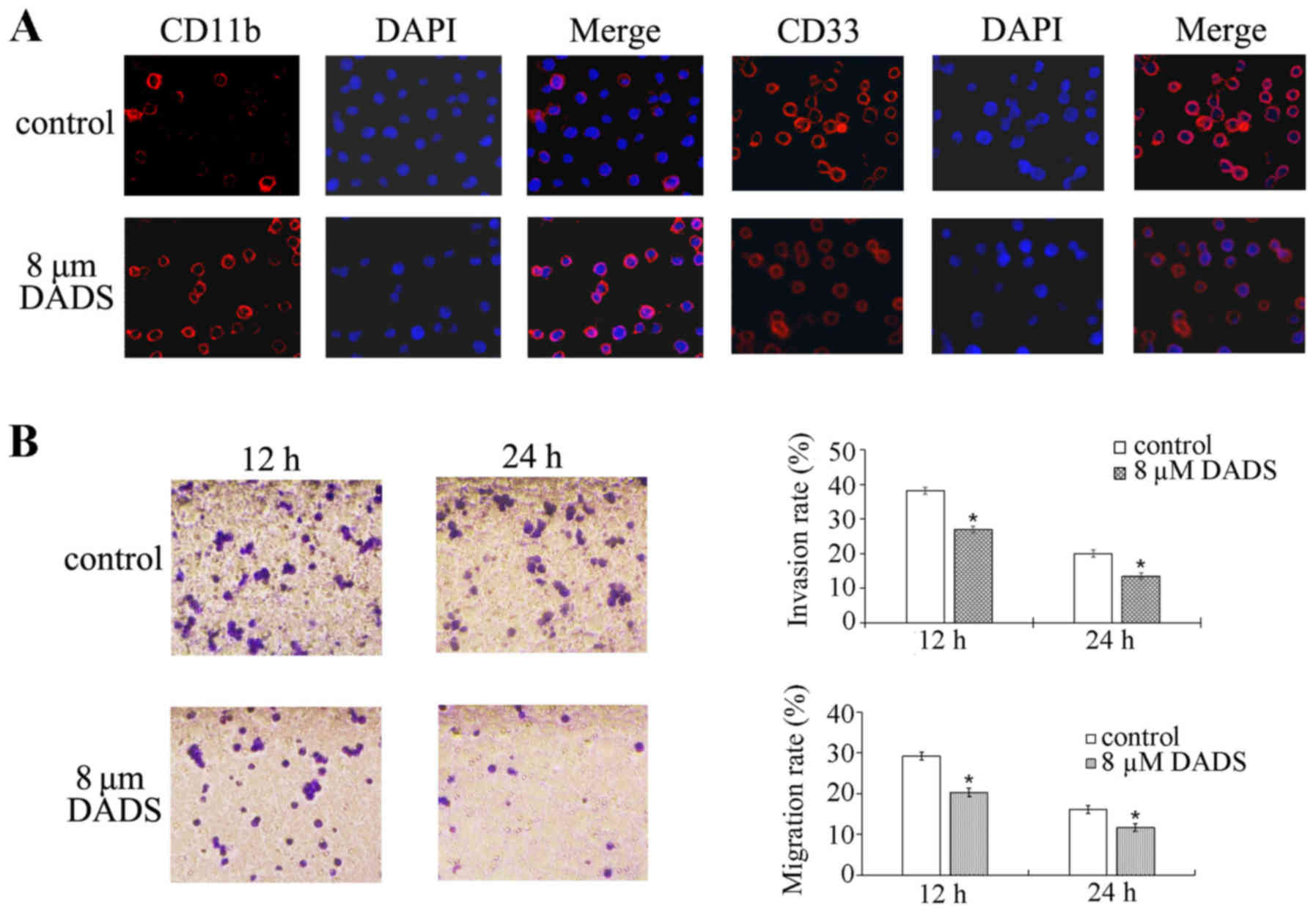
|
1
|
Mahmud H, ter Elst A, Scherpen FJG, de
Boer TM, Kampen KR, de Haas V, Guryev V, Peppelenbosch MM, Kornblau
SM and de Bont ESJM: Peptide microarray of pediatric acute myeloid
leukemia is related to relapse and reveals involvement of DNA
damage response and repair. Oncotarget. 10:4679–4690.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End
Results (SEER) Program, SEER*Stat Database: Incidence - SEER 9 Regs
Research Data, Nov 2017 Sub (1973-2015) - Linked To County
Attributes - Total U.S., 1969-2016 Counties. National Cancer
Institute, DCCPS, Surveillance Research Program. released April
2018, based on the November 2017 submission. https://www.seer.cancer.gov
|
|
3
|
Yi L and Su Q: Molecular mechanisms for
the anti-cancer effects of diallyl disulfide. Food Chem Toxicol.
