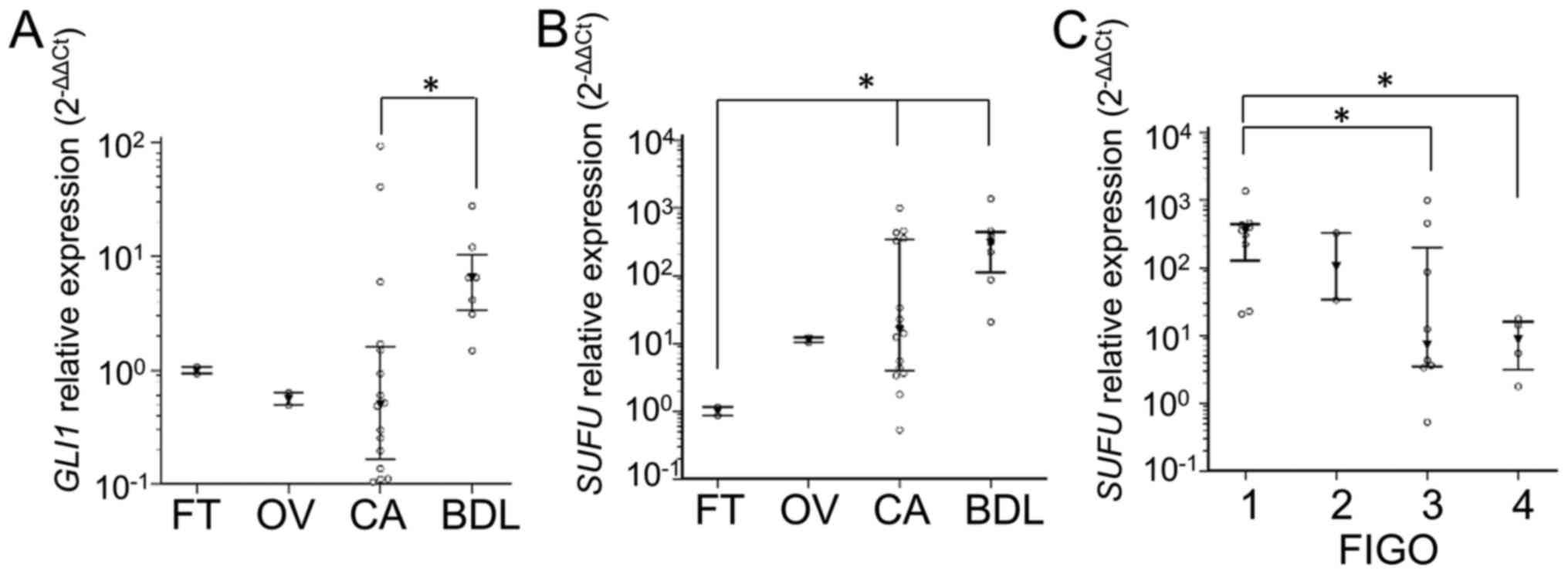
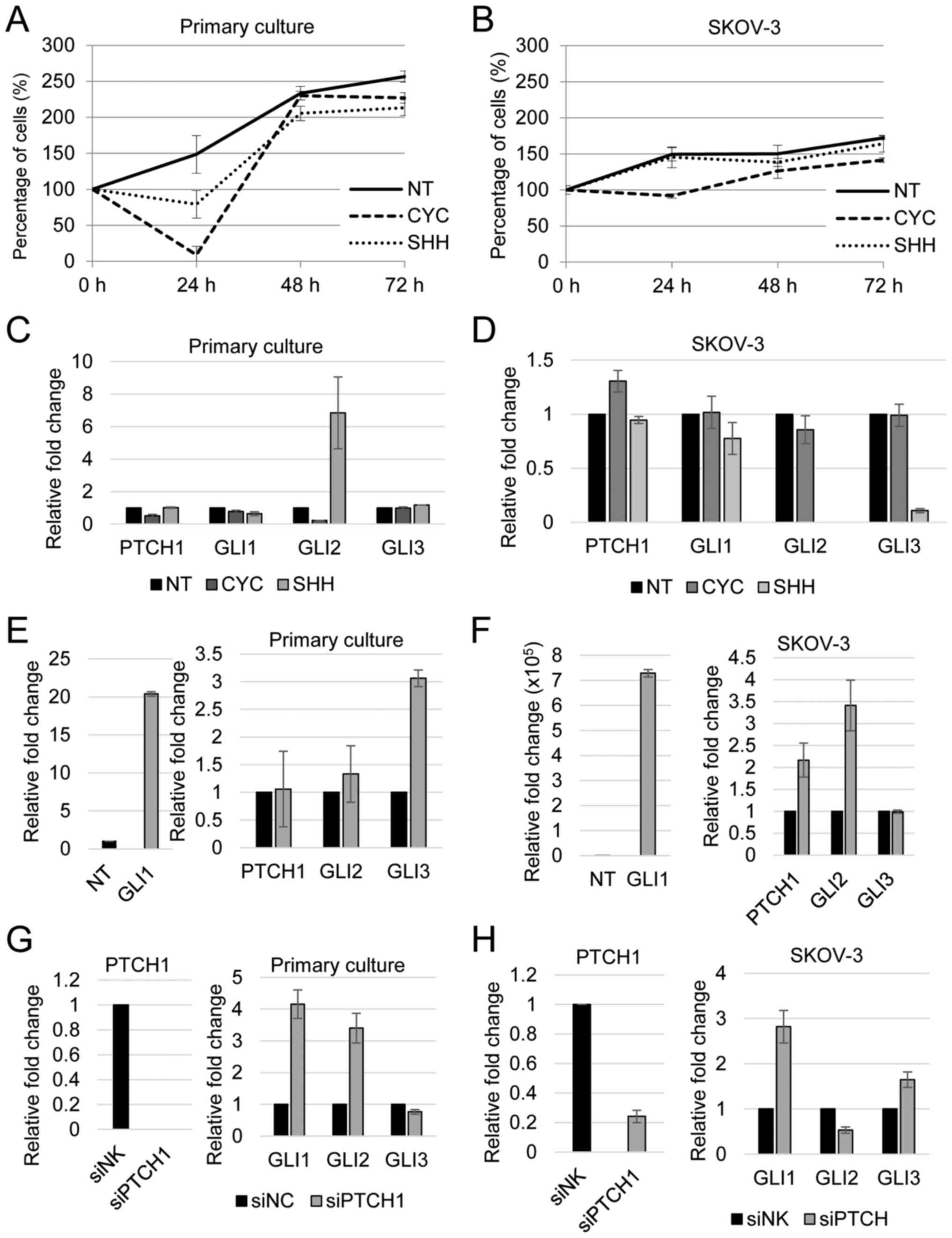
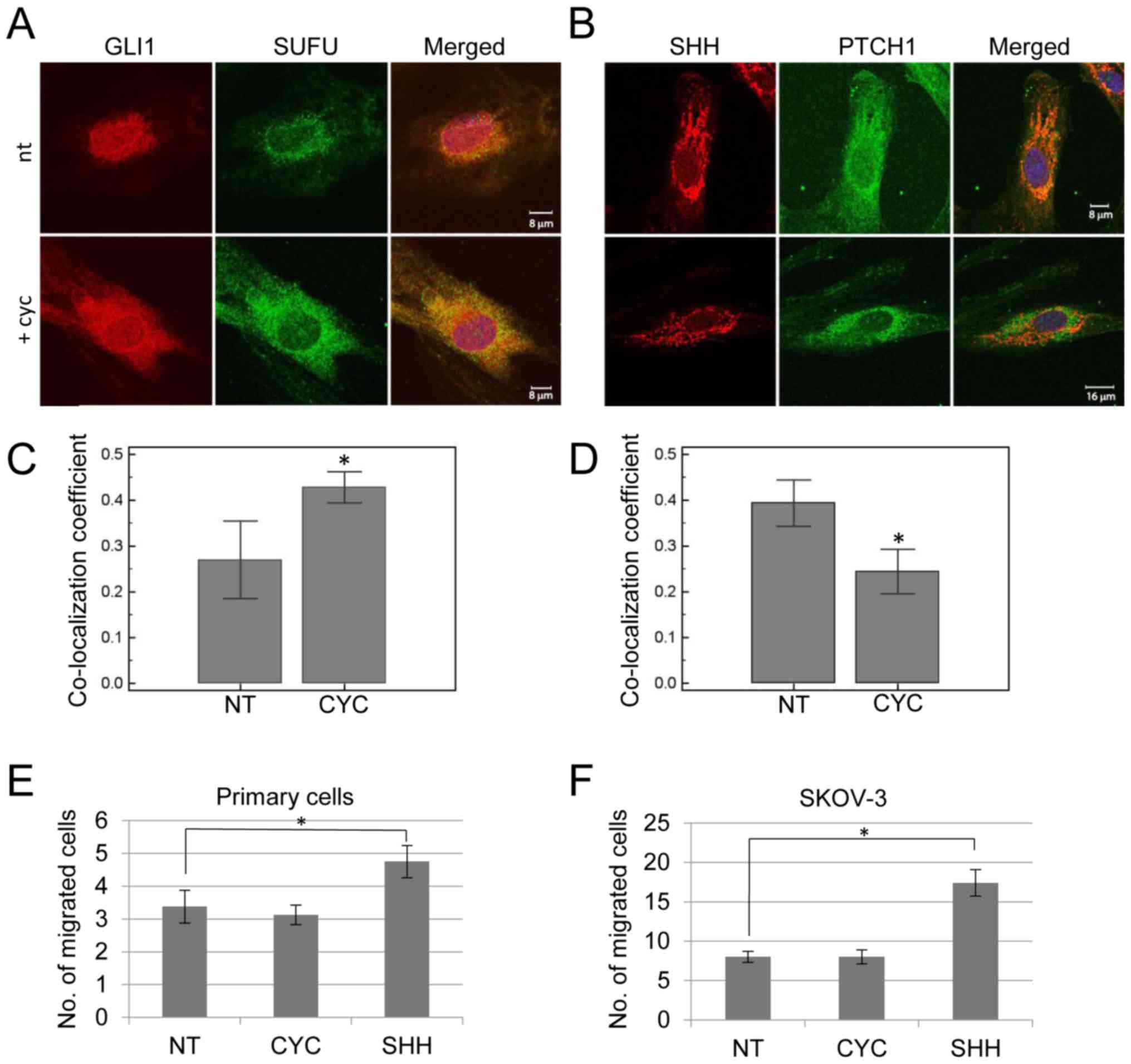
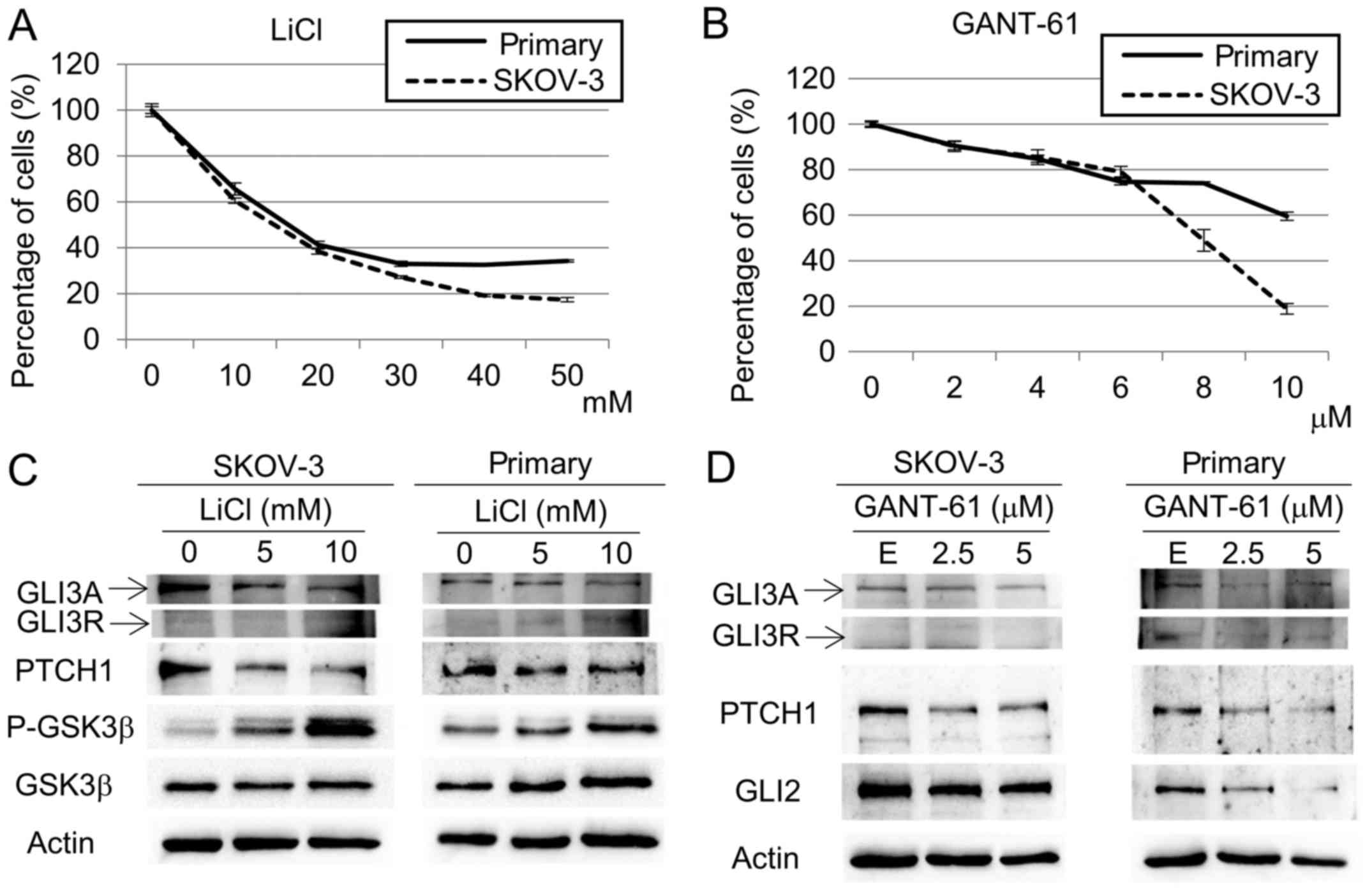
|
1
|
American Cancer Society: Global Cancer
Facts & Figures. 2nd Edition. American Cancer Society; Atlanta,
GA: 2011, https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/research/cancer-facts-and-statistics/global-cancer-facts-and-figures/global-cancer-facts-and-figures-2nd-edition.pdf.
|
|
2
|
Hart WR: Borderline epithelial tumors of
the ovary. Mod Pathol. 18(Suppl 2): S33–S50. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bell DA: Origins and molecular pathology
