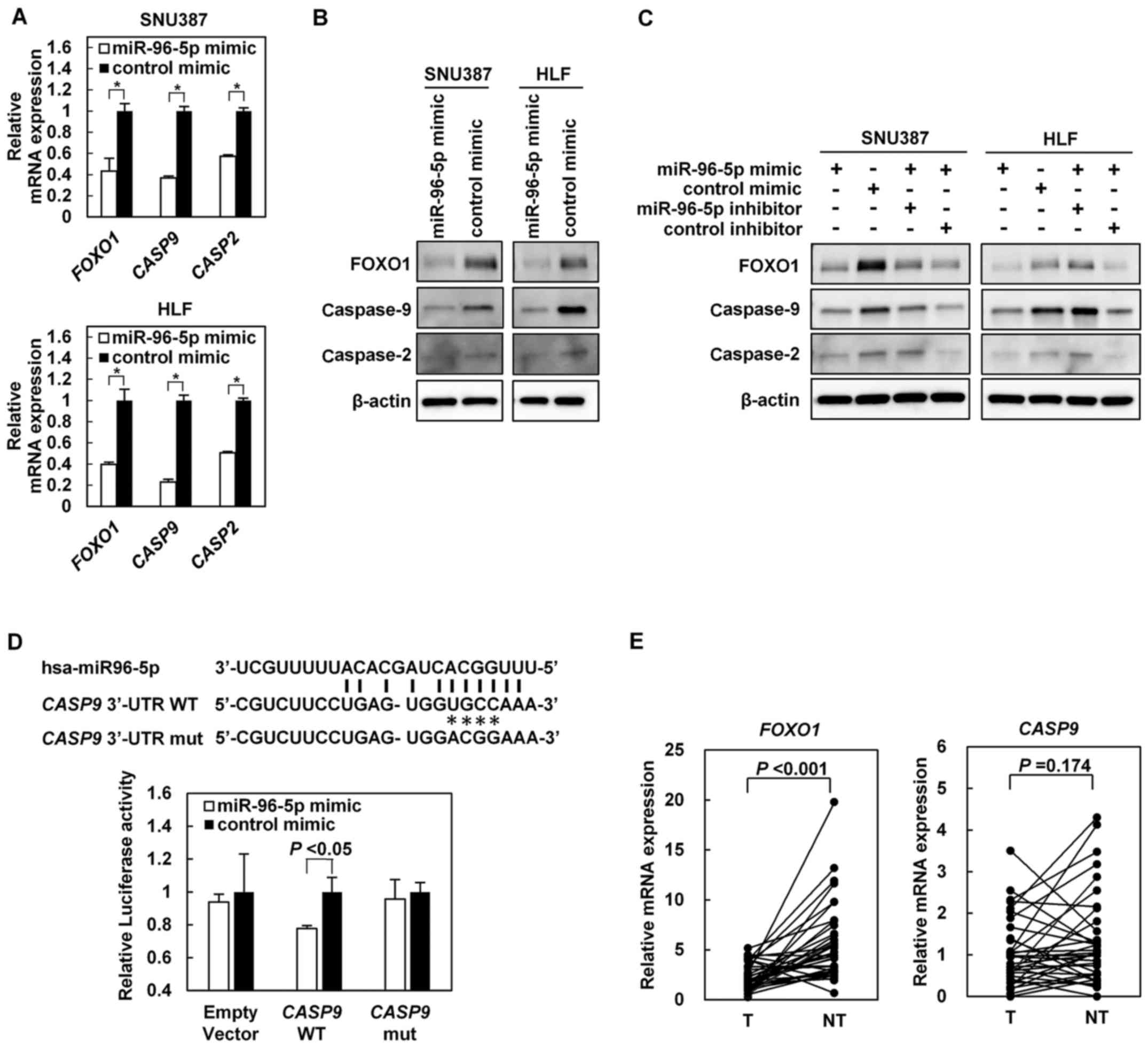
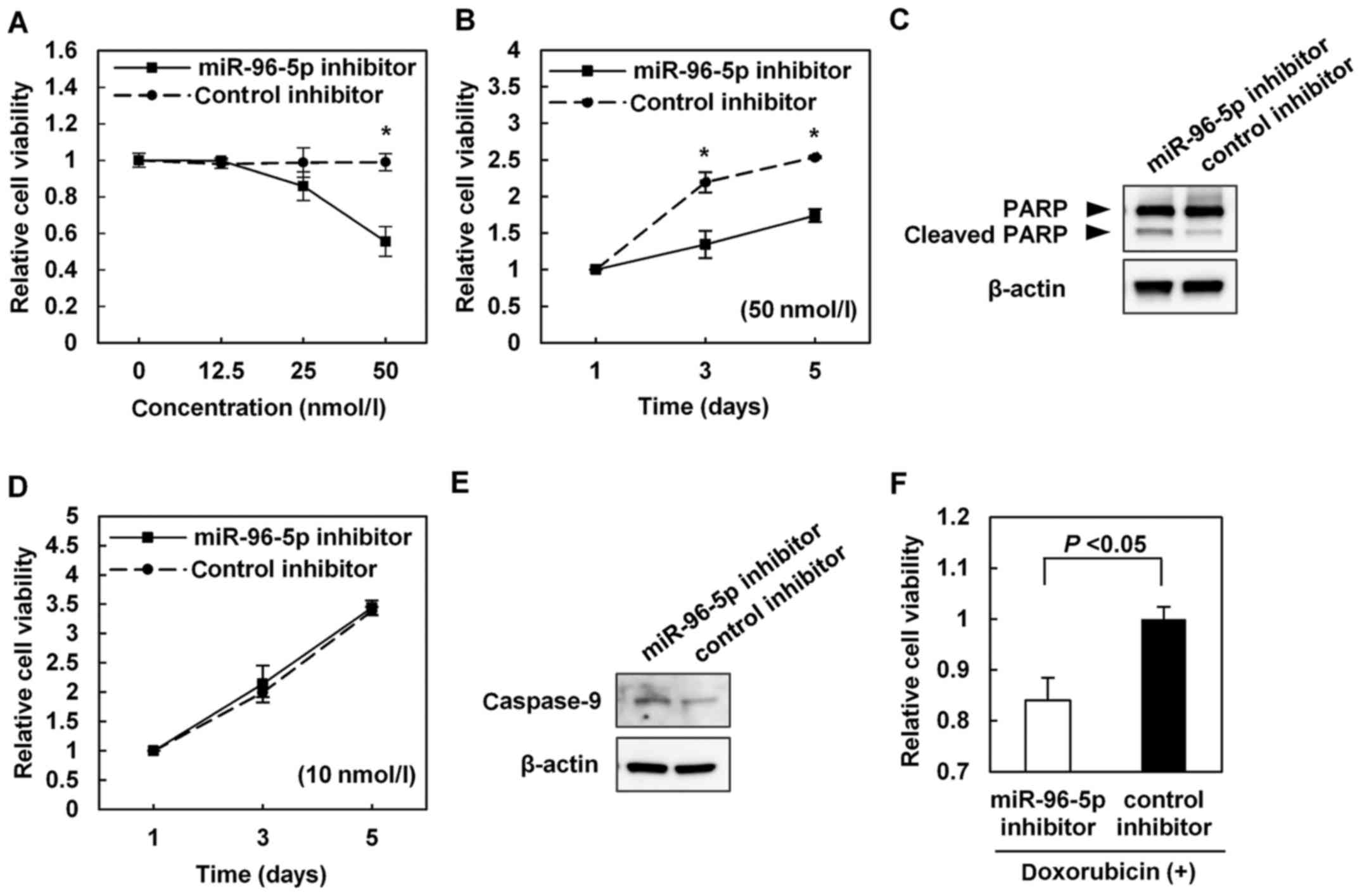
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
El-Serag HB: Hepatocellular carcinoma. N
Engl J Med. 365:1118–1127. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
He L and Hannon GJ: MicroRNAs: Small RNAs
with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 5:522–531. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R,
Zupo S, Noch E, Aldler H, Rattan S, Keating M, Rai K, et al:
Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes miR15 and
miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 99:15524–15529. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Lujambio A and Lowe SW: The microcosmos of
cancer. Nature. 482:347–355. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mao B and Wang G: MicroRNAs involved with
hepatocellular carcinoma (Review). Oncol Rep. 34:2811–2820. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mohammad RM, Muqbil I, Lowe L, Yedjou C,
Hsu HY, Lin LT, Siegelin MD, Fimognari C, Kumar NB, Dou QP, et al:
Broad targeting of resistance to apoptosis in cancer. Semin Cancer
Biol. 35(Suppl): S78–S103. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Crawford ED, McNew JA, Nagata S and Wells
J: Cell death. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 6th edition. Alberts
B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Morgan D, Raff M, Roberts K and Walter P:
Garland Science; New York: pp. 1021–1034. 2015
