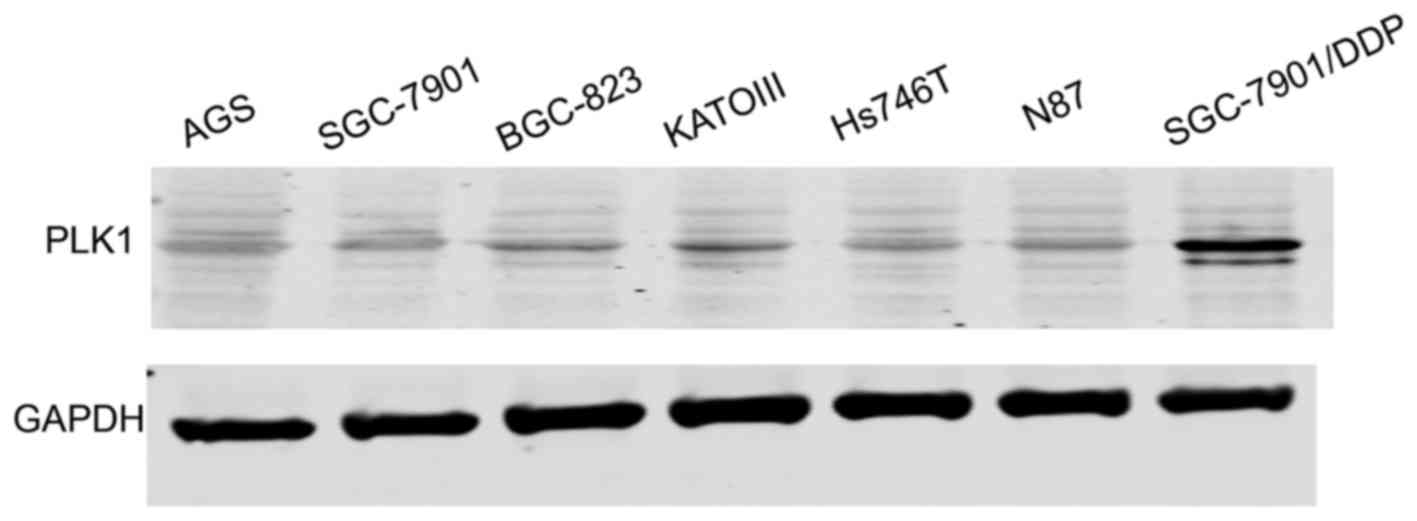
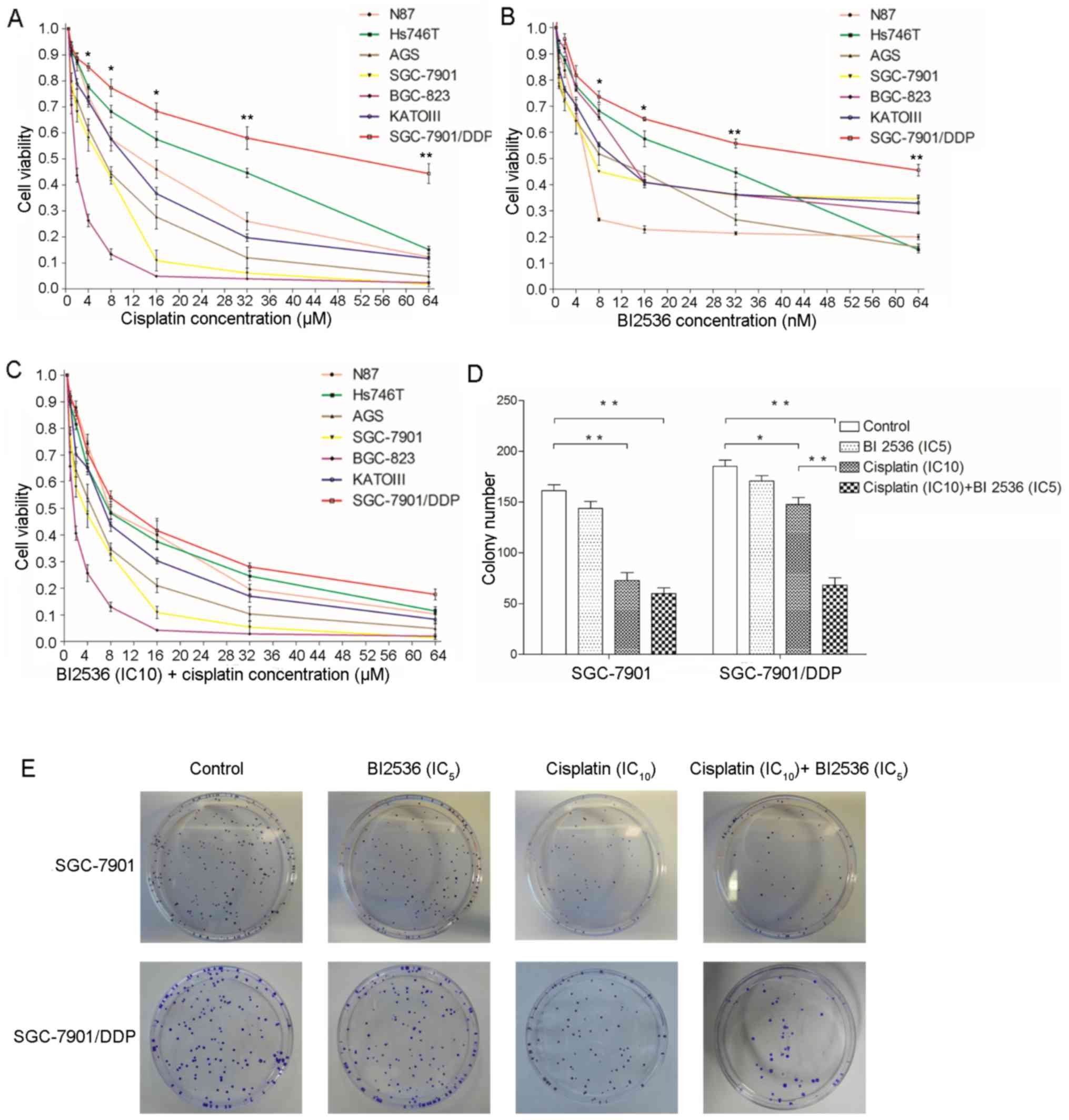
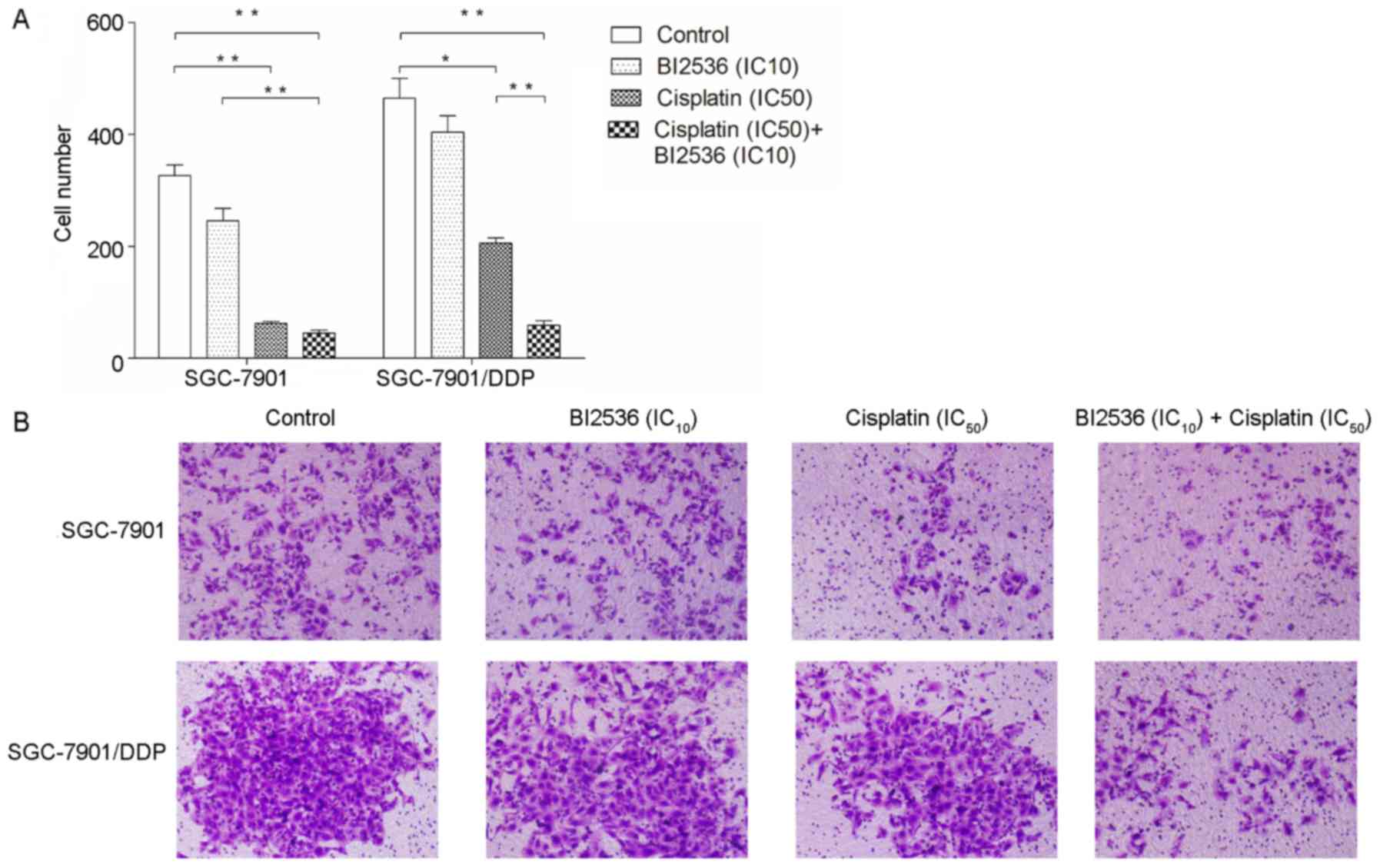
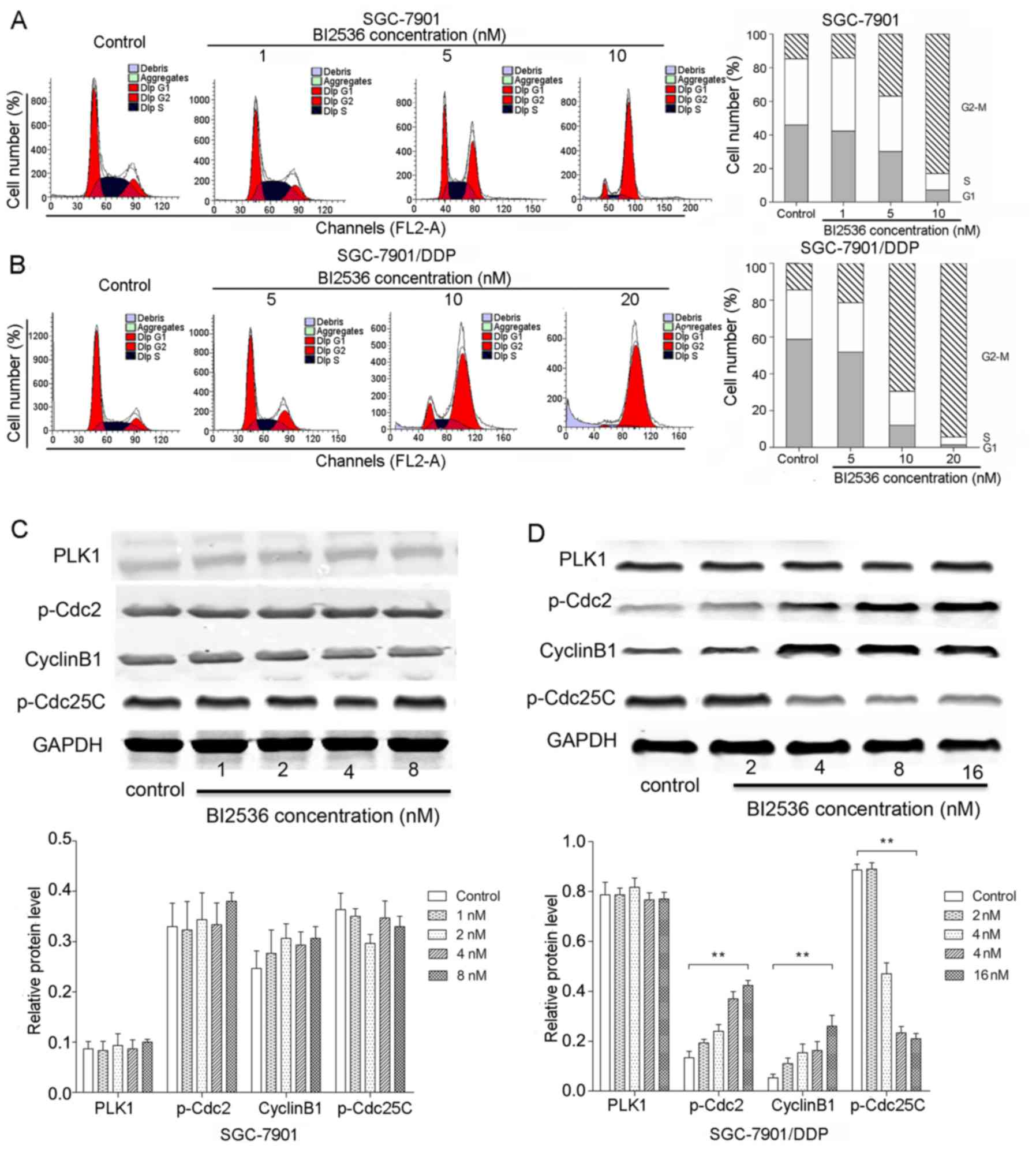
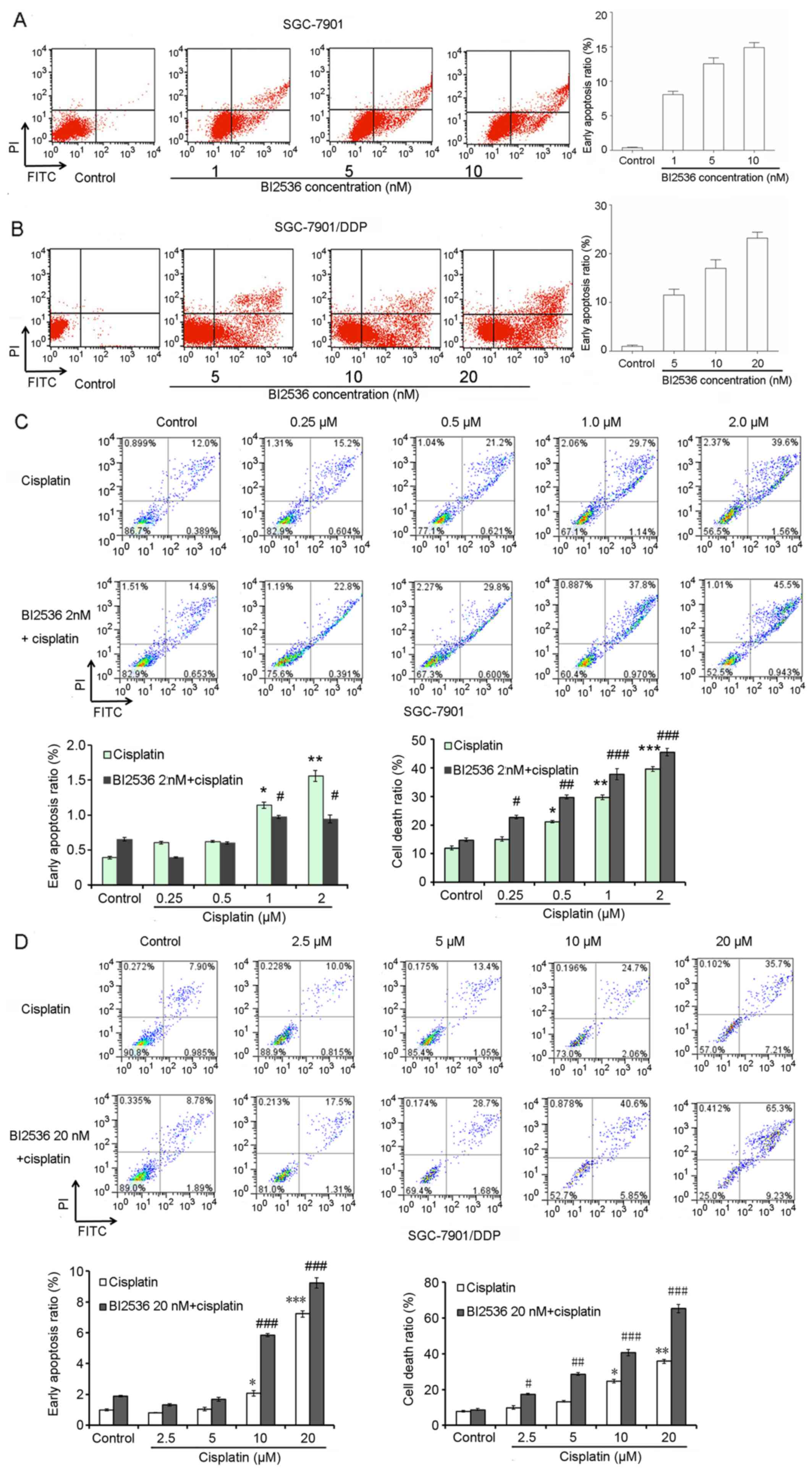
