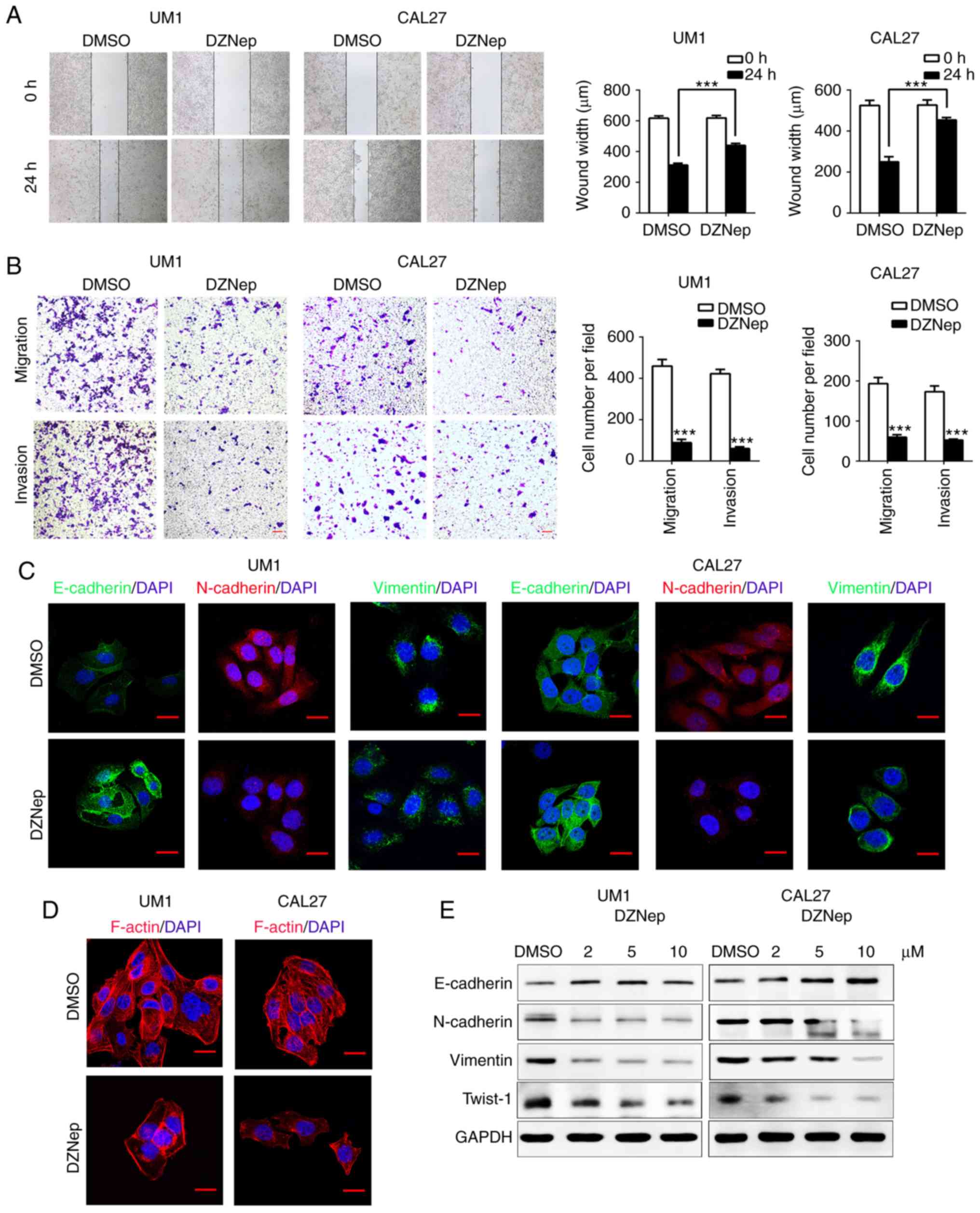
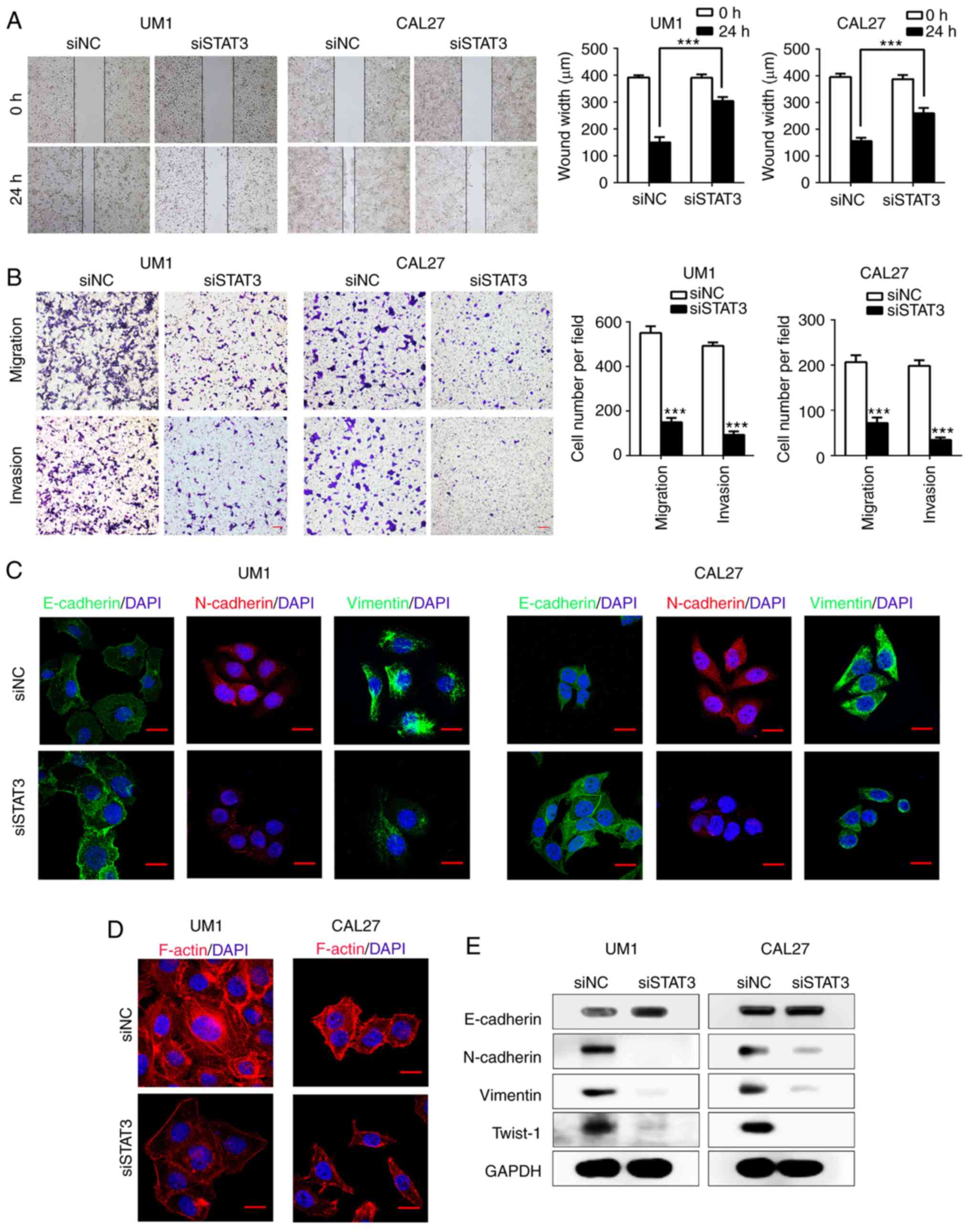
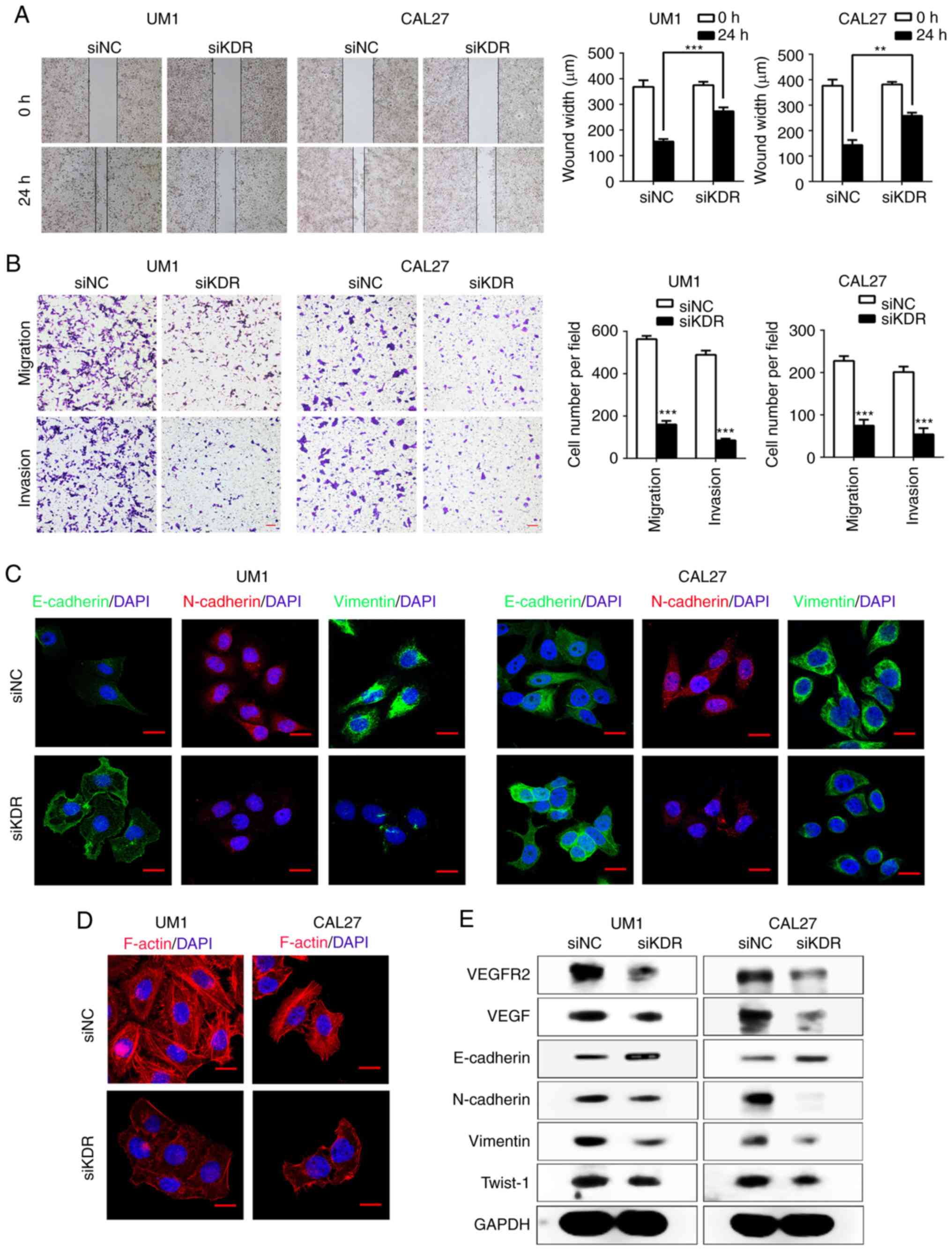
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Leemans CR, Braakhuis BJ and Brakenhoff
RH: The molecular biology of head and neck cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
11:9–22. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Smith A, Teknos TN and Pan Q: Epithelial
to mesenchymal transition in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Oral Oncol. 49:287–292. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
5
|
Sun SS, Zhou X, Huang YY, Kong LP, Mei M,
Guo WY, Zhao MH, Ren Y, Shen Q and Zhang L: Targeting STAT3/miR-21
axis inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition via regulating CDK5
in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 14:2132015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cao R, Wang L, Wang H, Xia L,
Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Jones RS and Zhang Y: Role of
histone H3 lysine 27 methylation in polycomb-group silencing.
Science. 298:1039–1043. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kuzmichev A, Nishioka K, Erdjument-Bromage
H, Tempst P and Reinberg D: Histone methyltransferase activity
associated with a human multiprotein complex containing the
enhancer of zeste protein. Genes Dev. 16:2893–2905. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Karanikolas BD, Figueiredo ML and Wu L:
Comprehensive evaluation of the role of EZH2 in the growth,
invasion, and aggression of a panel of prostate cancer cell lines.
