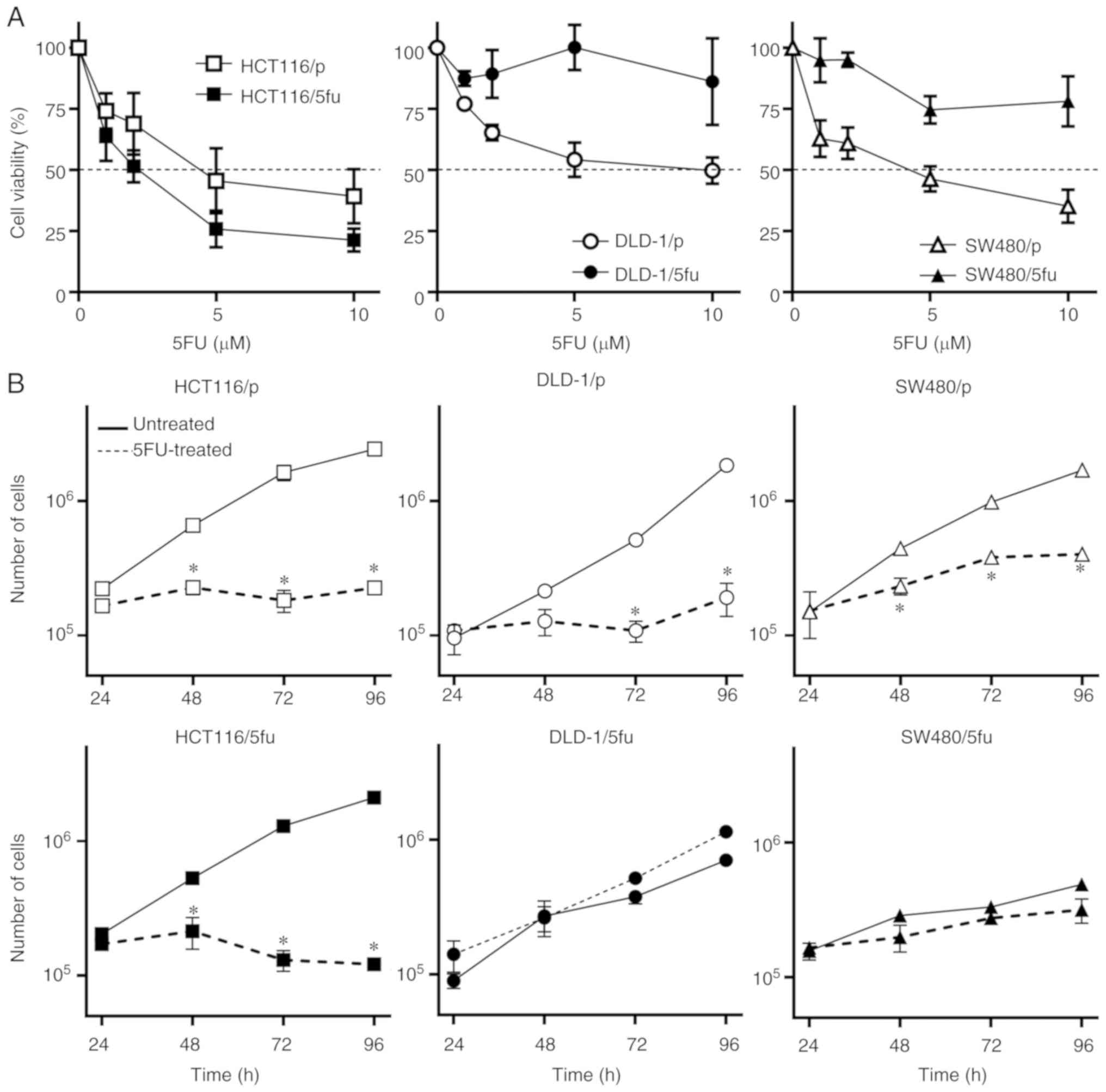
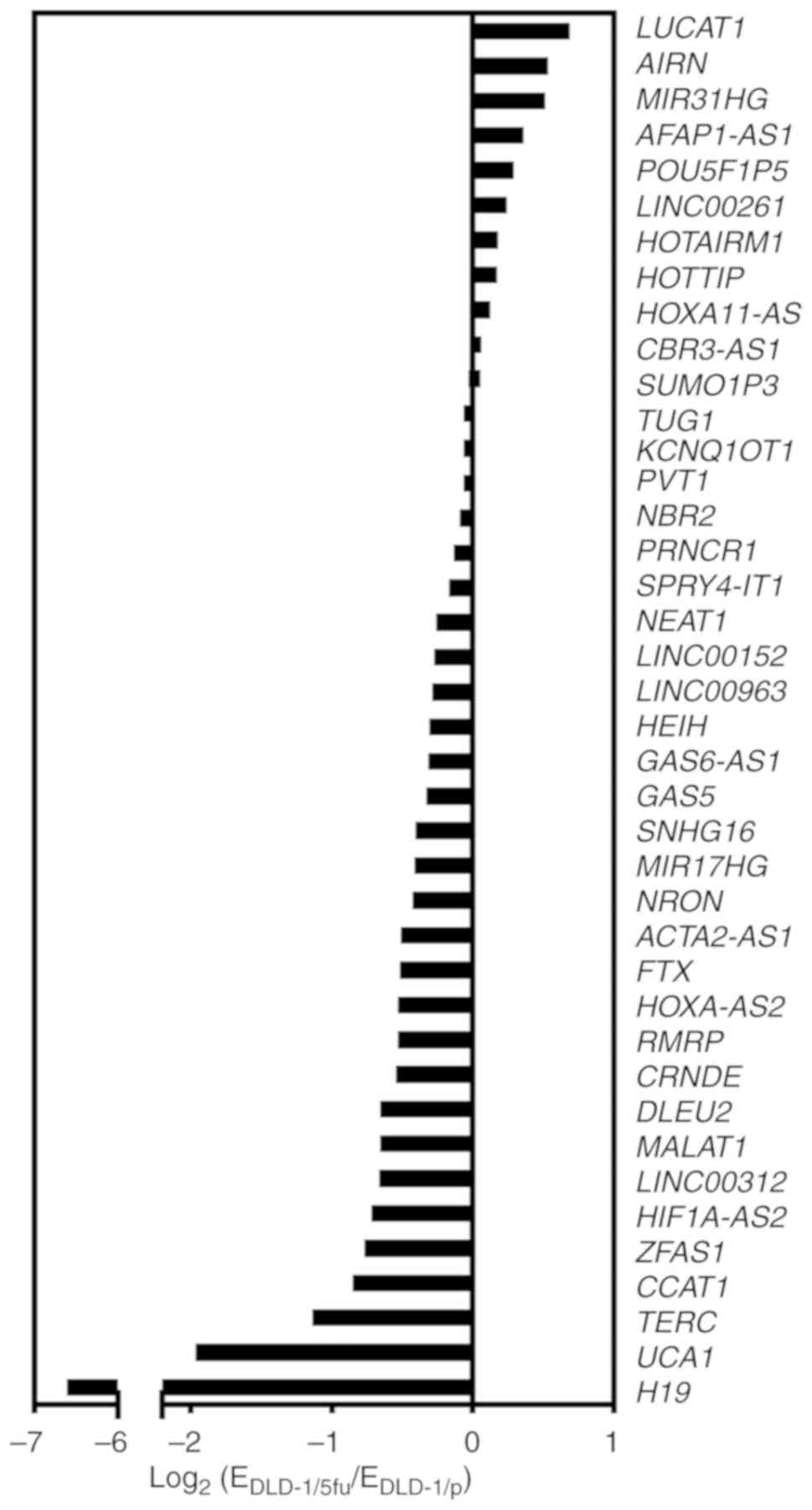
