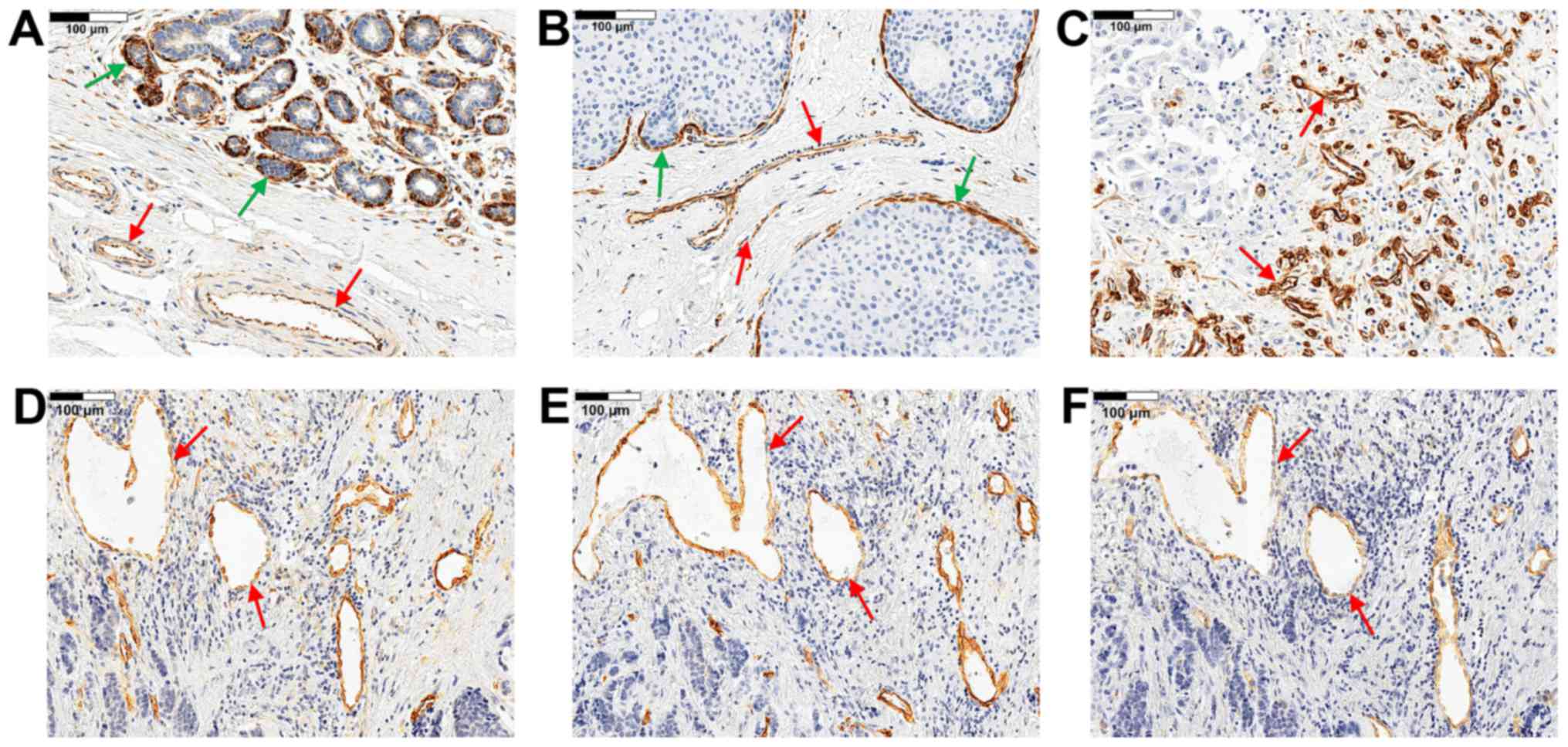
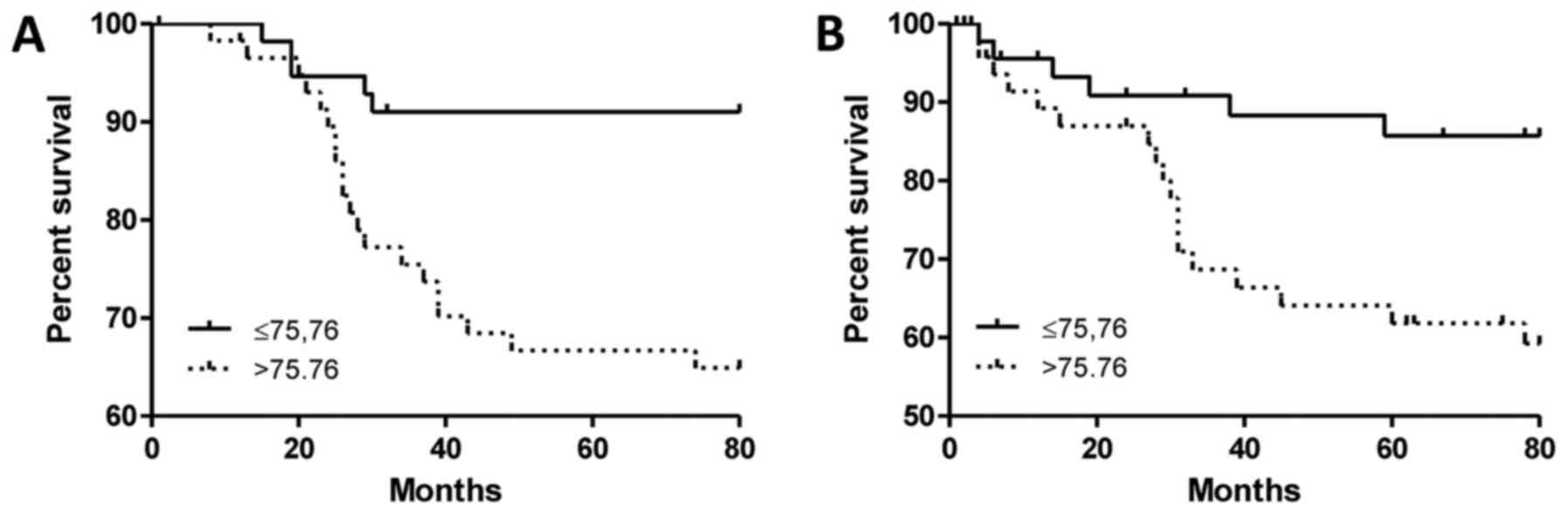
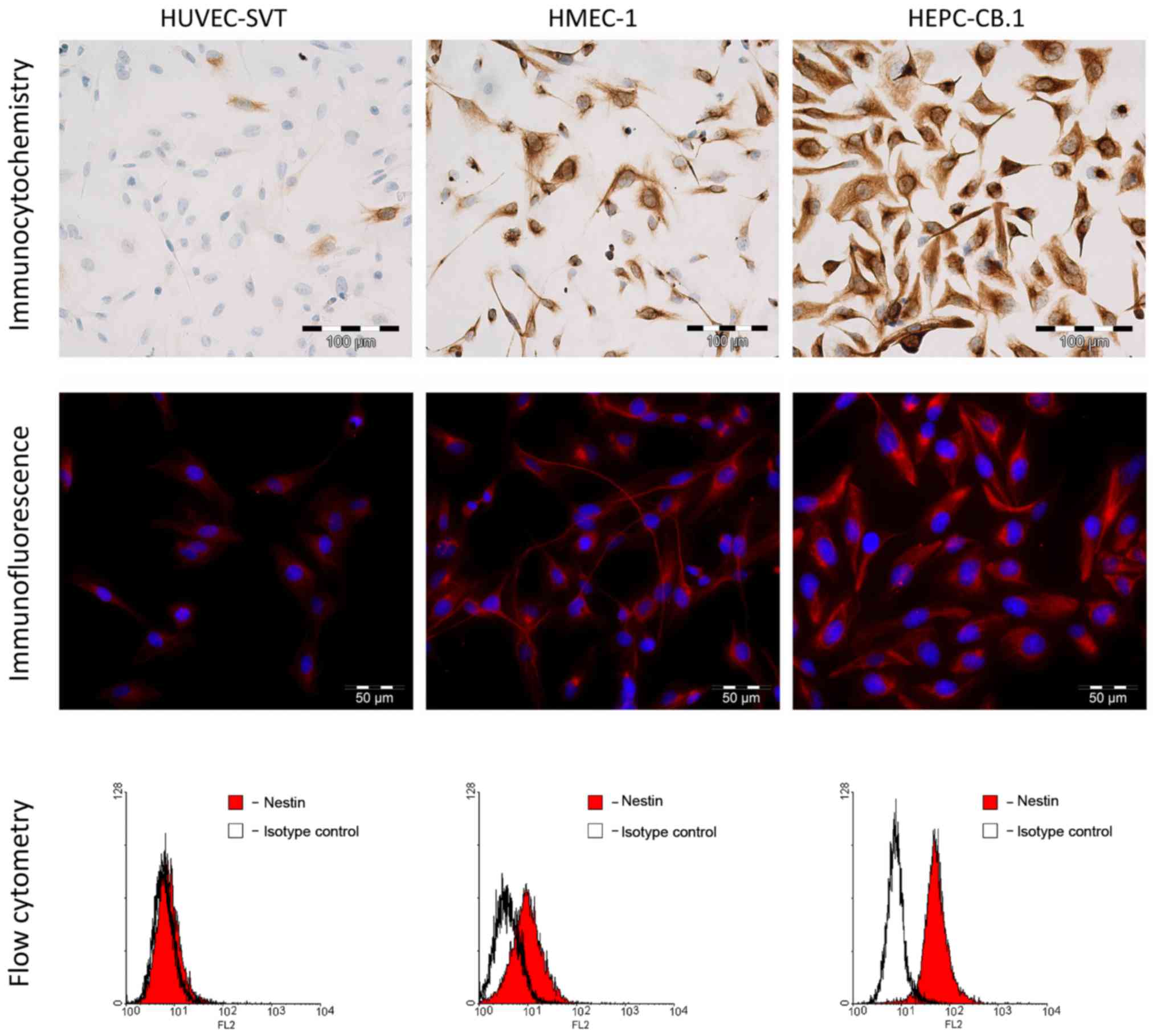
|
1
|
Folkman J: Tumor angiogenesis: Therapeutic
implications. N Engl J Med. 285:1182–1186. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shih T and Lindley C: Bevacizumab: An
angiogenesis inhibitor for the treatment of solid malignancies.
