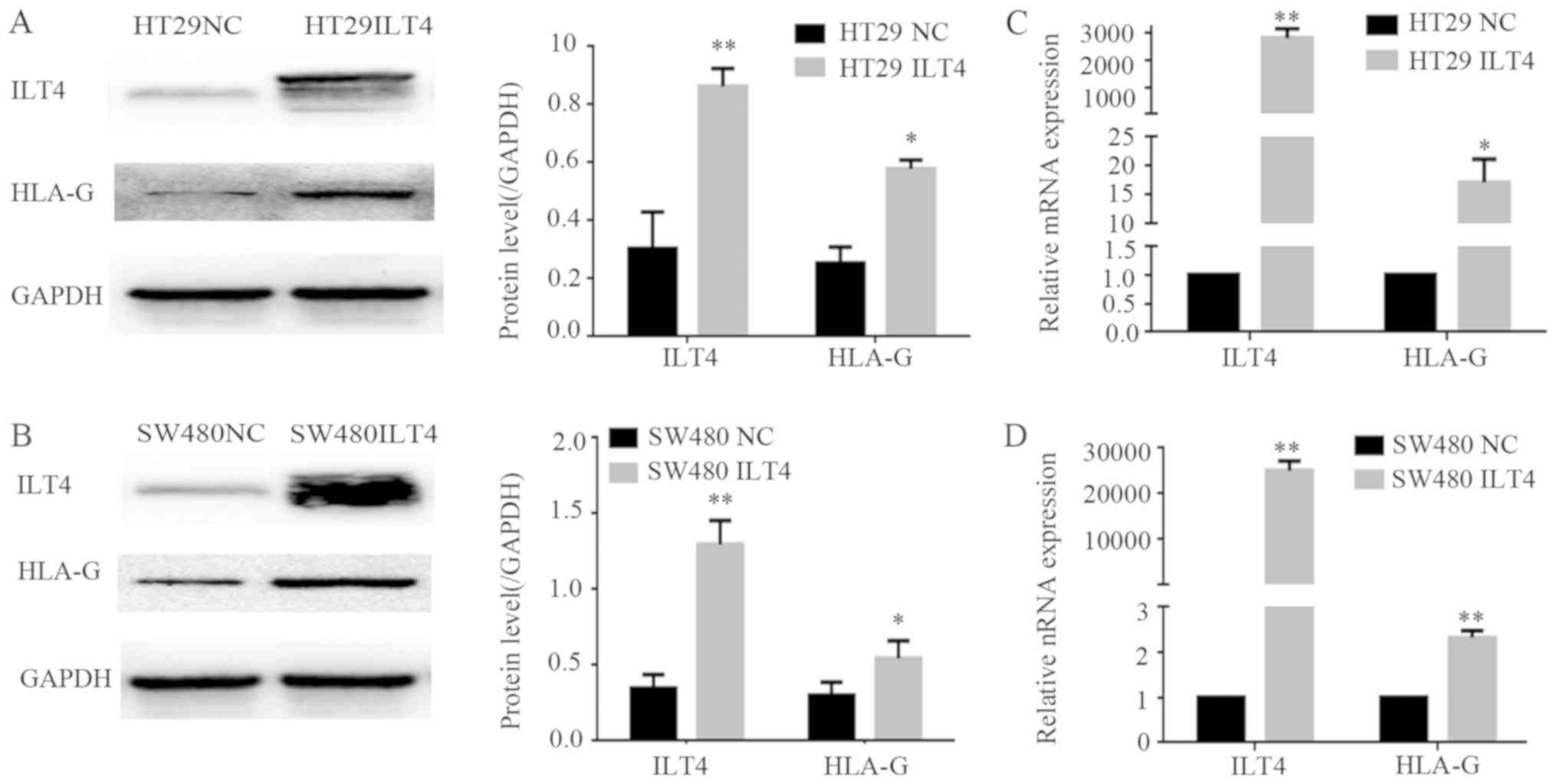
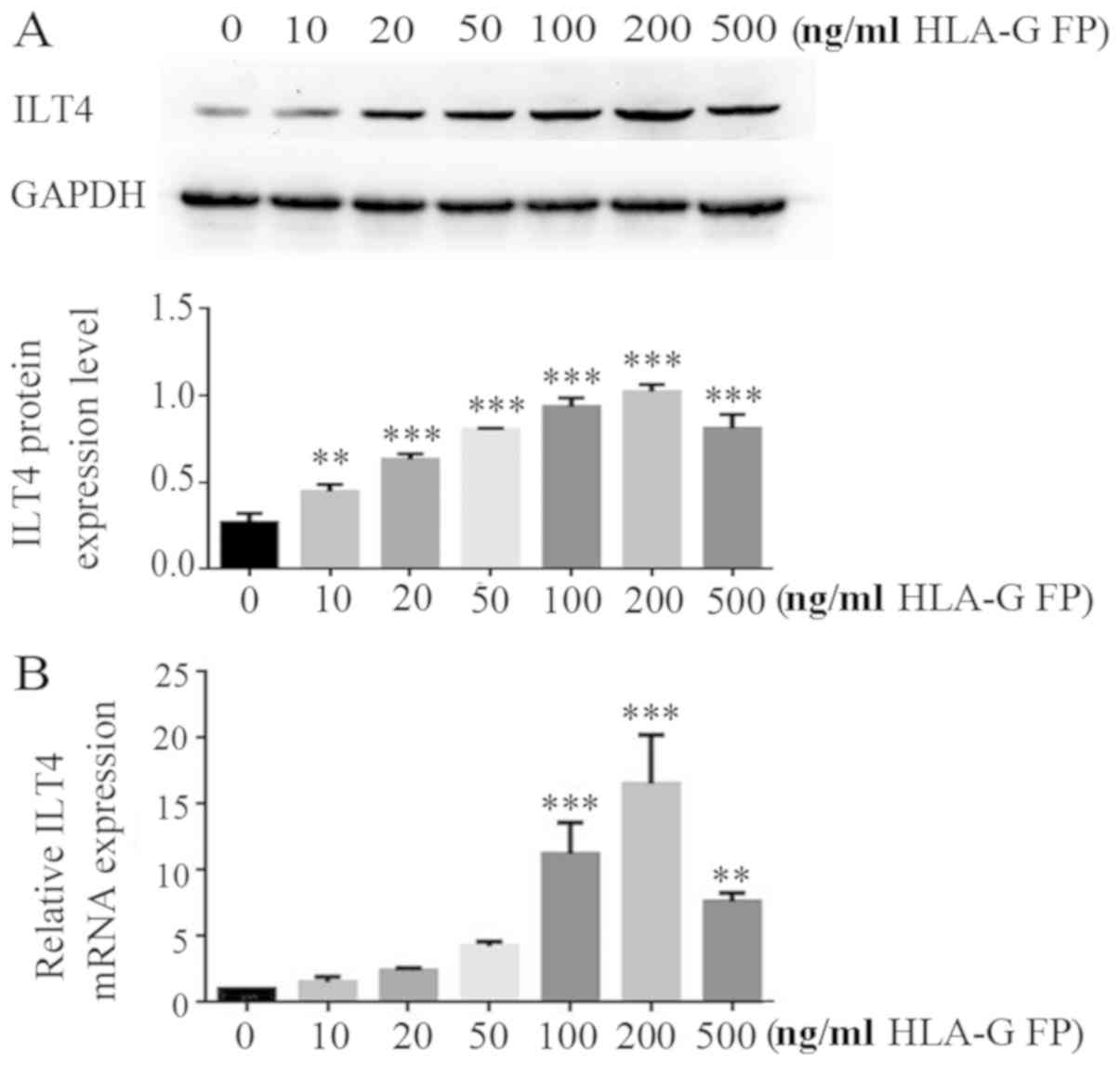
|
1
|
Liang R, Lin Y, Yuan CL, Liu ZH, Li YQ,
Luo XL, Ye JZ and Ye HH: High expression of estrogen related
receptor α is signifi cantly associated with poor prognosis in
patients with colorectal cancer. Oncol Lett. 15:5933–5939.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Petera J, Dušek L, Sirák I, Soumarova R
and Jarkovsky J: Cancer in the elderly in the Czech Republic. Eur J
Cancer Care (Engl). 24:163–178. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Pitule P, Vycital O, Bruha J, Novak P,
Hosek P, Treska V, Hlavata I, Soucek P, Kralickova M and Liska V:
Differential expression and prognostic role of selected genes in
colorectal cancer patients. Anticancer Res. 33:4855–4865.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Colonna M, Nakajima H and Cella M: A
family of inhibitory and activating Ig like receptors that modulate
function of lymphoid and myeloid cells. Semin Immunol. 12:121–127.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Borges L and Cosman D: LIRs/ILTs/MIRs,
inhibitory and stimulatory Ig superfamily receptors expressed in
myeloid and lymphoid cells. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 11:209–217.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shiroishi M, Tsumoto K, Amano K,
