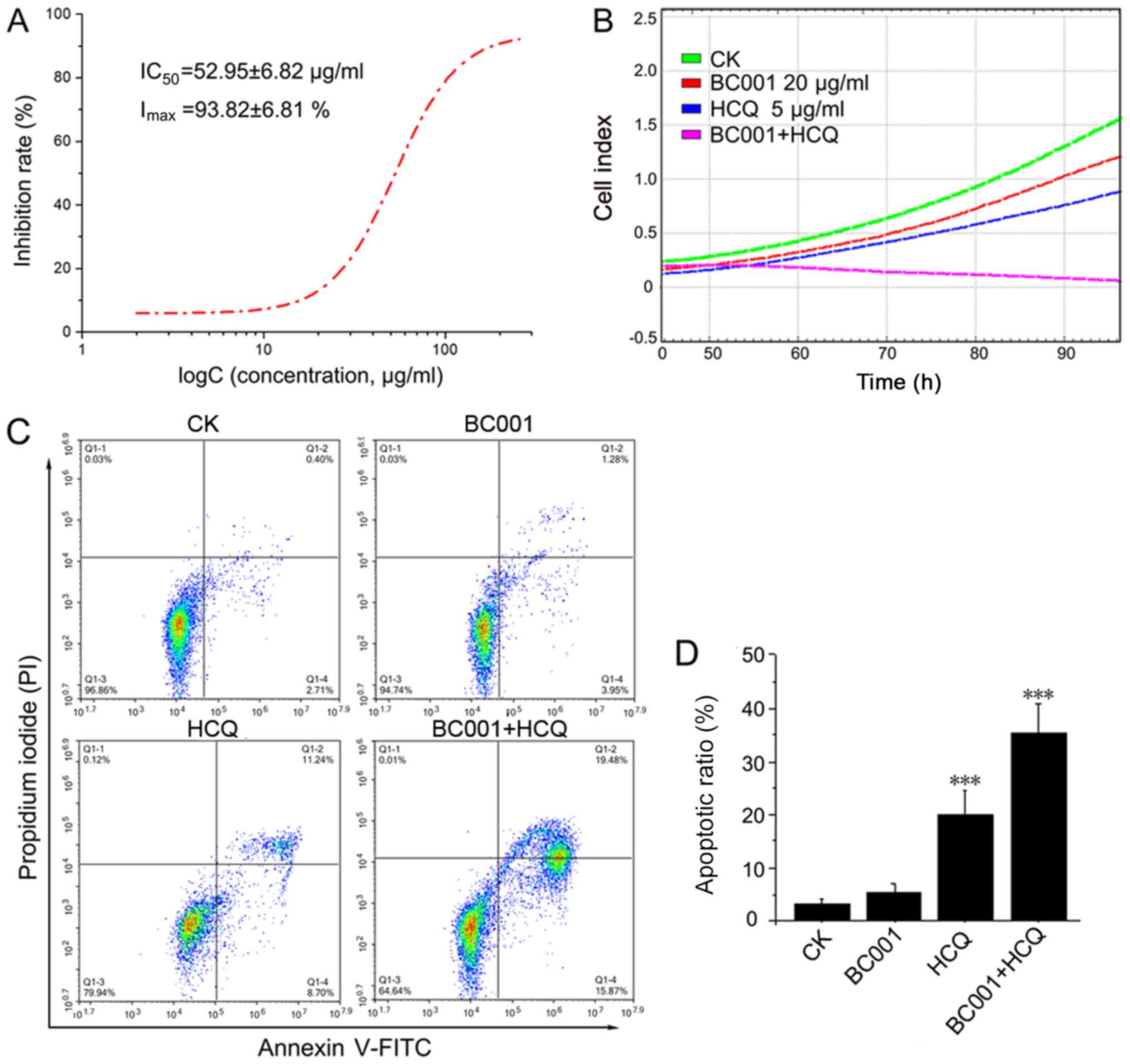
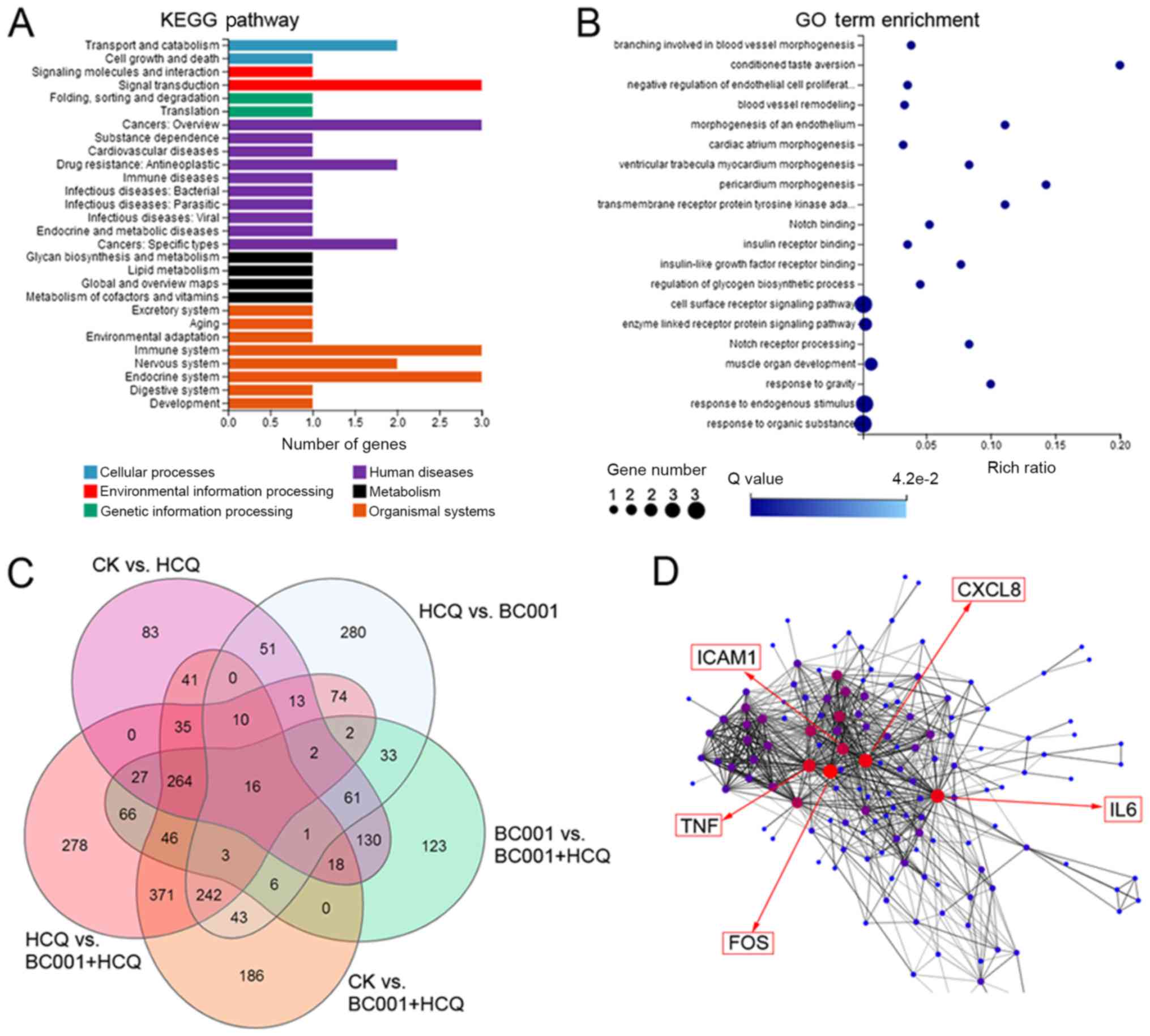
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sharma MR, Joshi SS, Karrison TG, Allen K,
Suh G, Marsh R, Kozloff MF, Polite BN, Catenacci DVT and Kindler
HLA: A UGT1A1 genotype-guided dosing study of modified FOLFIRINOX
in previously untreated patients with advanced gastrointestinal
malignancies. Cancer. 125:1629–1636. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Viallard C and Larrivée B: Tumor
angiogenesis and vascular normalization: Alternative therapeutic
targets. Angiogenesis. 20:409–426. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gilbert MR, Dignam JJ, Armstrong TS, Wefel
JS, Blumenthal DT, Vogelbaum MA, Colman H, Chakravarti A, Pugh S,
Won M, et al: A randomized trial of bevacizumab for newly diagnosed
glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 370:699–708. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Javle M, Smyth EC and Chau I: Ramucirumab:
Successfully targeting angiogenesis in gastric cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 20:5875–5881. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xuan ZX, Li LN, Zhang Q, Xu CW, Yang DX,
Yuan Y, An YH, Wang SS, Li XW and Yuan SJ: Fully human VEGFR2
monoclonal antibody BC001 attenuates tumor angiogenesis and
inhibits tumor growth. Int J Oncol. 45:2411–2420. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Han K, Jin J, Maia M, Lowe J, Sersch MA
and Allison DE: Lower exposure and faster clearance of bevacizumab