Clin Ther. 28:1779–1802. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Shaheen RM, Ahmad SA, Liu W, Reinmuth N,
Jung YD, Tseng WW, Drazan KE, Bucana CD, Hicklin DJ and Ellis LM:
Inhibited growth of colon cancer carcinomatosis by antibodies to
vascular endothelial and epidermal growth factor receptors. Br J
Cancer. 85:584–589. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Uzzan B, Nicolas P, Cucherat M and Perret
GY: Microvessel density as a prognostic factor in women with breast
cancer: A systematic review of the literature and meta-analysis.
Cancer Res. 64:2941–2955. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Weidner N, Semple JP, Welch WR and Folkman
J: Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis–correlation in invasive breast
carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 324:1–8. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Meert AP, Paesmans M, Martin B, Delmotte
P, Berghmans T, Verdebout JM, Lafitte JJ, Mascaux C and Sculier JP:
The role of microvessel density on the survival of patients with
lung cancer: A systematic review of the literature with
meta-analysis. Br J Cancer. 87:694–701. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lendahl U, Zimmerman LB and McKay RD: CNS
stem cells express a new class of intermediate filament protein.
Cell. 60:585–595. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sejersen T and Lendahl U: Transient
expression of the intermediate filament nestin during skeletal
muscle development. J Cell Sci. 106:1291–1300. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Terling C, Rass A, Mitsiadis TA, Fried K,
Lendahl U and Wroblewski J: Expression of the intermediate filament
nestin during rodent tooth development. Int J Dev Biol. 39:947–956.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fröjdman K, Pelliniemi LJ, Lendahl U,
Virtanen I and Eriksson JE: The intermediate filament protein
nestin occurs transiently in differentiating testis of rat and
mouse. Differentiation. 61:243–249. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lardon J, Rooman I and Bouwens L: Nestin
expression in pancreatic stellate cells and angiogenic endothelial
cells. Histochem Cell Biol. 117:535–540. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mokrý J, Cízková D, Filip S, Ehrmann J,
Osterreicher J, Kolár Z and English D: Nestin expression by newly
formed human blood vessels. Stem Cells Dev. 13:658–664. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Krupkova O Jr, Loja T, Zambo I and
Veselska R: Nestin expression in human tumors and tumor cell lines.
Neoplasma. 57:291–298. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu C, Chen B, Zhu J, Zhang R, Yao F, Jin
F, Xu H and Lu P: Clinical implications for nestin protein
expression in breast cancer. Cancer Sci. 101:815–819. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Sjöberg G, Jiang WQ, Ringertz NR, Lendahl
U and Sejersen T: Colocalization of nestin and vimentin/desmin in
skeletal muscle cells demonstrated by three-dimensional
fluorescence digital imaging microscopy. Exp Cell Res. 214:447–458.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim HS, Kang HS, Messam CA, Min KW and
Park CS: Comparative evaluation of angiogenesis in gastric
adenocarcinoma by nestin and CD34. Appl Immunohistochem Mol
Morphol. 10:121–127. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Klein T, Ling Z, Heimberg H, Madsen OD,
Heller RS and Serup P: Nestin is expressed in vascular endothelial
cells in the adult human pancreas. J Histochem Cytochem.
51:697–706. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Teranishi N, Naito Z, Ishiwata T, Tanaka
N, Furukawa K, Seya T, Shinji S and Tajiri T: Identification of
neovasculature using nestin in colorectal cancer. Int J Oncol.
30:593–603. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Suzuki S, Namiki J, Shibata S, Mastuzaki Y
and Okano H: The neural stem/progenitor cell marker nestin is
expressed in proliferative endothelial cells, but not in mature
vasculature. J Histochem Cytochem. 58:721–730. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bouïs D, Hospers GA, Meijer C, Molema G
and Mulder NH: Endothelium in vitro: A review of human vascular
endothelial cell lines for blood vessel-related research.
