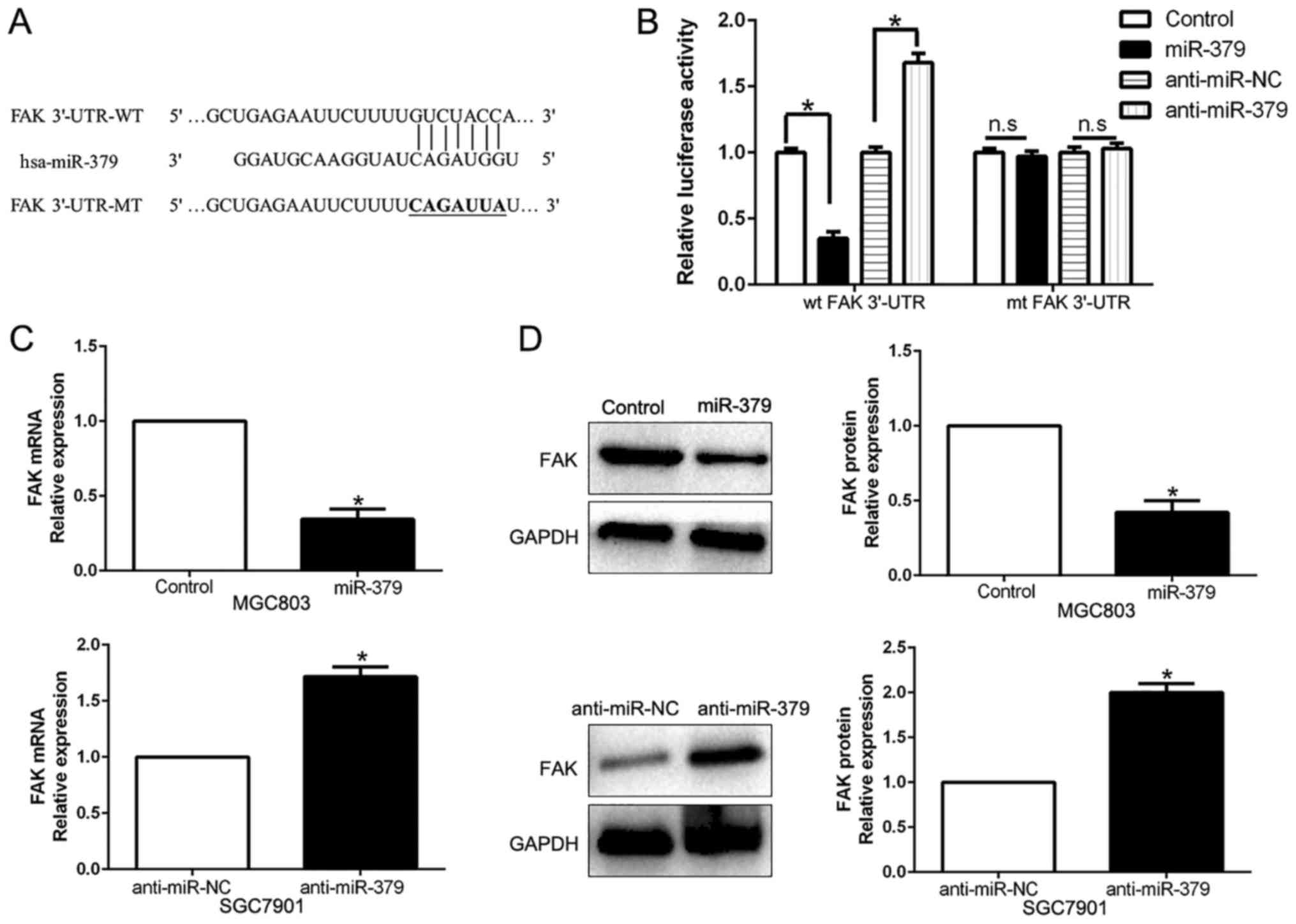
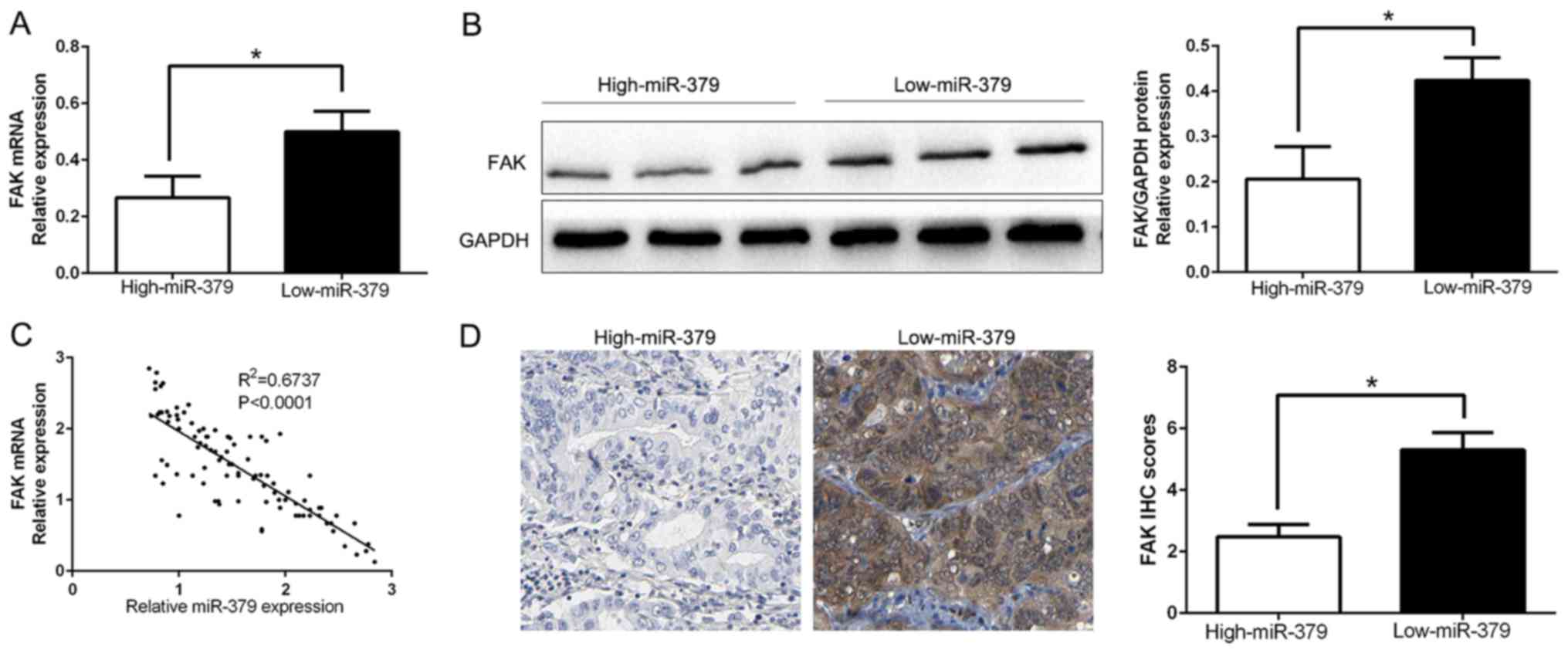
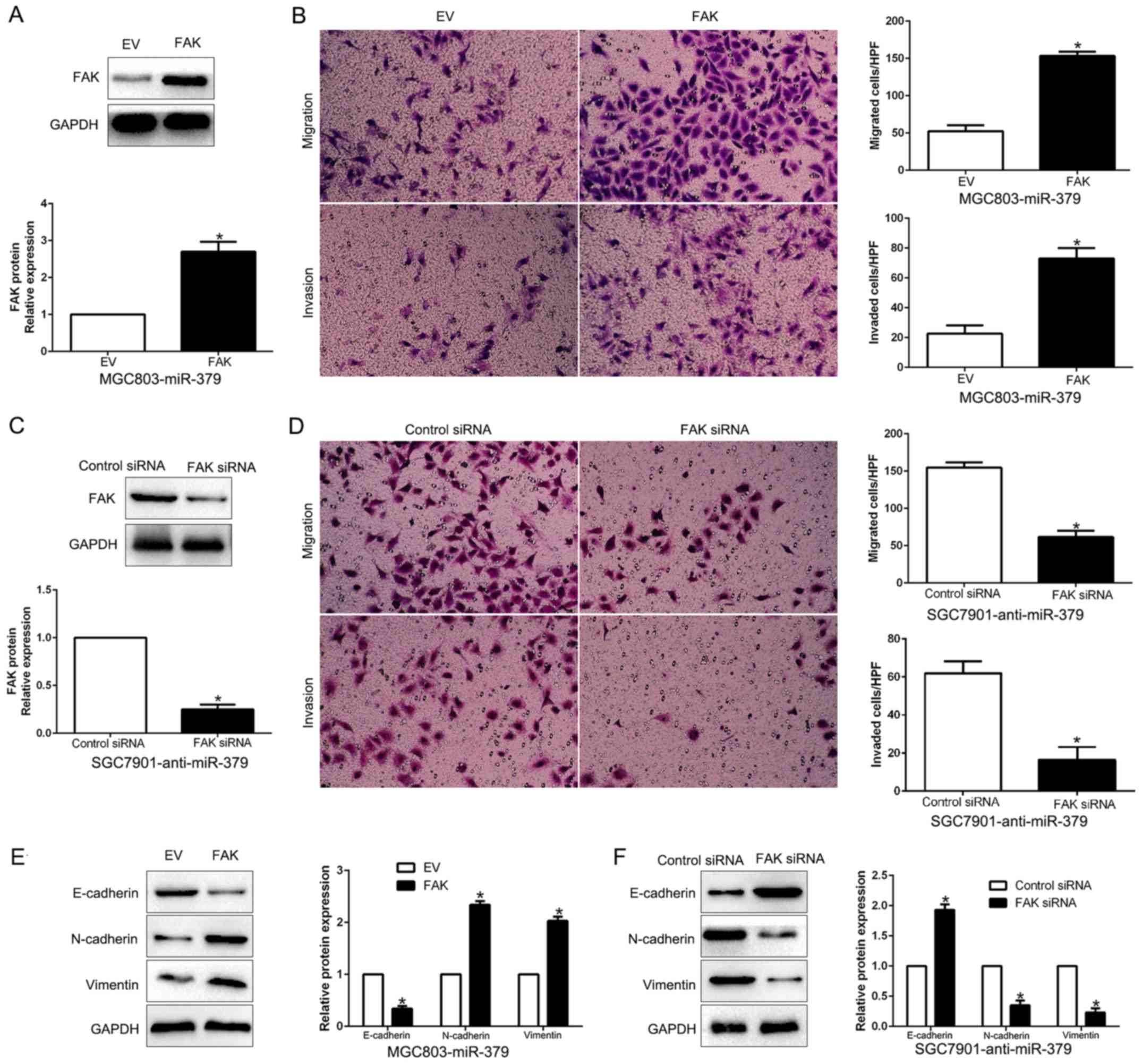
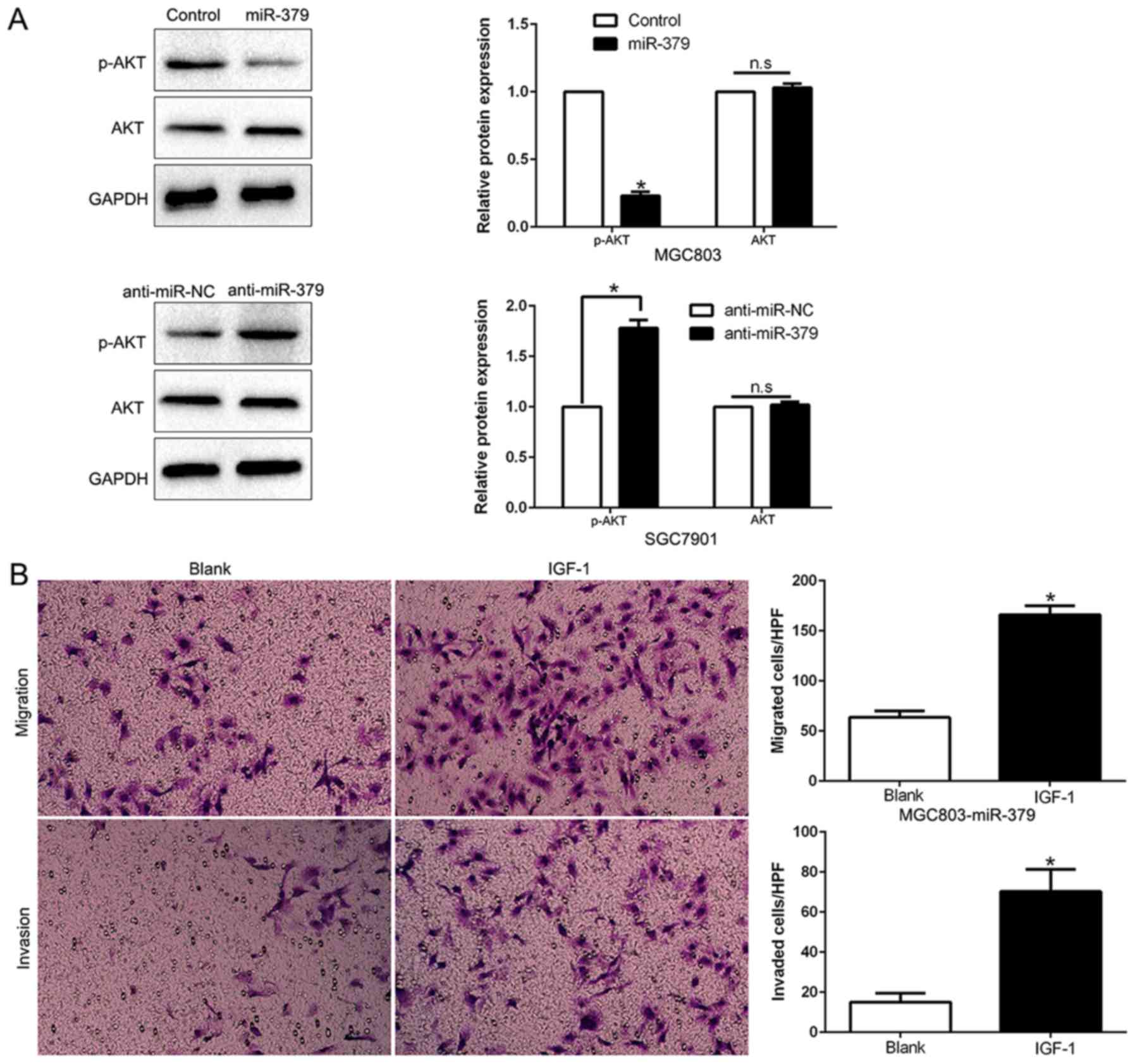
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
De Vita F, Vecchione L, Galizia G, Di
Martino N, Fabozzi T, Catalano G, Ciardiello F and Orditura M:
Perspectives in adjuvant therapy of gastric cancer. Oncology.
77(Suppl 1): 38–42. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kagawa S, Shigeyasu K, Ishida M, Watanabe
M, Tazawa H, Nagasaka T, Shirakawa Y and Fujiwara T: Molecular
diagnosis and therapy for occult peritoneal metastasis in gastric
cancer patients. World J Gastroenterol. 20:17796–17803.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bessette DC, Qiu D and Pallen CJ: PRL
PTPs: Mediators and markers of cancer progression. Cancer
Metastasis Rev. 27:231–252. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Alvarez-Garcia I and Miska EA: MicroRNA
functions in animal development and human disease. Development.
132:4653–4662. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA-cancer
connection: The beginning of a new tale. Cancer Res. 66:7390–7394.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li C, Song L, Zhang Z, Bai XX, Cui MF and
Ma LJ: MicroRNA-21 promotes TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in gastric cancer through up-regulating PTEN expression.
Oncotarget. 7:66989–67003. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zheng L, Jiao W, Mei H, Song H, Li D,
Xiang X, Chen Y, Yang F, Li H, Huang K, et al: miRNA-337-3p
inhibits gastric cancer progression through repressing myeloid zinc
