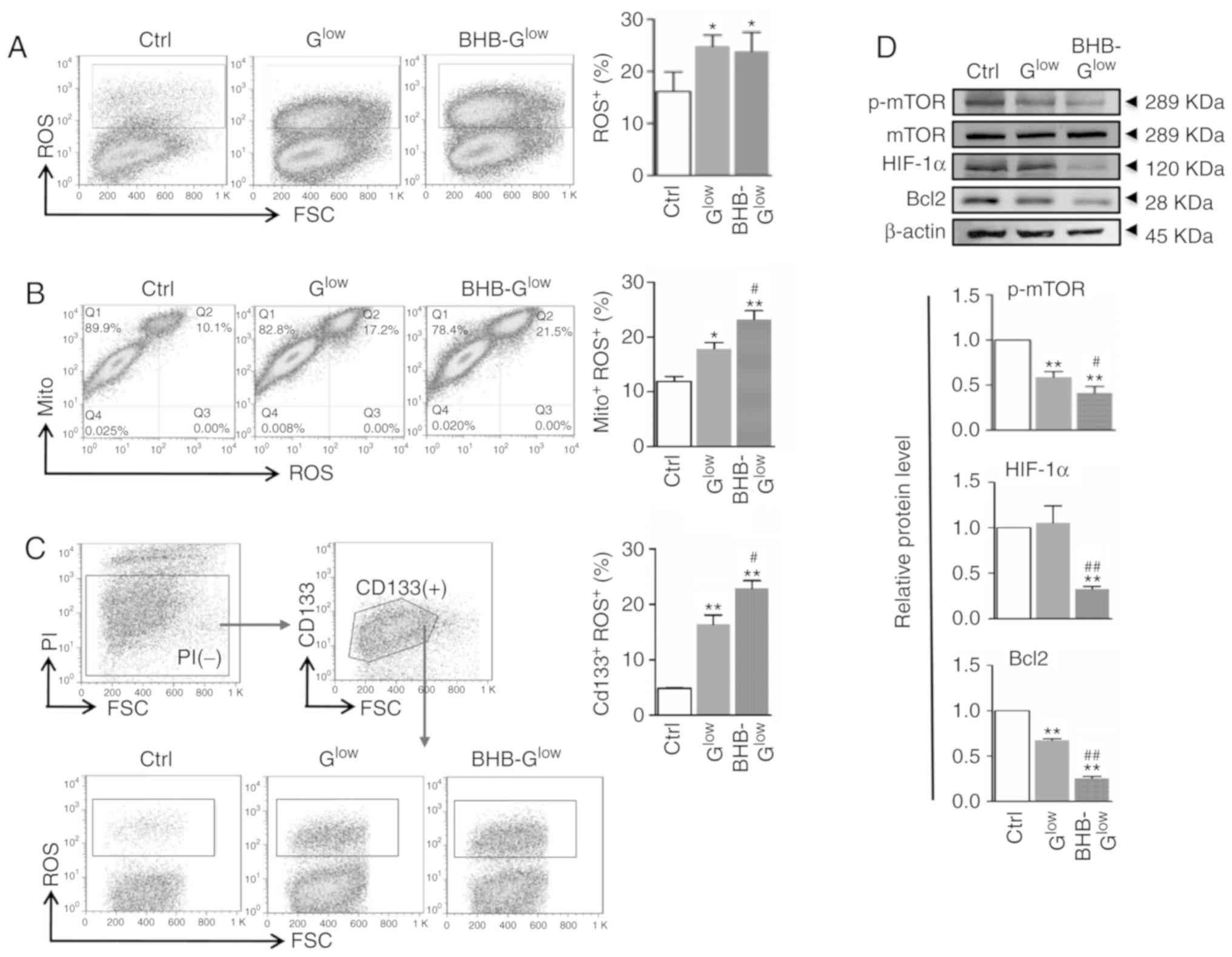
|
1
|
Poteet E, Choudhury GR, Winters A, Li W,
Ryou MG, Liu R, Tang L, Ghorpade A, Wen Y, Yuan F, et al: Reversing
the Warburg effect as a treatment for glioblastoma. J Biol Chem.
