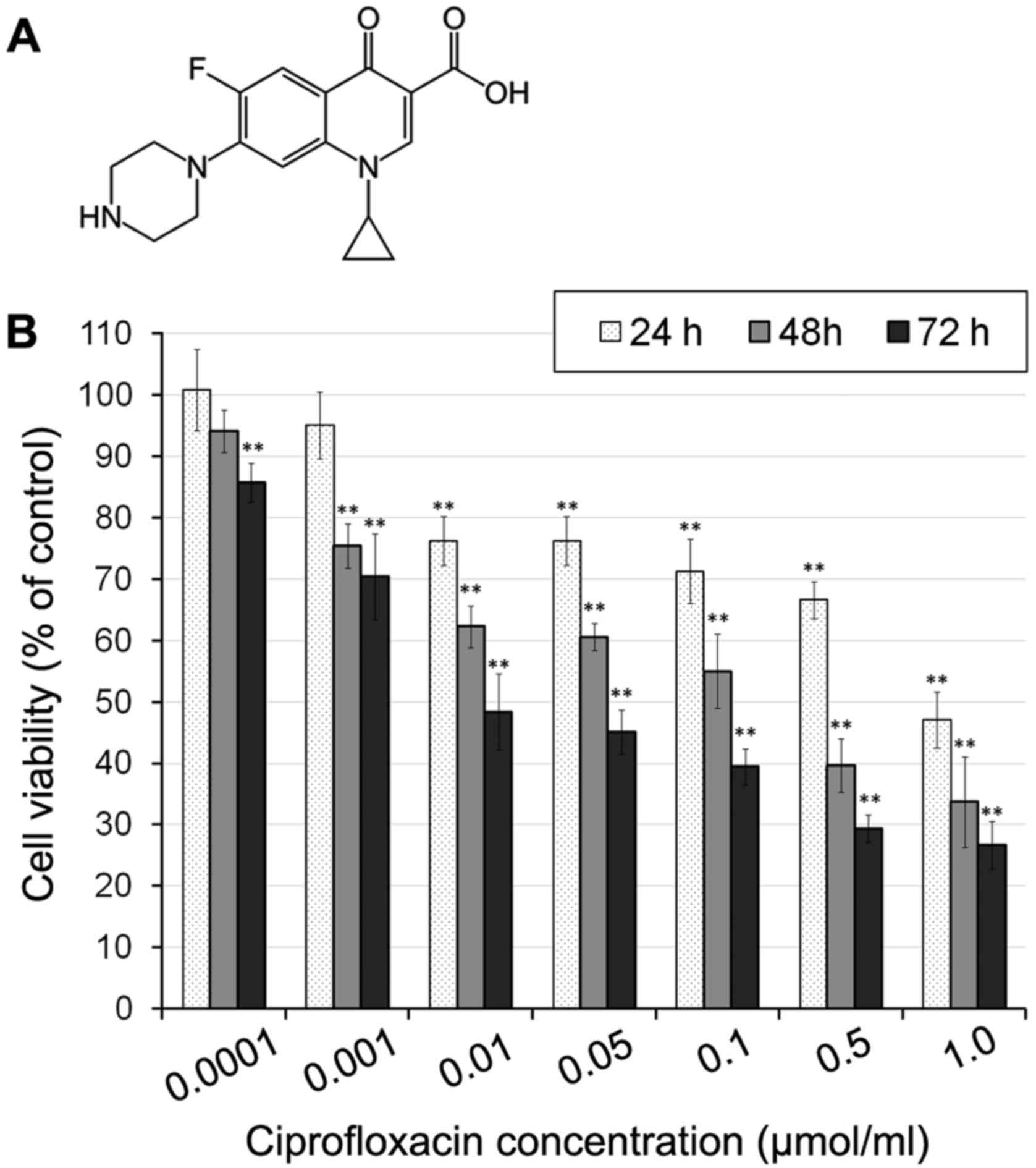
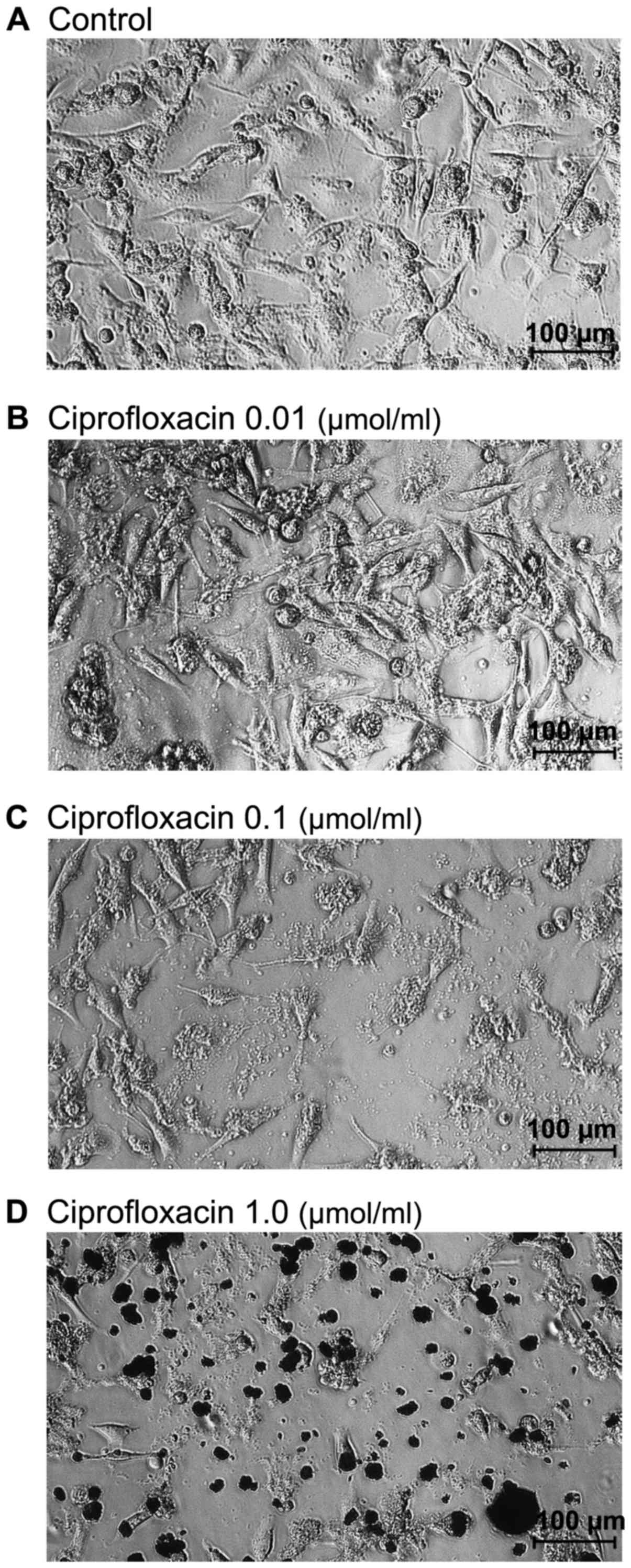
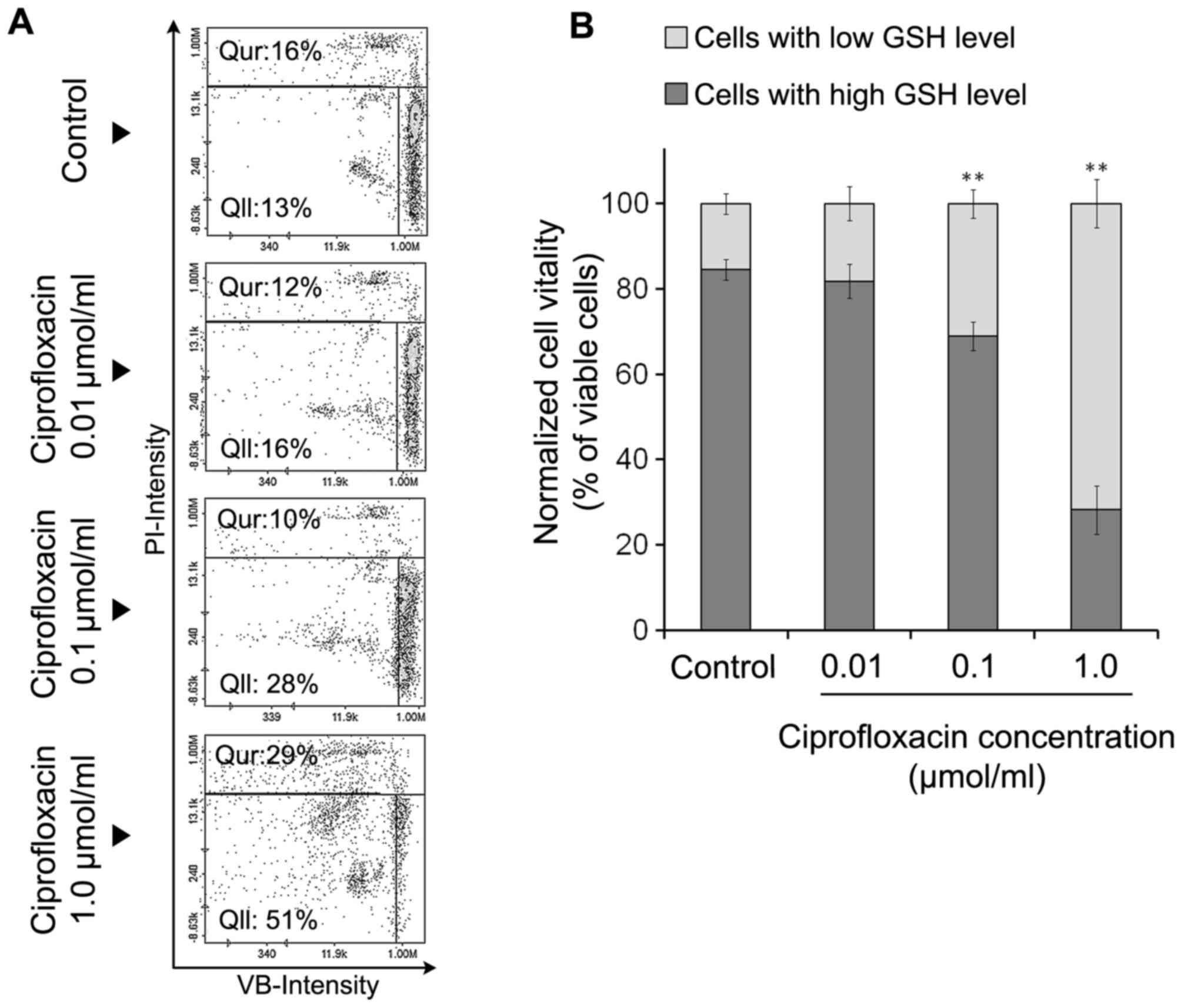
