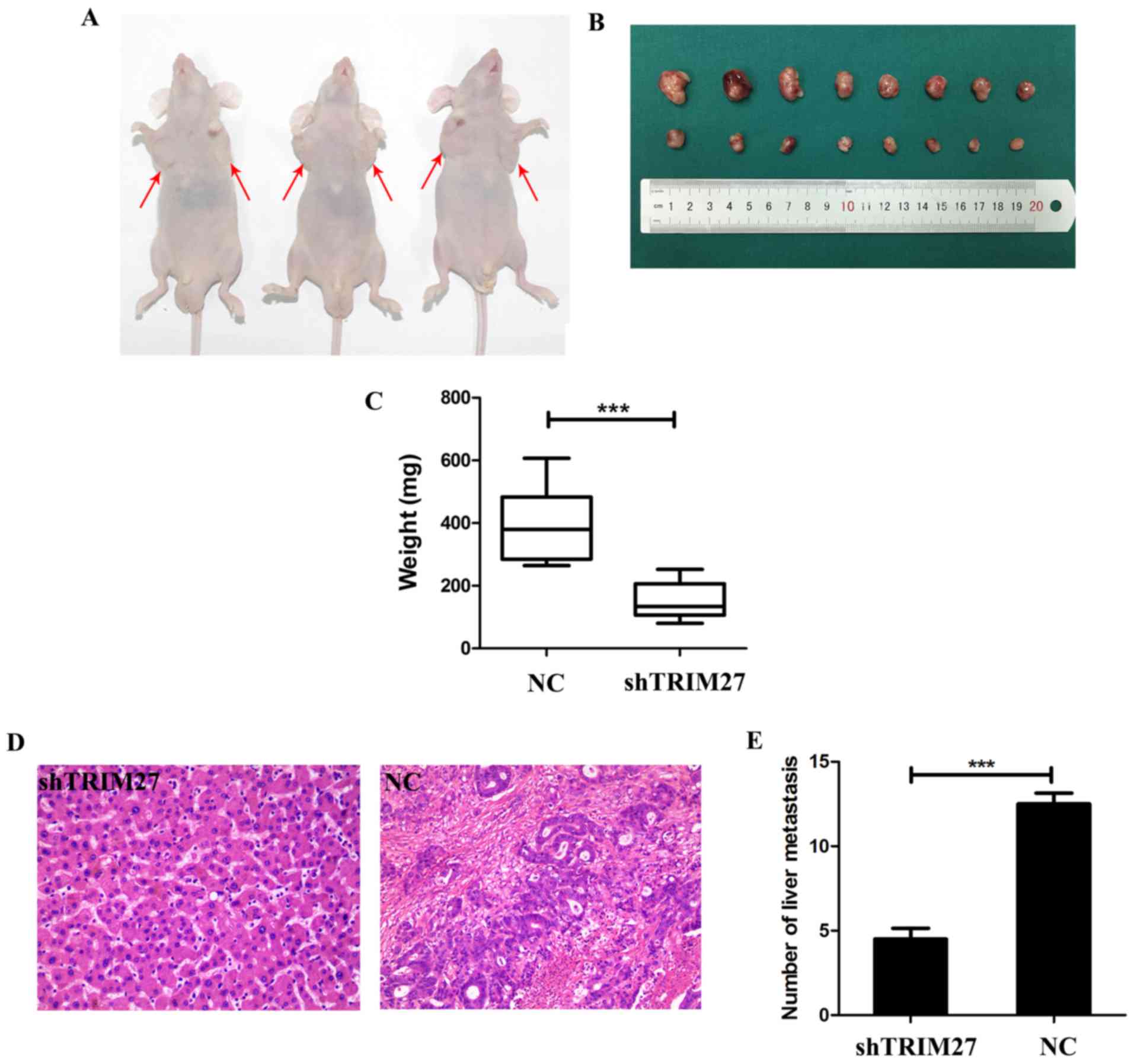
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Siegel R, DeSantis C, Virgo K, Stein K,
Mariotto A, Smith T, Cooper D, Gansler T, Lerro C, Fedewa S, et al:
Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J
Clin. 62:220–241. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Siegel R, Desantis C and Jemal A:
Colorectal cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:104–117.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Micale L, Chaignat E, Fusco C, Reymond A
and Merla G: The tripartite motif: Structure and function. Adv Exp
Med Biol. 770:11–25. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Miyamoto K, Nakamura N, Kashiwagi M, Honda
S, Kato A, Hasegawa S, Takei Y and Hirose S: RING finger, B-box,
and coiled-coil (RBCC) protein expression in branchial epithelial
cells of Japanese eel, Anguilla japonica. Eur J Biochem.
269:6152–6161. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Meroni G and Diez-Roux G: TRIM/RBCC, a
novel class of ‘single protein RING finger’ E3 ubiquitin ligases.
