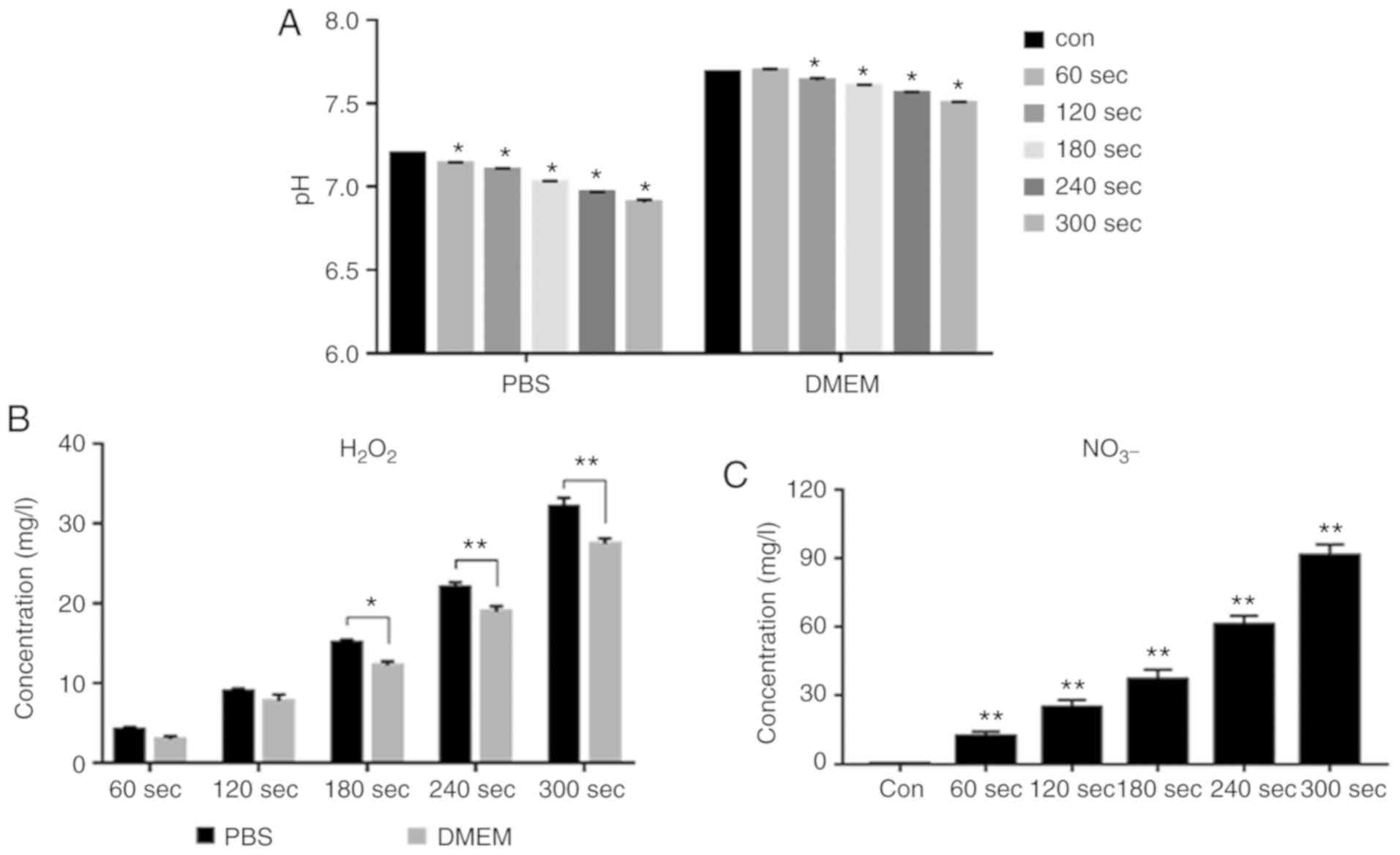
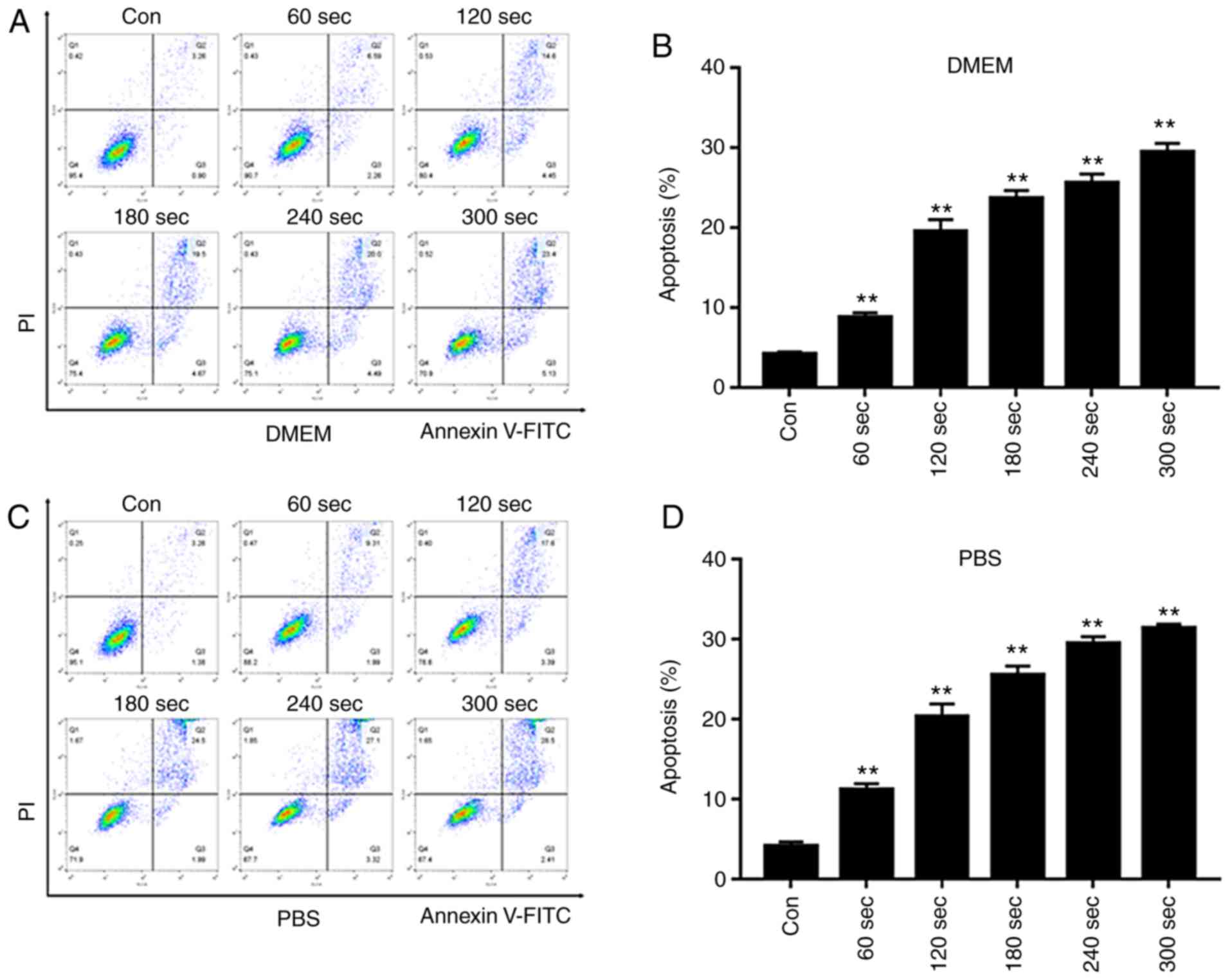
|
1
|
Verkouteren JAC, Ramdas KHR, Wakkee M and
Nijsten T: Epidemiology of basal cell carcinoma: Scholarly review.