57:362–370. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhao J, Huang WG, He J, Tan H, Liao QJ and
Su Q: Diallyl disulfide suppresses growth of HL-60 cell through
increasing histone acetylation and p21WAF1 expression in vivo and
in vitro. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 27:1459–1466. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ling H, He J, Tan H, Yi L, Liu F, Ji X, Wu
Y, Hu H, Zeng X, Ai X, et al: Identification of potential targets
for differentiation in human leukemia cells induced by diallyl
disulfide. Int J Oncol. 50:697–707. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nishida E, Maekawa S and Sakai H: Cofilin,
a protein in porcine brain that binds to actin filaments and
inhibits their interactions with myosin and tropomyosin.
Biochemistry. 23:5307–5313. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Van Troys M, Huyck L, Leyman S, Dhaese S,
Vandekerkhove J and Ampe C: Ins and outs of ADF/cofilin activity
and regulation. Eur J Cell Biol. 87:649–667. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Verdoni AM, Aoyama N, Ikeda A and Ikeda S:
Effect of destrin mutations on the gene expression profile in vivo.
Physiol Genomics. 34:9–21. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bernstein BW and Bamburg JR: ADF/cofilin:
A functional node in cell biology. Trends Cell Biol. 20:187–195.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ostrowska Z and Moraczewska J: Cofilin - a
protein controlling dynamics of actin filaments. Postepy Hig Med
Dosw. 71:339–351. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kapoor S: Cofilin-1 overexpression and its
role in tumor growth and progression in systemic malignancies. Int
J Radiat Biol. 90:1132014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Li D, Wang H, Song H, Xu H, Zhao B, Wu C,
Hu J, Wu T, Xie D, Zhao J, et al: The microRNAs miR-200b-3p and
miR-429-5p target the LIMK1/CFL1 pathway to inhibit growth and
motility of breast cancer cells. Oncotarget. 8:85276–85289.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang H, Gu H, Feng J, Qian Y, Yang L, Jin
F, Wang X, Chen J, Shi Y, Lu S, et al: Celastrus orbiculatus
extract suppresses the epithelial-mesenchymal transition by
mediating cytoskeleton rearrangement via inhibition of the Cofilin
1 signaling pathway in human gastric cancer. Oncol Lett.
14:2926–2932. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang TY, DerMardirossian C and Bokoch GM:
Cofilin phosphatases and regulation of actin dynamics. Curr Opin
Cell Biol. 18:26–31. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Schiapparelli P, Guerrero-Cazares H,
Magaña-Maldonado R, Hamilla SM, Ganaha S, Goulin Lippi Fernandes E,
Huang CH, Aranda-Espinoza H, Devreotes P and Quinones-Hinojosa A:
NKCC1 Regulates Migration Ability of Glioblastoma Cells by
Modulation of Actin Dynamics and Interacting with Cofilin.
EBioMedicine. 21:94–103. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhou J, Wang Y, Fei J and Zhang W:
Expression of cofilin 1 is positively correlated with the
differentiation of human epithelial ovarian cancer. Oncol Lett.
4:1187–1190. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Su B, Su J, He H, Wu Y, Xia H, Zeng X, Dai
W, Ai X, Ling H, Jiang H, et al: Identification of potential
targets for diallyl disulfide in human gastric cancer MGC-803 cells
using proteomics approaches. Oncol Rep. 33:2484–2494. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huang YS, Xie N, Su Q, Su J, Huang C and
Liao QJ: Diallyl disulfide inhibits the proliferation of HT-29
human colon cancer cells by inducing differentially expressed
genes. Mol Med Rep. 4:553–559. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Su B, Su J, Zeng Y, Liu F, Xia H, Ma YH,
Zhou ZG, Zhang S, Yang BM, Wu YH, et al: Diallyl disulfide
suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion and
proliferation by downregulation of LIMK1 in gastric cancer.
Oncotarget. 7:10498–10512. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ling H, Zhang LY, Su Q, Song Y, Luo ZY,
Zhou XT, Zeng X, He J, Tan H and Yuan JP: Erk is involved in the
differentiation induced by diallyl disulfide in the human gastric
cancer cell line MGC803. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 11:408–423. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang F, Wu D, Fu H, He F, Xu C, Zhou J, Li
D, Li G, Xu J, Wu Q, et al: Cofilin 1 promotes bladder cancer and
is regulated by TCF7L2. Oncotarget. 8:92043–92054. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nowak D, Mazur AJ, Popow-Woźniak A,
Radwańska A, Mannherz HG and Malicka-Błaszkiewicz M: Subcellular
distribution and expression of cofilin and ezrin in human colon
adenocarcinoma cell lines with different metastatic potential. Eur
J Histochem. 54:e142010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ma M, Zhou L, Guo X, Lv Z, Yu Y, Ding C,
Zhang P, Bi Y, Xie J, Wang L, et al: Decreased cofilin1 expression
is important for compaction during early mouse embryo development.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1793:1804–1810. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pfaendtner J, De La Cruz EM and Voth GA:
Actin filament remodeling by actin depolymerization factor/cofilin.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:7299–7304. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Collazo J, Zhu B, Larkin S, Martin SK, Pu
H, Horbinski C, Koochekpour S and Kyprianou N: Cofilin drives
cell-invasive and metastatic responses to TGF-β in prostate cancer.