|
|
11
|
Soengas MS, Alarcón RM, Yoshida H, Giaccia
AJ, Hakem R, Mak TW and Lowe SW: Apaf-1 and caspase-9 in
p53-dependent apoptosis and tumor inhibition. Science. 284:156–159.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xu D, He X, Chang Y, Xu C, Jiang X, Sun S
and Lin J: Inhibition of miR-96 expression reduces cell
proliferation and clonogenicity of HepG2 hepatoma cells. Oncol Rep.
29:653–661. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Leung WK, He M, Chan AW, Law PT and Wong
N: Wnt/β-catenin activates MiR-183/96/182 expression in
hepatocellular carcinoma that promotes cell invasion. Cancer Lett.
362:97–105. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Guttilla IK and White BA: Coordinate
regulation of FOXO1 by miR-27a, miR-96, and miR-182 in breast
cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 284:23204–23216. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Fendler A, Jung M, Stephan C, Erbersdobler
A, Jung K and Yousef GM: The antiapoptotic function of miR-96 in
prostate cancer by inhibition of FOXO1. PLoS One. 8:e808072013.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Myatt SS, Wang J, Monteiro LJ, Christian
M, Ho KK, Fusi L, Dina RE, Brosens JJ, Ghaem-Maghami S and Lam EW:
Definition of microRNAs that repress expression of the tumor
suppressor gene FOXO1 in endometrial cancer. Cancer Res.
70:367–377. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Yasui K, Konishi C, Gen Y, Endo M, Dohi O,