Br J Dermatol. 177:359–372. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Muzic JG, Schmitt AR, Wright AC, Alniemi
DT, Zubair AS, Olazagasti Lourido JM, Sosa Seda IM, Weaver AL and
Baum CL: Incidence and trends of basal cell carcinoma and cutaneous
squamous cell carcinoma: A population-based study in olmsted
county, minnesota, 2000 to 2010. Mayo Clin Proc. 92:890–898. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Garcovich S, Colloca G, Sollena P, Andrea
B, Balducci L, Cho WC, Bernabei R and Peris K: Skin cancer
epidemics in the elderly as an emerging issue in geriatric
oncology. Aging Dis. 8:643–661. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pyne JH, Myint E, Barr EM, Clark SP, David
M, Na R and Hou R: Superficial basal cell carcinoma: A comparison
of superficial only subtype with superficial combined with other
subtypes by age, sex and anatomic site in 3150 cases. J Cutan
Pathol. 44:677–683. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lipson EJ, Lilo MT, Ogurtsova A, Esandrio
J, Xu H, Brothers P, Schollenberger M, Sharfman WH and Taube JM:
Basal cell carcinoma: PD-L1/PD-1 checkpoint expression and tumor
regression after PD-1 blockade. J Immunother Cancer. 5:232017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mandel VD, Arginelli F, Pellacani G and
Greco M: Combined carbon dioxide laser with photodynamic therapy
for the treatment of nodular and infiltrative basal cell carcinoma.
G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 152:672–674. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wong CS, Strange RC and Lear JT: Basal
cell carcinoma. BMJ. 327:794–798. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim SJ and Chung TH: Cold atmospheric
plasma jet-generated RONS and their selective effects on normal and
carcinoma cells. Sci Rep. 6:203322016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rashmei Z, Bornasi H and Ghoranneviss M:
Evaluation of treatment and disinfection of water using cold
atmospheric plasma. J Water Health. 14:609–616. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Heinlin J, Morfill G, Landthaler M, Stolz
W, Isbary G, Zimmermann JL, Shimizu T and Karrer S: Plasma
medicine: Possible applications in dermatology. J Dtsch Dermatol
Ges. 8:968–976. 2010.In English, German. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang M, Holmes B, Cheng X, Zhu W, Keidar M
and Zhang LG: Cold atmospheric plasma for selectively ablating
metastatic breast cancer cells. PLoS One. 8:e737412013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Keidar M, Walk R, Shashurin A, Srinivasan
P, Sandler A, Dasgupta S, Ravi R, Guerrero-Preston R and Trink B:
Cold plasma selectivity and the possibility of a paradigm shift in
cancer therapy. Br J Cancer. 105:1295–1301. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ratovitski EA, Cheng X, Yan D, Sherman JH,
Canady J, Trink B and Keidar M: Anti-cancer therapies of 21st
century: Novel approach to treat human cancers using cold
atmospheric plasma. Plasma Proc Polymers. 11:1128–1137. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kalghatgi S, Kelly CM, Cerchar E, Torabi
B, Alekseev O, Fridman A, Friedman G and Azizkhan-Clifford J:
Effects of non-thermal plasma on mammalian cells. PLoS One.
6:e162702011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kaushik NK, Kaushik N, Park D and Choi EH:
Altered antioxidant system stimulates dielectric barrier discharge
plasma-induced cell death for solid tumor cell treatment. PLoS One.
9:e1033492014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Vandamme M, Robert E, Lerondel S, Sarron
V, Ries D, Dozias S, Sobilo J, Gosset D, Kieda C, Legrain B,
Pouvesle JM and Pape AL: ROS implication in a new antitumor
strategy based on non-thermal plasma. Int J Cancer. 130:2185–2194.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wang L, Yang X, Yang C, Gao J, Zhao Y,
Cheng C, Zhao G and Liu S: The inhibition effect of cold
atmospheric plasma-activated media in cutaneous squamous carcinoma
cells. Future Oncol. 15:495–505. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sun JK, Joh HM and Chung TH: Production of
intracellular reactive oxygen species and change of cell viability
induced by atmospheric pressure plasma in normal and cancer cells.