Shirakihara Y, Colonna M, Braud VM, Allan DS, Makadzange A, Rowland
Jones S, Willcox B, et al: Human inhibitory receptors Ig like
transcript 2 (ILT2) and ILT4 compete with CD8 for MHC class I
binding and bind preferentially to HLA-G. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:8856–8861. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Nakajima H, Asai A, Okada A, Ping L,
Hamajima F, Sata T and Isobe K: Transcriptional regulation of ILT
family receptors. J Immunol. 171:6611–6620. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sun Y, Liu J, Gao P, Wang Y and Liu C:
Expression of Ig like transcript 4 inhibitory receptor in human non
small cell lung cancer. Chest. 134:783–788. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu J, Wang L, Gao W, Li L, Cui X, Yang H,
Lin W, Dang Q, Zhang N and Sun Y: Inhibitory receptor
immunoglobulin like transcript 4 was highly expressed in primary
ductal and lobular breast cancer and significantly correlated with
IL 10. Diagn Pathol. 9:852014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zhang Y, Zhao J, Qiu L, Zhang P, Li J,
Yang D, Wei X, Han Y, Nie S and Sun Y: Co expression of ILT4/HLA-G
in human non small cell lung cancer correlates with poor prognosis
and ILT4 HLA-G interaction activates ERK signaling. Tumour Biol.
