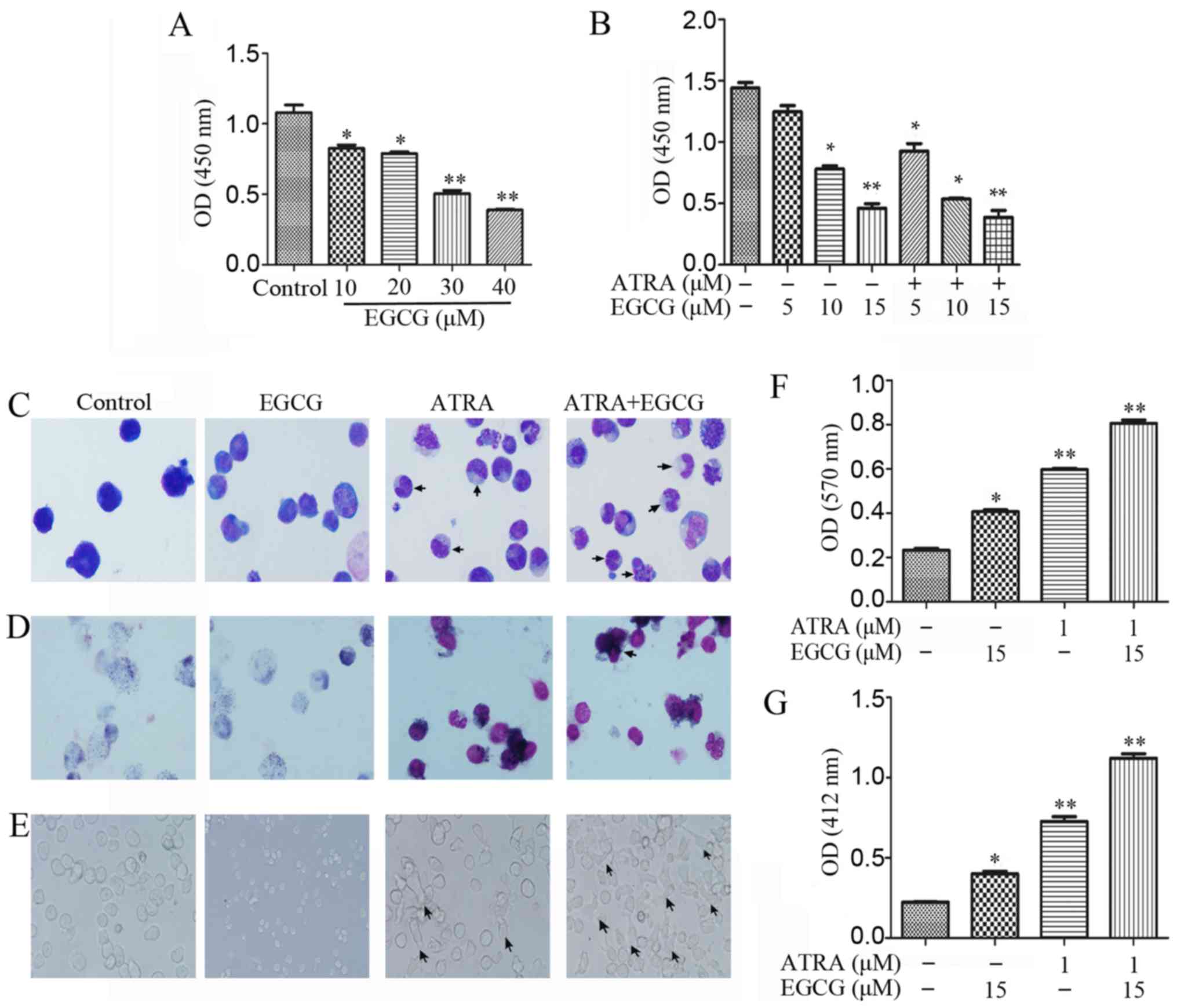
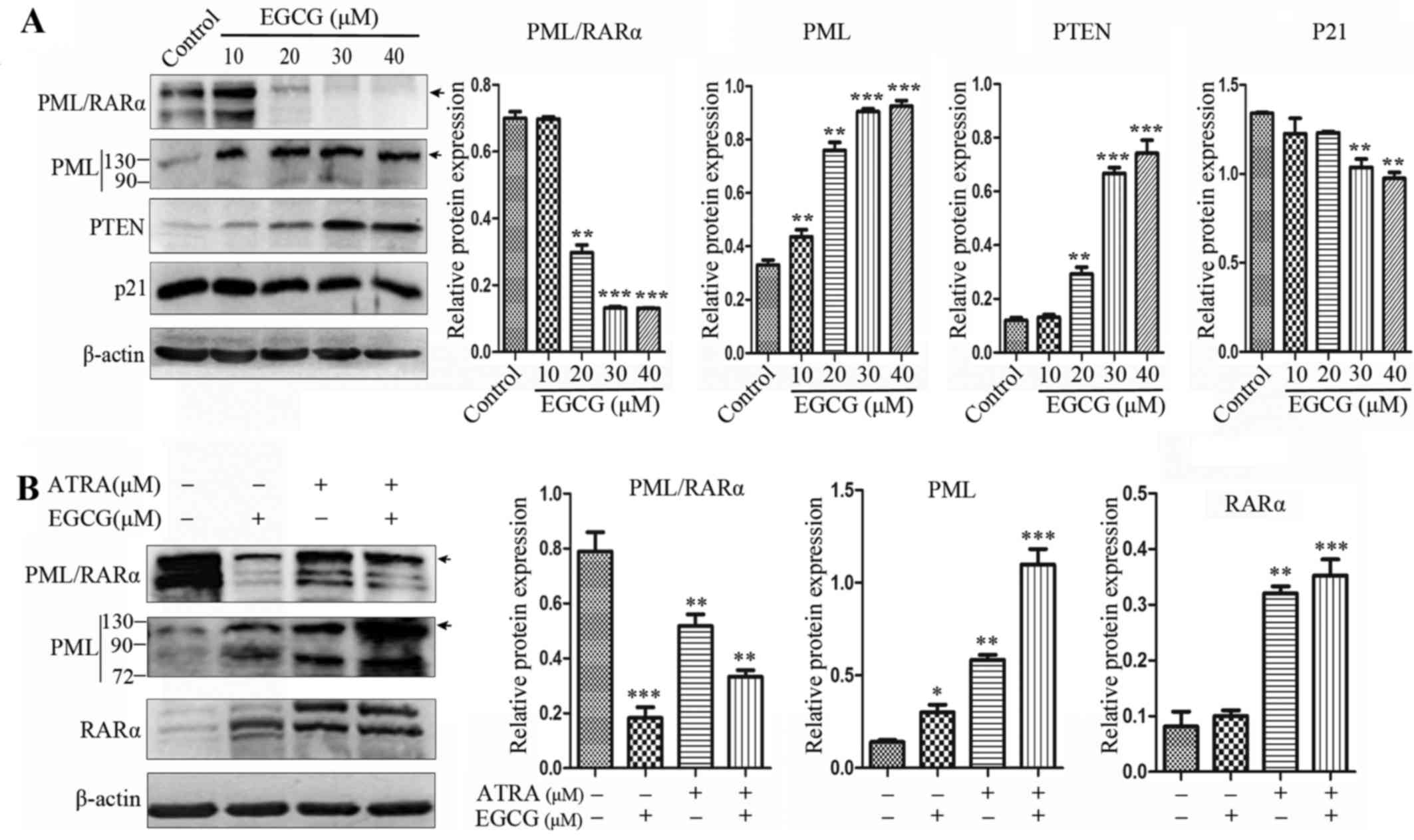
|
1
|
Melnick A and Licht JD: Deconstructing a
disease: RARalpha, its fusion partners, and their roles in the
pathogenesis of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Blood. 93:3167–3215.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lafage-Pochitaloff M, Alcalay M, Brunel V,
Longo L, Sainty D, Simonetti J, Birg F and Pelicci PG: Acute
promyelocytic leukemia cases with nonreciprocal PML/RARα or
RARα/PML fusion genes. Blood. 85:1169–1174. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mozziconacci MJ, Liberatore C, Brunel V,
Grignani F, Arnoulet C, Ferrucci PF, Fernandez F, Sainty D, Pelicci
PG, Birg F, et al: In vitro response to all-trans retinoic acid of
acute promyelocytic leukemias with nonreciprocal PML/RARA or
RARA/PML fusion genes. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 22:241–250. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gianni M, Fratelli M, Bolis M, Kurosaki M,
Zanetti A, Paroni G, Rambaldi A, Borleri G, Rochette-Egly C, Terao
M, et al: RARalpha2 and PML-RAR similarities in the control of
basal and retinoic acid induced myeloid maturation of acute myeloid
leukemia cells. Oncotarget. 8:37041–37060. 2016.
