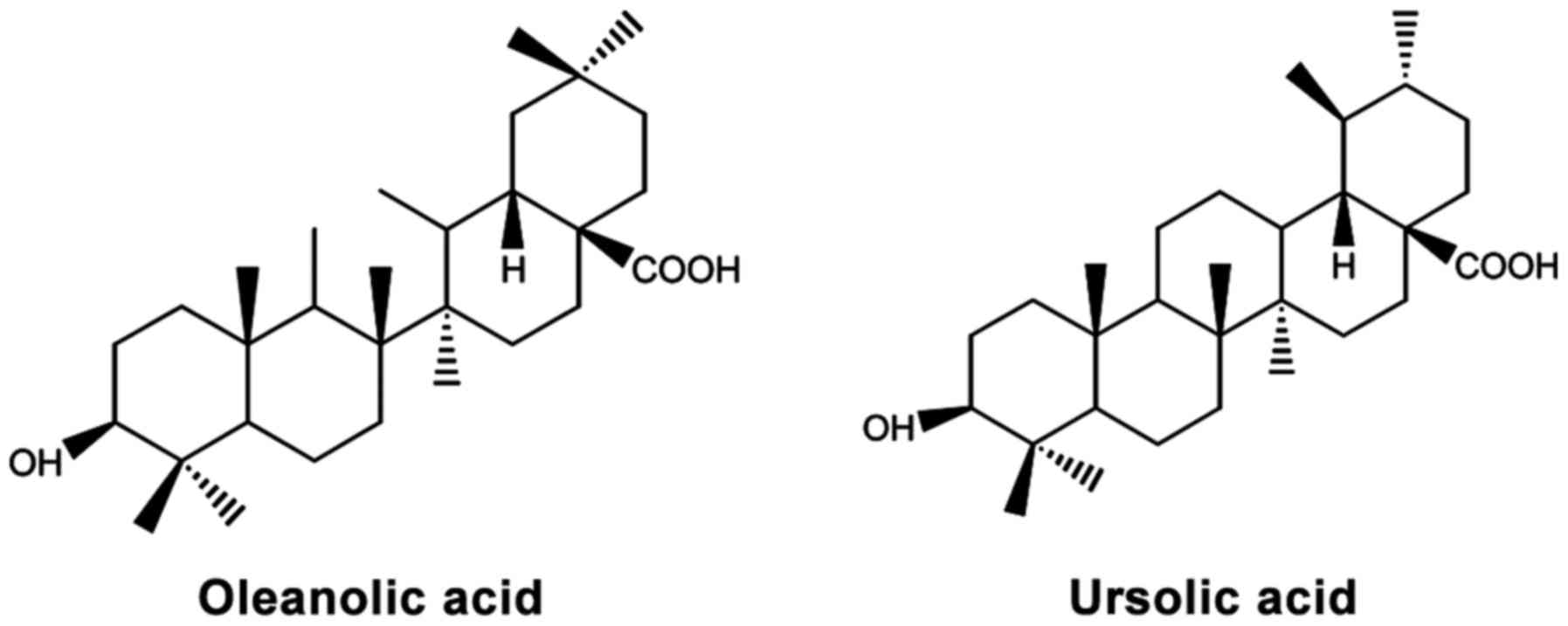
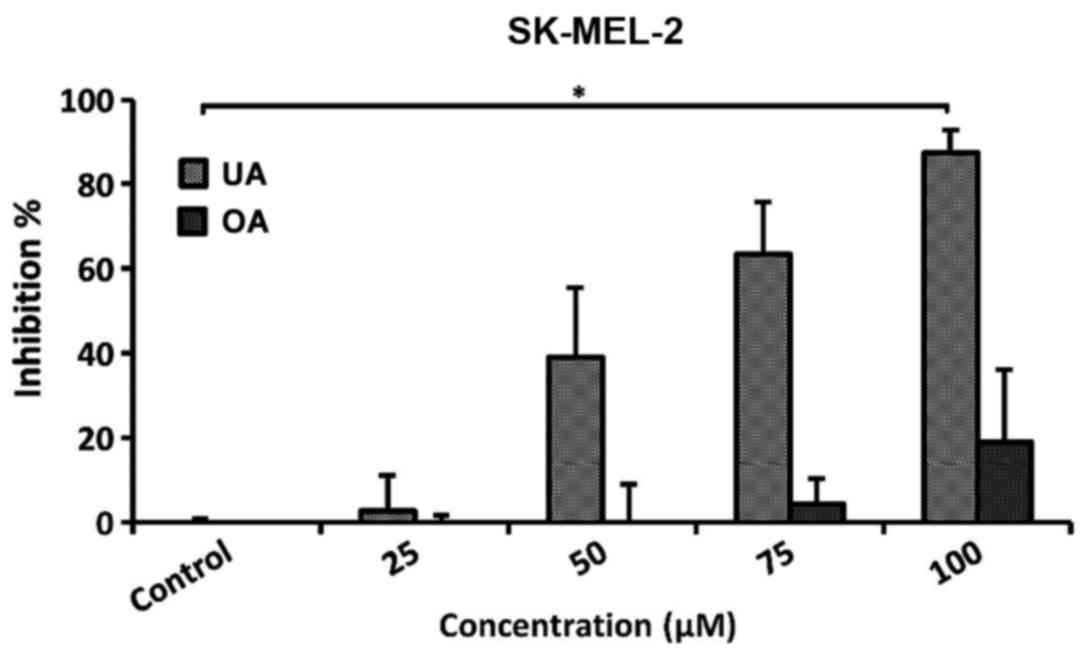
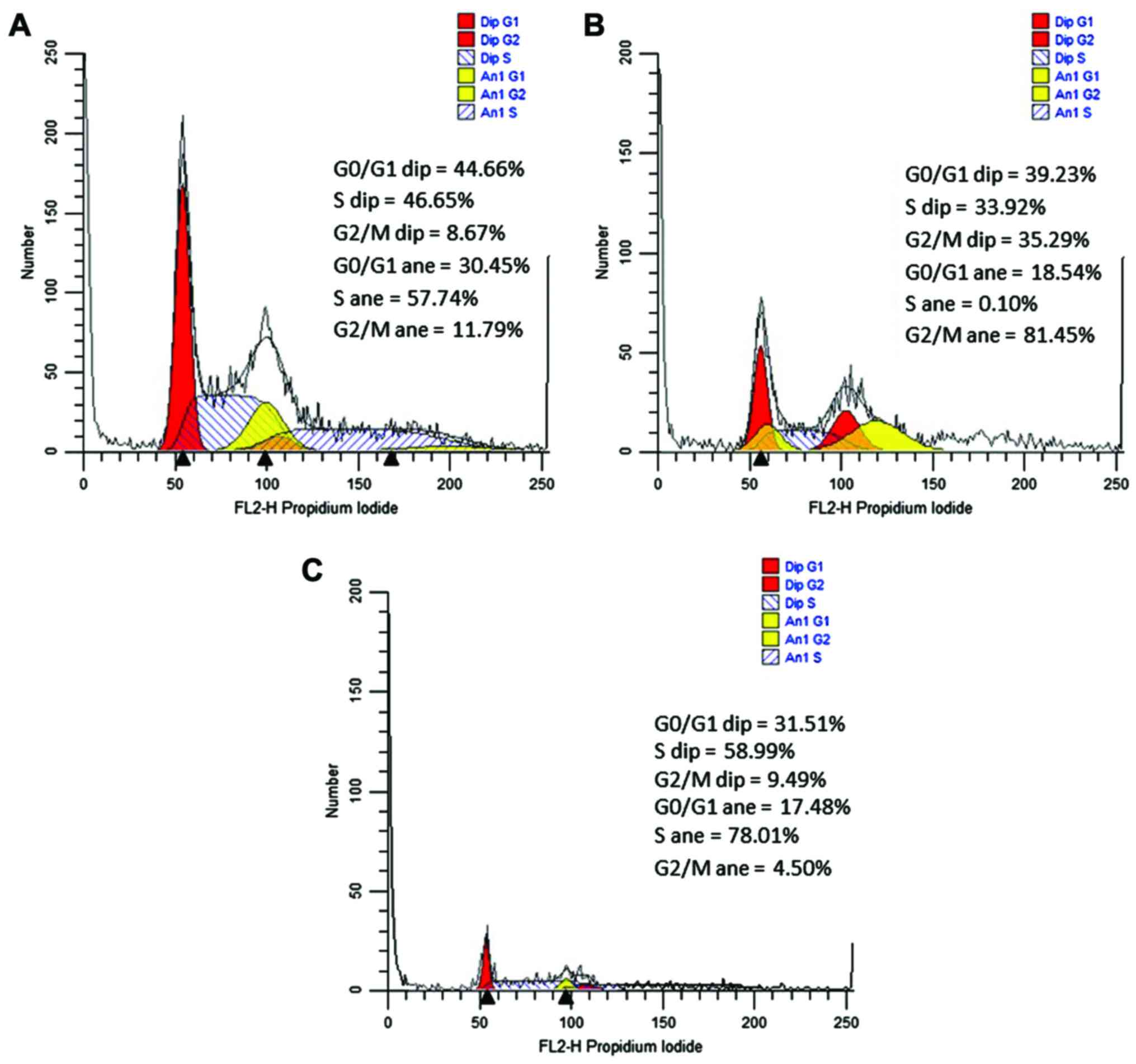
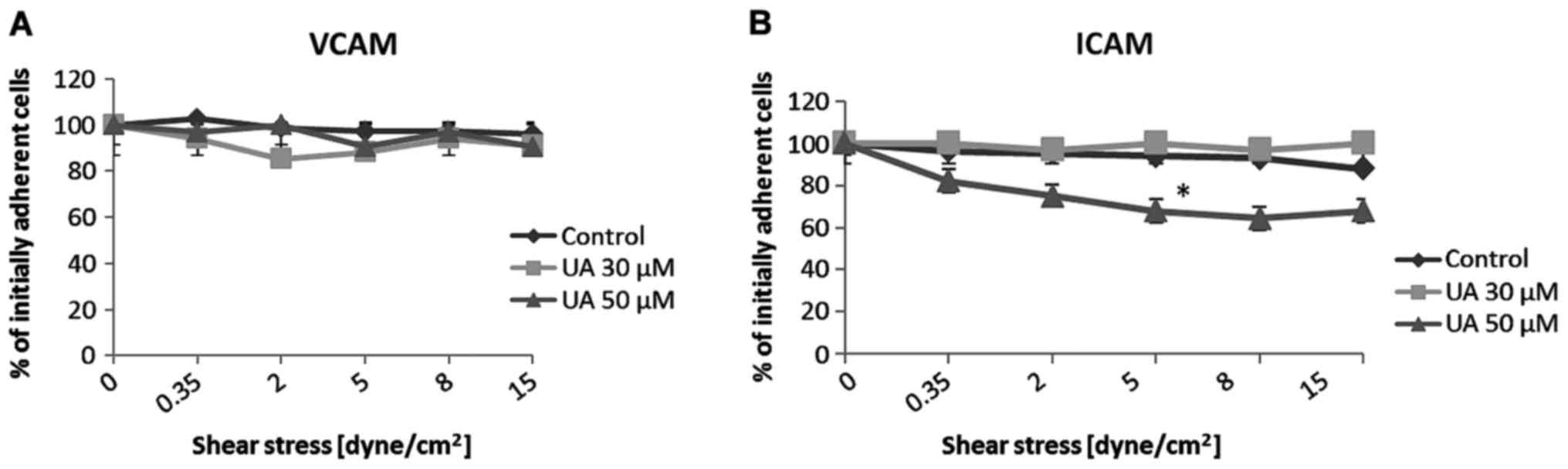
|
1
|
American Cancer Society: Key statistics
for melanoma skin cancer. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/melanoma-skin-cancer/about/key-statistics.html.
Accessed March 17, 2017.
|
|
2
|
Schadendorf D, Fisher DE, Garbe C,
Gershenwald JE, Grob JJ, Halpern A, Herlyn M, Marchetti MA,
McArthur G, Ribas A, et al: Melanoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers.