288:9153–9164. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller
M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn
U, et al: Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide
for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 352:987–996. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Maurer GD, Brucker DP, Bähr O, Harter PN,
Hattingen E, Walenta S, Mueller-Klieser W, Steinbach JP and Rieger
J: Differential utilization of ketone bodies by neurons and glioma
cell lines: A rationale for ketogenic diet as experimental glioma
therapy. BMC Cancer. 11:3152011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC and Thompson
CB: Understanding the Warburg effect: The metabolic requirements of
cell proliferation. Science. 324:1029–1033. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Seyfried TN, Flores R, Poff AM, D’Agostino
DP and Mukherjee P: Metabolic therapy: A new paradigm for managing
malignant brain cancer. Cancer Lett. 356:289–300. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Hoskin PJ, Sibtain A, Daley FM and Wilson
GD: GLUT1 and CAIX as intrinsic markers of hypoxia in bladder
cancer: Relationship with vascularity and proliferation as
predictors of outcome of ARCON. Br J Cancer. 89:1290–1297. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ward PS and Thompson CB: Metabolic
reprogramming: A cancer hallmark even warburg did not anticipate.
Cancer Cell. 21:297–308. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shen YA, Wang CY, Hsieh YT, Chen YJ and
Wei YH: Metabolic reprogramming orchestrates cancer stem cell
properties in naso-pharyngeal carcinoma. Cell Cycle. 14:86–98.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Klement RJ, Bandyopadhyay PS, Champ CE and
Walach H: Application of Bayesian evidence synthesis to modelling
the effect of ketogenic therapy on survival of high grade glioma
patients. Theor Biol Med Model. 15:122018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Augur ZM, Doyle CM, Li M, Mukherjee P and
Seyfried TN: Nontoxic targeting of energy metabolism in preclinical
VM-M3 experimental glioblastoma. Front Nutr. 5:912018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Champ CE, Palmer JD, Volek JS,
Werner-Wasik M, Andrews DW, Evans JJ, Glass J, Kim L and Shi W:
Targeting metabolism with a ketogenic diet during the treatment of
glioblastoma multiforme. J Neurooncol. 117:125–131. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Martuscello RT, Vedam-Mai V, McCarthy DJ,
Schmoll ME, Jundi MA, Louviere CD, Griffith BG, Skinner CL, Suslov
O, Deleyrolle LP and Reynolds BA: A supplemented high-fat
low-carbohydrate diet for the treatment of glioblastoma. Clin
Cancer Res. 22:2482–2495. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Poff A, Koutnik AP, Egan KM, Sahebjam S,
D’Agostino D and Kumar NB: Targeting the Warburg effect for cancer
treatment: Ketogenic diets for management of glioma. Semin Cancer
Biol. 56:135–148. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ito K and Suda T: Metabolic requirements
for the maintenance of self-renewing stem cells. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:243–256. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sell S: On the stem cell origin of cancer.
Am J Pathol. 176:2584–2594. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Batlle E and Clevers H: Cancer stem cells
revisited. Nat Med. 23:1124–1134. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Folmes CD, Dzeja PP, Nelson TJ and Terzic
A: Metabolic plasticity in stem cell homeostasis and
differentiation. Cell Stem Cell. 11:596–606. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nakano I: Therapeutic potential of
targeting glucose metabolism in glioma stem cells. Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 18:1233–1236. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cairns RA, Harris IS and Mak TW:
Regulation of cancer cell metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:85–95.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Flavahan WA, Wu Q, Hitomi M, Rahim N, Kim
Y, Sloan AE, Weil RJ, Nakano I, Sarkaria JN, Stringer BW, et al:
Brain tumor initiating cells adapt to restricted nutrition through
preferential glucose uptake. Nat Neurosci. 16:1373–1382. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Agnihotri S and Zadeh G: Metabolic
reprogramming in glioblastoma: The influence of cancer metabolism
on epigenetics and unanswered questions. Neuro Oncol. 18:160–172.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Zhou Y, Zhou Y, Shingu T, Feng L, Chen Z,
Ogasawara M, Keating MJ, Kondo S and Huang P: Metabolic alterations
in highly tumorigenic glioblastoma cells: Preference for hypoxia
and high dependency on glycolysis. J Biol Chem. 286:32843–32853.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Campos B, Wan F, Farhadi M, Ernst A,
Zeppernick F, Tagscherer KE, Ahmadi R, Lohr J, Dictus C, Gdynia G,
et al: Differentiation therapy exerts antitumor effects on
stem-like glioma cells. Clin Cancer Res. 16:2715–2728. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gao F, Zhang YF, Zhang ZP, Fu LA, Cao XL,
Zhang YZ, Guo CJ, Yan XC, Yang QC, Hu YY, et al: miR-342-5p
regulates neural stem cell proliferation and differentiation
downstream to Notch signaling in mice. Stem Cell Reports.