Appl Phys Lett. 103:1537052013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Ishaq M, Evans MD and Ostrikov KK:
Atmospheric pressure gas plasma-induced colorectal cancer cell
death is mediated by Nox2-ASK1 apoptosis pathways and oxidative
stress is mitigated by Srx-Nrf2 anti-oxidant system. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1843:2827–2837. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nguyen NH, Park HJ, Yang SS, Choi KS and
Lee JS: Anti-cancer efficacy of nonthermal plasma dissolved in a
liquid, liquid plasma in heterogeneous cancer cells. Sci Rep.
6:290202016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yan D, Nourmohammadi N, Bian K, Murad F,
Sherman JH and Keidar M: Stabilizing the cold plasma-stimulated
medium by regulating medium's composition. Sci Rep. 6:260162016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yan D, Sherman JH, Cheng X, Ratovitski E,
Canady J and Keidar M: Controlling plasma stimulated media in
cancer treatment application. Appl Phys Lett. 105:2241012014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Adachi T, Tanaka H, Nonomura S, Hara H,
Kondo S and Hori M: Plasma-activated medium induces A549 cell
injury via a spiral apoptotic cascade involving the
mitochondrial-nuclear network. Free Radic Biol Med. 79:28–44. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Tanaka H, Nakamura K, Mizuno M, Ishikawa
K, Takeda K, Kajiyama H, Utsumi F, Kikkawa F and Hori M:
Non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma activates lactate in
Ringer's solution for anti-tumor effects. Sci Rep. 6:362822016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yan D, Cui H, Zhu W, Nourmohammadi N,
Milberg J, Zhang LG, Sherman JH and Keidar M: The specific
vulnerabilities of cancer cells to the cold atmospheric
plasma-stimulated solutions. Sci Rep. 7:44792017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ishaq M, Kumar S, Varinli H, Han ZJ, Rider
AE, Evans MD, Murphy AB and Ostrikov K: Atmospheric gas
plasma-induced ROS production activates TNF-ASK1 pathway for the
induction of melanoma cancer cell apoptosis. Mol Biol Cell.
25:1523–1531. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Keidar M: Plasma for cancer treatment.
Post Communist Economies. 24:2015.
|
|
28
|
Xu H, Klas M, Liu Y, Stack MS and
Ptasinska S: DNA damage in oral cancer cells induced by nitrogen
atmospheric pressure plasma jet. Appl Phys Lett. 102:644–654.
2013.
|
|
29
|
Chang JW, Kang SU, Shin YS, Kim KI, Seo
SJ, Yang SS, Lee JS, Moon E, Baek SJ, Lee K and Kim CH: Non-thermal
atmospheric pressure plasma induces apoptosis in oral cavity
squamous cell carcinoma: Involvement of DNA-damage-triggering
sub-G(1) arrest via the ATM/p53 pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys.
545:133–140. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Utaipan T, Athipornchai A, Suksamrarn A,
Chunsrivirot S and Chunglok W: Isomahanine induces endoplasmic
reticulum stress and simultaneously triggers p38 MAPK-mediated
apoptosis and autophagy in multidrug-resistant human oral squamous
cell carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep. 37:1243–1252. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Menon MB, Gropengießer J, Fischer J,
Novikova L, Deuretzbacher A, Lafera J, Schimmeck H, Czymmeck N,
Ronkina N, Kotlyarov A, et al: p38MAPK/MK2-dependent
phosphorylation controls cytotoxic RIPK1 signalling in inflammation
and infection. Nat Cell Biol. 19:1248–1259. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nadeem A, Ahmad SF, Al-Harbi NO, Fardan
AS, El-Sherbeeny AM, Ibrahim KE and Attia SM: IL-17A causes
depression-like symptoms via NFκB and p38MAPK signaling pathways in
mice: Implications for psoriasis associated depression. Cytokine.