1:150032015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Danciu C, Oprean C, Coricovac DE, Andreea
C, Cimpean A, Radeke H, Soica C and Dehelean C: Behaviour of four
different B16 murine melanoma cell sublines: C57BL/6J skin. Int J
Exp Pathol. 96:73–80. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wu S and Singh RK: Resistance to
chemotherapy and molecularly targeted therapies: rationale for
combination therapy in malignant melanoma. Curr Mol Med.
11:553–563. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mouawad R, Sebert M, Michels J, Bloch J,
Spano JP and Khayat D: Treatment for metastatic malignant melanoma:
Old drugs and new strategies. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 74:27–39.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Khan MK, Khan N, Almasan A and Macklis R:
Future of radiation therapy for malignant melanoma in an era of
newer, more effective biological agents. Onco Targets Ther.
4:137–148. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Finn L, Markovic SN and Joseph RW: Therapy
for metastatic melanoma: The past, present, and future. BMC Med.
10:232012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Posch C, Moslehi H, Feeney L, Green GA,
Ebaee A, Feichtenschlager V, Chong K, Peng L, Dimon MT, Phillips T,
et al: Combined targeting of MEK and PI3K/mTOR effector pathways is
necessary to effectively inhibit NRAS mutant melanoma in vitro and
in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:4015–4020. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Johnson DB and Sosman JA: Update on the
targeted therapy of melanoma. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 14:280–292.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Posch C, Vujic I, Monshi B, Sanlorenzo M,
Weihsengruber F, Rappersberger K and Ortiz-Urda S: Searching for
the Chokehold of NRAS Mutant Melanoma. J Invest Dermatol.
136:1330–1336. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jiang Y-L and Liu Z-P: Natural products as
anti-invasive and anti-metastatic agents. Curr Med Chem.
18:808–829. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Cragg GM and Pezzuto JM: Natural products
as a vital source for the discovery of cancer chemotherapeutic and
chemopreventive agents. Med Princ Pract. 25(Suppl 2): 41–59. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Folkman J, Merler E, Abernathy C and
Williams G: Isolation of a tumor factor responsible for
angiogenesis. J Exp Med. 133:275–288. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ejaz S, Anwar K, Taj R and Ashraf M: A
novel link between angiogenesis and natural products:
Anti-angiogenic effects of Opuntia dillenii. Cent Eur J Biol.
9:298–308. 2013.
|
|
15
|
Li WW, Li VW, Hutnik M and Chiou AS: Tumor
angiogenesis as a target for dietary cancer prevention. J Oncol.
2012:8796232012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Hata K, Hori K and Takahashi S:
Differentiation- and apoptosis-inducing activities by pentacyclic
triterpenes on a mouse melanoma cell line. J Nat Prod. 65:645–648.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Allouche Y, Warleta F, Campos M,
Sánchez-Quesada C, Uceda M, Beltrán G and Gaforio JJ: Antioxidant,
antiproliferative, and pro-apoptotic capacities of pentacyclic
triterpenes found in the skin of olives on MCF-7 human breast
cancer cells and their effects on DNA damage. J Agric Food Chem.
59:121–130. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zhang W, Men X and Lei P: Review on
anti-tumor effect of triterpene acid compounds. J Cancer Res Ther.
10(Suppl 1): 14–19. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chudzik M, Korzonek-Szlacheta I and Król
W: Triterpenes as potentially cytotoxic compounds. Molecules.
20:1610–1625. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mencherini T, Picerno P, Scesa C and
Aquino R: Triterpene, antioxidant, and antimicrobial compounds from
Melissa officinalis. J Nat Prod. 70:1889–1894. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wójciak-Kosior M, Sowa I, Kocjan R and
Nowac R: Effect of different extraction techniques on
quantification of oleanolic and ursolic acid in Lamii albi flos.