Tomie A, Kitaichi T, Yamada N, Iwai N, Nishikawa T, et al: EVI1, a
target gene for amplification at 3q26, antagonizes transforming
growth factor-β-mediated growth inhibition in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 106:929–937. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zen K, Yasui K, Nakajima T, Zen Y, Zen K,
Gen Y, Mitsuyoshi H, Minami M, Mitsufuji S, Tanaka S, et al: ERK5
is a target for gene amplification at 17p11 and promotes cell
growth in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating mitotic entry.
Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 48:109–120. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Endo M, Yasui K, Zen Y, Gen Y, Zen K,
Tsuji K, Dohi O, Mitsuyoshi H, Tanaka S, Taniwaki M, et al:
Alterations of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodelling subunit-BRG1 and
BRM in hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 33:105–117. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Pineau P, Volinia S, McJunkin K, Marchio
A, Battiston C, Terris B, Mazzaferro V, Lowe SW, Croce CM and
Dejean A: miR-221 overexpression contributes to liver
tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:264–269. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Ress AL, Stiegelbauer V, Winter E,
Schwarzenbacher D, Kiesslich T, Lax S, Jahn S, Deutsch A,
Bauernhofer T, Ling H, et al: MiR-96-5p influences cellular growth
and is associated with poor survival in colorectal cancer patients.