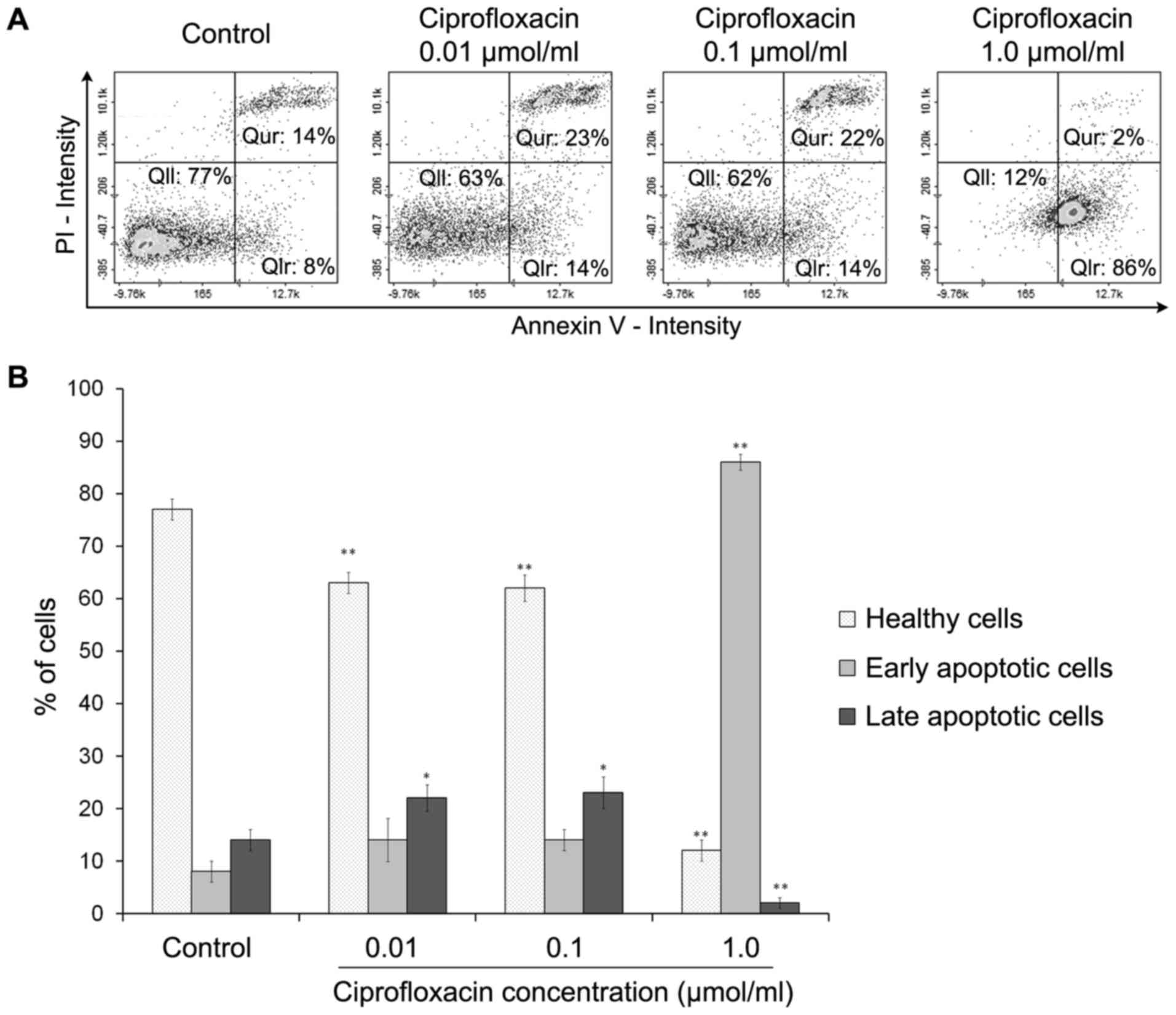
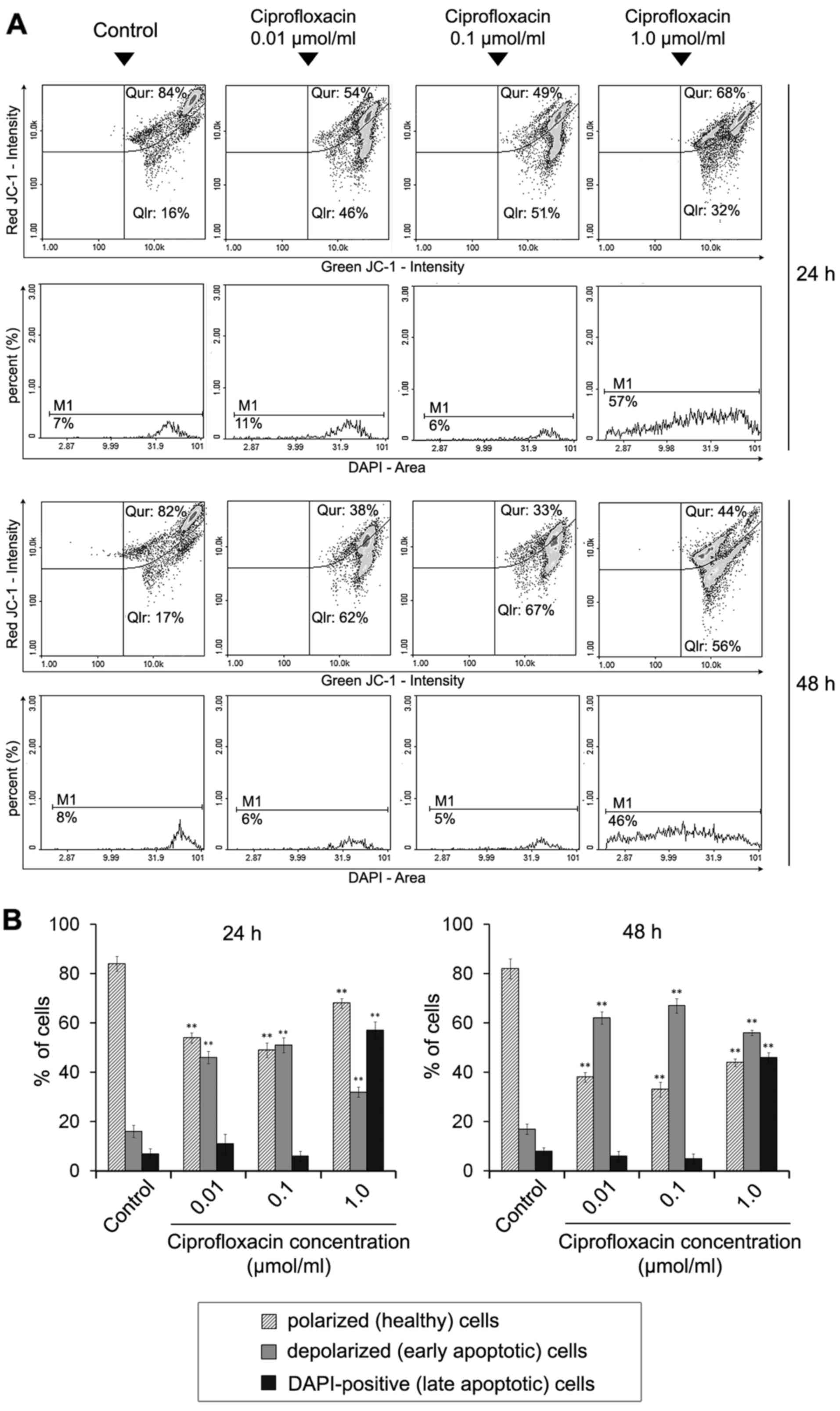
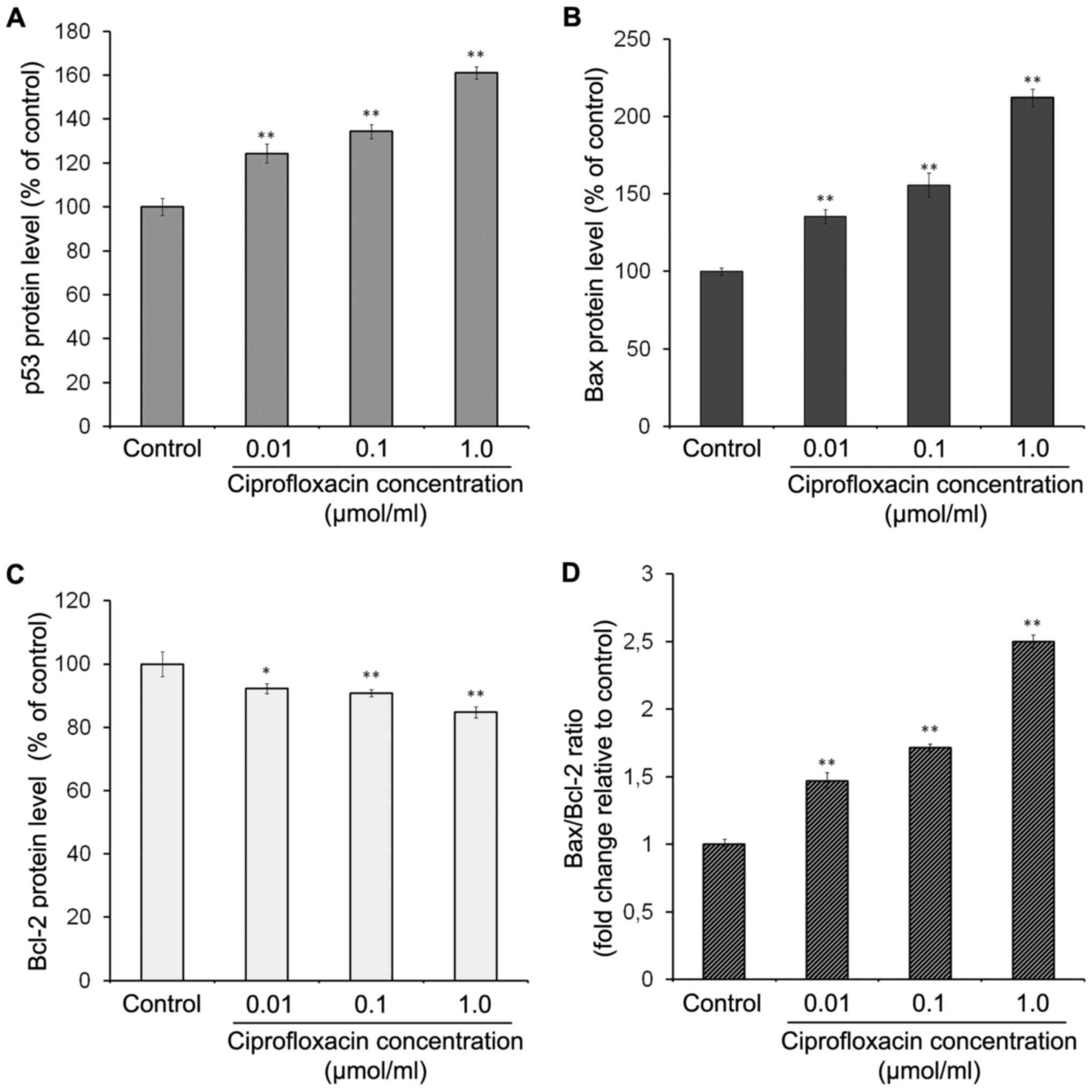