of ovarian cancer. Mod Pathol. 18(Suppl 2): S19–S32. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Takai N, Miyazaki T, Nishida M, Nasu K and
Miyakawa I: Expression of survivin is associated with malignant
potential in epithelial ovarian carcinoma. Int J Mol Med.
10:211–216. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hoogstraat M, de Pagter MS, Cirkel GA, van
Roosmalen MJ, Harkins TT, Duran K, Kreeftmeijer J, Renkens I,
Witteveen PO, Lee CC, et al: Genomic and transcriptomic plasticity
in treatment-naive ovarian cancer. Genome Res. 24:200–211. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Huntzicker EG, Estay IS, Zhen H, Lokteva
LA, Jackson PK and Oro AE: Dual degradation signals control Gli
protein stability and tumor formation. Genes Dev. 20:276–281. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Takenaka K, Kise Y and Miki H: GSK3beta
positively regulates Hedgehog signaling through Sufu in mammalian
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 353:501–508. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Brun SN, Markant SL, Esparza LA, Garcia G,
Terry D, Huang JM, Pavlyukov MS, Li XN, Grant GA, Crawford JR, et
al: Survivin as a therapeutic target in Sonic hedgehog-driven
medulloblastoma. Oncogene. 34:3770–3779. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Vlčková K, Ondrušová L, Vachtenheim J,
Réda J, Dundr P, Zadinová M, Žáková P and Poučková P: Survivin, a
novel target of the Hedgehog/GLI signaling pathway in human tumor
cells. Cell Death Dis. 7:e20482016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zhang Y and Kalderon D: Hedgehog acts as a
somatic stem cell factor in the Drosophila ovary. Nature.
410:599–604. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Russell MC, Cowan RG, Harman RM, Walker AL
and Quirk SM: The hedgehog signaling pathway in the mouse ovary.