8:1032–1045. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hu YY, Fu LA, Li SZ, Chen Y, Li JC, Han J,
Liang L, Li L, Ji CC, Zheng MH and Han H: Hif-1α and Hif-2α
differentially regulate Notch signaling through competitive
interaction with the intracellular domain of Notch receptors in
glioma stem cells. Cancer Lett. 349:67–76. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ilkhanizadeh S and Weiss WA: Starvation
favors glioma stem cells. Nat Neurosci. 16:1359–1361. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bassoy EY, Kasahara A, Chiusolo V,
Jacquemin G, Boydell E, Zamorano S, Riccadonna C, Pellegatta S,
Hulo N, Dutoit V, et al: ER-mitochondria contacts control surface
glycan expression and sensitivity to killer lymphocytes in glioma
stem-like cells. EMBO J. 36:1493–1512. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Halabe Bucay A: The biological
significance of cancer: Mitochondria as a cause of cancer and the
inhibition of glycolysis with citrate as a cancer treatment. Med
Hypotheses. 69:826–828. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mischel PS: HOT Models in flux:
Mitochondrial glucose oxidation fuels glioblastoma growth. Cell
Metab. 15:789–790. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bernini A, Masoodi M, Solari D, Miroz JP,
Carteron L, Christinat N, Morelli P, Beaumont M, Abed-Maillard S,
Hartweg M, et al: Modulation of cerebral ketone metabolism
following traumatic brain injury in humans. J Cereb Blood Flow
Metab. October 24–2018.Epub ahead of print. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fusco S, Leone L, Barbati SA, Samengo D,
Piacentini R, Maulucci G, Toietta G, Spinelli M, McBurney M, Pani G
and Grassi C: A CREB-Sirt1-Hes1 circuitry mediates neural stem cell
response to glucose availability. Cell Rep. 14:1195–1205. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rieger J, Bähr O, Maurer GD, Hattingen E,
Franz K, Brucker D, Walenta S, Kämmerer U, Coy JF, Weller M and
Steinbach JP: ERGO: A pilot study of ketogenic diet in recurrent
glioblastoma. Int J Oncol. 44:1843–1852. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Woolf EC, Curley KL, Liu Q, Turner GH,
Charlton JA, Preul MC and Scheck AC: The ketogenic diet alters the
hypoxic response and affects expression of proteins associated with
angiogenesis, invasive potential and vascular permeability in a
mouse glioma model. PLoS One. 10:e1303572015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Klement RJ and Champ CE: Calories,
carbohydrates, and cancer therapy with radiation: Exploiting the
five R’s through dietary manipulation. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
33:217–229. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Venneti S and Thompson CB: Metabolic
modulation of epigenetics in gliomas. Brain Pathol. 23:217–221.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Singer E, Judkins J, Salomonis N, Matlaf
L, Soteropoulos P, McAllister S and Soroceanu L: Reactive oxygen
species-mediated therapeutic response and resistance in
glioblastoma. Cell Death Dis. 6:e16012015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fu X, Chin RM, Vergnes L, Hwang H, Deng G,
Xing Y, Pai MY, Li S, Ta L, Fazlollahi F, et al: 2-Hydroxyglutarate
Inhibits ATP Synthase and mTOR Signaling. Cell Metab. 22:508–515.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sharma PK, Bhardwaj R, Dwarakanath BS and
Varshney R: Metabolic oxidative stress induced by a combination of
2-DG and 6-AN enhances radiation damage selectively in malignant
cells via non-coordinated expression of antioxidant enzymes. Cancer
Lett. 295:154–166. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhao Y, Hu X, Liu Y, Dong S, Wen Z, He W,
Zhang S, Huang Q and Shi M: ROS signaling under metabolic stress:
Cross-talk between AMPK and AKT pathway. Mol Cancer. 16:792017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Shimazu T, Hirschey MD, Newman J, He W,
Shirakawa K, Le Moan N, Grueter CA, Lim H, Saunders LR, Stevens RD,
et al: Suppression of oxidative stress by β-hydroxybutyrate, an
endogenous histone deacetylase inhibitor. Science. 339:211–214.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Benjamin JS, Pilarowski GO, Carosso GA,
Zhang L, Huso DL, Goff LA, Vernon HJ, Hansen KD and Bjornsson HT: A
keto-genic diet rescues hippocampal memory defects in a mouse model
of Kabuki syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 114:125–130. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Poff AM, Ari C, Arnold P, Seyfried TN and
D’Agostino DP: Ketone supplementation decreases tumor cell
viability and prolongs survival of mice with metastatic cancer. Int
J Cancer. 135:1711–1720. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chung H and Park YK: Rationale,
feasibility and acceptability of ketogenic diet for cancer
treatment. J Cancer Prev. 22:127–134. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|