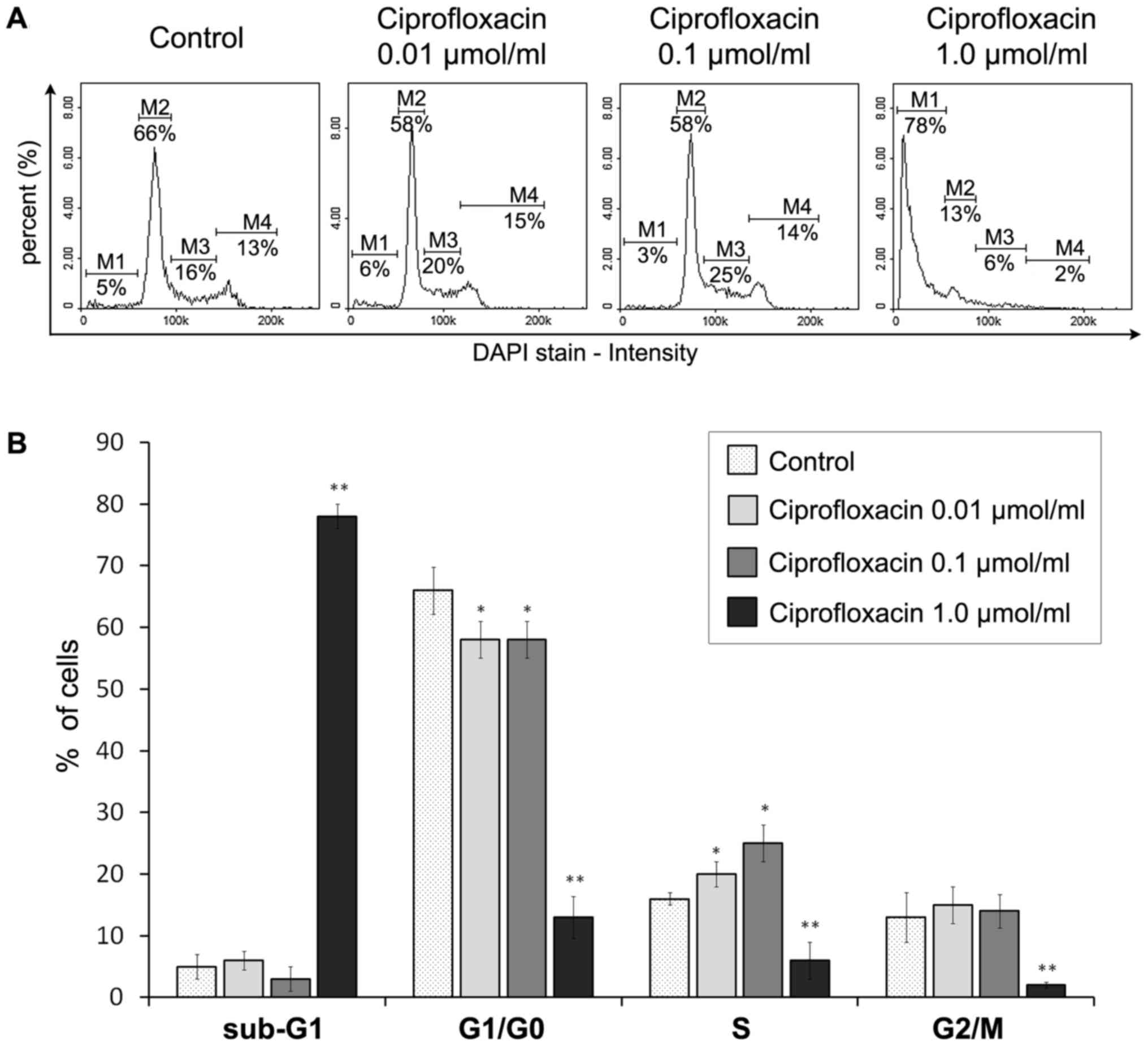
|
1
|
Torre LA, Siegel RL, Ward EM and Jemal A:
Global cancer incidence and mortality rates and trends-An update.
Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 25:16–27. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Yao H, He G, Yan S, Chen C, Song L, Rosol
TJ and Deng X: Triple-negative breast cancer: Is there a treatment
on the horizon? Oncotarget. 8:1913–1924. 2017.
|
|
3
|
Anders C and Carey LA: Understanding and
treating triple-negative breast cancer. Oncology (Williston Park).