Biol Reprod. 77:226–236. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huang C-CJ and Yao HH-C: Diverse functions
of Hedgehog signaling in formation and physiology of steroidogenic
organs. Mol Reprod Dev. 77:489–496. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wijgerde M, Ooms M, Hoogerbrugge JW and
Grootegoed JA: Hedgehog signaling in mouse ovary: Indian hedgehog
and desert hedgehog from granulosa cells induce target gene
expression in developing theca cells. Endocrinology. 146:3558–3566.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Spicer LJ, Sudo S, Aad PY, Wang LS, Chun
SY, Ben-Shlomo I, Klein C and Hsueh AJ: The hedgehog-patched
signaling pathway and function in the mammalian ovary: A novel role
for hedgehog proteins in stimulating proliferation and
steroidogenesis of theca cells. Reproduction. 138:329–339. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen X, Horiuchi A, Kikuchi N, Osada R,
Yoshida J, Shiozawa T and Konishi I: Hedgehog signal pathway is
activated in ovarian carcinomas, correlating with cell
proliferation: It's inhibition leads to growth suppression and
apoptosis. Cancer Sci. 98:68–76. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Liao X, Siu MKY, Au CWH, Wong ES, Chan HY,
Ip PP, Ngan HY and Cheung AN: Aberrant activation of hedgehog
signaling pathway in ovarian cancers: Effect on prognosis, cell
invasion and differentiation. Carcinogenesis. 30:131–140. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Bhattacharya R, Kwon J, Ali B, Wang E,
Patra S, Shridhar V and Mukherjee P: Role of hedgehog signaling in
ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 14:7659–7666. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Schmid S, Bieber M, Zhang F, Zhang M, He
B, Jablons D and Teng NNH: Wnt and hedgehog gene pathway expression
in serous ovarian cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 21:975–980. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang L, He J, Huang S, Zhang X, Bian Y, He
N, Zhang H and Xie J: Activation of hedgehog signaling is not a
frequent event in ovarian cancers. Mol Cancer. 8:1122009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ciucci A, De Stefano I, Vellone VG, Lisi
L, Bottoni C, Scambia G, Zannoni GF and Gallo D: Expression of the
glioma-associated oncogene homolog 1 (gli1) in advanced serous
ovarian cancer is associated with unfavorable overall survival.
PLoS One. 8:e601452013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen Q, Xu R, Zeng C, Lu Q, Huang D, Shi
C, Zhang W, Deng L, Yan R, Rao H, et al: Down-regulation of Gli
transcription factor leads to the inhibition of migration and
invasion of ovarian cancer cells via integrin β4-mediated FAK
signaling. PLoS One. 9:e883862014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Steg AD, Burke MR, Amm HM, Katre AA,
Dobbin ZC, Jeong DH and Landen CN: Proteasome inhibition reverses
hedgehog inhibitor and taxane resistance in ovarian cancer.
Oncotarget. 5:7065–7080. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
McCann CK, Growdon WB, Kulkarni-Datar K,
Curley MD, Friel AM, Proctor JL, Sheikh H, Deyneko I, Ferguson JA,
Vathipadiekal V, et al: Inhibition of Hedgehog signaling
antagonizes serous ovarian cancer growth in a primary xenograft
model. PLoS One. 6:e280772011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kandala PK and Srivastava SK:
Diindolylmethane-mediated Gli1 protein suppression induces anoikis
in ovarian cancer cells in vitro and blocks tumor formation ability
in vivo. J Biol Chem. 287:28745–28754. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ray A, Meng E, Reed E, Shevde LA and
Rocconi RP: Hedgehog signaling pathway regulates the growth of
ovarian cancer spheroid forming cells. Int J Oncol. 39:797–804.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Byrom J, Mudaliar V, Redman CW, Jones P,
Strange RC and Hoban PR: Loss of heterozygosity at chromosome
9q22-31 is a frequent and early event in ovarian tumors. Int J
Oncol. 24:1271–1277. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tsuji T, Catasus L and Prat J: Is loss of
heterozygosity at 9q22.3 (PTCH gene) and 19p13.3 (STK11 gene)
involved in the pathogenesis of ovarian stromal tumors? Hum Pathol.
36:792–796. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Levanat S, Musani V, Komar A and Oreskovic
S: Role of the hedgehog/patched signaling pathway in oncogenesis: A
new polymorphism in the PTCH gene in ovarian fibroma. Ann NY Acad
Sci. 1030:134–143. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Levanat S, Kappler R, Hemmerlein B, Döring
P, Musani V, Komar A, Oreskovic S, Pavelic B and Hahn H: Analysis
of the PTCH1 signaling pathway in ovarian dermoids. Int J Mol Med.
14:793–799. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Musani V, Sabol M, Car D, Ozretić P,
Kalafatić D, Maurac I, Orešković S and Levanat S: PTCH1 gene
polymorphisms in ovarian tumors: Potential protective role of
c.3944T allele. Gene. 517:55–59. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cretnik M, Musani V, Oreskovic S, Leovic D
and Levanat S: The Patched gene is epigenetically regulated in
ovarian dermoids and fibromas, but not in basocellular carcinomas.
