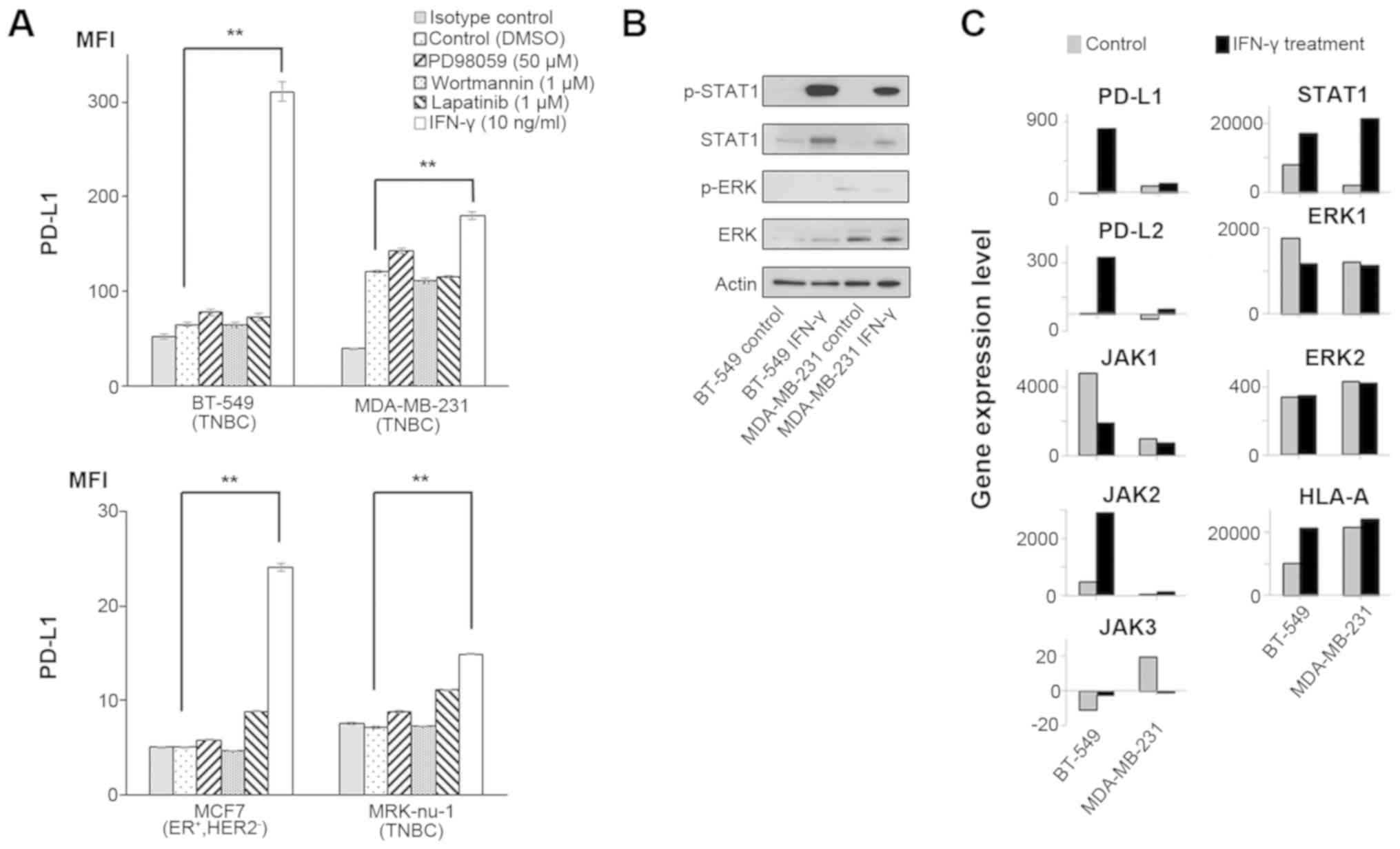
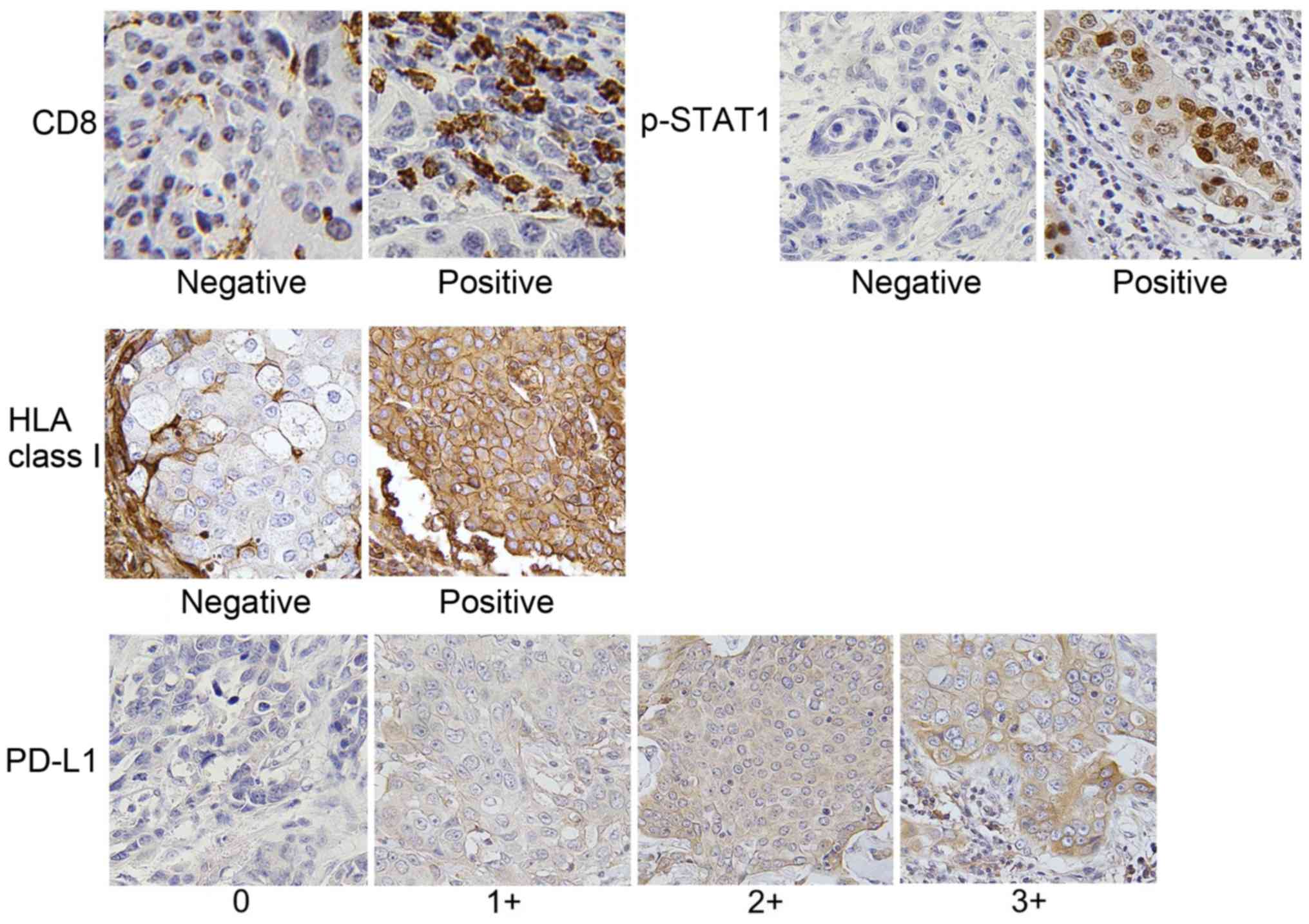
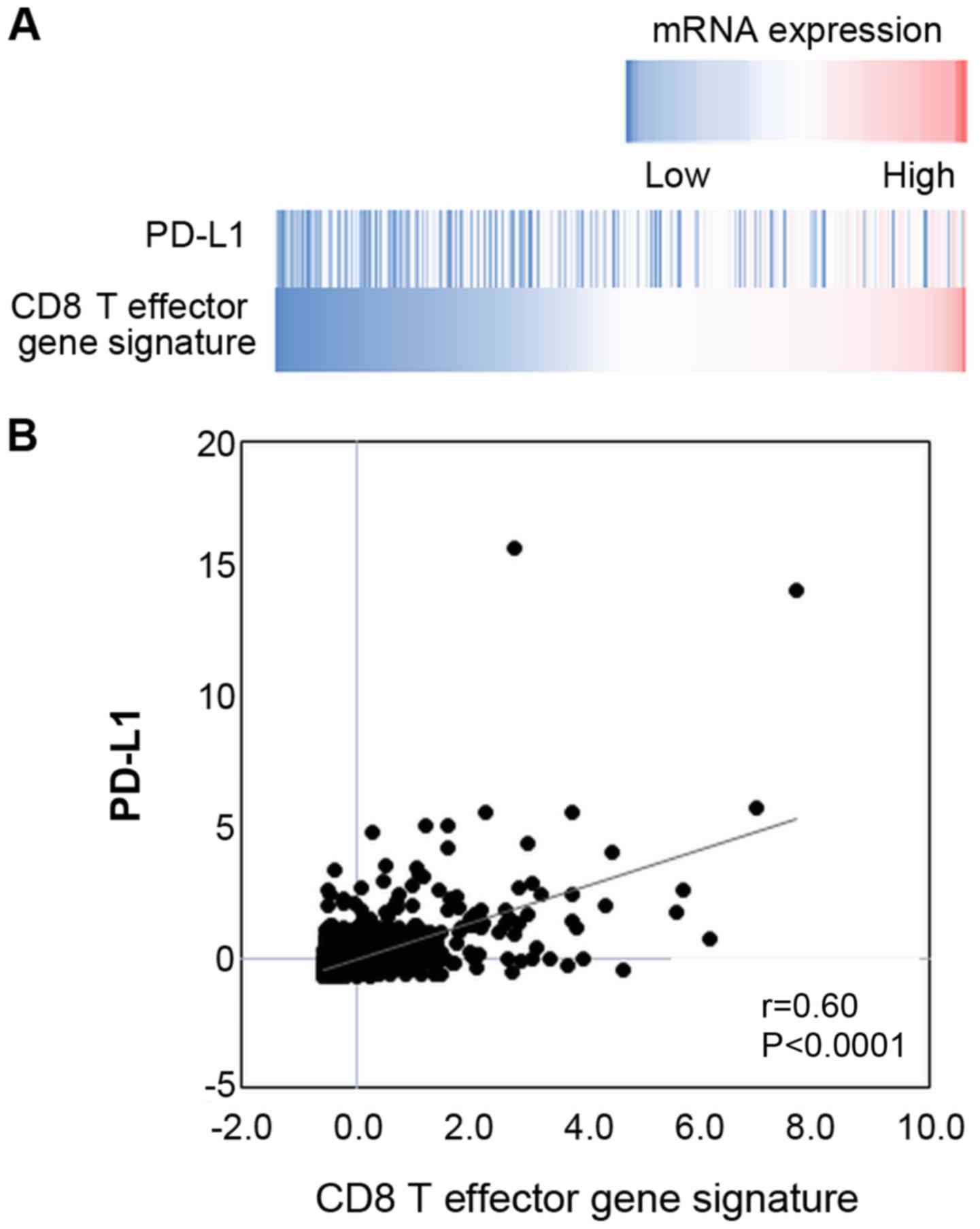
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang J, Lv H, Xue Z, Wang L and Bai Z:
Temporal Trends of Common Female Malignances on Breast, Cervical,
and Ovarian Cancer Mortality in Japan, Republic of Korea, and
Singapore: Application of the Age-Period-Cohort Model. BioMed Res
Int. 2018:53074592018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sørlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T,
Geisler S, Johnsen H, Hastie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey
SS, et al: Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas
distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 98:10869–10874. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Coates AS, Winer EP, Goldhirsch A, Gelber
RD, Gnant M, Piccart-Gebhart M, Thürlimann B and Senn HJ; Panel
Members: Tailoring therapies - improving the management of early
breast cancer: St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the
Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2015. Ann Oncol.
