|
1
|
Leon R, Wu H, Jin Y, Wei J, Buddhala C,
Prentice H and Wu JY: Protective function of taurine in
glutamate-induced apoptosis in cultured neurons. J Neurosci Res.
87:1185–1194. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Chang CY, Shen CY, Kang CK, Sher YP, Sheu
WHH, Chang CC and Lee TH: Taurine protects HK-2 cells from oxidized
LDL-induced cytotoxicity via the ROS-mediated mitochondrial and
p53-related apoptotic pathways. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
279:351–363. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Schaffer S, Azuma J, Takahashi K and
Mozaffari M: Why is taurine cytoprotective? Adv Exp Med Biol.
526:307–321. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Marcinkiewicz J and Kontny E: Taurine and
inflammatory diseases. Amino Acids. 46:7–20. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
5
|
Schuller-Levis GB and Park E: Taurine and
its chloramine: Modulators of immunity. Neurochem Res. 29:117–126.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Maher SG, Condron CE, Bouchier-Hayes DJ
and Toomey DM: Taurine attenuates CD3/interleukin-2-induced T cell
apoptosis in an in vitro model of activation-induced cell death
(AICD). Clin Exp Immunol. 139:279–286. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fukuda K, Hirai Y, Yoshida H, Nakajima T
and Usui T: Free amino acid content of lymphocytes and granulocytes
compared. Clin Chem. 28:1758–1761. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Capuozzo E, Pecci L, Baseggio Conrado A
and Fontana M: Thiotaurine prevents apoptosis of human neutrophils:
A putative role in inflammation. Adv Exp Med Biol. 775:227–236.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Redmond HP, Stapleton PP, Neary P and
Bouchier-Hayes D: Immunonutrition: The role of taurine. Nutrition.
14:599–604. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
William R, Watson G, Redmond HP, Wang JH
and Bouchier-Hayes D: Mechanisms involved in sodium
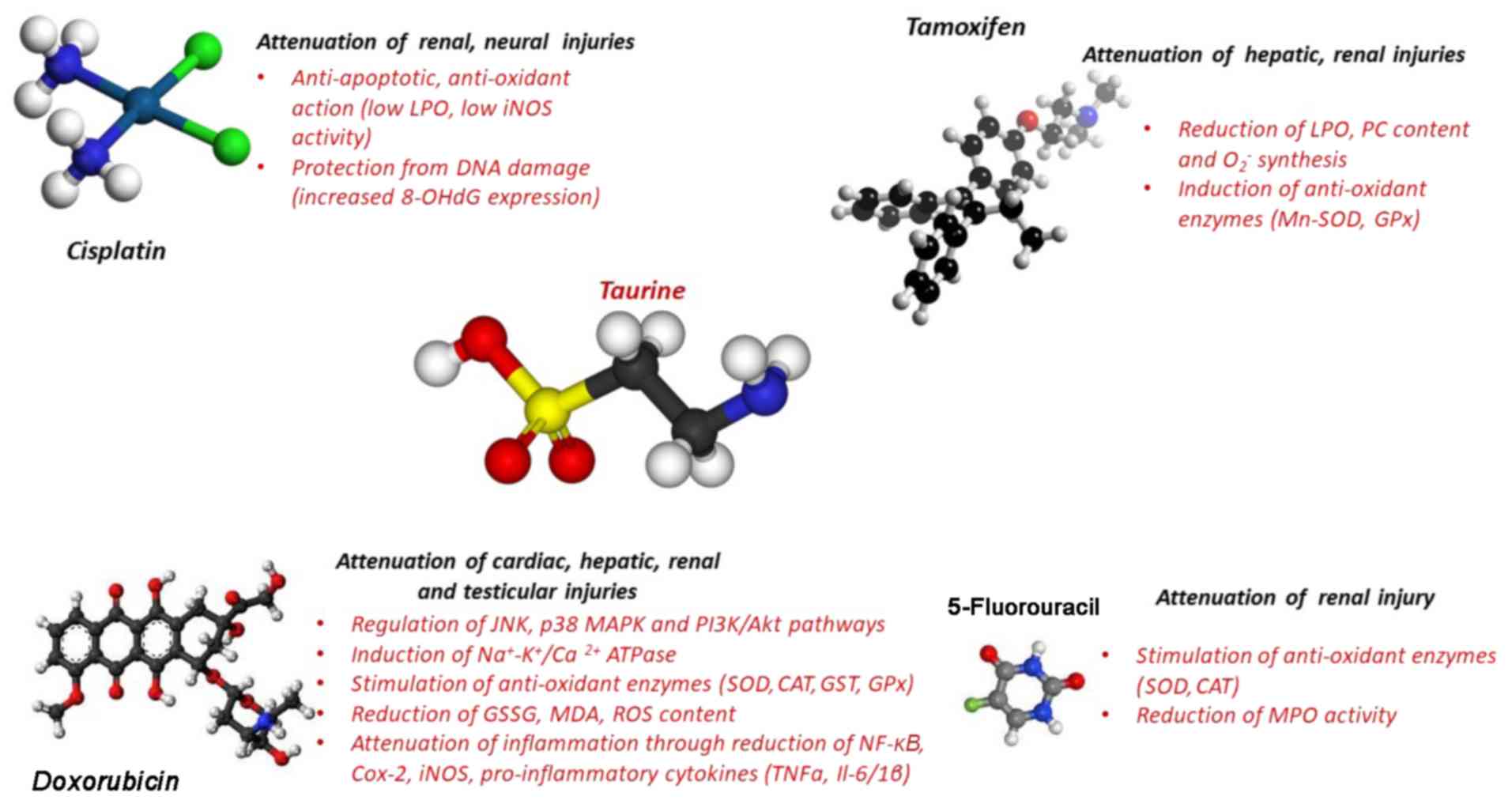
arse-nite-induced apoptosis of human neutrophils. J Leukoc Biol.
60:625–632. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Condron CM, Toomey DM, Casey RG, Creagh T
and Bouchier-Hayes DJ: Taurine protects against PMN dysfunction and
death in urine. Urol Res. 32:338–345. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Masuda M, Horisaka K and Koeda T: Effects
of taurine on neutrophil function in hyperlipidemic rats. Jpn J
Pharmacol. 40:478–480. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Schaffer SW, Azuma J and Mozaffari M: Role
of antioxidant activity of taurine in diabetes. Can J Physiol
Pharmacol. 87:91–99. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang L, Zhao N, Zhang F, Yue W and Liang
M: Effect of taurine on leucocyte function. Eur J Pharmacol.