|
|
5
|
Vitaliano-Prunier A, Halftermeyer J,
Ablain J, de Reynies A, Peres L, Le Bras M, Metzger D and de Thé H:
Clearance of PML/RARA-bound promoters suffice to initiate APL
differentiation. Blood. 124:3772–3780. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Marasca R, Zucchini P, Galimberti S,
Leonardi G, Vaccari P, Donelli A, Luppi M, Petrini M and Torelli G:
Missense mutations in the PML/RARalpha ligand binding domain in
ATRA-resistant As2O3 sensitive relapsed acute
promyelocytic leukemia. Haematologica. 84:963–968. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fatemi A, Safa M and Kazemi A: MST-312
induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in APL cells through
inhibition of telomerase activity and suppression of NF-kappaB
pathway. Tumour Biol. 36:8425–8437. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Huang Y, Kumazoe M, Bae J, Yamada S, Takai
M, Hidaka S, Yamashita S, Kim Y, Won Y, Murata M, et al: Green tea
polyphenol epigallocatechin-O-gallate induces cell death by acid
sphingomyelinase activation in chronic myeloid leukemia cells.
Oncol Rep. 34:1162–1168. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Iwasaki R, Ito K, Ishida T, Hamanoue M,
Adachi S, Watanabe T and Sato Y: Catechin, green tea component,
causes caspase-independent necrosis-like cell death in chronic
myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Sci. 100:349–356. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Vezina A, Chokor R and Annabi B: EGCG
targeting efficacy of NF-kappaB downstream gene products is
dictated by the monocytic/macrophagic differentiation status of
promyelocytic leukemia cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother.
61:2321–2331. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Lee HS, Jun JH, Jung EH, Koo BA and Kim
YS: Epigalloccatechin-3-gallate inhibits ocular neovascularization
and vascular permeability in human retinal pigment epithelial and
human retinal microvascular endothelial cells via suppression of
MMP-9 and VEGF activation. Molecules. 19:12150–12172. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu L, Hou L, Gu S, Zuo X, Meng D, Luo M,
Zhang X, Huang S and Zhao X: Molecular mechanism of
epigallocatechin-3-gallate in human esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Oncol Rep. 33:297–303. 2015.
|
|
13
|
Tsukamoto S, Kumazoe M, Huang Y, Lesnick
C, Kay NE, Shanafelt TD and Tachibana H: SphK1 inhibitor
potentiates the anti-cancer effect of EGCG on leukaemia cells. Br J
Haematol. 178:155–158. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Amin AR, Karpowicz PA, Carey TE, Arbiser
J, Nahta R, Chen ZG, Dong JT, Kucuk O, Khan GN, Huang GS, et al:
Evasion of anti-growth signaling: A key step in tumorigenesis and
potential target for treatment and prophylaxis by natural
compounds. Semin Cancer Biol. 35(Suppl): S55–S77. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Britschgi A, Simon HU, Tobler A, Fey MF
and Tschan MP: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate induces cell death in
acute myeloid leukaemia cells and supports all-trans retinoic
acid-induced neutrophil differentiation via death-associated
protein kinase 2. Br J Haematol. 149:55–64. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang L, Chen QS, Xu PP, Qian Y, Wang AH,
Xiao D, Zhao Y, Sheng Y, Wen XQ and Zhao WL: Catechins induced
acute promyelocytic leukemia cell apoptosis and triggered PML-RARα
oncoprotein degradation. J Hematol Oncol. 7:752014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Bermúdez Brito M, Goulielmaki E and
Papakonstanti EA: Focus on PTEN regulation. Front Oncol. 5:1662015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Whiteman DC, Zhou XP, Cummings MC, Pavey
S, Hayward NK and Eng C: Nuclear PTEN expression and
clinicopathologic features in a population-based series of primary
cutaneous melanoma. Int J Cancer. 99:63–67. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang J, Liu J, Zheng J, Du W, He Y, Liu W
and Huang S: A reappraisal by quantitative flow cytometry analysis
of PTEN expression in acute leukemia. Leukemia. 21:2072–2074. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Choorapoikayil S, Kers R, Herbomel P,
Kissa K and den Hertog J: Pivotal role of Pten in the balance
between proliferation and differentiation of hematopoietic stem
cells in zebrafish. Blood. 123:184–190. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Dragojlovic-Munther M and Martinez-Agosto
JA: Multifaceted roles of PTEN and TSC orchestrate growth and
differentiation of Drosophila blood progenitors. Development.