finger 1-facilitated expression of matrix metalloproteinase 14.
Oncotarget. 7:40314–40328. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang PF, Sheng LL, Wang G, Tian M, Zhu
LY, Zhang R, Zhang J and Zhu JS: miR-363 promotes proliferation and
chemo-resistance of human gastric cancer via targeting of FBW7
ubiquitin ligase expression. Oncotarget. 7:35284–35292. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bartels CL and Tsongalis GJ: MicroRNAs:
Novel biomarkers for human cancer. Clin Chem. 55:623–631. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Khan S, Brougham CL, Ryan J, Sahrudin A,
O'Neill G, Wall D, Curran C, Newell J, Kerin MJ and Dwyer RM:
miR-379 regulates cyclin B1 expression and is decreased in breast
cancer. PLoS One. 8:e687532013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gururajan M, Josson S, Chu GC, Lu CL, Lu
YT, Haga CL, Zhau HE, Liu C, Lichterman J, Duan P, et al: miR-154*
and miR-379 in the DLK1-DIO3 microRNA mega-cluster regulate
epithelial to mesenchymal transition and bone metastasis of
prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 20:6559–6569. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pollari S, Leivonen SK, Perälä M, Fey V,
Käkönen SM and Kallioniemi O: Identification of microRNAs
inhibiting TGF-β-induced IL-11 production in bone metastatic breast
cancer cells. PLoS One. 7:e373612012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Skalsky RL and Cullen BR: Reduced
expression of brain-enriched microRNAs in glioblastomas permits
