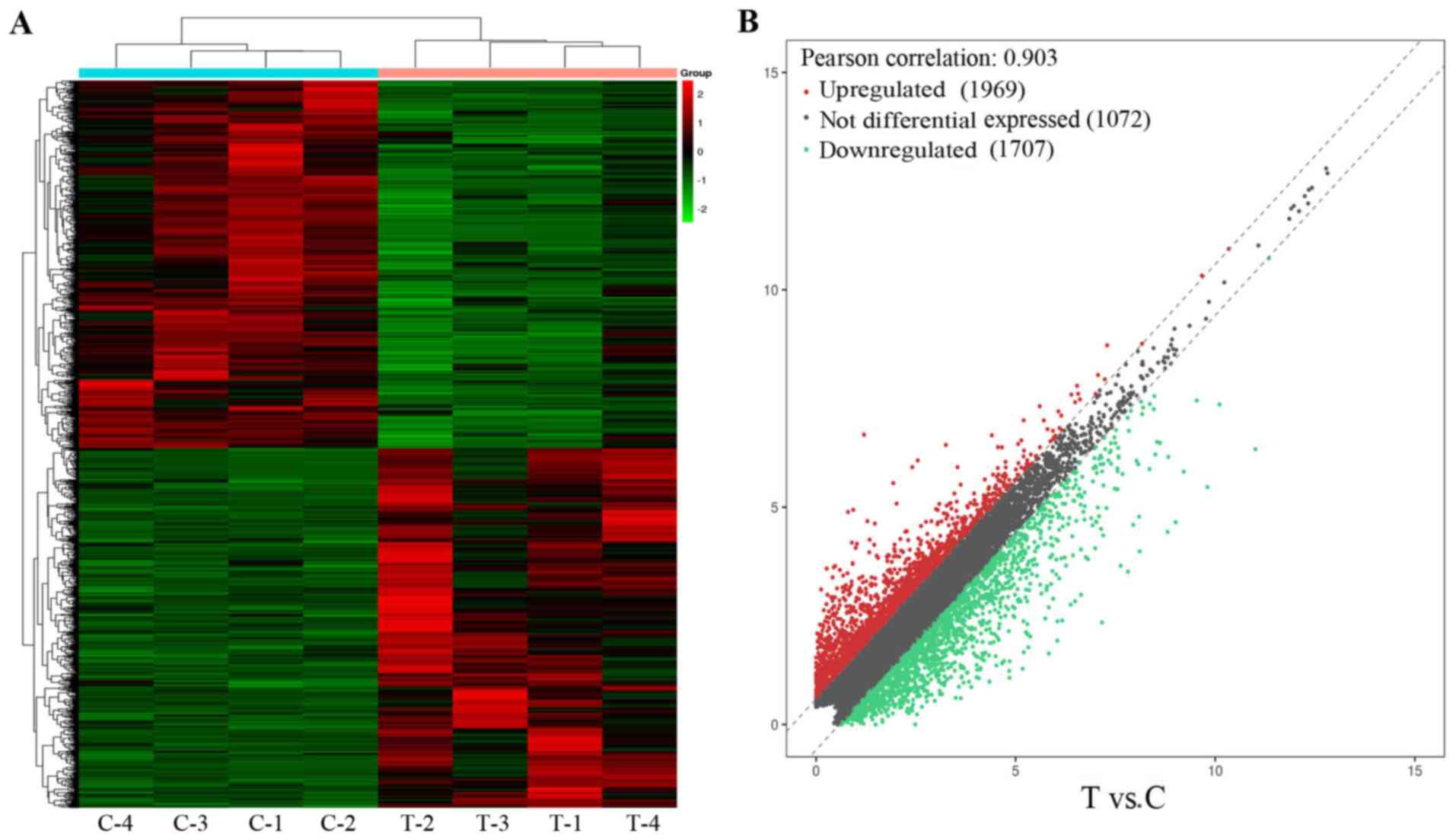
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Spiess PE, Agarwal N, Bangs R, Boorjian
SA, Buyyounouski MK, Clark PE, Downs TM, Efstathiou JA, Flaig TW,
Friedlander T, et al: Bladder Cancer, Version 5.2017, NCCN Clinical
Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw.
15:1240–1267. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cumberbatch MGK, Jubber I, Black PC,
Esperto F, Figueroa JD, Kamat AM, Kiemeney L, Lotan Y, Pang K,
Silverman DT, et al: Epidemiology of bladder cancer: A systematic
review and contemporary update of risk factors in 2018. Eur Urol.