Ind Crops Prod. 44:373–377. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
J C Furtado NA, Pirson L, Edelberg H, M
Miranda L, Loira-Pastoriza C, Preat V, Larondelle Y and André CM:
Pentacyclic triterpene bioavailability: An overview of in vitro and
in vivo studies. Molecules. 22:E4002017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Žiberna L, Šamec D, Mocan A, Nabavi SF,
Bishayee A, Farooqi AA, Sureda A and Nabavi SM: Oleanolic acid
alters multiple cell signaling pathways: implication in cancer
prevention and therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 18:E6432017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ikeda Y, Murakami A and Ohigashi H:
Ursolic acid: An anti- and pro-inflammatory triterpenoid. Mol Nutr
Food Res. 52:26–42. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bishayee A, Ahmed S, Brankov N and Perloff
M: Triterpenoids as potential agents for the chemoprevention and
therapy of breast cancer. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 16:980–996.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Meng QX, Roubin RH and Hanrahan JR:
Ethnopharmacological and bioactivity guided investigation of five
TCM anticancer herbs. J Ethnopharmacol. 148:229–238. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li J, Guo WJ and Yang QY: Effects of
ursolic acid and oleanolic acid on human colon carcinoma cell line
HCT15. World J Gastroenterol. 8:493–495. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yan SL, Huang CY, Wu ST and Yin MC:
Oleanolic acid and ursolic acid induce apoptosis in four human
liver cancer cell lines. Toxicol In Vitro. 24:842–848. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Lee IK, Kim DH, Lee SY, Kim KR, Choi SU,
Hong JK, Lee JH, Park YH and Lee KR: Triterpenoic acids of Prunella
vulgaris var. lilacina and their cytotoxic activities in vitro.
Arch Pharm Res. 31:1578–1583. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
George VC, Naveen Kumar DR, Suresh PK and
Kumar A: Oleanolic acid inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis
in A375 melanoma cells. Biomed Prev Nutr. 4:95–99. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Oprean C, Mioc M, Csányi E, Ambrus R,
Bojin F, Tatu C, Cristea M, Ivan A, Danciu C, Dehelean C, et al:
Improvement of ursolic and oleanolic acids' antitumor activity by
complexation with hydrophilic cyclodextrins. Biomed Pharmacother.
83:1095–1104. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Avram S, Avram S, Crisan L, Pacureanu L,
Kurunczi L and Bora A: Self-Organizing Map Classif Model. Rev Roum
Chim. 60:167–173. 2015.
|
|
33
|
Avram SI, Pacureanu LM, Bora A, Crisan L,
Avram S and Kurunczi L: ColBioS-FlavrC: A collection of
bioselective flavonoids and related compounds filtered from
high-throughput screening outcomes. J Chem Inf Model. 54:2360–2370.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bora A and Avram S, Ciucanu I, Raica M and
Avram S: Predictive models for fast and effective profiling of
kinase inhibitors. J Chem Inf Model. 56:895–905. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mu DW, Guo HQ, Zhou GB, Li JY and Su B:
Oleanolic acid suppresses the proliferation of human bladder cancer
by Akt/mTOR/S6K and ErK1/2 signaling. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:13864–13870. 2015.
|
|
36
|
Rufino-Palomares EE, Pérez-Jiménez A,
Reyes-Zurita FJ, García-Salguero L, Mokhtari K, Herrera-Merchán A,
Medina PP, Peragón J and Lupiáñez JA: Anti-cancer and
anti-angiogenic properties of various natural pentacyclic
tri-terpenoids and some of their chemical derivatives. Curr Org
Chem. 19:919–947. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Laszczyk MN: Pentacyclic triterpenes of
the lupane, oleanane and ursane group as tools in cancer therapy.
Planta Med. 75:1549–1560. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shanmugam MK, Nguyen AH, Kumar AP, Tan BKH
and Sethi G: Targeted inhibition of tumor proliferation, survival,
and metastasis by pentacyclic triterpenoids: Potential role in
prevention and therapy of cancer. Cancer Lett. 320:158–170. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shan J, Xuan Y, Zhang Q, Zhu C, Liu Z and
Zhang S: Ursolic acid synergistically enhances the therapeutic
effects of oxaliplatin in colorectal cancer. Protein Cell.