targeted regulation of a cell death gene. PLoS One. 6:e242482011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen JS, Li HS, Huang JQ, Dong SH, Huang
ZJ, Yi W, Zhan GF, Feng JT, Sun JC and Huang XH: MicroRNA-379-5p
inhibits tumor invasion and metastasis by targeting FAK/AKT
signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 375:73–83.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yamamoto K, Seike M, Takeuchi S, Soeno C,
Miyanaga A, Noro R, Minegishi Y, Kubota K and Gemma A: MiR-379/411
cluster regulates IL-18 and contributes to drug resistance in
malignant pleural mesothelioma. Oncol Rep. 32:2365–2372.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ge YZ, Xu LW, Xu Z, Wu R, Xin H, Zhu M, Lu
TZ, Geng LG, Liu H, Zhou CC, et al: Expression profiles and
clinical significance of MicroRNAs in papillary renal cell
carcinoma: A STROBE-Compliant Observational Study. Medicine
(Baltimore). 94:e7672015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zheng H and Kang Y: Multilayer control of
the EMT master regulators. Oncogene. 33:1755–1763. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Duan F, Jia D, Zhao J, Wu W, Min L, Song
S, Wu H, Wang L, Wang H, Ruan Y, et al: Loss of GFAT1 promotes
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and predicts unfavorable
prognosis in gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 7:38427–38439. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee J, Ha S, Jung CK and Lee HH:
High-mobility-group A2 overexpression provokes a poor prognosis of
gastric cancer through the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Int J