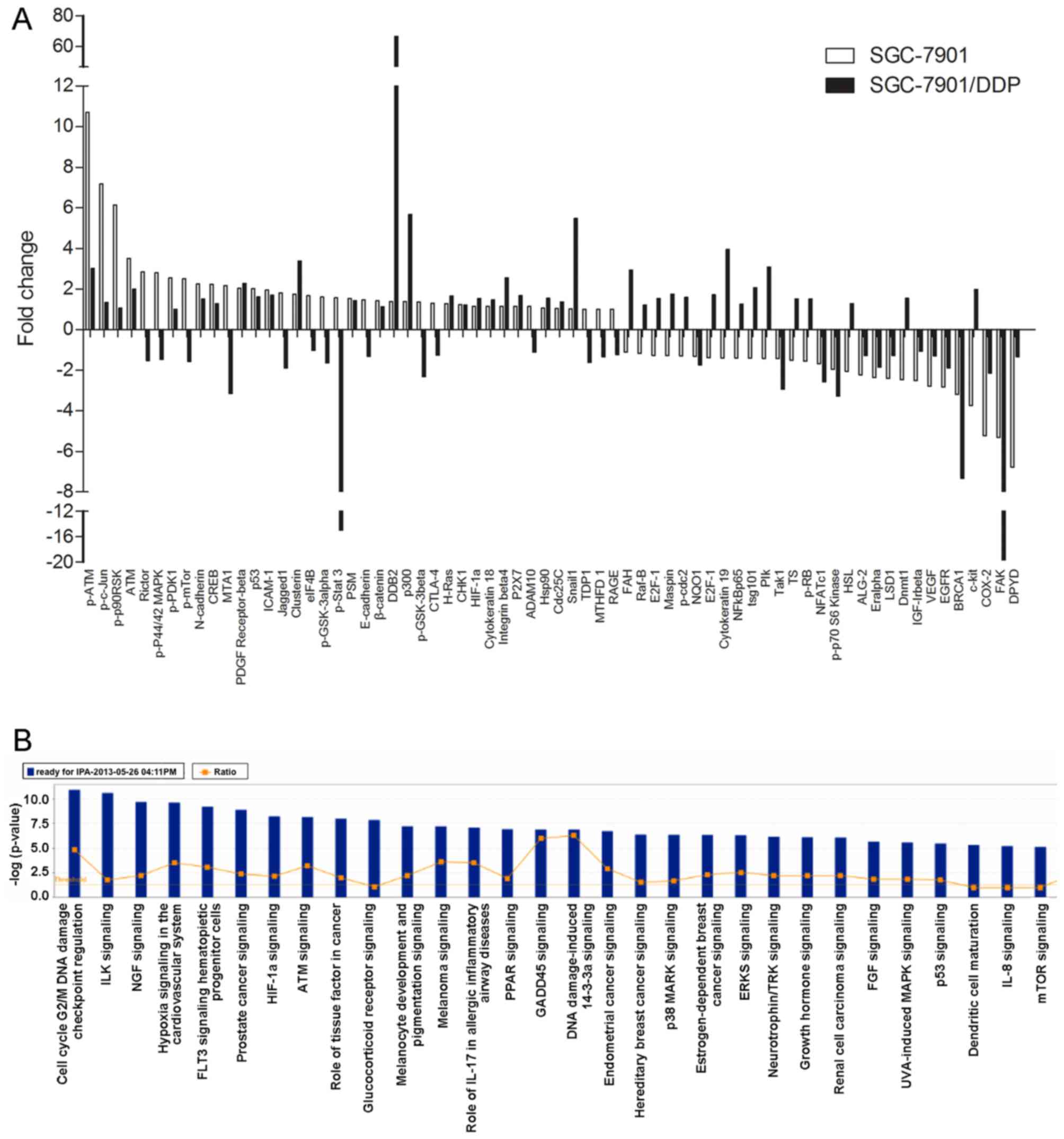
|
1
|
de Martel C, Forman D and Plummer M:
Gastric cancer: Epidemiology and risk factors. Gastroenterol Clin
North Am. 42:219–240. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Daniyal M, Ahmad S, Ahmad M, Asif HM,
Akram M, Ur Rehman S and Sultana S: Risk factors and epidemiology
of gastric cancer in Pakistan. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
16:4821–4824. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Orditura M, Galizia G, Sforza V,
Gambardella V, Fabozzi A, Laterza MM, Andreozzi F, Ventriglia J,
Savastano B, Mabilia A, et al: Treatment of gastric cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:1635–1649. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yasui W, Oue N, Ito R, Kuraoka K and
Nakayama H: Search for new biomarkers of gastric cancer through
serial analysis of gene expression and its clinical implications.