616:275–280. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pasantes-Morales H and Cruz C: Taurine and
hypotaurine inhibit light-induced lipid peroxidation and protect
rod outer segment structure. Brain Res. 330:154–157. 1985.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Son M, Kim HK, Kim WB, Yang J and Kim BK:
Protective effect of taurine on indomethacin-induced gastric
mucosal injury. Adv Exp Med Biol. 403:147–155. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Marcinkiewicz J, Grabowska A, Bereta J and
Stelmaszynska T: Taurine chloramine, a product of activated
neutrophils, inhibits in vitro the generation of nitric oxide and
other macrophage inflammatory mediators. J Leukoc Biol. 58:667–674.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nakajima Y, Osuka K, Seki Y, Gupta RC,
Hara M, Takayasu M and Wakabayashi T: Taurine reduces inflammatory
responses after spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 27:403–410.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhang F, Mao Y, Qiao H, Jiang H, Zhao H,
Chen X, Tong L and Sun X: Protective effects of taurine against
endotoxin-induced acute liver injury after hepatic ischemia
reperfusion. Amino Acids. 38:237–245. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Elson CO, Sartor RB, Tennyson GS and
Riddell RH: Experimental models of inflammatory bowel disease.
Gastroenterology. 109:1344–1367. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Abdih H, Kelly CJ, Bouchier-Hayes D, Barry
M and Kearns S: Taurine prevents interleukin-2-induced acute lung
injury in rats. Eur Surg Res. 32:347–352. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Sun M, Zhao Y, Gu Y and Xu C:
Anti-inflammatory mechanism of taurine against ischemic stroke is
related to down-regulation of PARP and NF-κB. Amino Acids.
42:1735–1747. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Son MW, Ko JI, Doh HM, Kim WB, Park TS,
Shim MJ and Kim BK: Protective effect of taurine on TNBS-induced
inflammatory bowel disease in rats. Arch Pharm Res. 21:531–536.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Shimizu M, Zhao Z, Ishimoto Y and Satsu H:
Dietary taurine attenuates dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced
experimental colitis in mice. Adv Exp Med Biol. 643:265–271. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhao Z, Satsu H, Fujisawa M, Hori M,
Ishimoto Y, Totsuka M, Nambu A, Kakuta S, Ozaki H and Shimizu M:
Attenuation by dietary taurine of dextran sulfate sodium-induced
colitis in mice and of THP-1-induced damage to intestinal Caco-2
cell monolayers. Amino Acids. 35:217–224. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yin Y, Wen K, Wu Y, Kang Y and Lou J:
Inhibition of sodium current by taurine magnesium coordination
compound prevents cesium chloride-induced arrhythmias. Biol Trace
Elem Res. 146:192–198. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wang Q, Fan W, Cai Y, Wu Q, Mo L, Huang Z
and Huang H: Protective effects of taurine in traumatic brain
injury via mitochondria and cerebral blood flow. Amino Acids.
48:2169–2177. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Megaraj V, Iida T, Jungsuwadee P, Hofmann
AF and Vore M: Hepatobiliary disposition of
3alpha,6alpha,7alpha,12alpha-tetra-hydroxy-cholanoyl taurine: A
substrate for multiple canalicular transporters. Drug Metab Dispos.
38:1723–1730. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Guler L, Tavlasoglu M, Yucel O, Guler A,
Sahin MA, Kurkluoglu M, Sirin Y, Eken A, Gamsizkan M, Dakak M, et
al: Taurine attenuates lung ischemia-reperfusion injury after lung
transplantation in rats. J Anesth. 28:347–353. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Park SH, Lee H, Park KK, Kim HW and Park
T: Taurine-responsive genes related to signal transduction as
identified by cDNA micro-array analyses of HepG2 cells. J Med Food.
9:33–41. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Song XD, Chen CZ, Dong B, Shi YY, Zhang W,
Yan LS and Luo GA: Study on the intervening mechanism of taurine on
streptozotocin-induced diabetic cataracts. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi.
39:605–609. 2003.In Chinese.
|
|
32
|
Schuller-Levis G, Mehta PD, Rudelli R and
Sturman J: Immunologic consequences of taurine deficiency in cats.
J Leukoc Biol. 47:321–331. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sapronov NS, Khnychenko LK and
Polevshchikov AV: Effects of new taurine derivatives on primary
immune response in rats. Bull Exp Biol Med. 131:142–144. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Negoro S and Hara H: The effect of taurine
on the age-related decline of the immune response in mice: The
restorative effect on the T cell proliferative response to
costimulation with ionomycin and phorbol myristate acetate. Adv Exp
Med Biol. 315:229–239. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tappaz ML: Taurine biosynthetic enzymes
and taurine transporter: Molecular identification and regulations.
Neurochem Res. 29:83–96. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Park E, Park SY, Dobkin C and
Schuller-Levis G: A novel cysteine sulfinic acid decarboxylase
knock-out mouse: Comparison between newborn and weanling mice. Adv
Exp Med Biol. 803:3–16. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Vogelstein B and Kinzler KW: Cancer genes
and the pathways they control. Nat Med. 10:789–799. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Luo J, Solimini NL and Elledge SJ:
Principles of cancer therapy: Oncogene and non-oncogene addiction.
Cell. 136:823–837. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sardesai VM: Role of antioxidants in
health maintenance. Nutr Clin Pract. 10:19–25. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Szatrowski TP and Nathan CF: Production of
large amounts of hydrogen peroxide by human tumor cells. Cancer
Res. 51:794–798. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Trachootham D, Alexandre J and Huang P:
Targeting cancer cells by ROS-mediated mechanisms: A radical
therapeutic approach? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 8:579–591. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang X, Tu S, Wang Y, Xu B and Wan F:
Mechanism of taurine-induced apoptosis in human colon cancer cells.
Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 46:261–272. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Liu Z, Xia Y, Zhang X, Liu L, Tu S, Zhu W,
Yu L, Wan H, Yu B and Wan F: Roles of the MST1-JNK signaling
pathway in apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells induced by Taurine.