Oncol. 46:2431–2438. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yan Y, Zhang J, Li JH, Liu X, Wang JZ, Qu
HY, Wang JS and Duan XY: High tumor-associated macrophages
infiltration is associated with poor prognosis and may contribute
to the phenomenon of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric
cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 9:3975–3983. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hu J, Shan Z, Hu K, Ren F, Zhang W, Han M,
Li Y, Feng K, Lei L and Feng Y: miRNA-223 inhibits
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric carcinoma cells via
Sp1. Int J Oncol. 49:325–335. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang LL, Zhang XH, Zhang X and Chu JK:
MiR-30a increases cisplatin sensitivity of gastric cancer cells
through suppressing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Eur
Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:1733–1739. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang LL, Liu J, Lei S, Zhang J, Zhou W
and Yu HG: PTEN inhibits the invasion and metastasis of gastric
cancer via downregulation of FAK expression. Cell Signal.
26:1011–1020. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang PF, Li KS, Shen YH, Gao PT, Dong ZR,
Cai JB, Zhang C, Huang XY, Tian MX, Hu ZQ, et al: Galectin-1
induces hepatocellular carcinoma EMT and sorafenib resistance by
activating FAK/PI3K/AKT signaling. Cell Death Dis. 7:e22012016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Feng R and Yang S: Effects of combining
erlotinib and RNA-interfered downregulation of focal adhesion