22:1233–1240. 12432008.
|
|
4
|
Wahba HA and El-Hadaad HA: Current
approaches in treatment of triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer
Biol Med. 12:106–116. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang JC: Cellular roles of DNA
topoisomerases: A molecular perspective. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
3:430–440. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tse-Dinh YC: Exploring DNA topoisomerases
as targets of novel therapeutic agents in the treatment of
infectious diseases. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 7:3–9. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kaur P, Kaur V and Kaur S: DNA
Topoisomerase II: promising target for anticancer drugs.
Multi-Targeted Approach to Treatment of Cancer. Springer; pp.
323–338. 2015
|
|
8
|
Cowell IG and Austin CA: Mechanism of
generation of therapy related leukemia in response to
anti-topoisomerase II agents. Int J Environ Res Public Health.
9:2075–2091. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Aldred KJ, Kerns RJ and Osheroff N:
Mechanism of quinolone action and resistance. Biochemistry.
53:1565–1574. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Seo K, Holt R, Jung YS, Rodriguez CO Jr,
Chen X and Rebhun RB: Fluoroquinolone-mediated inhibition of cell
growth, S-G2/M cell cycle arrest, and apoptosis in canine
osteosarcoma cell lines. PLoS One. 7:e429602012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Herold C, Ocker M, Ganslmayer M, Gerauer
H, Hahn EG and Schuppan D: Ciprofloxacin induces apoptosis and
inhibits proliferation of human colorectal carcinoma cells. Br J
Cancer. 86:443–448. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yadav V, Sultana S, Yadav J and Saini N:
Gatifloxacin induces S and G2-phase cell cycle arrest in pancreatic
cancer cells via p21/p27/p53. PLoS One. 7:e477962012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yadav V, Varshney P, Sultana S, Yadav J
and Saini N: Moxifloxacin and ciprofloxacin induces S-phase arrest
and augments apoptotic effects of cisplatin in human pancreatic
cancer cells via ERK activation. BMC Cancer. 15:5812015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Aranha O, Grignon R, Fernandes N,
McDonnell TJ, Wood DP Jr and Sarkar FH: Suppression of human
prostate cancer cell growth by ciprofloxacin is associated with
cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Int J Oncol. 22:787–794.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Aranha O, Wood DP Jr and Sarkar FH:
Ciprofloxacin mediated cell growth inhibition, S/G2-M cell cycle
arrest, and apoptosis in a human transitional cell carcinoma of the
bladder cell line. Clin Cancer Res. 6:891–900. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Oliphant CM and Green GM: Quinolones: A
comprehensive review. Am Fam Physician. 65:455–464. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Talla V and Veerareddy P: Oxidative stress
induced by fluoroquinolones on treatment for complicated urinary
tract infections in Indian patients. J Young Pharm. 3:304–309.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Bisacchi GS and Hale MR: A 'Double-Edged'
scaffold: Antitumor power within the antibacterial quinolone. Curr
Med Chem. 23:520–577. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
19
|
Arriola E, Marchio C, Tan DS, Drury SC,
Lambros MB, Natrajan R, Rodriguez-Pinilla SM, Mackay A, Tamber N,
Fenwick K, et al: Genomic analysis of the HER2/TOP2A amplicon in
breast cancer and breast cancer cell lines. Lab Invest. 88:491–503.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Żaczek AJ, Markiewicz A, Seroczyńska B,
Skokowski J, Jaśkiewicz J, Pieńkowski T, Olszewski WP, Szade J,
Rhone P, Welnicka-Jaskiewicz M, et al: Prognostic significance of
TOP2A gene dosage in HER-2-negative breast cancer. Oncologist.
17:1246–1255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shyur LF, Lee SH, Chang ST, Lo CP, Kuo YH
and Wang SY: Taiwanin A inhibits MCF-7 cancer cell activity through
induction of oxidative stress, upregulation of DNA damage
checkpoint kinases, and activation of p53 and FasL/Fas signaling
pathways. Phytomedicine. 18:16–24. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Panieri E and Santoro MM: ROS homeostasis
and metabolism: A dangerous liason in cancer cells. Cell Death Dis.
7:e22532016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Blaydes JP, Craig AL, Wallace M, Ball HM,
Traynor NJ, Gibbs NK and Hupp TR: Synergistic activation of
p53-dependent transcription by two cooperating damage recognition
pathways. Oncogene. 19:3829–3839. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Burns TF and El-Deiry WS: The p53 pathway
and apoptosis. J Cell Physiol. 181:231–239. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pietenpol JA and Stewart ZA: Cell cycle
checkpoint signaling: Cell cycle arrest versus apoptosis.