BioEssays. 27:1147–1157. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Nisole S, Stoye JP and Saïb A: TRIM family
proteins: Retroviral restriction and antiviral defence. Nat Rev
Microbiol. 3:799–808. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Takahashi M, Ritz J and Cooper GM:
Activation of a novel human transforming gene, ret, by DNA
rearrangement. Cell. 42:581–588. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Takahashi M and Cooper GM: ret
transforming gene encodes a fusion protein homologous to tyrosine
kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 7:1378–1385. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Takahashi M, Inaguma Y, Hiai H and Hirose
F: Developmentally regulated expression of a human
‘finger’-containing gene encoded by the 5′ half of the ret
transforming gene. Mol Cell Biol. 8:1853–1856. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Fagerberg L, Hallström BM, Oksvold P,
Kampf C, Djureinovic D, Odeberg J, Habuka M, Tahmasebpoor S,
Danielsson A and Edlund K: Analysis of the human tissue-specific
expression by genome-wide integration of transcriptomics and
antibody-based proteomics. Mol Cell Proteomics. 13:397–406. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ma Y, Wei Z, Bast RC Jr, Wang Z, Li Y, Gao
M, Liu Y, Wang X, Guo C, Zhang L, et al: Downregulation of TRIM27
expression inhibits the proliferation of ovarian cancer cells in
vitro and in vivo. Lab Invest. 96:37–48. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Tsukamoto H, Kato T, Enomoto A, Nakamura
N, Shimono Y, Jijiwa M, Asai N, Murakumo Y, Shibata K and Kikkawa
F: Expression of Ret finger protein correlates with outcomes in
endometrial cancer. Cancer Sci. 100:1895–1901. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Tezel GG, Uner A, Yildiz I, Guler G and
Takahashi M: RET finger protein expression in invasive breast
carcinoma: Relationship between RFP and ErbB2 expression. Pathol
Res Pract. 205:403–408. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Iwakoshi A, Murakumo Y, Kato T, Kitamura
A, Mii S, Saito S, Yatabe Y and Takahashi M: RET finger protein
expression is associated with prognosis in lung cancer with
epidermal growth factor receptor mutations. Pathol Int. 62:324–330.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Horio M, Kato T, Mii S, Enomoto A, Asai M,
Asai N, Murakumo Y, Shibata K, Kikkawa F and Takahashi M:
Expression of RET finger protein predicts chemoresistance in
epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Med. 1:218–229. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kato T, Shimono Y, Hasegawa M, Jijiwa M,
Enomoto A, Asai N, Murakumo Y and Takahashi M: Characterization of
the HDAC1 complex that regulates the sensitivity of cancer cells to
oxidative stress. Cancer Res. 69:3597–3604. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zoumpoulidou G, Broceño C, Li H, Bird D,
Thomas G and Mittnacht S: Role of the tripartite motif protein 27
in cancer development. J Natl Cancer Inst. 104:941–952. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Li L and Li W: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in human cancer: Comprehensive reprogramming of
metabolism, epigenetics, and differentiation. Pharmacol Ther.
150:33–46. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Satelli A and Li S: Vimentin in cancer and
its potential as a molecular target for cancer therapy. Cell Mol
Life Sci. 68:3033–3046. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Xu W, Yang Z and Lu N: A new role for the
PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in the epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Cell Adhes Migr. 9:317–324. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Benson AB III, Venook AP, Bekaii-Saab T,
Chan E, Chen YJ, Cooper HS, Engstrom PF, Enzinger PC, Fenton MJ,
Fuchs CS, et al: National Comprehensive Cancer Network: Colon
cancer, version 3.2014. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 12:1028–1059. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Xu W, Xu B, Yao Y, Yu X, Cao H, Zhang J,
Liu J and Sheng H: RNA interference against TRIM29 inhibits
migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells. Oncol Rep.
36:1411–1418. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Tan Z, Liu X, Yu E, Wang H, Tang L, Wang H
and Fu C: Lentivirus-mediated RNA interference of tripartite motif
68 inhibits the proliferation of colorectal cancer cell lines
SW1116 and HCT116 in vitro. Oncol Lett. 13:2649–2655. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Lee OH, Lee J, Lee KH, Woo YM, Kang JH,
Yoon HG, Bae SK, Songyang Z, Oh SH and Choi Y: Role of the focal
adhesion protein TRIM15 in colon cancer development. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1853.409–421. 2015.
|
|
28
|
Sun Y, Ji B, Feng Y, Zhang Y, Ji D, Zhu C,
Wang S, Zhang C, Zhang D and Sun Y: TRIM59 facilitates the
proliferation of colorectal cancer and promotes metastasis via the
PI3K/AKT pathway. Oncol Rep. 38:43–52. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Tezel GG, Ordulu Z, Hımmetoğlu C and
Usubütün A: The selective expression of ret finger protein in
endometrial cancer: Can RFP be a marker of serous carcinomas. Turk
Patoloji Derg. 28:213–219. 2012.
|
|
30
|
Radisky DC and LaBarge MA:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and the stem cell phenotype. Cell
Stem Cell. 2:511–512. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Yang J and Weinberg RA:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: At the crossroads of development
and tumor metastasis. Dev Cell. 14:818–829. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Guo Xu G, Xu Y, Wang D, Shen Y, Wang Y, Lv
F, Song Y, Jiang F and Zhang DY: TRIM14 regulates cell
proliferation and invasion in osteosarcoma via promotion of the AKT
signaling pathway. Sci Rep. 7:424112017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Tan H, Qi J, Chu G and Liu Z: Tripartite
motif 16 inhibits the migration and invasion in ovarian cancer
cells. Oncol Res. 25:551–558. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Suman S, Kurisetty V, Das TP, Vadodkar A,
Ramos G, Lakshmanaswamy R and Damodaran C: Activation of AKT
signaling promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor
growth in colorectal cancer cells. Mol Carcinog. 53(Suppl 1):
E151–E160. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|