26:1533–1546. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Topalian SL, Drake CG and Pardoll DM:
Immune checkpoint blockade: A common denominator approach to cancer
therapy. Cancer Cell. 27:450–461. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Borghaei H, Paz-Ares L, Horn L, Spigel DR,
Steins M, Ready NE, Chow LQ, Vokes EE, Felip E, Holgado E, et al:
Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Nonsquamous Non-Small-Cell
Lung Cancer. N Engl J Med. 373:1627–1639. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kang YK, Boku N, Satoh T, Ryu MH, Chao Y,
Kato K, Chung HC, Chen JS, Muro K, Kang WK, et al: Nivolumab in
patients with advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction
cancer refractory to, or intolerant of, at least two previous
chemotherapy regimens (ONO-4538-12 ATTRACTION-2): A randomised,
double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet.
390:2461–2471. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Escudier B, Motzer RJ, Sharma P, Wagstaff
J, Plimack ER, Hammers HJ, Donskov F, Gurney H, Sosman JA, Zalewski
PG, et al: Treatment Beyond Progression in Patients with Advanced
Renal Cell Carcinoma Treated with Nivolumab in CheckMate 025. Eur
Urol. 72:368–376. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nanda R, Chow LQ, Dees EC, Berger R, Gupta
S, Geva R, Pusztai L, Pathiraja K, Aktan G, Cheng JD, et al:
Pembrolizumab in Patients With Advanced Triple-Negative Breast
Cancer: Phase Ib KEYNOTE-012 Study. J Clin Oncol. 34:2460–2467.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Emens LA, Braiteh FS, Cassier P, Delord
JP, Eder JP, Fasso M, Xiao Y, Wang Y, Molinero L, Chen DS, et al:
Abstract 2859: Inhibition of PD-L1 by MPDL3280A leads to clinical
activity in patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer
(TNBC). Cancer Res. 75(Suppl 15): 28592015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Schmid P, Cruz C, Braiteh FS, Eder JP,
Tolaney S, Kuter I, Nanda R, Chung C, Cassier P, Delord JP, et al:
Abstract 2986: Atezolizumab in metastatic TNBC (mTNBC): Long-term
clinical outcomes and biomarker analyses. Cancer Res. 77(Suppl 13):
29862017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Mizukami Y, Kono K, Maruyama T, Watanabe
M, Kawaguchi Y, Kamimura K and Fujii H: Downregulation of HLA Class
I molecules in the tumour is associated with a poor prognosis in
patients with oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer.
99:1462–1467. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mimura K, Shiraishi K, Mueller A, Izawa S,
Kua LF, So J, Yong WP, Fujii H, Seliger B, Kiessling R and Kono K:
The MAPK pathway is a predominant regulator of HLA-A expression in
esophageal and gastric cancer. J Immunol. 191:6261–6272. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mimura K, Teh JL, Okayama H, Shiraishi K,
Kua LF, Koh V, Smoot DT, Ashktorab H, Oike T, Suzuki Y, et al:
PD-L1 expression is mainly regulated by interferon gamma associated
with JAK-STAT pathway in gastric cancer. Cancer Sci. 109:43–53.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Schumacher TN and Schreiber RD:
Neoantigens in cancer immunotherapy. Science. 348:69–74. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK and Wittekind
C: International Union against Cancer. TNM Classification of
Malignant Tumours Wiley-Blackwell; West Sussex, UK; Hoboken, NJ:
2010
|
|
17
|
Japanese Breast Cancer Society: General
Rules for Clinical and Pathological Recording of Breast Cancer.