Libyan J Med. 13:15003462018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tu S, Zhang XL, Wan HF, Xia YQ, Liu ZQ,
Yang XH and Wan FS: Effect of taurine on cell proliferation and
apoptosis human lung cancer A549 cells. Oncol Lett. 15:5473–5480.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang AS, Lodi A, Rivera LB,
Izquierdo-Garcia JL, Firpo MA, Mulvihill SJ, Tempero MA, Bergers G
and Ronen SM: HR-MAS MRS of the pancreas reveals reduced lipid and
elevated lactate and taurine associated with early pancreatic
cancer. NMR Biomed. 27:1361–1370. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Opstad KS, Bell BA, Griffiths JR and Howe
FA: Taurine: A potential marker of apoptosis in gliomas. Br J
Cancer. 100:789–794. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yu J and Kim AK: Effect of taurine on
antioxidant enzyme system in B16F10 melanoma cells. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 643:491–499. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Vanitha MK, Anandakumar P and
Sakthisekaran D: Taurine abrogates mammary carcinogenesis through
induction of apoptosis in Sprague-Dawley rats. J Biochem Mol
Toxicol. 32:e222042018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Vanitha MK, Baskaran K, Periyasamy K,
Selvaraj S, Ilakkia A, Saravanan D, Venkateswari R, Revathi Mani B,
Anandakumar P and Sakthisekaran D: Modulatory effect of taurine on
7,12-Dimethylbenz(a)Anthracene-induced alterations in
detoxifi-cation enzyme system, membrane bound enzymes, glycoprotein
profile and proliferative cell nuclear antigen in rat breast
tissue. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 30:414–423. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhang X, Lu H, Wang Y, Liu C, Zhu W, Zheng
S and Wan F: Taurine induces the apoptosis of breast cancer cells
by regulating apoptosis-related proteins of mitochondria. Int J Mol
Med. 35:218–226. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Choi EJ, Tang Y, Lee CB, Cheong SH, Sung
SH, Oh MR, Young Jang SY, Park PJ and Kim EK: Effect of taurine on
in vitro migration of MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 human breast carcinoma
cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 803:191–201. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
He F, Ma N, Midorikawa K, Hiraku Y, Oikawa
S, Zhang Z, Huang G, Takeuchi K and Murata M: Taurine exhibits an
apoptosis-inducing effect on human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells
through PTEN/Akt pathways in vitro. Amino Acids. 50:1749–1758.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Tang Y, Choi E-J, Cheong SH, Hwang YJ,
Arokiyaraj S, Park PJ, Moon SH and Kim EK: Effect of taurine on
prostate-specific antigen level and migration in human prostate
cancer cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 803:203–214. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Chatzakos V, Slätis K, Djureinovic T,
Helleday T and Hunt MC: N-acyl taurines are anti-proliferative in
prostate cancer cells. Lipids. 47:355–361. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Li H, Ruan WJ, Liu LQ, Wan HF, Yang XH,
Zhu WF, Yu LH, Zhang XL and Wan FS: Impact of taurine on the
proliferation and apoptosis of human cervical carcinoma cells and
its mechanism. Chin Med J (Engl). 132:948–956. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Srivastava S, Roy R, Singh S, Kumar P,
Dalela D and Sankhwar SN: Taurine - a possible fingerprint
biomarker in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: A pilot study by
1H NMR spectroscopy. Cancer Biomark. 6:11–20. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhang X, Du W, Shen F and Wang J: Research
on effects of taurine on the transplanted tumor of mice. Wei Sheng
Yan Jiu. 26:321–324. 1997.In Chinese.
|
|
58
|
Yousef HN and Aboelwafa HR: The potential
protective role of taurine against 5-fluorouracil-induced
nephrotoxicity in adult male rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 69:265–274.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Vanitha MK, Priya KD, Baskaran K,
Periyasamy K, Saravanan D, Venkateswari R, Mani BR, Ilakkia A,
Selvaraj S, Menaka R, et al: Taurine regulates mitochondrial
function during 7,12-dimethyl Benz[a]anthracene induced
experimental mammary carcinogenesis. J Pharmacopuncture. 18:68–74.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Tu S, Zhang X, Luo D, Liu Z, Yang X, Wan
H, Yu L, Li H and Wan F: Effect of taurine on the proliferation and
apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells. Exp Ther
Med. 10:193–200. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Sadzuka Y, Matsuura M and Sonobe T: The
effect of taurine, a novel biochemical modulator, on the antitumor
activity of doxo-rubicin. Biol Pharm Bull. 32:1584–1587. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Daigeler A, Chromik AM, Geisler A, Bulut
D, Hilgert C, Krieg A, Klein-Hitpass L, Lehnhardt M, Uhl W and
Mittelkötter U: Synergistic apoptotic effects of taurolidine and
TRAIL on squamous carcinoma cells of the esophagus. Int J Oncol.
32:1205–1220. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Jacobi CA, Menenakos C and Braumann C:
Taurolidine - a new drug with anti-tumor and anti-angiogenic
effects. Anticancer Drugs. 16:917–921. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Rodak R, Kubota H, Ishihara H, Eugster HP,
Könü D, Möhler H, Yonekawa Y and Frei K: Induction of reactive
oxygen intermediates-dependent programmed cell death in human
malignant ex vivo glioma cells and inhibition of the vascular
endothelial growth factor production by taurolidine. J Neurosurg.
102:1055–1068. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Refai NS, Louka ML, Halim HY and Montasser
I: Long non-coding RNAs (CASC2 and TUG1) in hepatocellular
carcinoma: Clinical significance. J Gene Med. 21:e31122019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Matés JM, Segura JA, Alonso FJ and Márquez
J: Oxidative stress in apoptosis and cancer: An update. Arch
Toxicol. 86:1649–1656. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Mates JM, Segura JA, Alonso FJ and Marquez
J: Sulphur-containing non enzymatic antioxidants: Therapeutic tools
against cancer. Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 4:722–748. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Okamoto K, Sugie S, Ohnishi M, Makita H,
Kawamori T, Watanabe T, Tanaka T and Mori H: Chemopreventive
effects of taurine on diethylnitrosamine and phenobarbital-induced
hepato-carcinogenesis in male F344 rats. Jpn J Cancer Res.
87:30–36. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Abd-Allah AR, Gado AM, Al-Majed AA,
Al-Yahya AA and Al-Shabanah OA: Protective effect of taurine
against cyclophosphamide-induced urinary bladder toxicity in rats.
Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 32:167–172. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Islambulchilar M, Asvadi I, Sanaat Z,
Esfahani A and Sattari M: Effect of taurine on attenuating
chemotherapy-induced adverse effects in acute lymphoblastic
leukemia. J Cancer Res Ther. 11:426–432. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Desai TK, Maliakkal J, Kinzie JL,
Ehrinpreis MN, Luk GD and Cejka J: Taurine deficiency after
intensive chemotherapy and/or radiation. Am J Clin Nutr.
55:708–711. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Tabassum H, Parvez S, Rehman H, Dev
Banerjee B, Siemen D and Raisuddin S: Nephrotoxicity and its
prevention by taurine in tamoxifen induced oxidative stress in
mice. Hum Exp Toxicol. 26:509–518. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Tabassum H, Rehman H, Banerjee BD,
Raisuddin S and Parvez S: Attenuation of tamoxifen-induced
hepatotoxicity by taurine in mice. Clin Chim Acta. 370:129–136.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Parvez S, Tabassum H, Banerjee BD and
Raisuddin S: Taurine prevents tamoxifen-induced mitochondrial
oxidative damage in mice. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol.
102:382–387. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Han X, Yue J and Chesney RW: Functional
TauT protects against acute kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol.
20:1323–1332. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Al-Asmari A, Al-Zahrani A, Khan A,
Al-Shahrani H and Ali Al Amri M: Taurine ameliorates
5-flourouracil-induced intestinal mucositis, hepatorenal and
reproductive organ damage in Wistar rats: A biochemical and
histological study. Hum Exp Toxicol. 35:10–20. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Das J, Ghosh J, Manna P and Sil PC:
Taurine protects rat testes against doxorubicin-induced oxidative
stress as well as p53, Fas and caspase 12-mediated apoptosis. Amino
Acids. 42:1839–1855. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Das J, Ghosh J, Manna P and Sil PC:
Taurine suppresses doxo-rubicin-triggered oxidative stress and
cardiac apoptosis in rat via up-regulation of PI3-K/Akt and
inhibition of p53, p38-JNK. Biochem Pharmacol. 81:891–909. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Neary PM, Hallihan P, Wang JH, Pfirrmann
RW, Bouchier-Hayes DJ and Redmond HP: The evolving role of
taurolidine in cancer therapy. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1135–1143. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Mobley JA and Brueggemeier RW: Estrogen
receptor-mediated regulation of oxidative stress and DNA damage in
breast cancer. Carcinogenesis. 25:3–9. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Huang S, Chong N, Lewis NE, Jia W, Xie G
and Garmire LX: Novel personalized pathway-based metabolomics
models reveal key metabolic pathways for breast cancer diagnosis.