74:784–795. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pang C, Guan Y, Li H, Chen W and Zhu G:
Urologic cancer in China. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 46:497–501. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Racioppi M, D'Agostino D, Totaro A, Pinto
F, Sacco E, D'Addessi A, Marangi F, Palermo G and Bassi PF: Value
of current chemotherapy and surgery in advanced and metastatic
bladder cancer. Urol Int. 88:249–258. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dy GW, Gore JL, Forouzanfar MH, Naghavi M
and Fitzmaurice C: Global burden of urologic cancers, 1990-2013.
Eur Urol. 71:437–446. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Chen Z, Luo Y, Yang W, Ding L, Wang J, Tu
J, Geng B, Cui Q and Yang J: Comparison analysis of dysregulated
lncrna profile in mouse plasma and liver after hepatic
ischemia/reperfusion injury. PLoS One. 10:e01334622015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liz J and Esteller M: lncRNAs and
microRNAs with a role in cancer development. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1859:169–176. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Qu S, Yang X, Li X, Wang J, Gao Y, Shang
R, Sun W, Dou K and Li H: Circular RNA: A new star of noncoding
RNAs. Cancer Lett. 365:141–148. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li J, Yang J, Zhou P, Le Y, Zhou C, Wang
S, Xu D, Lin HK and Gong Z: Circular RNAs in cancer: Novel insights
into origins, properties, functions and implications. Am J Cancer
Res. 5:472–480. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhao ZJ and Shen J: Circular RNA
participates in the carcinogenesis and the malignant behavior of
cancer. RNA Biol. 14:514–521. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Guo JU, Agarwal V, Guo H and Bartel DP:
Expanded identification and characterization of mammalian circular
RNAs. Genome Biol. 15:4092014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L and
Pandolfi PP: A ceRNA hypothesis: The Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA
language? Cell. 146:353–358. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Peng H, Lu M and Selaru FM: The
genome-wide gene expression profiling to predict competitive
endogenous RNA network in hepatocellular cancer. Genom Data.
4:93–95. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang YH, Yu XH, Luo SS and Han H:
Comprehensive circular RNA profiling reveals that circular
RNA100783 is involved in chronic CD28-associated CD8(+)T cell
ageing. Immun Ageing. 12:172015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fabian MR, Sonenberg N and Filipowicz W:
Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu Rev
Biochem. 79:351–379. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sun X, Jiao X, Pestell TG, Fan C, Qin S,
Mirabelli E, Ren H and Pestell RG: MicroRNAs and cancer stem cells:
The sword and the shield. Oncogene. 33:4967–4977. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Liu Y, Li M, Zhang G and Pang Z:
MicroRNA-10b overexpression promotes non-small cell lung cancer
cell proliferation and invasion. Eur J Med Res. 18:412013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Δ Δ C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Du H, Shi J, Wang M, An S, Guo X and Wang
Z: Analyses of gene expression profiles in the rat dorsal horn of
the spinal cord using RNA sequencing in chronic constriction injury
rats. J Neuroinflammation. 15:2802018.J. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: a
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Research. 13:2498–2504. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jin J, Sun Z, Yang F, Tang L, Chen W and
Guan X: miR-19b-3p inhibits breast cancer cell proliferation and
reverses saracatinib-resistance by regulating PI3K/Akt pathway.
Arch Biochem Biophys. 645:54–60. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu Z, Zhu X, Xu W, Zhang Y, Chen L, Qiu F,
Zhang B, Wu L, Peng Z and Tang H: Up-regulation of CIT promotes the
growth of colon cancer cells. Oncotarget. 8:71954–71964. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huang M, Zhong Z, Lv M, Shu J, Tian Q and
Chen J: Comprehensive analysis of differentially expressed profiles
of lncRNAs and circRNAs with associated co-expression and ceRNA
networks in bladder carcinoma. Oncotarget. 7:47186–47200. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li Y, Zheng F, Xiao X, Xie F, Tao D, Huang
C, Liu D, Wang M, Wang L, Zeng F, et al: CircHIPK3 sponges miR-558
to suppress heparanase expression in bladder cancer cells. EMBO
Rep. 18:1646–1659. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yang C, Yuan W, Yang X, Li P, Wang J, Han
J, Tao J, Li P, Yang H, Lv Q, et al: Circular RNA circ-ITCH
inhibits bladder cancer progression by sponging miR-17/miR-224 and
regulating p21, PTEN expression. Mol Cancer. 17:192018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xu J, Wang Y, Tan X and Jing H: MicroRNAs
in autophagy and their emerging roles in crosstalk with apoptosis.
