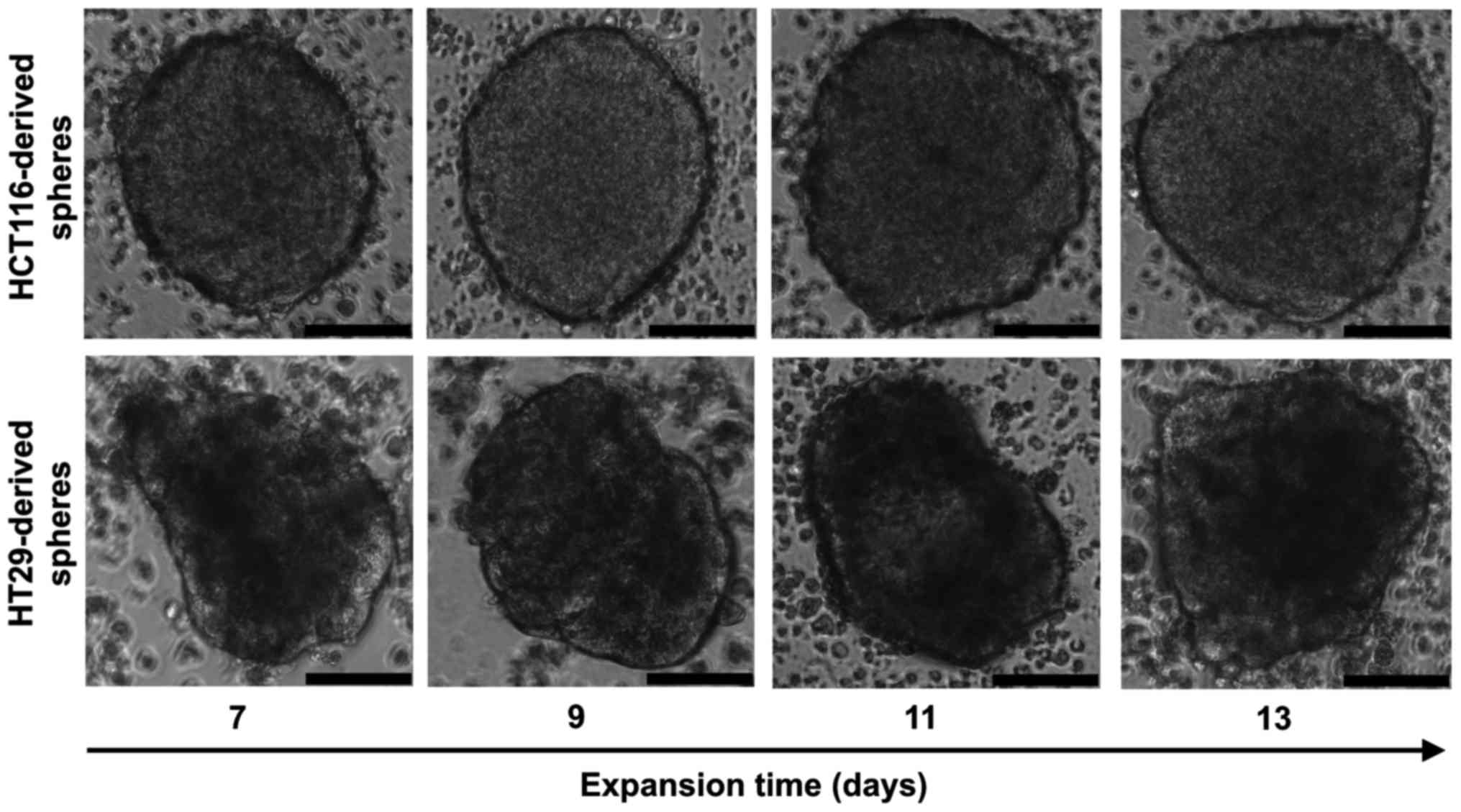
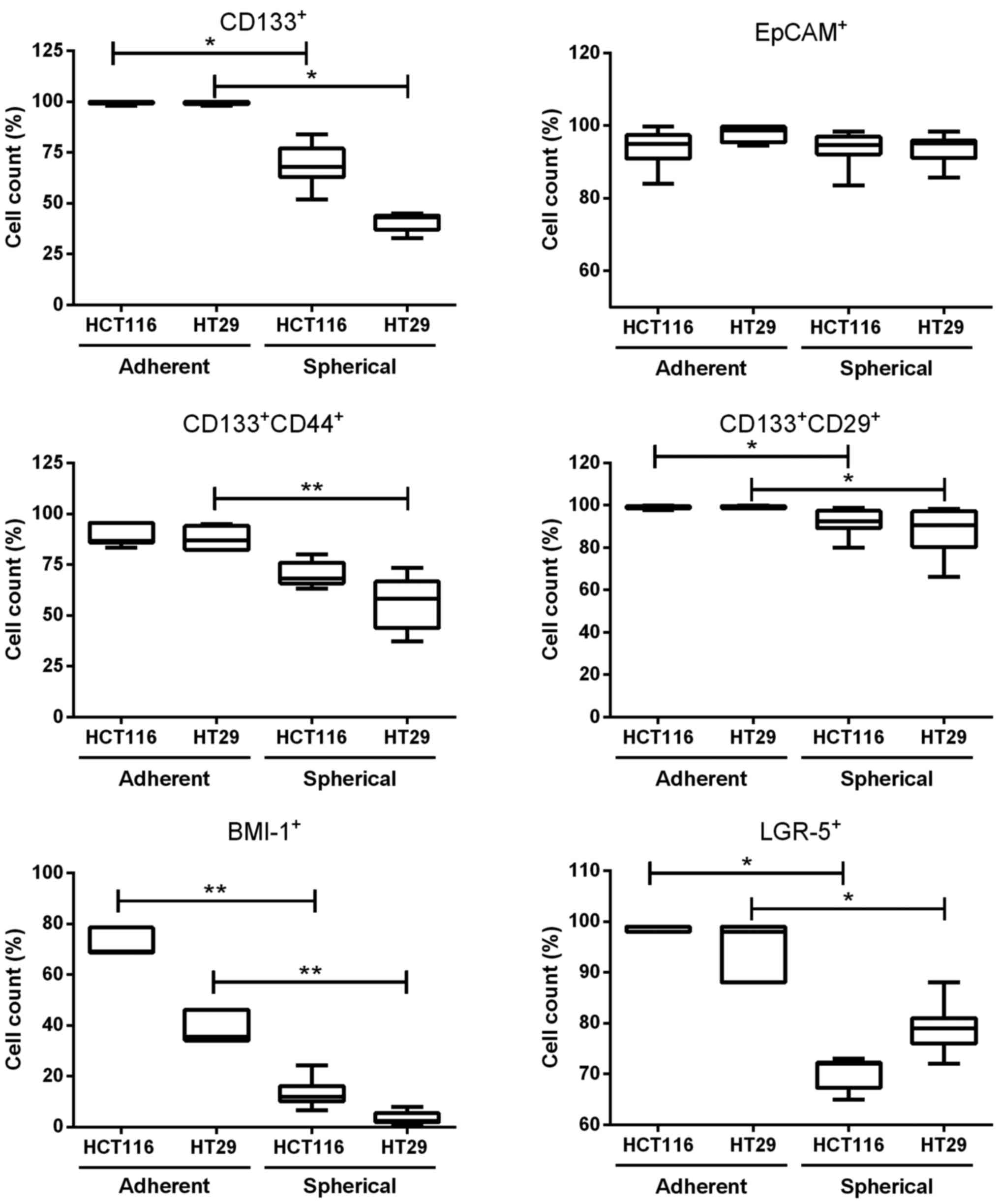
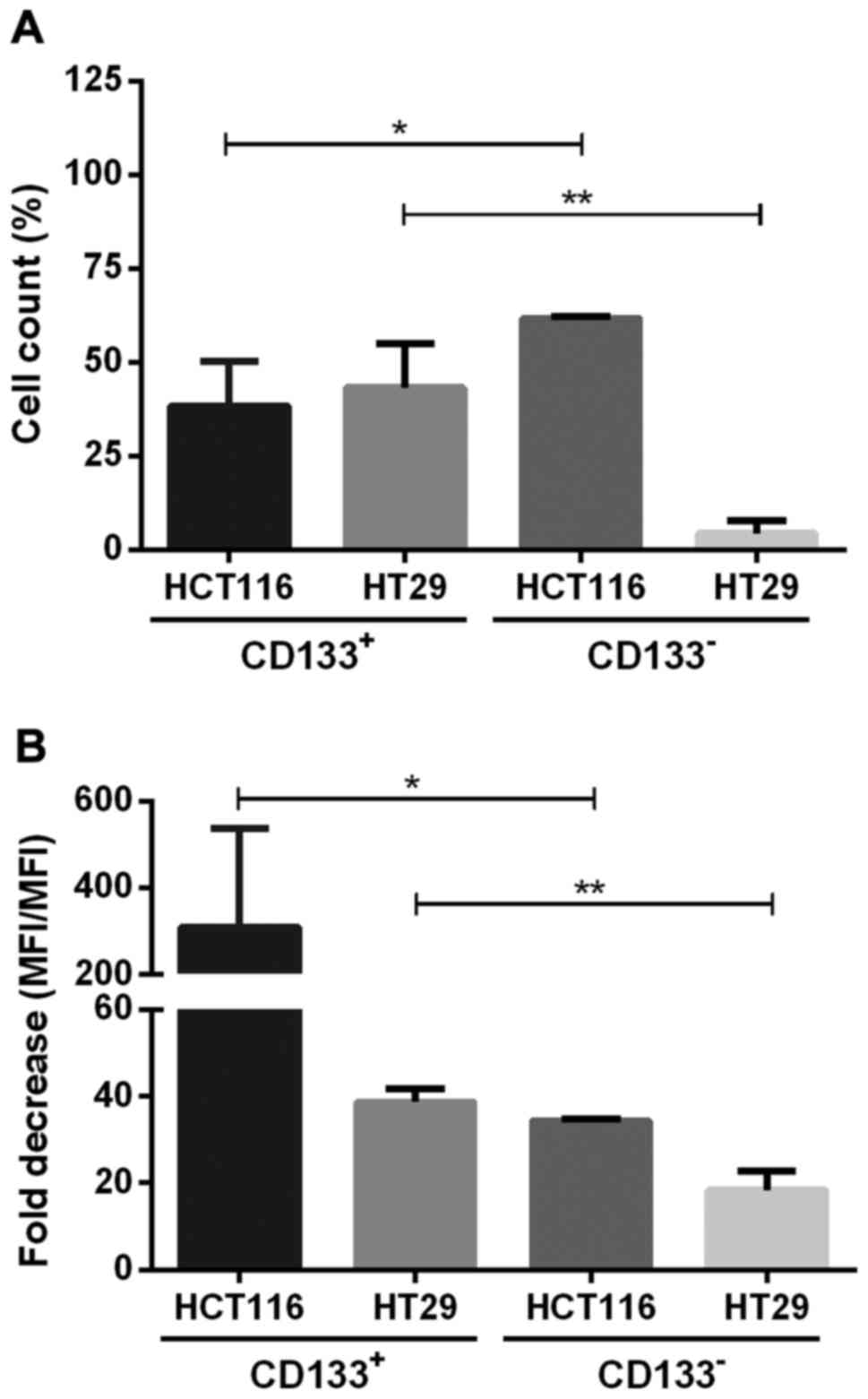
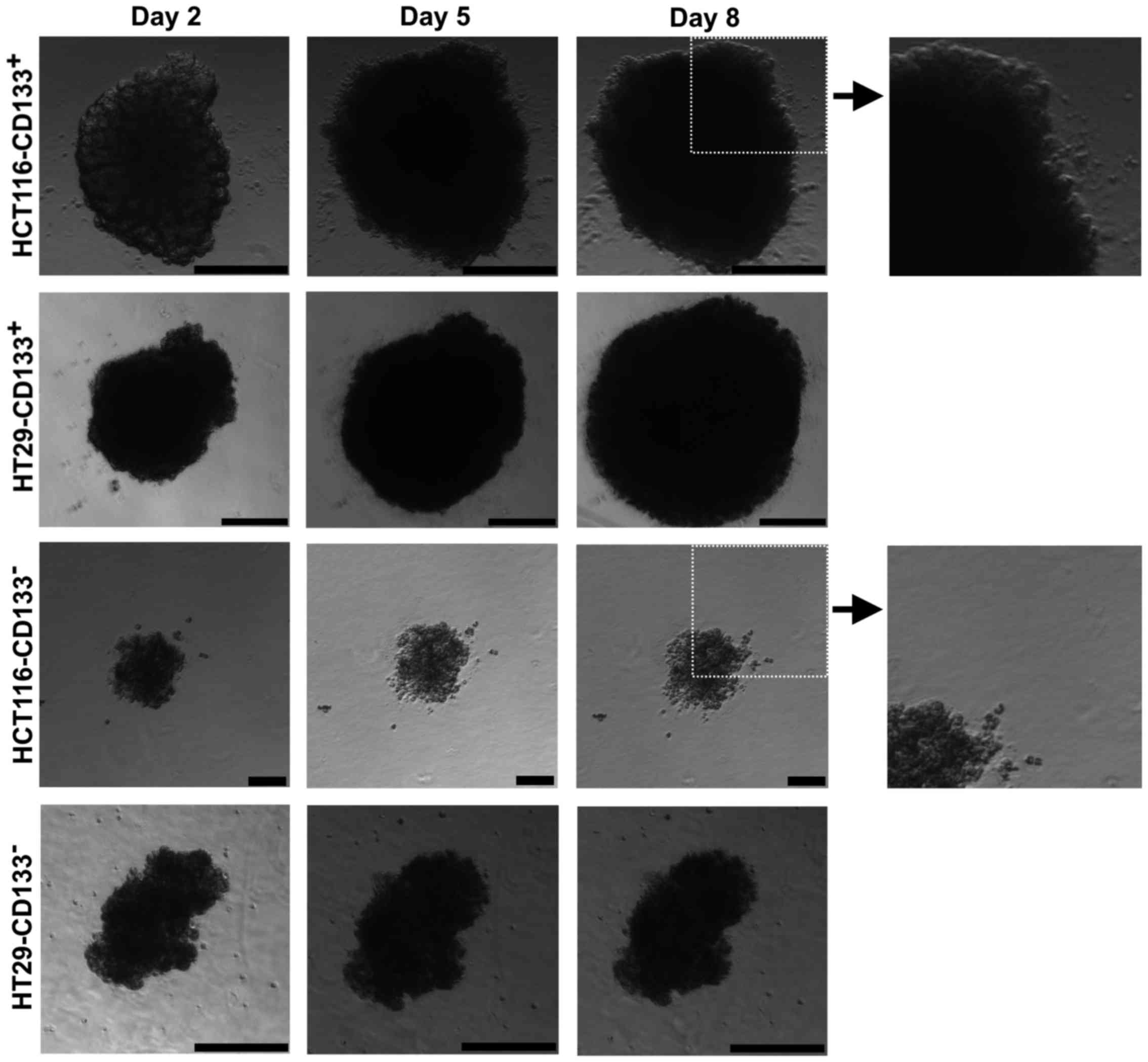
|
1
|
Manhas J, Bhattacharya A, Agrawal SK,
Gupta B, Das P, Deo SV, Pal S and Sen S: Characterization of cancer
stem cells from different grades of human colorectal cancer. Tumour
Biol. 37:14069–14081. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zeuner A, Todaro M, Stassi G and De Maria
R: Colorectal cancer stem cells: From the crypt to the clinic. Cell
Stem Cell. 15:692–705. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Farhana L, Nangia-Makker P, Arbit E,
Shango K, Sarkar S, Mahmud H, Hadden T, YU Y and Majumdar AP: Bile
acid: A potential inducer of colon cancer stem cells. Stem Cell Res
Ther. 7:1812016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Oshima N, yamada Y, Nagayama S, Kawada K,
Hasegawa S, Okabe H, Sakai Y and Aoi T: induction of cancer stem
cell properties in colon cancer cells by defined factors. PLoS One.