kinase expression on gastric cancer. J Int Med Res. 44:855–864.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen P, Zhao H, Huang J, Yan X, Zhang Y
and Gao Y: MicroRNA-17-5p promotes gastric cancer proliferation,
migration and invasion by directly targeting early growth response
2. Am J Cancer Res. 6:2010–2020. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sun J, Li J, Zhang W, Zhang J, Sun S, Li
G, Song H and Wan D: MicroRNA-509-3p inhibits cancer cell
proliferation and migration via upregulation of XIAP in gastric
cancer cells. Oncol Res. 25:455–461. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Park JH, Lee BL, Yoon J, Kim J, Kim MA,
Yang HK and Kim WH: Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) gene amplification
and its clinical implications in gastric cancer. Hum Pathol.
41:1664–1673. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhou Y, Dang J, Chang KY, Yau E, Aza-Blanc
P, Moscat J and Rana TM: miR-1298 inhibits mutant KRAS-driven tumor
growth by repressing FAK and LAMB3. Cancer Res. 76:5777–5787. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Guo LL, He ZC, Yang CQ, Qiao PT and Yin
GL: Epigenetic silencing of olfactomedin-4 enhances gastric cancer
cell invasion via activation of focal adhesion kinase signaling.
BMB Rep. 48:630–635. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Song G, Xu S, Zhang H, Wang Y, Xiao C,
Jiang T, Wu L, Zhang T, Sun X, Zhong L, et al: TIMP1 is a
prognostic marker for the progression and metastasis of colon
cancer through FAK-PI3K/AKT and MAPK pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 35:1482016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|