Autophagy. 8:873–882. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lan T, Li C, Yang G, Sun Y, Zhuang L, Ou
Y, Li H, Wang G, Kisseleva T, Brenner D, et al: Sphingosine kinase
1 promotes liver fibrosis by preventing miR-19b-3p-mediated
inhibition of CCR2. Hepatology. 68:1070–1086. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Selcuklu SD, Donoghue MT, Rehmet K, de
Souza Gomes M, Fort A, Kovvuru P, Muniyappa MK, Kerin MJ, Enright
AJ and Spillane C: MicroRNA-9 inhibition of cell proliferation and
identification of novel miR-9 targets by transcriptome profiling in
breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 287:29516–29528. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Su Z, Yang Z, Xu Y, Chen Y and Yu Q:
MicroRNAs in apoptosis, autophagy and necroptosis. Oncotarget.
6:8474–8490. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fichtlscherer S, De Rosa S, Fox H,
Schwietz T, Fischer A, Liebetrau C, Weber M, Hamm CW, Röxe T,
Müller-Ardogan M, et al: Circulating microRNAs in patients with
coronary artery disease. Circ Res. 107:677–684. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Olive V, Sabio E, Bennett MJ, De Jong CS,
Biton A, McGann JC, Greaney SK, Sodir NM, Zhou AY, Balakrishnan A,
et al: A component of the mir-17-92 polycistronic oncomir promotes
oncogene-dependent apoptosis. eLife. 2:e008222013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang WB, Li HP, Yan J, Zhuang F, Bao M,
Liu JT, Qi YX and Han Y: CTGF regulates cyclic stretch-induced
vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation via microRNA-19b-3p. Exp
Cell Res. 376:77–85. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mavrakis KJ, Wolfe AL, Oricchio E,
Palomero T, de Keersmaecker K, McJunkin K, Zuber J, James T, Khan
AA, Leslie CS, et al: Genome-wide RNA-mediated interference screen
identifies miR-19 targets in Notch-induced T-cell acute
lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nat Cell Biol. 12:372–379. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liang Z, Li Y, Huang K, Wagar N and Shim
H: Regulation of miR-19 to breast cancer chemoresistance through
targeting PTEN. Pharm Res. 28:3091–3100. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Niu S, Ma X, Zhang Y, Liu YN, Chen X, Gong
H, Yao Y, Liu K and Zhang X: MicroRNA-19a and microRNA-19b promote
the malignancy of clear cell renal cell carcinoma through targeting
the tumor suppressor RhoB. PLoS One. 13:e01927902018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wettschureck N and Offermanns S:
Rho/Rho-kinase mediated signaling in physiology and
pathophysiology. J Mol Med (Berl). 80:629–638. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
El Amine N, Kechad A, Jananji S and
Hickson GR: Opposing actions of septins and Sticky on Anillin
promote the transition from contractile to midbody ring. J Cell
Biol. 203:487–504. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Harding BN, Moccia A, Drunat S, Soukarieh
O, Tubeuf H, Chitty LS, Verloes A, Gressens P, El Ghouzzi V, Joriot
S, et al: Mutations in citron kinase cause recessive
microlissencephaly with multinucleated neurons. Am J Hum Genet.
99:511–520. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fu Y, Huang J, Wang KS, Zhang X and Han
ZG: RNA interference targeting CITRON can significantly inhibit the
proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Mol Biol Rep.
38:693–702. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Park OH, Ha H, Lee Y, Boo SH, Kwon DH,
Song HK and Kim YK: Endoribonucleolytic Cleavage of m6A-Containing
RNAs by RNase P/MRP Complex. Mol Cell. 74:494–507.e8. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Chen J: The cell-cycle arrest and
apoptotic functions of p53 in tumor initiation and progression.
Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 6:a0261042016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gai M, Camera P, Dema A, Bianchi F, Berto
G, Scarpa E, Germena G and Di Cunto F: Citron kinase controls
abscission through RhoA and anillin. Mol Biol Cell. 22:3768–3778.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sanz-Moreno V, Gaggioli C, Yeo M,
Albrengues J, Wallberg F, Viros A, Hooper S, Mitter R, Féral CC,
Cook M, et al: ROCK and JAK1 signaling cooperate to control
actomyosin contractility in tumor cells and stroma. Cancer Cell.
20:229–245. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|