Genome Med. 8:342016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Sitter B, Bathen TF, Singstad TE, Fjøsne
HE, Lundgren S, Halgunset J and Gribbestad IS: Quantification of
metabolites in breast cancer patients with different clinical
prognosis using HR MAS MR spectroscopy. NMR Biomed. 23:424–431.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
El Agouza IM, Eissa SS, El Houseini MM,
El-Nashar DE and Abd El Hameed OM: Taurine: A novel tumor marker
for enhanced detection of breast cancer among female patients.
Angiogenesis. 14:321–330. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
He YU, Li QQ and Guo SC: Taurine
attenuates dimethylbenz[a] anthracene-induced breast tumorigenesis
in rats: A plasma metabolomic study. Anticancer Res. 36:533–543.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Zhou DN, Deng YF, Li RH, Yin P and Ye CS:
Concurrent alterations of RAGE, RECK, and MMP9 protein expression
are relevant to Epstein-Barr virus infection, metastasis, and
survival in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
7:3245–3254. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Shennan D and Thomson J: Estrogen
regulation and ion dependence of taurine uptake by MCF-7 human
breast cancer cells. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 12:396–406. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Pine MJ, Kim U and Ip C: Free amino acid
pools of rodent mammary tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 69:729–735.
1982.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Brown NS and Bicknell R: Hypoxia and
oxidative stress in breast cancer. Oxidative stress: Its effects on
the growth, metastatic potential and response to therapy of breast
cancer. Breast Cancer. 3:323–327. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Ambrosone CB, Marshall JR, Vena JE,
Laughlin R, Graham S, Nemoto T and Freudenheim JL: Interaction of
family history of breast cancer and dietary antioxidants with
breast cancer risk (New York, United States). Cancer Causes.
6:407–415. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Freudenheim JL, Marshall JR, Vena JE,
Laughlin R, Brasure JR, Swanson MK, Nemoto T and Graham S:
Premenopausal breast cancer risk and intake of vegetables, fruits,
and related nutrients. J Natl Cancer Inst. 88:340–348. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Kubota A, Meguid MM and Hitch DC: Amino
acid profiles correlate diagnostically with organ site in three
kinds of malignant tumors. Cancer. 69:2343–2348. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Maeda J, Higashiyama M, Imaizumi A,
Nakayama T, Yamamoto H, Daimon T, Yamakado M, Imamura F and Kodama
K: Possibility of multivariate function composed of plasma amino
acid profiles as a novel screening index for non-small cell lung
cancer: A case control study. BMC Cancer. 10:6902010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Satsu H, Ishimoto Y, Nakano T, Mochizuki
T, Iwanaga T and Shimizu M: Induction by activated macrophage-like
THP-1 cells of apoptotic and necrotic cell death in intestinal
epithelial Caco-2 monolayers via tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Exp
Cell. 312:3909–3919. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Wang H, Tso VK, Slupsky CM and Fedorak RN:
Metabolomics and detection of colorectal cancer in humans: A
systematic review. Future Oncol. 6:1395–1406. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Scheel C, Eaton EN, Li SH, Chaffer CL,
Reinhardt F, Kah KJ, Bell G, Guo W, Rubin J, Richardson AL and
Weinberg RA: Paracrine and autocrine signals induce and maintain
mesen-chymal and stem cell states in the breast. Cell. 145:926–940.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Turman MV, Kingsley PJ, Rouzer CA, Cravatt
BF and Marnett LJ: Oxidative metabolism of a fatty acid amide
hydrolase-regulated lipid, arachidonoyltaurine. Biochemistry.
47:3917–3925. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
McKinney MK and Cravatt BF: Structure and
function of fatty acid amide hydrolase. Annu Rev. 74:411–432.
2005.
|
|
98
|
Saghatelian A, McKinney MK, Bandell M,
Patapoutian A and Cravatt BF: A FAAH-regulated class of N-acyl
taurines that activates TRP ion channels. Biochemistry.
45:9007–9015. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Ueki I, Roman HB, Hirschberger LL, Junior
C and Stipanuk MH: Extrahepatic tissues compensate for loss of
hepatic taurine synthesis in mice with liver-specific knockout of
cysteine dioxy-genase. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
302:E1292–E1299. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Timbrell JA, Seabra V and Waterfield CJ:
The in vivo and in vitro protective properties of taurine. Gen
Pharmacol. 26:453–462. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Heidari R, Babaei H and Eghbal MA:
Ameliorative effects of taurine against methimazole-induced
cytotoxicity in isolated rat hepatocytes. Sci Pharm. 80:987–999.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Boşgelmez İİ, Söylemezoğlu T and Güvendik
G: The protective and antidotal effects of taurine on hexavalent
chromium-induced oxidative stress in mice liver tissue. Biol Trace
Elem Res. 125:46–58. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Heidari R, Babaei H and Eghbal MA:
Amodiaquine-induced toxicity in isolated rat hepatocytes and the
cytoprotective effects of taurine and/or N-acetyl cysteine. Res
Pharm Sci. 9:97–105. 2014.
|
|
104
|
Sinha M, Manna P and Sil PC: Taurine, a
conditionally essential amino acid, ameliorates arsenic-induced
cytotoxicity in murine hepatocytes. Toxicol In Vitro. 21:1419–1428.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Vissers MC and Fantone JC: Inhibition of
hypochlorous acid-mediated reactions by desferrioxamine.
Implications for the mechanism of cellular injury by neutrophils.
Free Radic Biol Med. 8:331–337. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Riordan JD, Feddersen CR, Tschida BR,
Beckmann PJ, Keng VW, Linden MA, Amin K, Stipp CS, Largaespada DA
and Dupuy AJ: Chronic liver injury alters driver mutation profiles
in hepatocellular carcinoma in mice. Hepatology. 67:924–939. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
107
|
Glauert HP, Calfee-Mason K, Stemm DN,
Tharappel JC and Spear BT: Dietary antioxidants in the prevention
of hepatocar-cinogenesis: A review. Mol Nutr Food Res. 54:875–896.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Bansal AK, Trivedi R, Soni GL and
Bhatnagar D: Hepatic and renal oxidative stress in acute toxicity
of N-nitrosodiethylamine in rats. Indian J Exp Biol. 38:916–920.