Prostate. 70:675–688. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ahani N, Shirkoohi R, Rokouei M, Alipour
Eskandani M and Nikravesh A: Overexpression of enhancer of zeste
human homolog 2 (EZH2) gene in human cytomegalovirus positive
glioblastoma multiforme tissues. Med Oncol. 31:2522014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Reijm EA, Timmermans AM, Look MP,
Meijer-van Gelder ME, Stobbe CK, van Deurzen CH, Martens JW,
Sleijfer S, Foekens JA, Berns PM and Jansen MP: High protein
expression of EZH2 is related to unfavorable outcome to tamoxifen
in metastatic breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 25:2185–2190. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhou X, Ren Y, Kong LP, Cai GH, Sun SS,
Song WZ, Wang Y, Jin R, Qi L, Mei M, et al: Targeting EZH2
regulates tumor growth and apoptosis through modulating
mitochondria dependent cell-death pathway in HNSCC. Oncotarget.
6:33720–33732. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sun J, Zheng G, Gu Z and Guo Z: MiR-137
inhibits proliferation and angiogenesis of human glioblastoma cells
by targeting EZH2. J Neurooncol. 122:481–489. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Luo H, Jiang Y, Ma S, Chang H, Yi C, Cao
H, Gao H, Guo H, Hou J, Yan J, et al: EZH2 promotes invasion and
metastasis of laryngeal squamous cells carcinoma via
epithelial-mesenchymal transition through H3K27me3. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 479:253–259. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mu Z, Li H, Fernandez SV, Alpaugh KR,
Zhang R and Cristofanilli M: EZH2 knockdown suppresses the growth
and invasion of human inflammatory breast cancer cells. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 32:702013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang C, Liu X, Chen Z, Huang H, Jin Y,
Kolokythas A, Wang A, Dai Y, Wong DT and Zhou X: Polycomb group
protein EZH2-mediated E-cadherin repression promotes metastasis of
oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Carcinog. 52:229–236.
2013. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Frank DA: STAT3 as a central mediator of
neoplastic cellular transformation. Cancer Lett. 251:199–210. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Bar-Natan M, Nelson EA, Xiang M and Frank
DA: STAT signaling in the pathogenesis and treatment of myeloid
malignancies. JAKSTAT. 1:55–64. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xiong A, Yang Z, Shen Y, Zhou J and Shen
Q: Transcription factor STAT3 as a novel molecular target for
cancer prevention. Cancers (Basel). 6:926–957. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Masuda M, Suzui M, Yasumatu R, Nakashima
T, Kuratomi Y, Azuma K, Tomita K, Komiyama S and Weinstein IB:
Constitutive activation of signal transducers and activators of
transcription 3 correlates with cyclin D1 overexpression and may
provide a novel prognostic marker in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. Cancer Res. 62:3351–3355. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim E, Kim M, Woo DH, Shin Y, Shin J,
Chang N, Oh YT, Kim H, Rheey J, Nakano I, et al: Phosphorylation of
EZH2 activates STAT3 signaling via STAT3 methylation and promotes
tumorigenicity of glioblastoma stem-like cells. Cancer Cell.
23:839–852. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dasgupta M, Dermawan JK, Willard B and
Stark GR: STAT3-driven transcription depends upon the dimethylation
of K49 by EZH2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:3985–3990. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Neuchrist C, Erovic BM, Handisurya A,
Steiner GE, Rockwell P, Gedlicka C and Burian M: Vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) expression in
squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. Laryngoscope.
111:1834–1841. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lu W, Chen H, Ye F, Wang F and Xie X: VEGF
induces phosphorylation of STAT3 through binding VEGFR2 in ovarian
carcinoma cells in vitro. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 27:363–369.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhao M, Gao FH, Wang JY, Liu F, Yuan HH,
Zhang WY and Jiang B: JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway activation
mediates tumor angiogenesis by upregulation of VEGF and bFGF in
non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 73:366–374. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xie TX, Huang FJ, Aldape KD, Kang SH, Liu
M, Gershenwald JE, Xie K, Sawaya R and Huang S: Activation of stat3
in human melanoma promotes brain metastasis. Cancer Res.
66:3188–3196. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
U.S. National Institutes of Health:
Laboratory animal welfare: Public Health Service policy on humane
care and use of laboratory animals by awardee institutions; notice.