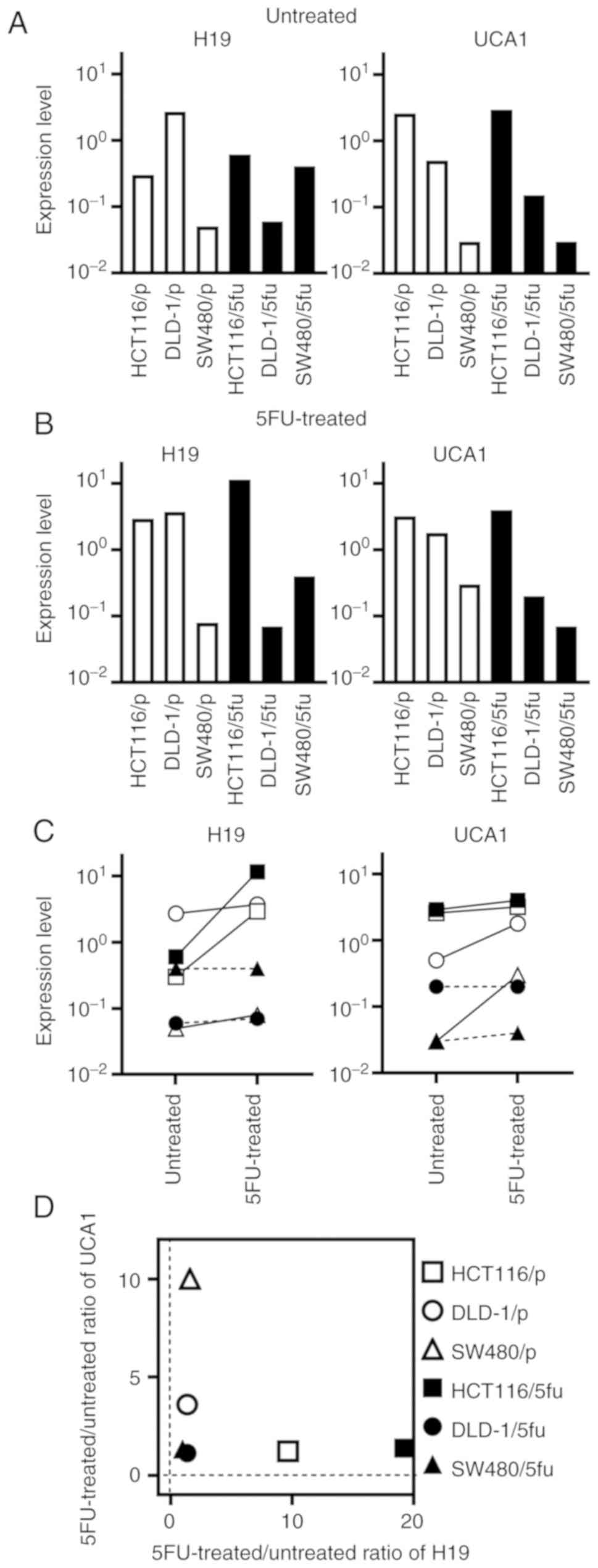
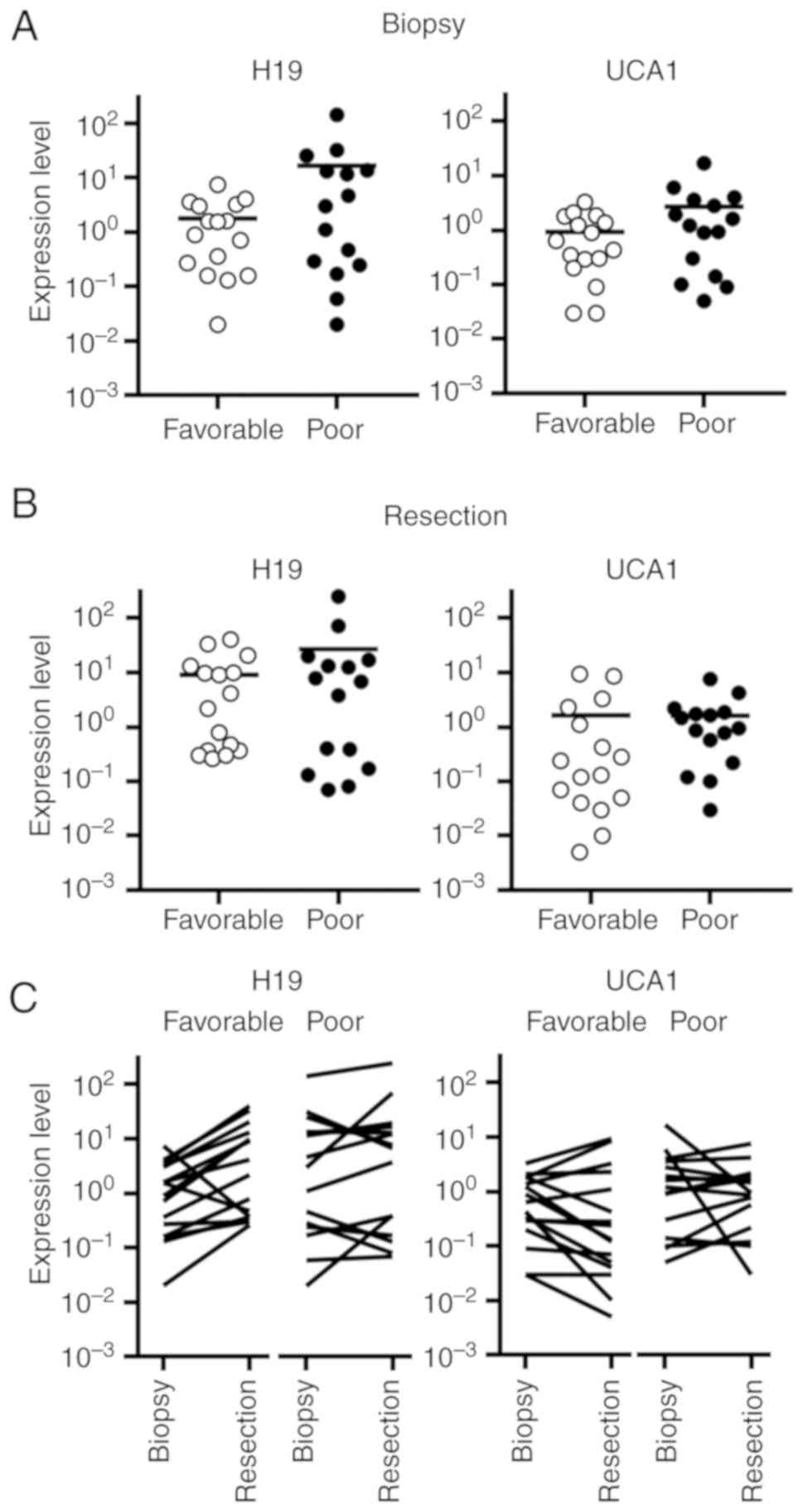
|
1
|
Rödel C, Martus P, Papadoupolos T, Füzesi
L, Klimpfinger M, Fietkau R, Liersch T, Hohenberger W, Raab R,
Sauer R and Wittekind C: Prognostic significance of tumor
regression after preoperative chemoradiotherapy for rectal cancer.