9:e1017352014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pan T, Xu J and Zhu Y: Self-renewal
molecular mechanisms of colorectal cancer stem cells. Int J Mol
Med. 39:9–20. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Yang G, Quan Y, Wang W, Fu Q, Wu J, Mei T,
Li J, Tang Y, Luo C, Ouyang Q, et al: Dynamic equilibrium between
cancer stem cells and non-stem cancer cells in human SW620 and
MCF-7 cancer cell populations. Br J Cancer. 106:1512–1519. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lapidot T, Sirard C, Vormoor J, Murdoch B,
Hoang T, Caceres-Cortes J, Minden M, Paterson B, Caligiuri MA and
Dick JE: A cell initiating human acute myeloid leukaemia after
transplantation into SCID mice. Nature. 367:645–648. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Al-Hajj M, Wicha MS, Benito-Hernandez A,
Morrison SJ and Clarke MF: Prospective identification of
tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:3983–3988. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Charafe-Jauffret E, Ginestier C, Iovino F,
Wicinski J, Cervera N, Finetti P, Hur MH, Diebel ME, Monville F,
Dutcher J, et al: Breast cancer cell lines contain functional
cancer stem cells with metastatic capacity and a distinct molecular
signature. Cancer Res. 69:1302–1313. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hermann PC, Huber SL, Herrler T, Aicher A,
Ellwart JW, Guba M, Bruns CJ and Heeschen C: Distinct populations
of cancer stem cells determine tumor growth and metastatic activity
in human pancreatic cancer. Cell Stem Cell. 1:313–323. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Li C, Lee CJ and Simeone DM:
identification of human pancreatic cancer stem cells. Methods Mol
Biol. 568:161–173. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fang D, Nguyen TK, Leishear K, Finko R,
Kulp AN, Hotz S, Van Belle PA, Xu X, Elder DE and Herlyn M: A
tumorigenic subpopulation with stem cell properties in melanomas.
Cancer Res. 65:9328–9337. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kim CF, Jackson EL, Woolfenden AE,
Lawrence S, Babar I, Vogel S, Crowley D, Bronson RT and Jacks T:
Identification of bronchioalveolar stem cells in normal lung and
lung cancer. Cell. 121:823–835. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu G, Yuan X, Zeng Z, Tunici P, NG H,
Abdulkadir IR, Lu L, Irvin D, Black KL and Yu JS: Analysis of gene
expression and chemoresistance of CD133+ cancer stem
cells in glioblastoma. Mol Cancer. 5:672006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Gilbertson RJ and Rich JN: Making a
tumour's bed: Glioblastoma stem cells and the vascular niche. Nat
Rev Cancer. 7:733–736. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Collins AT, Berry PA, Hyde C, Stower MJ
and Maitland NJ: prospective identification of tumorigenic prostate
cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 65:10946–10951. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ricci-Vitiani L, Lombardi DG, Pilozzi E,
Biffoni M, Todaro M, Peschle C and De Maria R: Identification and
expansion of human colon-cancer-initiating cells. Nature.
445:111–115. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
O'Brien CA, Pollett A, Gallinger S and
Dick JE: A human colon cancer cell capable of initiating tumour
growth in immunodeficient mice. Nature. 445:106–110. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Singh SK, Clarke ID, Terasaki M, Bonn VE,
Hawkins C, Squire J and Dirks PB: identification of a cancer stem
cell in human brain tumors. Cancer Res. 63:5821–5828.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Singh SK, Hawkins C, Clarke ID, Squire JA,
Bayani J, Hide T, Henkelman RM, Cusimano MD and Dirks PB:
identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature.
432:396–401. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dragu DL, Necula LG, Bleotu C, Diaconu CC
and Chivu-Economescu M: Therapies targeting cancer stem cells:
Current trends and future challenges. World J Stem Cells.