Fed Regist. 50:19584–19585. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Feldman AT and Wolfe D: Tissue processing
and hematoxylin and eosin staining. Methods Mol Biol. 1180:31–43.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang Y, Wang S, Wu Y, Ren Y, Li Z, Yao X,
Zhang C, Ye N, Jing C, Dong J, et al: Suppression of the growth and
invasion of human head and neck squamous cell carcinomas via
regulating STAT3 signaling and the miR-21/β-catenin axis with
HJC0152. Mol Cancer Ther. 16:578–590. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nieto MA: The ins and outs of the
epithelial to mesenchymal transition in health and disease. Annu
Rev Cell Dev Biol. 27:347–376. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Niu G, Wright KL, Huang M, Song L, Haura
E, Turkson J, Zhang S, Wang T, Sinibaldi D, Coppola D, et al:
Constitutive Stat3 activity up-regulates VEGF expression and tumor
angio-genesis. Oncogene. 21:2000–2008. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wei D, Le X, Zheng L, Wang L, Frey JA, Gao
AC, Peng Z, Huang S, Xiong HQ, Abbruzzese JL and Xie K: Stat3
activation regulates the expression of vascular endothelial growth
factor and human pancreatic cancer angiogenesis and metastasis.
Oncogene. 22:319–329. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xue C, Xie J, Zhao D, Lin S, Zhou T, Shi
S, Shao X, Lin Y, Zhu B and Cai X: The JAK/STAT3 signalling pathway
regulated angiogenesis in an endothelial cell/adipose-derived
stromal cell co-culture, 3D gel model. Cell Prolif. 50:2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Balakrishnan S, Bhat FA, Raja Singh P,
Mukherjee S, Elumalai P, Das S, Patra CR and Arunakaran J: Gold
nanoparticle-conjugated quercetin inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal
transition, angiogenesis and invasiveness via EGFR/VEGFR-2-mediated
pathway in breast cancer. Cell Prolif. 49:678–697. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Diniz-Freitas M, Garcia-Caballero T,
Antúnez-López J, Gándara-Rey JM and Garcia-Garcia A: Reduced
E-cadherin expression is an indicator of unfavourable prognosis in
oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 42:190–200. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Chang JW, Gwak SY, Shim GA, Liu L, Lim YC,
Kim JM, Jung MG and Koo BS: EZH2 is associated with poor prognosis
in head-and-neck squamous cell carcinoma via regulating the
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and chemosensitivity. Oral
Oncol. 52:66–74. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Priceman SJ, Kujawski M, Shen SD,
Cherryholmes GA, Lee H, Zhang C, Kruper L, Mortimer J, Jove R,
Riggs AD and Yu H: Regulation of adipose tissue T cell subsets by
Stat3 is crucial for diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:13079–13084. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Schroeder A, Herrmann A, Cherryholmes G,
Kowolik C, Buettner R, Pal S, Yu H, Müller-Newen G and Jove R: Loss
of androgen receptor expression promotes a stem-like cell phenotype
in prostate cancer through STAT3 signaling. Cancer Res.
74:1227–1237. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Yu H, Lee H, Herrmann A, Buettner R and
Jove R: Revisiting STAT3 signalling in cancer: New and unexpected
biological functions. Nat Rev Cancer. 14:736–746. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Xu Z, Sun Y, Guo Y, Qin G, Mu S, Fan R,
Wang B, Gao W, Wu H, Wang G and Zhang Z: NF-YA promotes invasion
and angiogenesis by upregulating EZH2-STAT3 signaling in human
melanoma cells. Oncol Rep. 35:3630–3638. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wen S, Tian J, Niu Y, Li L, Yeh S and
Chang C: ASC-J9(®), and not casodex or enzalutamide, suppresses
prostate cancer stem/progenitor cell invasion via altering the
EZH2-STAT3 signals. Cancer Lett. 376:377–386. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Steinman RA, Wentzel A, Lu Y, Stehle C and
Grandis JR: Activation of Stat3 by cell confluence reveals negative
regulation of Stat3 by cdk2. Oncogene. 22:3608–3615. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lee H, Lee HJ, Bae IJ, Kim JJ and Kim SH:
Inhibition of STAT3/VEGF/CDK2 axis signaling is critically involved
in the antiangiogenic and apoptotic effects of arsenic herbal
mixture PROS in non-small lung cancer cells. Oncotarget.
8:101771–101783. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hoeben A, Landuyt B, Highley MS, Wildiers
H, Van Oosterom AT and De Bruijn EA: Vascular endothelial growth
factor and angio-genesis. Pharmacol Rev. 56:549–580. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|