|
1
|
Grothey A, Sargent D, Goldberg RM and
Schmoll HJ: Survival of patients with advanced colorectal cancer
improves with the availability of fluorouracil-leucovorin,
irinotecan, and oxaliplatin in the course of treatment. J Clin
Oncol. 22:1209–1214. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fransén K, Klintenäs M, Osterström A,
Dimberg J, Monstein HJ and Söderkvist P: Mutation analysis of the
BRAF, ARAF and RAF-1 genes in human colorectal adenocarcinomas.
Carcinogenesis. 25:527–533. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Basu S, Haase G and Ben-Ze'ev A: Wnt
signaling in cancer stem cells and colon cancer metastasis.
F1000Res. 2016, 5:https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.7579.1.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kang YJ, Park HJ, Chung HJ, Min HY, Park
EJ, Lee MA, Shin Y and Lee SK: Wnt/β-catenin signaling mediates the
antitumor activity of magnolol in colorectal cancer cells. Mol
Pharmacol. 82:168–177. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lu Y, Xie S, Zhang W, Zhang C, Gao C, Sun
Q, Cai Y, Xu Z, Xiao M, Xu Y, et al: Twa1/Gid8 is a beta-catenin
nuclear retention factor in Wnt signaling and colorectal
tumorigenesis. Cell Res. 27:1422–1440. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Najdi R, Holcombe RF and Waterman ML: Wnt
signaling and colon carcinogenesis: Beyond APC. J Carcinog.
10:52011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tetsu O and McCormick F: Beta-catenin
regulates expression of cyclin D1 in colon carcinoma cells. Nature.
398:422–426. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
You Z, Saims D, Chen S, Zhang Z, Guttridge
DC, Guan KL, MacDougald OA, Brown AM, Evan G, Kitajewski J, et al:
Wnt signaling promotes oncogenic transformation by inhibiting
c-Myc-induced apoptosis. J Cell Biol. 157:429–440. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Morin PJ: beta-catenin signaling and
cancer. Bioessays. 21:1021–1030. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rivlin N, Brosh R, Oren M and Rotter V:
Mutations in the p53 tumor suppressor gene: Important milestones at
the various steps of tumorigenesis. Genes Cancer. 2:466–474. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Marine JC, Francoz S, Maetens M, Wahl G,
Toledo F and Lozano G: Keeping p53 in check: Essential and
synergistic functions of Mdm2 and Mdm4. Cell Death Differ.
13:927–934. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Meek DW: The p53 response to DNA damage.
DNA Repair (Amst). 3:1049–1056. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Liebermann DA, Hoffman B and Vesely D: p53
induced growth arrest versus apoptosis and its modulation by
survival cytokines. Cell Cycle. 6:166–170. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Giaccia AJ and Kastan MB: The complexity
of p53 modulation: Emerging patterns from divergent signals. Genes
Dev. 12:2973–2983. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Moll UM and Petrenko O: The MDM2-p53
interaction. Mol Cancer Res. 1:1001–1008. 2003.
|
|
16
|
Al-Kuraya KS: KRAS and TP53 mutations in
colorectal carcinoma. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 15:217–219. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Iacopetta B: TP53 mutation in colorectal
cancer. Hum Mutat. 21:271–276. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sadot E, Geiger B, Oren M and Ben-Ze'ev A:
Down-regulation of beta-catenin by activated p53. Mol Cell Biol.
21:6768–6781. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Riascos-Bernal DF, Chinnasamy P, Cao LL,
Dunaway CM, Valenta T, Basler K and Sibinga NE: β-catenin
C-terminal signals suppress p53 and are essential for artery
formation. Nat Commun. 7:123892016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Griffiths-Jones S: The microRNA registry.
Nucleic Acids Res. 32(Database issue): D109–D111. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Chen C, Ridzon DA, Broomer AJ, Zhou Z, Lee
DH, Nguyen JT, Barbisin M, Xu NL, Mahuvakar VR, Andersen MR, et al:
Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic
Acids Res. 33:e1792005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee Y, Kim M, Han J, Yeom KH, Lee S, Baek
SH and Kim VN: MicroRNA genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II.