in gastric cancer and the impact of patient variables: Analysis of
individual data from AVAGAST phase III trial. AAPS J.
16:105610632014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hu Y-L, Jahangiri A, De Lay M and Aghi MK:
Hypoxia-induced tumor cell autophagy mediates resistance to
anti-angiogenic therapy. Autophagy. 8:979–981. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Levy JMM, Towers CG and Thorburn A:
Targeting autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 17:528–542. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mokarram P, Albokashy M, Zarghooni M,
Moosavi MA, Sepehri Z, Chen QM, Hudecki A, Sargazi A, Alizadeh J,
Moghadam AR, et al: New frontiers in the treatment of colorectal
cancer: Autophagy and the unfolded protein response as promising
targets. Autophagy. 13:781–819. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cook KL, Warri A, Soto- Pantoja DR, Clarke
PA, Cruz MI, Zwart A and Clarke R: Hydroxychloroquine inhibits
autophagy to potentiate antiestrogen responsiveness in
ER+ breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 20:3222–3232. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rosenfeld MR, Ye X, Supko JG, Desideri S,
Grossman SA, Brem S, Mikkelson T, Wang D, Chang YC, Hu J, et al: A
phase I/II trial of hydroxychloroquine in conjunction with
radiation therapy and concurrent and adjuvant temozolomide in
patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme. Autophagy.