2000.
|
|
109
|
Kang JS, Wanibuchi H, Morimura K, Gonzalez
FJ and Fukushima S: Role of CYP2E1 in diethylnitrosamine-induced
hepatocarcinogenesis in vivo. Cancer Res. 67:11141–11116. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Başaran-Küçükgergin C, Bingül I, Tekkeşin
MS, Olgaç V, Doğru-Abbasoğlu S and Uysal M: Effects of carnosine,
taurine, and betaine pretreatments on diethylnitrosamine-induced
oxida-tive stress and tissue injury in rat liver. Toxicol Ind
Health. 32:1405–1413. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Chang YY, Chou CH, Chiu CH, Yang KT, Lin
YL, Weng WL and Chen YC: Preventive effects of taurine on
development of hepatic steatosis induced by a high-fat/cholesterol
dietary habit. J Agric Food Chem. 59:450–457. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Kalaz EB, Çoban J, Aydın AF, Doğan-Ekici
I, Doğru- Abbasoğlu S, Öztezcan S and Uysal M: Carnosine and
taurine treatments decreased oxidative stress and tissue damage
induced by D-galactose in rat liver. J Physiol Biochem. 70:15–25.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Kerai MD, Waterfield CJ, Kenyon SH, Asker
DS and Timbrell JA: The effect of taurine depletion by beta-alanine
treatment on the susceptibility to ethanol-induced hepatic
dysfunction in rats. Alcohol. 36:29–38. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
You JS and Chang KJ: Taurine protects the
liver against lipid peroxidation and membrane disintegration during
rat hepatocar-cinogenesis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 442:105–112. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Liu Y, Li F, Zhang L, Wu J, Wang Y and Yu
H: Taurine alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced liver injury by
anti-inflammation and antioxidants in rats. Mol Med Rep.
16:6512–6517. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Seabra V, Stachlewitz RF and Thurman RG:
Taurine blunts LPS-induced increases in intracellular calcium and
TNF-alpha production by Kupffer cells. J Leukoc Biol. 64:615–621.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Wu G, Yang Q, Yu Y, Lin S, Feng Y, Lv Q,
Yang J and Hu J: Taurine inhibits kupffer cells activation induced
by lipopolysac-charide in alcoholic liver damaged rats. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 975:789–800. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Kim SK and Kim YC: Attenuation of
bacterial lipopolysaccha-ride-induced hepatotoxicity by betaine or
taurine in rats. Food Chem Toxicol. 40:545–549. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Abd-Rabou AA, Zoheir KMA and Ahmed HH:
Potential impact of curcumin and taurine on human hepatoma cells
using Huh-7 cell line. Clin. 45:1519–1521. 2012.
|
|
120
|
El-Houseini ME, El-Agoza IA, Sakr MM and
El-Malky GM: Novel protective role of curcumin and taurine
combination against experimental hepatocarcinogenesis. Exp Ther
Med. 13:29–36. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Kim YS, Cheong SH, Hwang JW, Lodhi G, Lee
KH, Choi DK, Song H, Lee SH, Park DJ, Ahn CB, et al: Effect of
taurine on viability and proliferation of murine melanoma B16F10
cells. Adv Exp Med Bio. 803:167–177. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Finnegan N, Toomey D, Condron C, Redmond
HP, Da Costa M and Bouchier-Hayes DJ: Potentiation of the
therapeutic index of interleukin-2 immunotherapy by combination
with taurine in a syngeneic murine tumour model. Ir J Med Sci.
171:85–88. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Son YI, Dallal RM and Lotze MT: Combined
treatment with interleukin-18 and low-dose interleukin-2 induced
regression of a murine sarcoma and memory response. J Immunother
Hagerstown Md. 26:234–240. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Da Costa ML, Redmond HP and Bouchier-Hayes
DJ: Taurolidine improves survival by abrogating the accelerated
development and proliferation of solid tumors and development of
organ metastases from circulating tumor cells released following
surgery. J Surg Res. 101:111–119. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Logotheti S, Khoury N, Vlahopoulos SA,
Skourti E, Papaevangeliou D, Liloglou T, Gorgoulis V, Budunova I,
Kyriakopoulos AM and Zoumpourlis V: N-bromotaurine surrogates for
loss of antiproliferative response and enhances cisplatin efficacy
in cancer cells with impaired glucocorticoid receptor. Transl Res.
173:58–73.e2. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Gottardi W and Nagl M: N-chlorotaurine, a
natural antiseptic with outstanding tolerability. J Antimicrob
Chemother. 65:399–409. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Carr C, Ng J and Wigmore T: The side
effects of chemotherapeutic agents. Curr Anaesth Crit Care.
19:70–79. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Bergkvist K and Wengström Y: Symptom
experiences during chemotherapy treatment-With focus on nausea and
vomiting. Eur J Oncol Nurs. 10:21–29. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
129
|
Kim KS, Tsuji M, Kimura T and Sezaki H:
Effect of taurine on the gastrointestinal absorption of drugs -
Ionic requirement for the action. J Pharmacobiodyn. 5:172–178.
1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Zeybek A, Ercan F, Çetinel Ş, Çikler E,
Sağlam B and Şener G: Taurine ameliorates water avoidance
stress-induced degenerations of gastrointestinal tract and liver.
Dig Dis Sci. 51:1853–1861. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Abe M, Takahashi M, Takeuchi K and Fukuda
M: Studies on the significance of taurine in radiation injury.
Radiat Res. 33:5631968. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Sener G, Sehirli O, Cetinel S, Midillioğlu
S, Gedik N and Ayanoğlu-Dülger G: Protective effect of taurine
against alendronate-induced gastric damage in rats. Fundam Clin
Pharmacol. 19:93–100. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Saransaari P and Oja SS: Taurine and
neural cell damage. Amino Acids. 19:509–526. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Waters E, Wang JH, Redmond HP, Wu QD, Kay
E and Bouchier-Hayes D: Role of taurine in preventing
acetaminophen-induced hepatic injury in the rat. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 280:G1274–G1279. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Erdem A, Gündogan NÜ, Usubütün A, Kılınç
K, Erdem ŞR, Kara A and Bozkurt A: The protective effect of taurine
against gentamicin-induced acute tubular necrosis in rats. Nephrol
Dial Transplant. 15:1175–1182. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Piao J, Meng F, Fang H, Piao F, Jin B, Li
M and Li W: Effect of taurine on thymus differentiation of
dex-induced immunosup-pressive mice. Adv Exp Med Biol.
1155:381–390. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
137
|
Hamaguchi T, Azuma J, Awata N, Ohta H,
Takihara K, Harada H, Kishimoto S and Sperelakis N: Reduction of
doxo-rubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in mice by taurine. Res Commun
Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 59:21–30. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Refik Mas M, Comert B, Oncu K, Vural SA,
Akay C, Tasci I, Ozkomur E, Serdar M, Mas N, Alcigir G and Yener N:
The effect of taurine treatment on oxidative stress in experimental
liver fibrosis. Hepatol Res. 28:207–215. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Kato T, Tsunekawa M, Wang S, Yamashita T
and Ma N: Effect of taurine on iNOS-mediated DNA damage in
drug-induced renal injury. Adv Exp Med Biol. 975:717–727. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Gewirtz D: A critical evaluation of the
mechanisms of action proposed for the antitumor effects of the
anthracycline antibiotics adriamycin and daunorubicin. Biochem
Pharmacol. 57:727–741. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Milic V and Dragojevic V:
Doxorubicin-induced oxida-tive injury of cardiomyocytes - do we
have right strategies for prevention? Cardiotoxicity of oncologic
treatments. Fiuza M: InTech; 2012, http://www.intechopen.com/books/cardiotoxicity-of-oncologic-treatments/doxorubicin-induced-oxidative-injury-of-cardiomyocytes-do-we-have-right-strategies-for-prevention-.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
142
|
Ujhazy P, Zaleskis G, Mihich E, Ehrke MJ
and Berleth ES: Doxorubicin induces specific immune functions and
cytokine expression in peritoneal cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother.