7:1185–1201. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen K, Huang YH and Chen JL:
Understanding and targeting cancer stem cells: Therapeutic
implications and challenges. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 34:732–740. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Touil Y, Igoudjil W, Corvaisier M, Dessein
AF, Vandomme J, Monté D, Stechly L, Skrypek N, Langlois C, Grard G,
et al: Colon cancer cells escape 5FU chemotherapy-induced cell
death by entering stemness and quiescence associated with the
c-yes/ YAP axis. Clin Cancer Res. 20:837–846. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Islam F, Gopalan V, Smith RA and Lam AK:
Translational potential of cancer stem cells: A review of the
detection of cancer stem cells and their roles in cancer recurrence
and cancer treatment. Exp Cell Res. 335:135–147. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fang DD, Kim YJ, Lee CN, Aggarwal S,
McKinnon K, Mesmer D, Norton J, Birse CE, He T, Ruben SM, et al:
Expansion of CD133+ colon cancer cultures retaining stem
cell properties to enable cancer stem cell target discovery. Br J
Cancer. 102:1265–1275. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li Z: CD133: A stem cell biomarker and
beyond. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2:172013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shmelkov SV, Butler JM, Hooper AT, Hormigo
A, Kushner J, Milde T, St Clair R, Baljevic M, White I, Jin DK, et
al: CD133 expression is not restricted to stem cells, and both
CD133+ and CD133− metastatic colon cancer
cells initiate tumors. J Clin Invest. 118:2111–2120.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Weiswald LB, Bellet D and Dangles-Marie V:
Spherical cancer models in tumor biology. Neoplasia. 17:1–15. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Qureshi-Baig K, Ullmann P, Rodriguez F,
Frasquilho S, Nazarov PV, Haan S and Letellier E: What do we learn
from spheroidculture systems? Insights from tumorspheres derived
from primary colon cancer tissue. PLoS One. 11:e01460522016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Collura A, Marisa L, Trojan D, Buhard O,
Lagrange A, Saget A, Bombled M, Méchighel P, Ayadi M, Muleris M, et
al: Extensive characterization of sphere models established from
colorectal cancer cell lines. Cell Mol Life Sci. 70:729–742. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Weiswald LB, Richon S, Massonnet G,
Guinebretière JM, Vacher S, Laurendeau I, Cottu P, Marangoni E,
Nemati F, Validire P, et al: A short-term colorectal cancer sphere
culture as a relevant tool for human cancer biology investigation.
Br J Cancer. 108:1720–1731. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chandrasekaran S, Marshall JR, Messing JA,
Hsu JW and King MR: TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in breast cancer cells
cultured as 3D spheroids. PLoS One. 9:e1114872014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Endo H, Okami J, Okuyama H, Kumagai T,
Uchida J, Kondo J, Takehara T, Nishizawa Y, Imamura F, Higashiyama
M, et al: Spheroid culture of primary lung cancer cells with
neuregulin 1/Her3 pathway activation. J Thorac Oncol. 8:131–139.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tong JG, Valdes YR, Barrett JW, Bell JC,
Stojdl D, McFadden G, McCart JA, DiMattia GE and Shepherd TG:
Evidence for differential viral oncolytic efficacy in an in vitro
model of epithelial ovarian cancer metastasis. Mol Ther Oncolytics.
2:150132015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hirschhaeuser F, Menne H, Dittfeld C, West
J, Mueller-Klieser W and Kunz-Schughart LA: Multicellular tumor
spheroids: An underestimated tool is catching up again. J
Biotechnol. 148:3–15. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nath S and Devi GR: Three-dimensional
culture systems in cancer research: Focus on tumor spheroid model.
Pharmacol Ther. 163:94–108. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lee SH, Hong JH, Park HK, Park JS, Kim BK,
Lee JY, Jeong JY, Yoon GS, Inoue M, Choi GS, et al: Colorectal
cancer-derived tumor spheroids retain the characteristics of
original tumors. Cancer Lett. 367:34–42. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Stankevicius V, Kunigenas L, Stankunas E,
Kuodyte K, Strainiene E, Cicenas J, Samalavicius NE and Suziedelis
K: The expression of cancer stem cell markers in human colorectal
carcinoma cells in a microenvironment dependent manner. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 484:726–733. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Vermeulen L, Todaro M, de Sousa Mello F,
Sprick MR, Kemper K, perez Alea M, Richel DJ, Stassi G and Medema
JP: Single-cell cloning of colon cancer stem cells reveals a
multi-lineage differentiation capacity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:13427–13432. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Calvet CY, André FM and Mir LM: The
culture of cancer cell lines as tumorspheres does not
systematically result in cancer stem cell enrichment. PLoS One.
9:e896442014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Botchkina IL, Rowehl RA, Rivadeneira DE,
Karpeh MS Jr, Crawford H, Dufour A, Ju J, Wang Y, Leyfman Y and
Botchkina GI: Phenotypic subpopulations of metastatic colon cancer
stem cells: Genomic analysis. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 6:19–29.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Shaheen S, Ahmed M, Lorenzi F and Nateri
AS: Spheroid-formation (Colonosphere) assay for in vitro sssessment
and expansion of stem cells in colon cancer. Stem Cell Rev.
12:492–499. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yeung TM, Gandhi SC, Wilding JL, Muschel R
and Bodmer WF: Cancer stem cells from colorectal cancer-derived
cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:3722–3727. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Dittfeld C, Dietrich A, Peickert S, Hering
S, Baumann M, Grade M, Ried T and Kunz-Schughart LA: CD133
expression is not selective for tumor-initiating or radioresistant
cell popu-lations in the CrC cell lines HCT-116. Radiother Oncol.