10:1359–1368. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Selvakumaran M, Amaravadi RK, Vasilevskaya
IA and O'Dwyer PJ: Autophagy inhibition sensitizes colon cancer
cells to antiangiogenic and cytotoxic therapy. Clin Cancer Res.
19:2995–3007. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chiu CH, Lei KF, Yeh WL, Chen P, Chan YS,
Hsu KY and Chen AC: Comparison between xCELLigence biosensor
technology and conventional cell culture system for real-time
monitoring human tenocytes proliferation and drugs cytotoxicity
screening. J Orthop Surg Res. 12:1492017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang Y, Zhang J, Huang Z-H, Huang X-H,
Zheng W-B, Yin X-F, Li Y-L, Li B and He Q-Y: Isodeoxyelephantopin
induces protective autophagy in lung cancer cells via Nrf2- p62-
keap1 feedback loop. Cell Death Dis. 8:e28762017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Gump JM and Thorburn A: Sorting cells for
basal and induced autophagic flux by quantitative ratiometric flow
cytometry. Autophagy. 10:1327–1334. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Alirezaei M, Flynn CT, Wood MR, Harkins S
and Whitton JL: Coxsackievirus can exploit LC3 in both autophagy-
dependent and - independent manners in vivo. Autophagy.
11:1389–1407. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
Dong J-K, Lei H-M, Liang Q, Tang Y-B, Zhou
Y, Wang Y, Zhang S, Li W-B, Tong Y, Zhuang G, et al: Overcoming
erlotinib resistance in EGFR mutation-positive lung adenocarcinomas
through repression of phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase. Theranostics.
8:1808–1823. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Han J, Chen M, Wang Y, Gong B, Zhuang T,
Liang L and Qiao H: Identification of biomarkers based on
differentially expressed genes in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Sci
Rep. 8:99122018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pirola L, Ciesielski O and Balcerczyk A:
The methylation status of the epigenome: Its emerging role in the
regulation of tumor angiogenesis and tumor growth, and potential
for drug targeting. Cancers (Basel). 10:2682018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Mulcahy Levy JM, Zahedi S, Griesinger AM,
Morin A, Davies KD, Aisner DL, Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK,
Fitzwalter BE, Goodall ML, Thorburn J, et al: Autophagy inhibition
overcomes multiple mechanisms of resistance to BRAF inhibition in
brain tumors. eLife. 6:e196712017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhao Z, Xia G, Li N, Su R, Chen X and
Zhong L: Autophagy inhibition promotes bevacizumab- induced
apoptosis and proliferation inhibition in colorectal cancer cells.
J Cancer. 9:3407–3416. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Maes H, Kuchnio A, Carmeliet P and
Agostinis P: Chloroquine anticancer activity is mediated by
autophagy-independent effects on the tumor vasculature. Mol Cell
Oncol. 3:e9700972015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Chen D, Xie J, Fiskesund R, Dong W, Liang
X, Lv J, Jin X, Liu J, Mo S, Zhang T, et al: Chloroquine modulates
antitumor immune response by resetting tumor-associated macrophages
toward M1 phenotype. Nat Commun. 9:8732018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang H, Wang Y, Cao Y, Wu B, Li Y, Fan L,
Tan Z, Jiang Y, Tang J, Hu J, et al: Interleukin- 6, tumor necrosis
factor- alpha and receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa ligand
are elevated in hypertrophic gastric mucosa of
pachydermoperiostosis. Sci Rep. 7:96862017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yin S, Xia C, Wang Y, Wan D, Rao J, Tang
X, Wei J, Wang X, Li M, Zhang Z, et al: Dual receptor recognizing
liposomes containing paclitaxel and hydroxychloroquine for primary
and metastatic melanoma treatment via autophagy-dependent and
independent pathways. J Control Release. 288:148–160. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Figenschau SL, Knutsen E, Urbarova I,
Fenton C, Elston B, Perander M, Mortensen ES and Fenton KA: ICAM1
expression is induced by proinflammatory cytokines and associated
with TLS formation in aggressive breast cancer subtypes. Sci Rep.
8:117202018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
van IJzendoorn DGP, Forghany Z, Liebelt F,
Vertegaal AC, Jochemsen AG, Bovée JVMG, Szuhai K and Baker DA:
Functional analyses of a human vascular tumor FOS variant identify
a novel degradation mechanism and a link to tumorigenesis. J Biol
Chem. 292:21282–21290. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
National Research Council: Guide for the
Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th edition. The National
Academies Press; Washington, DC: 2011
|