52:463–472. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Kim YS, Kim EK, Hwang JW, Kim WS, Shin WB,
Natarajan SB, Moon SH, Jeon BT and Park PJ: Taurine attenuates
doxoru-bicin-induced toxicity on B16F10 cells. Adv Exp Med Biol.
975:1179–1190. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
144
|
Grenier MA and Lipshultz SE: Epidemiology
of anthracycline cardiotoxicity in children and adults. Semin
Oncol. 25(Suppl 10): S72–S85. 1998.
|
|
145
|
Volkova M and Russell R III: Anthracycline
cardiotoxicity: Prevalence, pathogenesis and treatment. Curr
Cardiol Rev. 7:214–220. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Comereski CR, Peden WM, Davidson TJ,
Warner GL, Hirth RS and Frantz JD: BR96-doxorubicin conjugate
(BMS-182248) versus doxorubicin: A comparative toxicity assessment
in rats. Toxicol Pathol. 22:473–488. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Nagai K, Fukuno S, Oda A and Konishi H:
Protective effects of taurine on doxorubicin-induced acute
hepatotoxicity through suppression of oxidative stress and
apoptotic responses. Anticancer Drugs. 27:17–23. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
148
|
Kim YS, Sung SH, Tang Y, Choi EJ, Choi YJ,
Hwang YJ, Park PJ and Kim EK: Protective effect of taurine on mice
with doxorubicin-induced acute kidney injury. Adv Exp Med Biol.
975:1191–1201. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Adedara IA, Ojuade TJD, Olabiyi BF, Idris
UF, Onibiyo EM, Ajeigbe OF and Farombi EO: Taurine ameliorates
renal oxida-tive damage and thyroid dysfunction in rats chronically
exposed to fluoride. Biol Trace Elem Res. 175:388–395. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
150
|
Mohamed RH, Karam RA and Amer MG:
Epicatechin attenuates doxorubicin-induced brain toxicity: Critical
role of TNF-α, iNOS and NF-κB. Brain Res Bull. 86:22–28. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Gradishar WJ and Vokes EE: 5-Fluorouracil
cardiotoxicity: A critical review. Ann Oncol. 1:409–414. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
D'Souza UJ and Narayana K: Induction of
seminiferous tubular atrophy by single dose of 5-fluorouracil
(5-FU) in Wistar rats. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol. 45:87–94.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Narayana K, D'Souza UJ, Sanyal AK and Rao
KP: 5-fluoro-uracil (5-FU) induces the formation of giant cells and
sloughing of seminiferous epithelium in the rat testis. Indian J
Physiol Pharmacol. 44:317–322. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Cheah KY, Howarth GS, Yazbeck R, Wright
TH, Whitford EJ, Payne C, Butler RN and Bastian SE: Grape seed
extract protects IEC-6 cells from chemotherapy-induced cytotoxicity
and improves parameters of small intestinal mucositis in rats with
experimentally-induced mucositis. Cancer Biol Ther. 8:382–390.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Son JY, Shin JW, Wang JH, Park HJ, Kim HG,
Raghavendran HR and Son CG: Chemotherapy-induced myelotoxicity and
incidence of lung metastasis in an animal model. Hum Exp Toxicol.
30:649–655. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
156
|
Tsibiribi P, Bui-Xuan C, Bui-Xuan B,
Lombard-Bohas C, Duperret S, Belkhiria M, Tabib A, Maujean G,
Descotes J and Timour Q: Cardiac lesions induced by 5-fluorouracil
in the rabbit. Hum Exp Toxicol. 25:305–309. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Rashid S, Ali N, Nafees S, Hasan SK and
Sultana S: Mitigation of 5-Fluorouracil induced renal toxicity by
chrysin via targeting oxidative stress and apoptosis in wistar
rats. Food Chem Toxicol. 66:185–193. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Heidari R, Rasti M, Shirazi Yeganeh B,
Niknahad H, Saeedi A and Najibi A: Sulfasalazine-induced renal and
hepatic injury in rats and the protective role of taurine.
Bioimpacts. 6:3–8. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Han X: Targeting Taurine Transporter
(TauT) for cancer immu-notherapy of p53 mutation mediated cancers -
molecular basis and preclinical implication. Adv Exp Med Biol.
1155:543–553. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
160
|
Nazarewicz RR, Zenebe WJ, Parihar A,
Larson SK, Alidema E, Choi J and Ghafourifar P: Tamoxifen induces
oxidative stress and mitochondrial apoptosis via stimulating
mitochondrial nitric oxide synthase. Cancer Res. 67:1282–1290.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Deng X, Liang J, Lin ZX, Wu FS, Zhang YP
and Zhang ZW: Natural taurine promotes apoptosis of human hepatic
stel-late cells in proteomics analysis. World J Gastroenterol.
16:1916–1923. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Alam SS, Hafiz NA and Abd El-Rahim AH:
Protective role of taurine against genotoxic damage in mice treated
with methotrexate and tamoxfine. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol.
31:143–152. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Fontanelli R, Spatti G, Raspagliesi F,
Zunino F and Di Re F: A preoperative single course of high-dose
cisplatin and bleomycin with glutathione protection in bulky stage
IB/II carcinoma of the cervix. Ann Oncol. 3:117–122. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Panici PB, Greggi S, Scambia G, Ragusa G,
Baiocchi G, Battaglia F, Coronetta F and Mancuso S: High-dose
cisplatin and bleomycin neoadjuvant chemotherapy plus radical
surgery in locally advanced cervical carcinoma: A preliminary
report. Gynecol Oncol. 41:212–216. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Pabla N and Dong Z: Cisplatin
nephrotoxicity: Mechanisms and renoprotective strategies. Kidney
Int. 73:994–1007. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Ries F and Klastersky J: Nephrotoxicity
induced by cancer chemotherapy with special emphasis on cisplatin
toxicity. Am J Kidney Dis. 8:368–379. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Townsend DM, Deng M, Zhang L, Lapus MG and
Hanigan MH: Metabolism of cisplatin to a nephrotoxin in proximal
tubule cells. J Am Soc Nephrol. 14:1–10. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
168
|
Francescato HDC, Costa RS, Scavone C and
Coimbra TM: Parthenolide reduces cisplatin-induced renal damage.