7:571–585. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ribatti D: The chick embryo
chorioallantoic membrane in the study of tumor angiogenesis. Rom J
Morphol Embryol. 49:131–135. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ribatti D: The Chick Embryo
Chorioallantoic Membrane in the Study of Angiogenesis and
Metastasis. 1st edition. Springer; Netherlands: 2010, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Bacabac RG, Smit TH, Cowin SC, Van Loon
JJ, Nieuwstadt FT, Heethaar R and Klein-Nulend J: Dynamic shear
stress in parallel-plate flow chambers. J Biomech. 38:159–167.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Zhang Y and Neelamegham S: An analysis
tool to quantify the efficiency of cell tethering and firm-adhesion
in the parallel-plate flow chamber. J immunol Methods. 278:305–317.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhao L, Liao FL, Han D and Zhou H:
Application of parallel-plate flow chamber in cancer research. Bull
Acad Mil Med Sci. 33:482–485. 2009.
|
|
45
|
Griffiths AJF, Miller JH, Suzuki DT,
Lewontin RC and Gelbart WM: Cancer: The Genetics Of Aberrant Cell
Control An introduction to Genetic Analysis. 7th edition. W.H.
Freeman & Co; New York, NY: 2000
|
|
46
|
Pfarr K, Danciu C, Arlt O, Neske C,
Dehelean C, Pfeilschifter JM and Radeke HH: Simultaneous and dose
dependent melanoma cytotoxic and immune stimulatory activity of
betulin. PLoS One. 10:e01188022015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wong SY and Hynes RO: Lymphatic or
hematogenous dissemination: How does a metastatic tumor cell
decide? Cell Cycle. 5:812–817. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Meng Y, Lin ZM, Ge N, Zhang DL, Huang J
and Kong F: Ursolic acid induces apoptosis of prostate cancer cells
via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Am J Chin Med. 43:1471–1486. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Beagle B and Fruman DA: The PI3K-AKT-mTOR
signaling network in AML. Targeted Therapy of Acute Myeloid
Leukemia. Andreeff M: Springer; New York, NY: pp. 335–362. 2015
|
|
50
|
Fuliaş A, Ledeţi I, Vlase G, Vlase T,
Şoica C, Dehelean C, Oprean C, Bojin F, Şuta LM, Bercean V and
Avram S: Thermal degradation, kinetic analysis, and apoptosis
induction in human melanoma for oleanolic and ursolic acids. J
Therm Anal Calorim. 125:759–768. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Oprean C, Zambori C, Borcan F, Soica C,
Zupko I, Minorics R, Bojin F, Ambrus R, Muntean D, Danciu C, et al:
Anti-proliferative and antibacterial in vitro evaluation of the
polyurethane nanostructures incorporating pentacyclic triterpenes.
Pharm Biol. 54:2714–2722. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Trandafirescu C, Antal D, Soica C, Zupko
I, Minorics R, Ambrus R, Borcan F, Oprean C, Danciu C, Avram S, et
al: Cyclodextrin complexes of oleanolic and ursolic acid
physico-chemical and biological preliminary evaluation. Rev Chim.
65:1163–1167. 2014.
|
|
53
|
Pinzaru I, Trandafirescu C, Szabadai Z,
Mioc M, Ledeti I, Coricovac D, Ciurlea S, Ghiulai RM, Crainiceanu Z
and Simu G: Synthesis and biological evaluation of some pentacyclic
lupane triterpenoid esters. Rev Chim. 65:848–851. 2014.
|
|
54
|
wiseGEEK: What is cell cycle arrest?
http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-cell-cycle-arrest.htm.
Accessed Aug 15, 2017.
|
|
55
|
Cyclacel: Cell cycle in cancer. http://www.cyclacel.com/research_science_cell-cycle.shtml.