139:3752–3763. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee JE, Lim MS, Park JH, Park CH and Koh
HC: PTEN promotes dopaminergic neuronal differentiation through
regulation of ERK-dependent inhibition of S6K signaling in human
neural stem cells. Stem Cells Transl Med. 5:1319–1329. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Neri LM, Borgatti P, Tazzari PL, Bortul R,
Cappellini A, Tabellini G, Bellacosa A, Capitani S and Martelli AM:
The phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT1 pathway involvement in drug and
all-trans-retinoic acid resistance of leukemia cells. Mol Cancer
Res. 1:234–246. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huang J, Yan J, Zhang J, Zhu S, Wang Y,
Shi T, Zhu C, Chen C, Liu X, Cheng J, et al: SUMO1 modification of
PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with
the plasma membrane. Nat Commun. 3:9112012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Morotti A, Panuzzo C, Crivellaro S, Carrà
G, Guerrasio A and Saglio G: HAUSP compartmentalization in chronic
myeloid leukemia. Eur J Haematol. 94:318–321. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Trotman LC, Wang X, Alimonti A, Chen Z,
Teruya-Feldstein J, Yang H, Pavletich NP, Carver BS, Cordon-Cardo
C, Erdjument-Bromage H, et al: Ubiquitination regulates PTEN
nuclear import and tumor suppression. Cell. 128:141–156. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Song MS, Salmena L, Carracedo A, Egia A,
Lo-Coco F, Teruya-Feldstein J and Pandolfi PP: The
deubiquitinylation and localization of PTEN are regulated by a
HAUSP-PML network. Nature. 455:813–817. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Trotman LC, Alimonti A, Scaglioni PP,
Koutcher JA, Cordon-Cardo C and Pandolfi PP: Identification of a
tumour suppressor network opposing nuclear Akt function. Nature.
441:523–527. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ferruzzi L, Turrini E, Burattini S,
Falcieri E, Poli F, Mandrone M, Sacchetti G, Tacchini M, Guerrini
A, Gotti R, et al: Hemidesmus indicus induces apoptosis as well as
differentiation in a human promyelocytic leukemic cell line. J
Ethnopharmacol. 147:84–91. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kim SH, Danilenko M and Kim TS:
Differential enhancement of leukaemia cell differentiation without
elevation of intracellular calcium by plant-derived sesquiterpene
lactone compounds. Br J Pharmacol. 155:814–825. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Misra S, Selvam AK, Wallenberg M, Ambati
A, Matolcsy A, Magalhaes I, Lauter G and Björnstedt M: Selenite
promotes all-trans retinoic acid-induced maturation of acute
promyelocytic leukemia cells. Oncotarget. 7:74686–74700.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Song H, Li L, Zhong L, Yang R, Jiang K,
Yang X and Liu B: NLS-RARα modulates acute promyelocytic leukemia
NB4 cell proliferation and differentiation via the PI3K/AKT
pathway. Mol Med Rep. 14:5495–5500. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Goebbels S, Wieser GL, Pieper A, Spitzer
S, Weege B, Yan K, Edgar JM, Yagensky O, Wichert SP, Agarwal A, et
al: A neuronal PI(3,4,5)P3-dependent program of oligodendrocyte
precursor recruitment and myelination. Nat Neurosci. 20:10–15.
2017. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Li Y, Prasad A, Jia Y, Roy SG, Loison F,
Mondal S, Kocjan P, Silberstein LE, Ding S and Luo HR: Pretreatment
with phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN)
inhibitor SF1670 augments the efficacy of granulocyte transfusion
in a clinically relevant mouse model. Blood. 117:6702–6713. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Van Aller GS, Carson JD, Tang W, Peng H,
Zhao L, Copeland RA, Tummino PJ and Luo L: Epigallocatechin gallate
(EGCG), a major component of green tea, is a dual
phosphoinositide-3-kinase/mTOR inhibitor. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 406:194–199. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu S, Wang XJ, Liu Y and Cui YF:
PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling is involved in
(−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate-induced apoptosis of human
pancreatic carcinoma cells. Am J Chin Med. 41:629–642. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Li RA, Traver D, Matthes T and Bertrand
JY: Ndrg1b and fam49ab modulate the PTEN pathway to control T-cell
lymphopoiesis in the zebrafish. Blood. 128:3052–3060.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yang JM, Schiapparelli P, Nguyen HN,
Igarashi A, Zhang Q, Abbadi S, Amzel LM, Sesaki H,
Quiñones-Hinojosa A and Iijima M: Characterization of PTEN
mutations in brain cancer reveals that pten mono-ubiquitination
promotes protein stability and nuclear localization. Oncogene.
36:3673–3685. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ciechanover A: Proteolysis: From the
lysosome to ubiquitin and the proteasome. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
6:79–87. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|