Toxicology. 230:64–75. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
169
|
Yao X, Panichpisal K, Kurtzman N and
Nugent K: Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: A review. Am J Med Sci.
334:115–124. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Chtourou Y, Aouey B, Aroui S, Kebieche M
and Fetoui H: Anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory effects of
naringin on cisplatin-induced renal injury in the rat. Chem Biol
Interact. 243:1–9. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
171
|
Torre LA, Trabert B, DeSantis CE, Miller
KD, Samimi G, Runowicz CD, Gaudet MM, Jemal A and Siegel RL:
Ovarian cancer statistics 2018: Ovarian cancer statistics 2018. CA
Cancer J Clin. 68:284–296. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Han X and Chesney RW: Regulation of TauT
by cisplatin in LLC-PK1 renal cells. Pediatr Nephrol. 20:1067–1072.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Shalby AB, Assaf N and Ahmed HH: Possible
mechanisms for N-acetyl cysteine and taurine in ameliorating acute
renal failure induced by cisplatin in rats. Toxicol Mech Methods.
21:538–546. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Kim T and Kim AK: Taurine enhances
anticancer activity of cisplatin in human cervical cancer cells.
Adv Exp Med Biol. 776:189–198. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Tsunekawa M, Wang S, Kato T, Yamashita T
and Ma N: Taurine administration mitigates cisplatin induced acute
neph-rotoxicity by decreasing DNA damage and inflammation: An
Immunocytochemical Study. Adv Exp Med Biol. 975:703–716. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
176
|
Sørensen BH, Thorsteinsdottir UA and
Lambert IH: Acquired cisplatin resistance in human ovarian A2780
cancer cells correlates with shift in taurine homeostasis and
ability to volume regulate. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
307:C1071–C1080. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Sugiura H, Okita S, Kato T, Naka T,
Kawanishi S, Ohnishi S, Oshida Y and Ma N: Protection by taurine
against INOS-dependent DNA damage in heavily exercised skeletal
muscle by inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 775:237–246. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
178
|
Ma N, Kato T, Isogai T, Gu Y and Yamashita
T: The potential effects of taurine in mitigation of radiation
nephropathy. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1155:497–505. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Owoeye O, Adedara IA and Farombi EO:
Pretreatment with taurine prevented brain injury and exploratory
behaviour associated with administration of anticancer drug
cisplatin in rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 102:375–384. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Bishnu A, Sakpal A, Ghosh N, Choudhury P,
Chaudhury K and Ray P: Long term treatment of metformin impedes
development of chemoresistance by regulating cancer stem cell
differentiation through taurine generation in ovarian cancer cells.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 107:116–127. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
181
|
Badary OA: Taurine attenuates fanconi
syndrome induced by ifosfamide without compromising its antitumor
activity. Oncol Res. 10:355–360. 1998.
|
|
182
|
Han X and Chesney RW: The role of taurine
in renal disorders. Amino Acids. 43:2249–2263. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Bouckenooghe T, Remacle C and Reusens B:
Is taurine a functional nutrient? Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care.
9:728–733. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Dotan E, Aggarwal C and Smith MR: Impact
of rituximab (Rituxan) on the treatment of B-cell Non-Hodgkin's
lymphoma. P T. 35:148–157. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Han YM, Awng N, Nu LH, Thway NM and
McLiesh P: Orthopaedic nursing in developing nations: A
collaboration between the Republic of the Union of Myanmar (Burma)
and Australia. Int J Orthop Trauma Nurs. 27:41–45. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Dong JF, Zheng X-Q and Rui HB: Effect of
taurine on immune function in mice with T-cell lymphoma during
chemotherapy. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 10:1090–1094. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
187
|
D'souza M, Jaimini A, Bansal A, Tripathi
M, Sharma R, Mondal A and Tripathi RP: FDG-PET/CT in lymphoma.
Indian J Radiol Imaging. 23:354–365. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
188
|
Marcinkiewicz J, Grabowska A, Bereta J,
Bryniarski K and Nowak B: Taurine chloramine down-regulates the
generation of murine neutrophil inflammatory mediators.
Immunopharmacology. 40:27–38. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Klebanoff SJ:
Myeloperoxidase-halide-hydrogen peroxide antibacterial system. J
Bacteriol. 95:2131–2138. 1968. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Thomas EL: Myeloperoxidase-hydrogen
peroxide-chloride antimicrobial system: Effect of exogenous amines
on antibacterial action against Escherichia coli. Infect Immun.
25:110–116. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Babior BM: Oxygen-dependent microbial
killing by phagocytes (first of two parts). N Engl J Med.
298:659–668. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Henderson JP, Byun J, Williams MV, Mueller
DM, McCormick ML and Heinecke JW: Production of brominating
intermediates by myeloperoxidase. A transhalogenation pathway for
generating mutagenic nucleobases during inflammation. J Biol Chem.
276:7867–7875. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
193
|
Klebanoff SJ: Myeloperoxidase: Friend and
foe. J Leukoc Biol. 77:598–625. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
van Dalen CJ and Kettle AJ: Substrates and
products of eosino-phil peroxidase. Biochem J. 358:233–239. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Weiss SJ, Klein R, Slivka A and Wei M:
Chlorination of taurine by human neutrophils. Evidence for
hypochlorous acid generation. J Clin Invest. 70:598–607. 1982.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Marcinkiewicz J, Strus M, Walczewska M,
Machul A and Mikołajczyk D: Influence of taurine haloamines (TauCl
and TauBr) on the development of pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm: A
preliminary study. Adv Exp Med Biol. 775:269–283. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Tokunaga S, Kanayama A and Miyamoto Y:
Modification of IkappaBalpha by taurine bromamine inhibits tumor
necrosis factor alpha-induced NF-kappaB activation. Inflamm Res.
56:479–486. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
198
|
Midwinter RG, Peskin AV, Vissers MC and
Winterbourn CC: Extracellular oxidation by taurine chloramine
activates ERK via the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol
Chem. 279:32205–32211. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
199
|
Grisham MB, Jefferson MM, Melton DF and
Thomas EL: Chlorination of endogenous amines by isolated
neutrophils. Ammonia-dependent bactericidal, cytotoxic, and
cytolytic activities of the chloramines. J Biol Chem.
259:10404–10413. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
200
|
Thomas EL, Grisham MB and Jefferson MM:
Myeloperoxidase- dependent effect of amines on functions of
isolated neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 72:441–454. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
201
|
Kim C and Kang IS: Taurine chloramine, a
taurine metabolite from activated neutrophils, inhibits
osteoclastogenesis by suppressing NFATc1 expression. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 803:99–107. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
202
|
Walczewska M, Peruń A, Białecka A, Śróttek
M, Jamróz W, Dorożyński P, Jachowicz R, Kulinowski P, Nagl M,
Gottardi W and Marcinkiewicz J: Comparative analysis of
microbicidal and anti-inflammatory properties of novel taurine
bromamine derivatives and bromamine T. Adv Exp Med Biol.