37:11187–11198. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Djurisic S and Hviid TV: HLA Class Ib
Molecules and Immune Cells in Pregnancy and Preeclampsia. Front
Immunol. 5:6522014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
LeMaoult J, Zafaranloo K, Le Danff C and
Carosella ED: HLA-G up regulates ILT2, ILT3, ILT4, and KIR2DL4 in
antigen presenting cells, NK cells, and T cells. FASEB J.
19:662–664. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Köstlin N, Ostermeir AL, Spring B, Schwarz
J, Marmé A, Walter CB, Poets CF and Gille C: HLA-G promotes myeloid
derived suppressor cell accumulation and suppressive activity
during human pregnancy through engagement of the receptor ILT4. Eur
J Immunol. 47:374–384. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Rouas Freiss N, Moreau P, LeMaoult J and
Carosella ED: The dual role of HLA-G in cancer. J Immunol Res.
2014:3597482014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rouas Freiss N, LeMaoult J, Verine J,
Tronik Le, Roux D, Culine S, Hennequin C, Desgrandchamps F and
Carosella ED: Intratumor heterogeneity of immune checkpoints in
primary renal cell cancer: Focus on HLA-G/ILT2/ILT4.
OncoImmunology. 6:e13420232017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Özgül Özdemir RB, Özdemir AT, Oltulu F,
Kurt K, Yiğittürk G and Kırmaz C: A comparison of cancer stem cell
markers and nonclassical major histocompatibility complex antigens
in colorectal tumor and noncancerous tissues. Ann Diagn Pathol.
25:60–63. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Alaoui L, Palomino G, Zurawski S, Zurawski
G, Coindre S, Dereuddre Bosquet N, Lecuroux C, Goujard C, Vaslin B,
Bourgeois C, et al: Early SIV and HIV infection promotes the
LILRB2/MHC I inhibitory axis in cDCs. Cell Mol Life Sci.
75:1871–1887. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Nowak I, Wilczyńska K, Wilczyński JR,
Malinowski A, Radwan P, Radwan M and Kuśnierczyk P: KIR, LILRB and
their Ligands’ Genes as Potential Biomarkers in Recurrent
Implantation Failure. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 65:391–399.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Guerra de Blas PC, Villaseñor Talavera YS,
Cruz González DJ, Ba randa L, Doníz Padilla L, Abud Mendoza C,
González Amaro R and Monsiváis Urenda AE: Analysis of the
Expression and Function of Immunoglobulin Like Transcript 4 (ILT4,
LILRB2) in Dendritic Cells from Patients with Systemic Lupus
Erythematosus. J Immunol Res. 2016:41630942016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Edge SB and Compton CC: The American Joint
Committee on Cancer: The 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging
manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1471–1474. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real time quantitative PCR and
the 2(Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Gao A, Sun Y and Peng G: ILT4 functions as
a potential checkpoint molecule for tumor immunotherapy. Biochim
Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 1869:278–285. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Castellaneta A, Mazariegos GV, Nayyar N,
Zeevi A and Thomson AW: HLA-G level on monocytoid dendritic cells
correlates with regulatory T cell Foxp3 expression in liver
transplant tolerance. Transplantation. 91:1132–1140. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liang S, Ristich V, Arase H, Dausset J,
Carosella ED and Horuzsko A: Modulation of dendritic cell
differentiation by HLA-G and ILT4 requires the IL 6 STAT3 signaling
pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:8357–8362. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Ristich V, Zhang W, Liang S and Horuzsko
A: Mechanisms of prolongation of allograft survival by HLA-G/ILT4
modified dendritic cells. Hum Immunol. 68:264–271. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Carosella ED, Rouas Freiss N, Tronik Le,
Roux D, Moreau P and LeMaoult J: HLA-G: An Immune Checkpoint
Molecule. Adv Immunol. 127:33–144. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Apps R, Gardner L and Moffett A: A
critical look at HLA-G. Trends Immunol. 29:313–321. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zeestraten EC, Reimers MS, Saadatmand S,
Goossens Beumer IJ, Dekker JW, Liefers GJ, van den Elsen PJ, van de
Velde CJ and Kuppen PJ: Combined analysis of HLA class I, HLA E and
HLA-G predicts prognosis in colon cancer patients. Br J Cancer.
110:459–468. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Guo ZY, Lv YG, Wang L, Shi SJ, Yang F,
Zheng GX, Wen WH and Yang AG: Predictive value of HLA-G and HLA E
in the prognosis of colorectal cancer patients. Cell Immunol.
293:10–16. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Reimers MS, Engels CC, Putter H, Morreau
H, Liefers GJ, van de Velde CJ and Kuppen PJ: Prognostic value of
HLA class I, HLA E, HLA-G and Tregs in rectal cancer: A
retrospective cohort study. BMC Cancer. 14:4862014. View Article : Google Scholar
|