Cancer Sci. 95:385–392. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lordick F, Kang YK, Chung HC, Salman P, Oh
SC, Bodoky G, Kurteva G, Volovat C, Moiseyenko VM, Gorbunova V, et
al: Arbeitsgemeinschaft Internistische Onkologie and EXPAND
Investigators: Capecitabine and cisplatin with or without cetuximab
for patients with previously untreated advanced gastric cancer
(EXPAND): A randomised, open-label phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol.
14:490–499. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Köhne CH, Wils JA and Wilke HJ:
Developments in the treatment of gastric cancer in Europe. Oncology
(Williston Park). 14(Suppl 14): 22–25. 2000.
|
|
7
|
Catalano V, Labianca R, Beretta GD, Gatta
G, de Braud F and Van Cutsem E: Gastric cancer. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 71:127–164. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tong W, Ye F, He L, Cui L, Cui M, Hu Y, Li
W, Jiang J, Zhang DY and Suo J: Serum biomarker panels for
diagnosis of gastric cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 9:2455–2463.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ngeow J, Tan IB and Choo SP: Targeted
therapies in the treatment of gastric cancer. Asia Pac J Clin
Oncol. 7:224–235. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Takai N, Hamanaka R, Yoshimatsu J and
Miyakawa I: Polo-like kinases (Plks) and cancer. Oncogene.
24:287–291. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chopra P, Sethi G, Dastidar SG and Ray A:
Polo-like kinase inhibitors: An emerging opportunity for cancer
therapeutics. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 19:27–43. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Jang YJ, Kim YS and Kim WH: Oncogenic
effect of Polo-like kinase 1 expression in human gastric
carcinomas. Int J Oncol. 29:589–594. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zha X, Huang L, Yang M, Jingmin OU, Chen D
and Fei Z: Study on folate deficiency and Polo-like kinase-1
(PLK-1) siRNA in synergistically inhibiting the growth of gastric
carcinoma cell lines. Modern J Integrated Trad Chin Western Med.
24:917–920. 2015.
|
|
14
|
Otsu H, Iimori M, Ando K, Saeki H, Aishima
S, Oda Y, Morita M, Matsuo K, Kitao H, Oki E, et al: Gastric cancer
patients with high PLK1 expression and DNA aneuploidy correlate
with poor prognosis. Oncology. 91:31–40. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Weiss L and Efferth T: Polo-like kinase 1
as target for cancer therapy. Exp Hematol Oncol. 1:382012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cholewa BD, Liu X and Ahmad N: The role of
polo-like kinase 1 in carcinogenesis: Cause or consequence. Cancer
Res. 73:6848–6855. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mross K, Frost A, Steinbild S, Hedbom S,
Rentschler J, Kaiser R, Rouyrre N, Trommeshauser D, Hoesl CE and
Munzert G: Phase I dose escalation and pharmacokinetic study of BI
2536, a novel Polo-like kinase 1 inhibitor, in patients with
advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 26:5511–5517. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Steegmaier M, Hoffmann M, Baum A, Lénárt
P, Petronczki M, Krssák M, Gürtler U, Garin-Chesa P, Lieb S, Quant
J, et al: BI 2536, a potent and selective inhibitor of polo-like
kinase 1, inhibits tumor growth in vivo. Curr Biol. 17:316–322.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lénárt P, Petronczki M, Steegmaier M, Di
Fiore B, Lipp JJ, Hoffmann M, Rettig WJ, Kraut N and Peters JM: The
small-molecule inhibitor BI 2536 reveals novel insights into
mitotic roles of polo-like kinase 1. Curr Biol. 17:304–315. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chou T and Martin N: CompuSyn for drug
combinations: PC software and user's guide: A computer program for
quantitation of synergism and antagonism in drug combinations, and
the determination of IC50 and ED and LD NJ, 50 50
values. ComboSyn, Paramus. 2005.