92:353–361. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Huang R, Wang G, Song Y, Tang Q, You Q,
Liu Z, Chen Y, Zhang Q, Li J, Muhammand S, et al: Colorectal cancer
stem cell and chemoresistant colorectal cancer cell phenotypes and
increased sensitivity to Notch pathway inhibitor. Mol Med Rep.
12:2417–2424. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Fan X, Ouyang N, Teng H and Yao H:
isolation and characterization of spheroid cells from the HT29
colon cancer cell line. Int J Colorectal Dis. 26:1279–1285. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Pang C, Xie J, Guo J, Manning HC, Gore JC
and Guo N: Evaluation of CD44 and CD133 as cancer stem cell markers
for colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 28:1301–1308. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Chan CW, Wong NA, Liu Y, Bicknell D,
Turley H, Hollins L, Miller CJ, Wilding JL and Bodmer WF:
Gastrointestinal differentiation marker Cytokeratin 20 is regulated
by homeobox gene CDX1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:1936–1941. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ning Y, Hanna DL, Zhang W, Mendez A, Yang
D, El-Khoueiry R, Matsusaka S, Sunakawa Y, Stremitzer S, Parekh A,
et al: Cytokeratin-20 and survivin-expressing circulating tumor
cells predict survival in metastatic colorectal cancer patients by
a combined immunomagnetic qRT-PCR approach. Mol Cancer Ther.
14:2401–2408. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Imai Y, Yamagishi H, Fukuda K, Okamura T,
Ono Y, Ban S, Inoue T and Ueda Y: Expression of cytokeratin 20
indicates invasive histological phenotype in poorly differentiated
colorectal adenocarcinoma. Anticancer Res. 34:159–167.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yanai H, Atsumi N, Tanaka T, nakamura N,
Komai Y, Omachi T, Tanaka K, ishigaki K, Saiga K, Ohsugi H, et al:
Intestinal cancer stem cells marked by Bmi1 or Lgr5 expression
contribute to tumor propagation via clonal expansion. Sci Rep.
7:418382017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Shimokawa M, Ohta Y, Nishikori S, Matano
M, Takano A, Fujii M, Date S, Sugimoto S, Kanai T and Sato T:
visualization and targeting of LGR5+ human colon cancer
stem cells. Nature. 545:187–192. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Hirsch D, Barker N, Mcneil N, Hu Y, Camps
J, McKinnon K, Clevers H, ried T and Gaiser T: LGr5 positivity
defines stem-like cells in colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis.
35:849–858. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
54
|
de Sousa E, Melo F, Kurtova AV, Harnoss
JM, Kljavin N, Hoeck JD, Hung J, Anderson je, Storm EE, Modrusan Z,
Koeppen H, et al: A distinct role for LGR5+ stem cells in primary
and metastatic colon cancer. Nature. 543:676–680. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Walker F, Zhang HH, Odorizzi A and Burgess
AW: LGR5 is a negative regulator of tumourigenicity, antagonizes
Wnt signal-ling and regulates cell adhesion in colorectal cancer
cell lines. PLoS One. 6:e227332011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Parvathi MV, Murthy PB, Vennila M and
Suresh BV: Regulation of BMI1 Polycomb gene expression in
histological grades of invasive ductal breast carcinomas and its
correlation with hormone receptor status. Tumour Biol.