Int J Mol Med. 19:875–883. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Löf-Öhlin ZM, Levanat S, Sabol M, Sorbe B
and Nilsson TK: Promoter methylation in the PTCH gene in cervical
epithelial cancer and ovarian cancer tissue as studied by eight
novel Pyrosequencing® assays. Int J Oncol. 38:685–692.
2011.
|
|
33
|
Maurac I, Sabol M, Musani V, Car D,
Ozretic P, Kalafatic D, Oreskovic S, Babic D and Levanat S: A
low-grade ovarian carcinoma case with coincident LOH of PTCH1 and
BRCA1, and a mutation in BRCA1. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 31:264–271.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Leovic D, Sabol M, Ozretic P, Musani V,
Car D, Marjanovic K, Zubcic V, Sabol I, Sikora M, Grce M, et al:
Hh-Gli signaling pathway activity in oral and oropharyngeal
squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck. 34:104–112. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
McCall MN, McMurray HR, Land H and
Almudevar A: On non- detects in qPCR data. Bioinformatics.
30:2310–2316. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Colton T: Statistics in Medicine. Little
Brown & Co; Boston: 1974
|
|
37
|
Xing J, Jia C-R, Wang Y, Guo J and Cai Y:
Effect of shRNA targeting survivin on ovarian cancer. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 138:1221–1229. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kurman RJ and Shih IeM: The origin and
pathogenesis of epithelial ovarian cancer: A proposed unifying
theory. Am J Surg Pathol. 34:433–443. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jope RS: Lithium and GSK-3: One inhibitor,
two inhibitory actions, multiple outcomes. Trends Pharmacol Sci.
24:441–443. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Stecca B, Ruiz I and Altaba A:
Context-dependent regulation of the GLI code in cancer by HEDGEHOG
and non-HEDGEHOG signals. J Mol Cell Biol. 2:84–95. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Koshiyama M, Matsumura N and Konishi I:
Recent concepts of ovarian carcinogenesis: type I and type II.
Biomed Res Int. 2014:9342612014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sabol M, Trnski D, Uzarevic Z, Ozretic P,
Musani V, Rafaj M, Cindric M and Levanat S: Combination of
cyclopamine and tamoxifen promotes survival and migration of mcf-7
breast cancer cells - interaction of hedgehog-gli and estrogen
receptor signaling pathways. PLoS One. 9:e1145102014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Shakoori A, Ougolkov A, Yu ZW, Zhang B,
Modarressi MH, Billadeau DD, Mai M, Takahashi Y and Minamoto T:
Deregulated GSK3β activity in colorectal cancer: Its association
with tumor cell survival and proliferation. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 334:1365–1373. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Trnski D, Sabol M, Gojević A, Martinić M,
Ozretić P, Musani V, Ramić S and Levanat S: GSK3β and Gli3 play a
role in activation of Hedgehog-Gli pathway in human colon cancer -
Targeting GSK3β downregulates the signaling pathway and reduces
cell proliferation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1852:2574–2584. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Rask K, Nilsson A, Brännström M, Carlsson
P, Hellberg P, Janson PO, Hedin L and Sundfeldt K: Wnt-signalling
pathway in ovarian epithelial tumours: Increased expression of
β-catenin and GSK3β. Br J Cancer. 89:1298–1304. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hilliard TS, Gaisina IN, Muehlbauer AG,
Gaisin AM, Gallier F and Burdette JE: Glycogen synthase kinase 3β
inhibitors induce apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells and inhibit
in-vivo tumor growth. Anticancer Drugs. 22:978–985. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lauth M, Bergström A, Shimokawa T and
Toftgård R: Inhibition of GLI-mediated transcription and tumor cell
growth by small- molecule antagonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:8455–8460. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Tostar U, Toftgård R, Zaphiropoulos PG and
Shimokawa T: Reduction of human embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma tumor
growth by inhibition of the hedgehog signaling pathway. Genes
Cancer. 1:941–951. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Gonnissen A, Isebaert S and Haustermans K:
Targeting the Hedgehog signaling pathway in cancer: Beyond
Smoothened. Oncotarget. 6:13899–13913. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Elias KM, Emori MM, Papp E, MacDuffie E,
Konecny GE, Velculescu VE and Drapkin R: Beyond genomics: Critical
evaluation of cell line utility for ovarian cancer research.
Gynecol Oncol. 139:97–103. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|