Mol Carcinog. 54:1442–1450. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Schaefer A, Jung M, Mollenkopf HJ, Wagner
I, Stephan C, Jentzmik F, Miller K, Lein M, Kristiansen G and Jung
K: Diagnostic and prognostic implications of microRNA profiling in
prostate carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 126:1166–1176. 2010.
|
|
23
|
Han Y, Chen J, Zhao X, Liang C, Wang Y,
Sun L, Jiang Z, Zhang Z, Yang R, Chen J, et al: MicroRNA expression
signatures of bladder cancer revealed by deep sequencing. PLoS One.
6:e182862011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li C, Yin Y, Liu X, Xi X, Xue W and Qu Y:
Non-small cell lung cancer associated microRNA expression
signature: Integrated bioinformatics analysis, validation and
clinical significance. Oncotarget. 8:24564–24578. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Siu MK, Tsai YC, Chang YS, Yin JJ, Suau F,
Chen WY and Liu YN: Transforming growth factor-β promotes prostate
bone metastasis through induction of microRNA-96 and activation of
the mTOR pathway. Oncogene. 34:4767–4776. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Ma Y, Yang HZ, Dong BJ, Zou HB, Zhou Y,
Kong XM and Huang YR: Biphasic regulation of autophagy by miR-96 in
prostate cancer cells under hypoxia. Oncotarget. 5:9169–9182. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jeong HJ, Park SY, Yang WM and Lee W: The
induction of miR-96 by mitochondrial dysfunction causes impaired
glycogen synthesis through translational repression of IRS-1 in
SK-Hep1 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 434:503–508. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Calnan DR and Brunet A: The FoxO code.
Oncogene. 27:2276–2288. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Dong XY, Chen C, Sun X, Guo P, Vessella
RL, Wang RX, Chung LW, Zhou W and Dong JT: FOXO1A is a candidate
for the 13q14 tumor suppressor gene inhibiting androgen receptor
signaling in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 66:6998–7006. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lin H, Dai T, Xiong H, Zhao X, Chen X, Yu
C, Li J, Wang X and Song L: Unregulated miR-96 induces cell
proliferation in human breast cancer by downregulating
transcriptional factor FOXO3a. PLoS One. 5:e157972010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Jalvy-Delvaille S, Maurel M, Majo V,
Pierre N, Chabas S, Combe C, Rosenbaum J, Sagliocco F and Grosset
CF: Molecular basis of differential target regulation by miR-96 and
miR-182: The Glypican-3 as a model. Nucleic Acids Res.
40:1356–1365. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Zhang J, Kong X, Li J, Luo Q, Li X, Shen
L, Chen L and Fang L: miR-96 promotes tumor proliferation and
invasion by targeting RECK in breast cancer. Oncol Rep.
31:1357–1363. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Xu L, Zhong J, Guo B, Zhu Q, Liang H, Wen
N, Yun W and Zhang L: miR-96 promotes the growth of prostate
carcinoma cells by suppressing MTSS1. Tumour Biol. 37:12023–12032.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hong Y, Liang H, Uzair-Ur-Rehman, Wang Y,
Zhang W, Zhou Y, Chen S, Yu M, Cui S, Liu M, et al: miR-96 promotes
cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting PTPN9 in
breast cancer. Sci Rep. 6:374212016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Velagapudi SP, Gallo SM and Disney MD:
Sequence-based design of bioactive small molecules that target
precursor microRNAs. Nat Chem Biol. 10:291–297. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Velagapudi SP, Cameron MD, Haga CL,
Rosenberg LH, Lafitte M, Duckett DR, Phinney DG and Disney MD:
Design of a small molecule against an oncogenic noncoding RNA. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 113:5898–5903. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|