Cancer Res. 74:2362–2373. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Huang X, Pan Q, Sun D, Chen W, Shen A,
Huang M, Ding J and Geng M: O-GlcNAcylation of cofilin promotes
breast cancer cell invasion. J Biol Chem. 288:36418–36425. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chung H, Kim B, Jung SH, Won KJ, Jiang X,
Lee CK, Lim SD, Yang SK, Song KH and Kim HS: Does phosphorylation
of cofilin affect the progression of human bladder cancer? BMC
Cancer. 13:452013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tang Q, Ji Q, Tang Y, Chen T, Pan G, Hu S,
Bao Y, Peng W, Yin P, Shimizu H, et al: Mitochondrial translocation
of cofilin-1 promotes apoptosis of gastric cancer BGC-823 cells
induced by ursolic acid. Tumour Biol. 35:2451–2459. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Xiao P, Ma T, Zhou C, Xu Y, Liu Y and
Zhang H: Anticancer effect of docetaxel induces apoptosis of
prostate cancer via the cofilin-1 and paxillin signaling pathway.
Mol Med Rep. 13:4079–4084. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Becker M, De Bastiani MA, Müller CB,
Markoski MM, Castro MA and Klamt F: High cofilin-1 levels correlate
with cisplatin resistance in lung adenocarcinomas. Tumour Biol.
35:1233–1238. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Satoh M, Takano S, Sogawa K, Noda K,
Yoshitomi H, Ishibashi M, Mogushi K, Takizawa H, Otsuka M, Shimizu
H, et al: Immune-complex level of cofilin-1 in sera is associated
with cancer progression and poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer.
Cancer Sci. 108:795–803. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zheng Y, Fang Y, Li S and Zheng B:
Detection of plasma cofilin protein for diagnosis of lung cancer.
Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 33:1551–1553. 2013.In Chinese.
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhou Y, Su J, Shi L, Liao Q and Su Q: DADS
downregulates the Rac1-ROCK1/PAK1-LIMK1-ADF/cofilin signaling
pathway, inhibiting cell migration and invasion. Oncol Rep.
29:605–612. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Borensztajn K, Peppelenbosch MP and Spek
CA: Coagulation Factor Xa inhibits cancer cell migration via
LIMK1-mediated cofilin inactivation. Thromb Res. 125:e323–e328.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Niit M, Arulanandam R, Cass J, Geletu M,
Hoskin V, Côté G, Gunning P, Elliott B and Raptis L: Regulation of
HC11 mouse breast epithelial cell differentiation by the
E-cadherin/Rac axis. Exp Cell Res. 361:112–125. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yang L, Dai F, Tang L, Le Y and Yao W:
Macrophage differentiation induced by PMA is mediated by activation
of RhoA/ROCK signaling. J Toxicol Sci. 42:763–771. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Aggelou H, Chadla P, Nikou S, Karteri S,
Maroulis I, Kalofonos HP, Papadaki H and Bravou V: LIMK/cofilin
pathway and Slingshot are implicated in human colorectal cancer
progression and chemoresistance. Virchows Arch. 472:727–737. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Prunier C, Prudent R, Kapur R, Sadoul K
and Lafanechère L: LIM kinases: Cofilin and beyond. Oncotarget.
8:41749–41763. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gai WT, Yu DP, Wang XS and Wang PT:
Anti-cancer effect of ursolic acid activates apoptosis through
ROCK/PTEN mediated mitochondrial translocation of cofilin-1 in
prostate cancer. Oncol Lett. 12:2880–2885. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ishaq M, Lin BR, Bosche M, Zheng X, Yang
J, Huang D, Lempicki RA, Aguilera-Gutierrez A and Natarajan V: LIM
kinase 1 - dependent cofilin 1 pathway and actin dynamics mediate
nuclear retinoid receptor function in T lymphocytes. BMC Mol Biol.
12:412011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kaji N, Muramoto A and Mizuno K: LIM
kinase-mediated cofilin phosphorylation during mitosis is required
for precise spindle positioning. J Biol Chem. 283:4983–4992. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Zhou T, Wang CH, Yan H, Zhang R, Zhao JB,
Qian CF, Xiao H and Liu HY: Inhibition of the Rac1-WAVE2-Arp2/3
signaling pathway promotes radiosensitivity via downregulation of
cofilin-1 in U251 human glioma cells. Mol Med Rep. 13:4414–4420.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|