97:14–24. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kang SU, Cho JH, Chang JW, Shin YS, Kim
KI, Park JK, Yang SS, Lee JS, Moon E, Lee K and Kim CH: Nonthermal
plasma induces head and neck cancer cell death: The potential
involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent
mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. Cell Death Dis. 5:e10562014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tanaka H, Mizuno M, Toyokuni S, Maruyama
S, Kodera Y, Terasaki H, Adachi T, Kato M, Kikkawa F and Hori M:
Cancer therapy using non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma with
ultra-high electron density. Phys Plasmas. 22:391–400. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Arndt S, Unger P, Berneburg M, Bosserhoff
AK and Karrer S: Cold atmospheric plasma (CAP) activates
angiogenesis-related molecules in skin keratinocytes, fibroblasts
and endothelial cells and improves wound angiogenesis in an
autocrine and paracrine mode. J Dermatol Sci. 89:181–190. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Haertel B, von Woedtke T, Weltmann KD and
Lindequist U: Non-thermal atmospheric-pressure plasma possible
application in wound healing. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 22:477–490.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Bekeschus S, Kolata J, Winterbourn C,
Kramer A, Turner R, Weltmann KD, Bröker B and Masur K: Hydrogen
peroxide: A central player in physical plasma-induced oxidative
stress in human blood cells. Free Radical Res. 48:542–549. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Yan D, Talbot A, Nourmohammadi N, Sherman
JH, Cheng X and Keidar M: Toward understanding the selective
anticancer capacity of cold atmospheric plasma-a model based on
aquapo-rins (Review). Biointerphases. 10:408012015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Yan D, Sherman JH and Keidar M: Cold
atmospheric plasma, a novel promising anti-cancer treatment
modality. Oncotarget. 8:15977–15995. 2017.
|
|
40
|
Canal C, Fontelo R, Hamouda I,
Guillem-Marti J, Cvelbar U and Ginebra MP: Plasma-induced
selectivity in bone cancer cells death. Free Radic Biol Med.
110:72–80. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhao S, Xiong Z, Xiang M, Meng D, Lei Q,
Li Y, Deng P, Chen M, Tu M, Lu X, et al: Atmospheric pressure room
temperature plasma jets facilitate oxidative and nitrative stress
and lead to endoplasmic reticulum stress dependent apoptosis in
HepG2 cells. PLoS One. 8:e736652013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Arjunan KP and Clyne AM: Non-thermal
dielectric barrier discharge plasma induces angiogenesis through
reactive oxygen species. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc.
2011:2447–2450. 2011.
|
|
43
|
Sun JK, Chung TH, Bae SH and Leem SH:
Induction of apoptosis in human breast cancer cells by a pulsed
atmospheric pressure plasma jet. Appl Phys Lett. 97:237022010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Yan D, Talbot A, Nourmohammadi N, Cheng X,
Canady J, Sherman J and Keidar M: Principles of using cold
atmospheric plasma stimulated media for cancer treatment. Sci Rep.
5:183392015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Almasalmeh A, Krenc D, Wu B and Beitz E:
Structural determinants of the hydrogen peroxide permeability of
aquaporins. FEBS J. 281:647–656. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Bienert GP and Chaumont F:
Aquaporin-facilitated trans-membrane diffusion of hydrogen
peroxide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1840:1596–1604. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Kawasaki T, Kusumegi S, Kudo A,
Sakanoshita T, Tsurumaru T, Sato A, Uchida G, Koga K and Shiratani
M: Effects of irradiation distance on supply of reactive oxygen
species to the bottom of a Petri dish filled with liquid by an
atmospheric O2/He plasma jet. J Appl Phys. 119:1733012016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Miller EW, Dickinson BC and Chang CJ:
Aquaporin-3 mediates hydrogen peroxide uptake to regulate
downstream intracellular signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:15681–15686. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Xiang L, Xu X, Zhang S, Cai D and Dai X:
Cold atmospheric plasma conveys selectivity on triple negative
breast cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo. Free Radic Biol Med.
124:205–213. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|