34:3807–3815. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Peng HX, Liu XD, Luo ZY, Zhang XH, Luo XQ,
Chen X, Jiang H and Xu L: Upregulation of the proto-oncogene bmi-1
predicts a poor prognosis in pediatric acute lymphoblastic
leukemia. BMC Cancer. 17:762017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Li X, Zheng X, Xu B, Zhang D, Xu Y, Xie Q,
Hu W, Zheng Z, Shao Y, Wu J, et al: Lower Bmi-1 expression may
predict longer survival of colon cancer patients. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 39:2421–2426. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Siddique HR and Saleem M: role of bMi1, a
stem cell factor, in cancer recurrence and chemoresistance:
Preclinical and clinical evidences. Stem Cells. 30:372–378. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Yan KS, Chia LA, Li X, Ootani A, Su J, Lee
JY, Su N, Luo Y, Heilshorn SC, Amieva MR, et al: The intestinal
stem cell markers Bmi1 and Lgr5 identify two functionally distinct
populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:466–471. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
61
|
Charafe-Jauffret E, Monville F, Ginestier
C, Dontu G, Birnbaum D and Wicha MS: Cancer stem cells in breast:
Current opinion and future challenges. Pathobiology. 75:75–84.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Kim SY, Hong SH, Basse PH, WU C, Bartlett
DL, Kwon YT and Lee YJ: Cancer stem cells protect non-stem cells
from anoikis: bystander effects. J Cell Biochem. 117:2289–2301.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Sato R, Semba T, Saya H and Arima Y:
Concise review: Stem cells and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
cancer: Biological implications and therapeutic targets. Stem
Cells. 34:1997–2007. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Merlos-Suárez A, Barriga FM, Jung P,
Iglesias M, Céspedes MV, Rossell D, Sevillano M, Hernando-Momblona
X, da Silva-Diz V, Muñoz P, et al: The intestinal stem cell
signature identifies colorectal cancer stem cells and predicts
disease relapse. Cell Stem Cell. 8:511–524. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Albini A and Noonan DM: The
'chemoinvasion' assay, 25 years and still going strong: The use of
reconstituted basement membranes to study cell invasion and
angiogenesis. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 22:677–689. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Benton G, Arnaoutova I, George J, Kleinman
HK and Koblinski J: Matrigel: From discovery and ECM mimicry to
assays and models for cancer research. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 79–80.
3–18. 2014.
|
|
67
|
Brattain MG, brattain DE, Fine WD, Khaled
FM, Marks ME, Kimball PM, Arcolano LA and Danbury BH: initiation
and characterization of cultures of human colonic carcinoma with
different biological characteristics utilizing feeder layers of
confluent fibroblasts. Oncodev Biol Med. 2:355–366. 1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Brattain MG, Fine WD, Khaled FM, Thompson
J and brattain DE: Heterogeneity of malignant cells from a human
colonic carcinoma. Cancer Res. 41:1751–1756. 1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Fogh J and Trempe G: New human tumor cell
lines. Human Tumor Cells in Vitro. Fogh J: Springer; US, Boston,
MA: pp. 115–159. 1975, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Ahmed D, Eide PW, Eilertsen IA, Danielsen
SA, Eknæs M, Hektoen M, Lind GE and Lothe RA: epigenetic and
genetic features of 24 colon cancer cell lines. Oncogenesis.
2:e712013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Aksamitiene E, Kiyatkin A and Kholodenko
BN: Cross-talk between mitogenic RAS/MAPK and survival PI3K/Akt
pathways: A fine balance. Biochem Soc Trans. 40:139–146. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Zenonos K and Kyprianou K: RAS signaling
pathways, mutations and their role in colorectal cancer. World J
Gastrointest Oncol. 5:97–101. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Bazan V, Migliavacca M, Zanna I, Tubiolo
C, Grassi N, Latteri MA, La Farina M, Albanese I, Dardanoni G,
Salerno S, et al: Specific codon 13 K-ras mutations are predictive
of clinical outcome in colorectal cancer patients, whereas codon 12
K-ras mutations are associated with mucinous histotype. Ann Oncol.
13:1438–1446. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Knickelbein K and Zhang L: Mutant KRAS as
a critical deter-minant of the therapeutic response of colorectal
cancer. Genes Dis. 2:4–12. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Raats DA, Frenkel N, van Schelven SJ,
Rinkes IH, Laoukili J and Kranenburg O: CD95 ligand induces
senescence in mismatch repair-deficient human colon cancer via
chronic caspase-medi-ated induction of DNA damage. Cell Death Dis.
8:e26692017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Szarynska M, Olejniczak A, Wierzbicki P,
Kobiela J, Laski D, Sledzinski Z, Adrych K, Guzek M and Kmiec Z:
Fasr and FasL in colorectal cancer. Int J Oncol. 51:975–986.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Therkildsen C, Bergmann TK,
Henrichsen-Schnack T, Ladelund S and Nilbert M: The predictive
value of KRAS, NRAS, BRAF, PIK3CA and PTEN for anti-EGFR treatment
in metastatic colorectal cancer: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Acta Oncol. 53:852–864. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|