J Clin Oncol. 23:8688–8696. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Beddy D, Hyland JM, Winter DC, Lim C,
White A, Moriarty M, Armstrong J, Fennelly D, Gibbons D and Sheahan
K: A simplified tumor regression grade correlates with survival in
locally advanced rectal carcinoma treated with neoadjuvant
chemoradiotherapy. Ann Surg Oncol. 15:3471–3477. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Marijnen CA, van de Velde CJ, Putter H,
van den Brink M, Maas CP, Martijn H, Rutten HJ, Wiggers T,
Kranenbarg EK, Leer JW and Stiggelbout AM: Impact of short-term
preoperative radiotherapy on health-related quality of life and
sexual functioning in primary rectal cancer: Report of a
multicenter randomized trial. J Clin Oncol. 23:1847–1858. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Parc Y, Zutshi M, Zalinski S, Ruppert R,
Fürst A and Fazio VW: Preoperative radiotherapy is associated with
worse functional results after coloanal anastomosis for rectal
cancer. Dis Colon Rectum. 52:2004–2014. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hasegawa S, Goto S, Matsumoto T, Hida K,
Kawada K, Matsusue R, Yamaguchi T, Nishitai R, Manaka D, Kato S, et
al: A multicenter phase 2 study on the feasibility and efficacy of
neoadjuvant chemotherapy without radiotherapy for locally advanced
rectal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 24:3587–3595. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Koike J, Funahashi K, Yoshimatsu K,
Yokomizo H, Kan H, Yamada T, Ishida H, Ishibashi K, Saida Y,
Enomoto T, et al: Efficacy and safety of neoadjuvant chemotherapy
with oxali-platin, 5-fluorouracil, and levofolinate for T3 or T4
stage II/III rectal cancer: The FACT trial. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 79:519–525. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Koizumi M, Yamada T, Shinji S, Yokoyama Y,
Takahashi G, Iwai T, Takeda K, Hara K, Ohta K, Uchida E and Yoshida
H: Feasibility of neoadjuvant FOLFOX therapy without radiotherapy
for baseline resectable rectal cancer. In Vivo. 32:937–943. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hong YS, Nam BH, Kim KP, Kim JE, Park SJ,
Park YS, Park JO, Kim SY, Kim TY, Kim JH, et al: Oxaliplatin,
fluorouracil, and leucovorin versus fluorouracil and leucovorin as
adjuvant chemotherapy for locally advanced rectal cancer after
preoperative chemoradiotherapy (ADORE): An open-label, multicentre,
phase 2, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 15:1245–1253.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Oki E, Murata A, Yoshida K, Maeda K,
Ikejiri K, Munemoto Y, Sasaki K, Matsuda C, Kotake M, Suenaga T, et
al: A randomized phase III trial comparing S-1 versus UFT as
adjuvant chemotherapy for stage II/III rectal cancer (JFMC35-C1:
ACTS-RC). Ann Oncol. 27:1266–1272. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Longley DB, Harkin DP and Johnston PG:
5-fluorouracil: Mechanisms of action and clinical strategies. Nat
Rev Cancer. 3:330–338. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Soong R, Shah N, Salto-Tellez M, Tai BC,
Soo RA, Han HC, Ng SS, Tan WL, Zeps N, Joseph D, et al: Prognostic
significance of thymidylate synthase, dihydropyrimidine
dehydrogenase and thymidine phosphorylase protein expression in
colorectal cancer patients treated with or without
5-fluorouracil-based chemotherapy. Ann Oncol. 19:915–919. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Salonga D, Danenberg KD, Johnson M,
Metzger R, Groshen S, Tsao-Wei DD, Lenz HJ, Leichman CG, Leichman
L, Diasio RB, et al: Colorectal tumors responding to 5-fluorouracil
have low gene expression levels of dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase,
thymidylate synthase, and thymidine phosphorylase. Clin Cancer Res.
6:1322–1327. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tokunaga Y, Sasaki H and Saito T: Clinical
role of orotate phosphoribosyl transferase and dihydropyrimidine
dehydrogenase in colorectal cancer treated with postoperative
fluoropyrimidine. Surgery. 141:346–353. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ribic CM, Sargent DJ, Moore MJ, Thibodeau
SN, French AJ, Goldberg RM, Hamilton SR, Laurent-Puig P, Gryfe R,
Shepherd LE, et al: Tumor microsatellite-instability status as a
predictor of benefit from fluorouracil-based adjuvant chemotherapy
for colon cancer. N Eng J Med. 349:247–257. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Lee H, Kim C, Ku JL, Kim W, Yoon SK, Kuh
HJ, Lee JH, Nam SW and Lee EK and Lee EK: A long non-coding RNA
snaR contributes to 5-fluorouracil resistance in human colon cancer
cells. Mol Cells. 37:540–546. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bian Z, Jin L, Zhang J, Yin Y, Quan C, Hu
Y, Feng Y, Liu H, Fei B, Mao Y, et al: LncRNA-UCA1 enhances cell
proliferation and 5-fluorouracil resistance in colorectal cancer by
inhibiting miR-204-5p. Sci Rep. 6:238922016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xie T, Huang M, Wang Y, Wang L, Chen C and
Chu X: MicroRNAs as regulators, biomarkers and therapeutic targets
in the drug resistance of colorectal cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem.