EMBO J. 23:4051–4060. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Piriyapongsa J and Jordan IK: A family of
human microRNA genes from miniature inverted-repeat transposable
elements. PLoS One. 2:e2032007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Piriyapongsa J, Marino-Ramirez L and
Jordan IK: Origin and evolution of human microRNAs from
transposable elements. Genetics. 176:1323–1337. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Finnegan DJ: Retrotransposons. Curr Biol.
22:R432–R437. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li M, Marin-Muller C, Bharadwaj U, Chow
KH, Yao Q and Chen C: MicroRNAs: Control and loss of control in
human physiology and disease. World J Surg. 33:667–684. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Lytle JR, Yario TA and Steitz JA: Target
mRNAs are repressed as efficiently by microRNA-binding sites in the
5′ UTR as in the 3′UTR. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:9667–9672.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Jansson MD and Lund AH: MicroRNA and
cancer. Mol Oncol. 6:590–610. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wu WK, Law PT, Lee CW, Cho CH, Fan D, Wu
K, Yu J and Sung JJ: MicroRNA in colorectal cancer: From benchtop
to bedside. Carcinogenesis. 32:247–253. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Cao J, Yan XR, Liu T, Han XB, Yu JJ, Liu
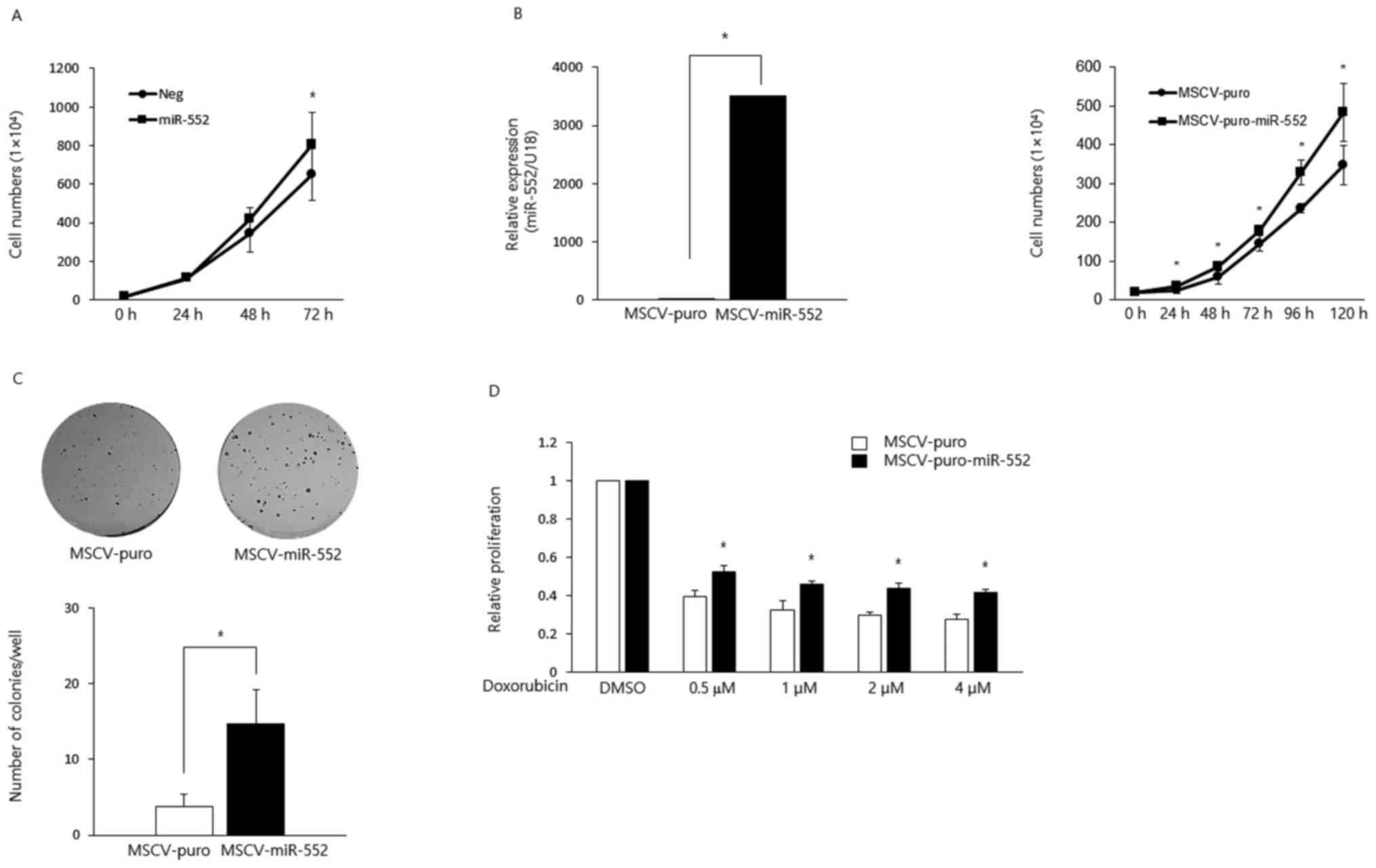
SH and Wang LB: MicroRNA-552 promotes tumor cell proliferation and
migration by directly targeting DACH1 via the Wnt/beta-catenin
signaling pathway in colorectal cancer. Oncol Lett. 14:3795–802.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang J, Li H, Wang Y, Wang L, Yan X, Zhang
D, Ma X, Du Y, Liu X and Yang Y: MicroRNA-552 enhances metastatic
capacity of colorectal cancer cells by targeting a disintegrin and
metalloprotease 28. Oncotarget. 7:70194–7210. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jeong D, Kim J, Nam J, Sun H, Lee YH, Lee
TJ, Aguiar RC and Kim SW: MicroRNA-124 links p53 to the NF-κB
pathway in B-cell lymphomas. Leukemia. 29:1868–1874. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Dalby B, Cates S, Harris A, Ohki EC,