Angiogenesis. 4:91–102. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Paprocka M, Krawczenko A, Dus D, Kantor A,
Carreau A, Grillon C and Kieda C: CD133 positive progenitor
endothelial cell lines from human cord blood. Cytometry A.
79:594–602. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Goldhirsch A, Ingle JN, Gelber RD, Coates
AS, Thürlimann B and Senn HJ; Panel members: Thresholds for
therapies: Highlights of the St Gallen International Expert
Consensus on the primary therapy of early breast cancer 2009. Ann
Oncol. 20:1319–1329. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mueller-Holzner E, Fink V, Frede T and
Marth C: Immunohistochemical determination of HER2 expression in
breast cancer from core biopsy specimens: A reliable predictor of
HER2 status of the whole tumor. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 69:13–19.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dahlstrand J, Collins VP and Lendahl U:
Expression of the class VI intermediate filament nestin in human
central nervous system tumors. Cancer Res. 52:5334–5341.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kobayashi M, Sjöberg G, Söderhäll S,
Lendahl U, Sandstedt B and Sejersen T: Pediatric rhabdomyosarcomas
express the intermediate filament nestin. Pediatr Res. 43:386–392.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mokrý J and Nemecek S: Cerebral
angiogenesis shows nestin expression in endothelial cells. Gen
Physiol Biophys. 18(Suppl 1): 25–29. 1999.
|
|
29
|
Gravdal K, Halvorsen OJ, Haukaas SA and
Akslen LA: Proliferation of immature tumor vessels is a novel
marker of clinical progression in prostate cancer. Cancer Res.
69:4708–4715. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Krüger K, Stefansson IM, Collett K, Arnes
JB, Aas T and Akslen LA: Microvessel proliferation by co-expression
of endothelial nestin and Ki-67 is associated with a basal-like
phenotype and aggressive features in breast cancer. Breast.
22:282–288. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Piras F, Ionta MT, Lai S, Perra MT, Atzori
F, Minerba L, Pusceddu V, Maxia C, Murtas D, Demurtas P, et al:
Nestin expression associates with poor prognosis and
triple-negative phenotype in locally advanced (T4) breast cancer.
Eur J Histochem. 55:e392011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Parry S, Savage K, Marchiò C and
Reis-Filho JS: Nestin is expressed in basal-like and
triple-negative breast cancers. J Clin Pathol. 61:1045–1050. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Krüger K, Wik E, Knutsvik G, Nalwoga H,
Klingen TA, Arnes JB, Chen Y, Mannelqvist M, Dimitrakopoulou K,
Stefansson IM, et al: Expression of Nestin associates with BRCA1
mutations, a basal-like phenotype and aggressive breast cancer. Sci
Rep. 7:10892017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Paduch R: The role of lymphangiogenesis
and angiogenesis in tumor metastasis. Cell Oncol (Dordr).
39:397–410. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Popiela TJ, Sikora J, Klimek M, Basta P,
Niemiec T, Dobrogowski J, Kotlarz A, Rudnicka-Sosin L and
Dutsch-Wicherek M: The analysis of CD34 antigen immunoreactivity
level in invasive ductal breast cancer with respect to the presence
of lymph node metastases. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 29:443–446.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xie XD, Qu SX, Liu ZZ, Zhang F and Zheng
ZD: Study on relationship between angiogenesis and micrometastases
of peripheral blood in breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
135:413–419. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Ribatti D: The discovery of endothelial
progenitor cells. An historical review Leuk Res. 31:439–444.
2007.
|
|
38
|
Nagatsuka H, Hibi K, Gunduz M, Tsujigiwa
H, Tamamura R, Sugahara T, Sasaki A and Nagai N: Various
immunostaining patterns of CD31, CD34 and endoglin and their
relationship with lymph node metastasis in oral squamous cell
carcinomas. J Oral Pathol Med. 34:70–76. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Walzer SM, Cetin E, Grübl-Barabas R,
Sulzbacher I, Rueger B, Girsch W, Toegel S, Windhager R and Fischer
MB: Vascularization of primary and secondary ossification centres
in the human growth plate. BMC Dev Biol. 14:362014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Corselli M, Chen CW, Crisan M, Lazzari L
and Péault B: Perivascular ancestors of adult multipotent stem
cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 30:1104–1109. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Klein D, Meissner N, Kleff V, Jastrow H,
Yamaguchi M, Ergün S and Jendrossek V: Nestin(+) tissue-resident
multipotent stem cells contribute to tumor progression by
differentiating into pericytes and smooth muscle cells resulting in
blood vessel remodeling. Front Oncol. 4:1692014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|