40:62–76. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bian Z, Zhang J, Li M, Feng Y, Yao S, Song
M, Qi X, Fei B, Yin Y, Hua D and Huang Z: Long non-coding RNA
LINC00152 promotes cell proliferation, metastasis, and confers 5-FU
resistance in colorectal cancer by inhibiting miR-139-5p.
Oncogenesis. 6:3952017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li P, Zhang X, Wang L, Du L, Yang Y, Liu
T, Li C and Wang C: lncRNA HOTAIR Contributes to 5FU resistance
through suppressing miR-218 and activating NF-κB/TS signaling in
colorectal cancer. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 8:356–369. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li J, Li X, Cen C, Ai X, Lin C and Hu G:
The long non-coding RNA ENST00000547547 reduces 5-fluorouracil
resistance of colorectal cancer cells via competitive binding to
microRNA-31. Oncol Rep. 39:217–226. 2018.
|
|
21
|
Qiao L, Liu X, Tang Y, Zhao Z, Zhang J and
Liu H: Knockdown of long non-coding RNA prostate cancer-associated
ncRNA transcript 1 inhibits multidrug resistance and
c-Myc-dependent aggressiveness in colorectal cancer Caco-2 and
HT-29 cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 441:99–108. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wang M, Han D, Yuan Z, Hu H, Zhao Z, Yang
R, Jin Y, Zou C, Chen Y, Wang G, et al: Long non-coding RNA H19
confers 5-Fu resistance in colorectal cancer by promoting
SIRT1-mediated autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 9:11492018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kopp F and Mendell JT: Functional
classification and experimental dissection of long noncoding RNAs.
Cell. 172:393–407. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sanchez Calle A, Kawamura Y, Yamamoto Y,
Takeshita F and Ochiya T: Emerging roles of long non-coding RNA in
cancer. Cancer Sci. 109:2093–2100. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Deng H, Zhang J, Shi J, Guo Z, He C, Ding
L, Tang JH and Hou Y: Role of long non-coding RNA in tumor drug
resistance. Tumour Biol. 37:11623–11631. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Murakami Y, Kazuno H, Emura T, Tsujimoto
H, Suzuki N and Fukushima M: Different mechanisms of acquired
resistance to fluorinated pyrimidines in human colorectal cancer
cells. Int J Oncol. 17:277–283. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Japanese Society for Cancer of the Colon
and Rectum: Japanese Classification of Colorectal, Appendiceal, and
Anal Carcinoma. 9th Edition. Tokyo: Kanehara; 2018
|
|
29
|
Yoshikawa R, Kusunoki M, Yanagi H, Noda M,
Furuyama JI, Yamamura T and Hashimoto-Tamaoki T: Dual antitumor
effects of 5-fluorouracil on the cell cycle in colorectal carcinoma
cells: A novel target mechanism concept for pharmacokinetic
modulating chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 61:1029–1037. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tsang WP, Ng EK, Ng SS, Jin H, Yu J, Sung
JJ and Kwok TT: Oncofetal H19-derived miR-675 regulates tumor
suppressor RB in human colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis.
31:350–358. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Huang J, Zhou N, Watabe K, Lu Z, Wu F, Xu
M and Mo YY: Long non-coding RNA UCA1 promotes breast tumor growth
by suppression of p27 (Kip1). Cell Death Dis. 5:e10082014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tani H, Onuma Y, Ito Y and Torimura M:
Long non-coding RNAs as surrogate indicators for chemical stress
responses in human-induced pluripotent stem cells. PLoS One.
9:e1062822014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|