Tilkins ML, Price PJ and Ciccarone VC: Advanced transfection with
Lipofectamine 2000 reagent: Primary neurons, siRNA, and
high-throughput applications. Methods. 33:95–103. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cho Y, Song SH, Lee JJ, Choi N, Kim CG,
Dean A and Kim A: The role of transcriptional activator GATA-1 at
human beta-globin HS2. Nucleic Acids Res. 36:4521–4528. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang N and Liu W: Increased expression of
miR-552 acts as a potential predictor biomarker for poor prognosis
of colorectal cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:412–416.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rowan AJ, Lamlum H, Ilyas M, Wheeler J,
Straub J, Papadopoulou A, Bicknell D, Bodmer WF and Tomlinson IP:
APC mutations in sporadic colorectal tumors: A mutational 'hotspot'
and interdependence of the 'two hits'. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
97:3352–3357. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Kim NH, Cha YH, Kang SE, Lee Y, Lee I, Cha
SY, Ryu JK, Na JM, Park C, Yoon HG, et al: p53 regulates nuclear
GSK-3 levels through miR-34-mediated Axin2 suppression in
colorectal cancer cells. Cell Cycle. 12:1578–1587. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kim NH, Kim HS, Kim NG, Lee I, Choi HS, Li
XY, Kang SE, Cha SY, Ryu JK, Na JM, et al: p53 and microRNA-34 are
suppressors of canonical Wnt signaling. Sci Signal. 4:ra712011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hermeking H: p53 enters the microRNA
world. Cancer Cell. 12:414–418. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ha TY: The role of microRNAs in regulatory
T cells and in the immune response. Immune Netw. 11:11–41. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Schultz NA, Werner J, Willenbrock H,
Roslind A, Giese N, Horn T, Wøjdemann M and Johansen JS: MicroRNA
expression profiles associated with pancreatic adenocarcinoma and
ampullary adenocarcinoma. Mod Pathol. 25:1609–1622. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|