|
|
21
|
Pace A, Savarese A, Picardo M, Maresca V,
Pacetti U, Del Monte G, Biroccio A, Leonetti C, Jandolo B, Cognetti
F, et al: Neuroprotective effect of vitamin E supplementation in
patients treated with cisplatin chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol.
21:927–931. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kawabe T: Kawabe. Mol Cancer Ther.
3:513–519. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Anderson HJ, Andersen RJ and Roberge M:
Inhibitors of the G2 DNA damage checkpoint and their potential for
cancer therapy. Prog Cell Cycle Res. 5:423–430. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Smits VA, Klompmaker R, Arnaud L, Rijksen
G, Nigg EA and Medema RH: Polo-like kinase-1 is a target of the DNA
damage checkpoint. Nat Cell Biol. 2:672–676. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
van Vugt MA, Smits VA, Klompmaker R and
Medema RH: Inhibition of Polo-like kinase-1 by DNA damage occurs in
an ATM- or ATR-dependent fashion. J Biol Chem. 276:41656–41660.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
van Vugt MA and Medema RH: Getting in and
out of mitosis with Polo-like kinase-1. Oncogene. 24:2844–2859.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim SA, Kwon SM, Yoon JH and Ahn SG: The
antitumor effect of PLK1 and HSF1 double knockdown on human oral
carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 36:867–872. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jimeno A, Rubio-Viqueira B, Rajeshkumar V,
Chan A, Solomon A and Hidalgo M: A fine-needle aspirate-based
vulnerability assay identifies polo-like kinase 1 as a mediator of
gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer Ther.
9:311–318. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wong N and Khan M: Abstract 4915: High
degree of G2/M arrest induced by Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1)
inhibition is associated with radiosensitization. Cancer Res.
74:49152014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Liu YF, Chen YJ and Chen CL: MS275
synergistically enhances the growth inhibitory effects of BI2536 in
non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Pharm Biotechnol. 18:308–312.
2011.
|
|
31
|
Gleixner KV, Ferenc V, Gruze A, Kneidinger
M, Baumgartner C, Mayerhofer M, et al: The Plk-1 Inhibitor BI 2536
Counteracts Proliferation and Viability of CML Cells and Synergizes
with Imatinib and Nilotinib (AMN107) in Producing Growth
Inhibition. Blood. 110:317A2007.
|
|
32
|
Mao J, Fan S, Ma W, Fan P, Wang B, Zhang
J, Wang H, Tang B, Zhang Q, Yu X, et al: Roles of Wnt/β-catenin
signaling in the gastric cancer stem cells proliferation and
salinomycin treatment. Cell Death Dis. 5:e10392014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Shrivastava S, Kumar P, Jeengar MK and
Naidu VG: T3038 - Inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin pathway by
niclosamide: A therapeutic target for gastric cancer. National
Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research (NIPER).
2014.
|
|
34
|
Nam HJ, Kim S, Lee MW, Lee BS, Hara T,
Saya H, Cho H and Lee JH: The ERK-RSK1 activation by growth factors
at G2 phase delays cell cycle progression and reduces mitotic
aberrations. Cell Signal. 20:1349–1358. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li R, Chen DF, Zhou R, Jia SN, Yang JS,
Clegg JS and Yang WJ: Involvement of polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) in
mitotic arrest by inhibition of mitogen-activated protein
kinase-extracellular signal-regulated kinase-ribosomal S6 kinase 1
(MEK-ERK-RSK1) cascade. J Biol Chem. 287:15923–15934. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|