Toxicology. 181–182:475–481. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: A review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chavez KJ, Garimella SV and Lipkowitz S:
Triple negative breast cancer cell lines: One tool in the search
for better treatment of triple negative breast cancer. Breast Dis.
32:35–48. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Beberok A, Wrześniok D, Szlachta M, Rok J,
Rzepka Z, Respondek M and Buszman E: Lomefloxacin induces oxidative
stress and apoptosis in COLO829 melanoma cells. Int J Mol Sci.
18:E21942017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bai L and Wang S: Targeting apoptosis
pathways for new cancer therapeutics. Annu Rev Med. 65:139–155.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kloskowski T, Gurtowska N, Olkowska J,
Nowak JM, Adamowicz J, Tworkiewicz J, Dębski R, Grzanka A and Drewa
T: Ciprofloxacin is a potential topoisomerase II inhibitor for the
treatment of NSCLC. Int J Oncol. 41:1943–1949. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Thadepalli H, Salem F, Chuah SK and
Gollapudi S: Antitumor activity of trovafloxacin in an animal
model. In Vivo. 19:269–276. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Beberok A, Buszman E, Otręba M and
Wrześniok D: Impact of lomefloxacin on antioxidant enzymes activity
in normal melanocytes HEMa-LP. Curr Issues Pharm Med Sci.
25:426–429. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Beberok A, Wrześniok D, Otręba M, Miliński
M, Rok J and Buszman E: Effect of norfloxacin and moxifloxacin on
melanin synthesis and antioxidant enzymes activity in normal human
melanocytes. Mol Cell Biochem. 401:107–114. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
35
|
Beberok A, Wrześniok D, Otręba M and
Buszman E: Impact of sparfloxacin on melanogenesis and antioxidant
defense system in normal human melanocytes HEMa-LP - An in vitro
study. Pharmacol Rep. 67:38–43. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liou GY and Storz P: Reactive oxygen
species in cancer. Free Radic Res. 44:479–496. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hall AG: Review: The role of glutathione
in the regulation of apoptosis. Eur J Clin Invest. 29:238–245.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mirkovic N, Voehringer DW, Story MD,
McConkey DJ, McDonnell TJ and Meyn RE: Resistance to
radiation-induced apoptosis in Bcl-2-expressing cells is reversed
by depleting cellular thiols. Oncogene. 15:1461–1470. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Dai J, Weinberg RS, Waxman S and Jing Y:
Malignant cells can be sensitized to undergo growth inhibition and
apoptosis by arsenic trioxide through modulation of the glutathione
redox system. Blood. 93:268–277. 1999.
|
|
40
|
Blau H, Klein K, Shalit I, Halperin D and
Fabian I: Moxifloxacin but not ciprofloxacin or azithromycin
selectively inhibits IL-8, IL-6, ERK1/2, JNK, and NF-kappaB
activation in a cystic fibrosis epithelial cell line. Am J Physiol
Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 292:L343–L352. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Beberok A, Wrześniok D, Minecka A, Rok J,
Delijewski M, Rzepka Z, Respondek M and Buszman E:
Ciprofloxacin-mediated induction of S-phase cell cycle arrest and
apoptosis in COLO829 melanoma cells. Pharmacol Rep. 70:6–13. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Shah A, Lettieri J, Kaiser L, Echols R and
Heller AH: Comparative pharmacokinetics and safety of ciprofloxacin
400 mg i.v. thrice daily versus 750 mg po twice daily. J Antimicrob
Chemother. 33:795–801. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Rohwedder R, Bergan T, Caruso E,
Thorsteinsson SB, Della Torre H and Scholl H: Penetration of
ciprofloxacin and metabolites into human lung, bronchial and
pleural tissue after 250 and 500 mg oral ciprofloxacin.
Chemotherapy. 37:229–238. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Beberok A, Buszman E, Wrześniok D, Otręba
M and Trzcionka J: Interaction between ciprofloxacin and melanin:
The effect on proliferation and melanization in melanocytes. Eur J
Pharmacol. 669:32–37. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
d'Ischia M, Wakamatsu K, Cicoira F, Di
Mauro E, Garcia-Borron JC, Commo S, Galván I, Ghanem G, Kenzo K,
Meredith P, et al: Melanins and melanogenesis: From pigment cells
to human health and technological applications. Pigment Cell
Melanoma Res. 28:520–544. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wyatt AJ, Agero ALC, Delgado R, Busam KJ
and Marghoob AA: Cutaneous metastatic breast carcinoma with
melanocyte colonization: A clinical and dermoscopic mimic of
malignant melanoma. Dermatol Surg. 32:949–954. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|