Accessed Aug 17, 2017.
|
|
56
|
Chakravarti B, Maurya R, Siddiqui JA, Bid
HK, Rajendran SM, Yadav PP and Konwar R: In vitro anti-breast
cancer activity of ethanolic extract of Wrightia tomentosa: Role of
pro-apoptotic effects of oleanolic acid and urosolic acid. J
Ethnopharmacol. 142:72–79. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Es-Saady D, Simon A, Jayat-Vignoles C,
Chulia AJ and Delage C: MCF-7 cell cycle arrested at G1 through
ursolic acid, and increased reduction of tetrazolium salts.
Anticancer Res. 16:481–486. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Park JH, Kwon H-Y, Sohn EJ, Kim KA, Kim B,
Jeong SJ, Song JH, Koo JS and Kim S-H: Inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin
signaling mediates ursolic acid-induced apoptosis in pC-3 prostate
cancer cells. Pharmacol Rep. 65:1366–1374. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Lawrence MB, Mcintire LV and Eskin SG:
Effect of flow on polymorphonuclear leukocyte/endothelial cell
adhesion. Blood. 70:1284–1290. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Mitchell MJ and King MR: Computational and
experimental models of cancer cell response to fluid shear stress.
Front Oncol. 3:442013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Bendas G and Borsig L: Cancer cell
adhesion and metastasis: selectins, integrins, and the inhibitory
potential of heparins. Int J Cell Biol. 2012:6767312012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Olivier LA and Truskey GA: A numerical
analysis of forces exerted by laminar flow on spreading cells in a
parallel plate flow chamber assay. Biotechnol Bioeng. 42:963–973.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Chen C, Zhang Q, Liu S, Parajuli KR, Qu Y,
Mei J, Chen Z, Zhang H, Khismatullin DB and You Z: IL-17 and
insulin/iGF1 enhance adhesion of prostate cancer cells to vascular
endothelial cells through CD44-VCAM-1 interaction. Prostate.
75:883–895. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Eibl RH and Benoit M: Molecular resolution
of cell adhesion forces. IEE Proc, Nanobiotechnol. 151:128–132.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Paschos KA, Canovas D and Bird NC: The
role of cell adhesion molecules in the progression of colorectal
cancer and the development of liver metastasis. Cell Signal.
21:665–674. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Zhang P, Goodrich C, Fu C and Dong C:
Melanoma upregulates ICAM-1 expression on endothelial cells through
engagement of tumor CD44 with endothelial E-selectin and activation
of a PKCα-p38-Sp-1 pathway. FASEB J. 28:4591–4609. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Nowak-Sliwinska P, Segura T and
Iruela-Arispe ML: The chicken chorioallantoic membrane model in
biology, medicine and bioengineering. Angiogenesis. 17:779–804.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Deryugina Ei and Quigley JP: Chick embryo
chorioallantoic membrane model systems to study and visualize human
tumor cell metastasis. Histochem Cell Biol. 130:1119–1130. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Cárdenas C, Quesada AR and Medina MA:
Effects of ursolic acid on different steps of the angiogenic
process. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 320:402–408. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Lin J, Chen Y, Wei L, Hong Z, Sferra TJ
and Peng J: Ursolic acid inhibits colorectal cancer angiogenesis
through suppression of multiple signaling pathways. Int J Oncol.
43:1666–1674. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Lin CC, Huang CY, Mong MC, Chan CY and Yin
MC: Antiangiogenic potential of three triterpenic acids in human
liver cancer cells. J Agric Food Chem. 59:755–762. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Sun JJ, Zhou XD, Liu YK, Tang ZY, Feng JX,
Zhou G, Xue Q and Chen J: Invasion and metastasis of liver cancer:
Expression of intercellular adhesion molecule 1. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 125:28–34. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Gho YS, Kim PN, Li HC, Elkin M and
Kleinman HK: Stimulation of tumor growth by human soluble
intercellular adhesion molecule-1. Cancer Res. 61:4253–4257.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Sohn KH, Lee HY, Chung HY, Young HS, Yi SY
and Kim KW: Anti-angiogenic activity of triterpene acids. Cancer
Lett. 94:213–218. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Kiran MS, Viji RI, Sameer Kumar VB and
Sudhakaran PR: Modulation of angiogenic factors by ursolic acid.
Biochem Biophys res Commun. 371:556–560. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|