17th edition. Kanehara & Co. Ltd.; Tokyo: 2012
|
|
18
|
Mimura K, Kua LF, Shiraishi K, Kee Siang
L, Shabbir A, Komachi M, Suzuki Y, Nakano T, Yong WP, So J, et al:
Inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway can induce
upregulation of human leukocyte antigen class I without
PD-L1-upregulation in contrast to interferon-γ treatment. Cancer
Sci. 105:1236–1244. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ayers M, Lunceford J, Nebozhyn M, Murphy
E, Loboda A, Kaufman DR, Albright A, Cheng JD, Kang SP, Shankaran
V, et al: IFN-γ-related mRNA profile predicts clinical response to
PD-1 blockade. J Clin Invest. 127:2930–2940. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wallin JJ, Bendell JC, Funke R, Sznol M,
Korski K, Jones S, Hernandez G, Mier J, He X, Hodi FS, et al:
Atezolizumab in combination with bevacizumab enhances
antigen-specific T-cell migration in metastatic renal cell
carcinoma. Nat Commun. 7:126242016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, Dresdner G,
Gross B, Sumer SO, Sun Y, Jacobsen A, Sinha R, Larsson E, et al:
Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical
profiles using the cBio-Portal. Sci Signal. 6:pl12013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, Gross BE,
Sumer SO, Aksoy BA, Jacobsen A, Byrne CJ, Heuer ML, Larsson E, et
al: The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring
multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2:401–404.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sun D and Ding A: MyD88-mediated
stabilization of interferon-gamma-induced cytokine and chemokine
mRNA. Nat Immunol. 7:375–381. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu J, Hamrouni A, Wolowiec D, Coiteux V,
Kuliczkowski K, Hetuin D, Saudemont A and Quesnel B: Plasma cells
from multiple myeloma patients express B7-H1 (PD-L1) and increase
expression after stimulation with IFN-{gamma} and TLR ligands via a
MyD88-, TRAF6-, and MEK-dependent pathway. Blood. 110:296–304.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yamamoto R, Nishikori M, Tashima M, Sakai
T, Ichinohe T, Takaori-Kondo A, Ohmori K and Uchiyama T: B7-H1
expression is regulated by MEK/ERK signaling pathway in anaplastic
large cell lymphoma and Hodgkin lymphoma. Cancer Sci.
100:2093–2100. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Townsend A and Bodmer H: Antigen
recognition by class I-restricted T lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol.
7:601–624. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Šmahel M: PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade Therapy for
Tumors with Downregulated MHC Class I Expression. Int J Mol Sci.
18:182017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Mittendorf EA, Philips AV, Meric-Bernstam
F, Qiao N, Wu Y, Harrington S, Su X, Wang Y, Gonzalez-Angulo AM,
Akcakanat A, et al: PD-L1 expression in triple-negative breast
cancer. Cancer Immunol Res. 2:361–370. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fourcade J, Sun Z, Benallaoua M, Guillaume
P, Luescher IF, Sander C, Kirkwood JM, Kuchroo V and Zarour HM:
Upregulation of Tim-3 and PD-1 expression is associated with tumor
antigen-specific CD8+ T cell dysfunction in melanoma patients. J
Exp Med. 207:2175–2186. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu B, Arakawa Y, Yokogawa R, Tokunaga S,
Terada Y, Murata D, Matsui Y, Fujimoto KI, Fukui N, Tanji M, et al:
PD-1/PD-L1 expression in a series of intracranial germinoma and its
association with Foxp3+ and CD8+ infiltrating lymphocytes. PLoS
One. 13:e01945942018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Huang AC, Postow MA, Orlowski RJ, Mick R,
Bengsch B, Manne S, Xu W, Harmon S, Giles JR, Wenz B, et al: T-cell
invigoration to tumour burden ratio associated with anti-PD-1
response. Nature. 545:60–65. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang ZQ, Milne K, Derocher H, Webb JR,
Nelson BH and Watson PH: PD-L1 and intratumoral immune response in
breast cancer. Oncotarget. 8:51641–51651. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Muenst S, Schaerli AR, Gao F, Däster S,
Trella E, Droeser RA, Muraro MG, Zajac P, Zanetti R, Gillanders WE,
et al: Expression of programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) is
associated with poor prognosis in human breast cancer. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 146:15–24. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mori H, Kubo M, Yamaguchi R, Nishimura R,
Osako T, Arima N, Okumura Y, Okido M, Yamada M, Kai M, et al: The
combination of PD-L1 expression and decreased tumor-infiltrating
lymphocytes is associated with a poor prognosis in triple-negative
breast cancer. Oncotarget. 8:15584–15592. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yagi T, Baba Y, Ishimoto T, Iwatsuki M,
Miyamoto Y, Yoshida N, Watanabe M and Baba H: PD-L1 Expression,
Tumor-infiltrating Lymphocytes, and Clinical Outcome in Patients
With Surgically Resected Esophageal Cancer. Ann Surg. 269:471–478.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Kawazoe A, Kuwata T, Kuboki Y, Shitara K,
Nagatsuma AK, Aizawa M, Yoshino T, Doi T, Ohtsu A and Ochiai A:
Clinicopathological features of programmed death ligand 1
expression with tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte, mismatch repair, and
Epstein-Barr virus status in a large cohort of gastric cancer
patients. Gastric Cancer. 20:407–415. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|