975:515–534. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
203
|
Gottardi W, Hagleitner M and Nagl M: N,
N-Dichlorotaurine: Chemical and bactericidal properties. Arch Pharm
(Weinheim). 338:473–483. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
204
|
Gottardi W and Nagl M: Chlorine covers on
living bacteria: The initial step in antimicrobial action of active
chlorine compounds. J Antimicrob Chemother. 55:475–482. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
205
|
Roos D, Eckmann CM and Yazdanbakhsh M:
Killing of schis-tosomula by taurine chloramine and taurine
bromamine. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 37:106–110. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
206
|
Nagl M, Nguyen VA, Gottardi W, Ulmer H and
Höpfl R: Tolerability and efficacy of N-chlorotaurine in comparison
with chloramine T for the treatment of chronic leg ulcers with a
purulent coating: A randomized phase II study. Br J Dermatol.
149:590–597. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
207
|
Marcinkiewicz J, Wojas-Pelc A, Walczewska
M, Lipko- Godlewska S, Jachowicz R, Maciejewska A, Białecka A and
Kasprowicz A: Topical taurine bromamine, a new candidate in the
treatment of moderate inflammatory acne vulgaris: A pilot study.
Eur J Dermatol. 18:433–439. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
208
|
Nagl M, Hess MW, Pfaller K, Hengster P and
Gottardi W: Bactericidal activity of micromolar N-chlorotaurine:
Evidence for its antimicrobial function in the human defense
system. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 44:2507–2513. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
209
|
Nagl M, Teuchner B, Pöttinger E, Ulmer H
and Gottardi W: Tolerance of N-chlorotaurine, a new antimicrobial
agent, in infectious conjunctivitis - a phase II pilot study.
Ophthalmologica. 214:111–114. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
210
|
Neher A, Gstöttner M, Nagl M, Scholtz A
and Gunkel AR: N-chlorotaurine - a new safe substance for
postoperative ear care. Auris Nasus Larynx. 34:19–22. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
211
|
Neher A, Nagl M, Appenroth E, Gstöttner M,
Wischatta M, Reisigl F, Schindler M, Ulmer H and Stephan K: Acute
otitis externa: Efficacy and tolerability of n-chlorotaurine, a
novel endogenous antiseptic agent. Laryngoscope. 114:850–854. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
212
|
Mainnemare A, Mégarbane B, Soueidan A,
Daniel A and Chapple IL: Hypochlorous acid and
taurine-N-monochloramine in periodontal diseases. J Dent Res.
83:823–831. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
213
|
Marcinkiewicz J: Taurine bromamine (TauBr)
- its role in immunity and new perspectives for clinical use. J
Biomed Sci. 17(Suppl 1): S32010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
214
|
Eitzinger C, Ehrlenbach S, Lindner H,
Kremser L, Gottardi W, Debabov D, Anderson M, Nagl M and Orth D:
N-chlorotaurine, a long-lived oxidant produced by human leukocytes,
inactivates Shiga toxin of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. PLoS
One. 7:e471052012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
215
|
Kim C, Jang JS, Cho MR, Agarawal SR and
Cha YN: Taurine chloramine induces heme oxygenase-1 expression via
Nrf2 activation in murine macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol.
10:440–446. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
216
|
Schuller-Levis GB and Park E: Taurine: New
implications for an old amino acid. FEMS Microbiol Lett.
226:195–202. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
217
|
Green TR, Fellman JH, Eicher AL and Pratt
KL: Antioxidant role and subcellular location of hypotaurine and
taurine in human neutrophils. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1073:91–97.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
218
|
Jeon SH, Lee MY, Rahman MM, Kim SJ, Kim
GB, Park SY, Hong CU, Kim SZ, Kim JS and Kang HS: The antioxidant,
taurine reduced lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced generation of ROS,
and activation of MAPKs and Bax in cultured pneumo-cytes. Pulm
Pharmacol Ther. 22:562–566. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
219
|
Oliveira MWS, Minotto JB, de Oliveira MR,
Zanotto-Filho A, Behr GA, Rocha RF, Moreira JC and Klamt F:
Scavenging and antioxidant potential of physiological taurine
concentrations against different reactive oxygen/nitrogen species.
Pharmacol Rep. 62:185–193. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
220
|
Marcinkiewicz J, Mak M, Bobek M, Biedroń
R, Białecka A, Koprowski M, Kontny E and Maśliński W: Is there a
role of taurine bromamine in inflammation? Interactive effects with
nitrite and hydrogen peroxide. Inflamm Res. 54:42–49. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
221
|
Kontny E, Chorąży-Massalska M, Rudnicka W,
Marcinkiewicz J and Maśliński W: Comparison of taurine chloramine
and taurine bromamine effects on rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes.
Amino Acids. 32:447–452. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
222
|
Park E, Schuller-Levis G, Jia JH and Quinn
MR: Preactivation exposure of RAW 264.7 cells to taurine chloramine
attenuates subsequent production of nitric oxide and expression of
iNOS mRNA. J Leukoc Biol. 61:161–166. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
223
|
Park E, Jia J, Quinn MR and Schuller-Levis
G: Taurine chlora-mine inhibits lymphocyte proliferation and
decreases cytokine production in activated human leukocytes. Clin
Immunol. 102:179–184. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
224
|
Kontny E, Maśliński W and Marcinkiewicz J:
Anti-inflammatory activities of taurine chloramine: Implication for
immunoregulation and pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Adv Exp
Med Biol. 526:329–340. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
225
|
Olszanecki R and Marcinkiewicz J: Taurine
chloramine and taurine bromamine induce heme oxygenase-1 in resting
and LPS-stimulated J774.2 macrophages. Amino Acids. 27:29–35. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
226
|
Kim K, Choi HM, Oh D, Kim C, Jeong JS, Yoo
M and Yang HI: Effect of taurine chloramine on the production of
matrix metal-loproteinases (MMPs) in adiponectin- or
IL-1beta-stimulated fibroblast-like synoviocytes. J Biomed Sci.
17(Suppl 1): S272010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
227
|
Olszanecki R, Kurnyta M, Biedroń R,
Chorobik P, Bereta M and Marcinkiewicz J: The role of heme
oxygenase-1 in down regulation of PGE2 production by taurine
chloramine and taurine bromamine in J774.2 macrophages. Amino
Acids. 35:359–364. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
228
|
Araujo JA, Zhang M and Yin F: Heme
oxygenase-1, oxidation, inflammation, and atherosclerosis. Front
Pharmacol. 3:1192012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
229
|
Idelman G, Smith DLH and Zucker SD:
Bilirubin inhibits the up-regulation of inducible nitric oxide
synthase by scavenging reactive oxygen species generated by the
toll-like receptor 4-dependent activation of NADPH oxidase. Redox
Biol. 5:398–408. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
230
|
Jong CJ, Azuma J and Schaffer S: Mechanism
underlying the antioxidant activity of taurine: Prevention of
mitochondrial oxidant production. Amino Acids. 42:2223–2232. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
231
|
Tallan HH, Jacobson E, Wright CE,
Schneidman K and Gaull GE: Taurine uptake by cultured human
lymphoblastoid cells. Life Sci. 33:1853–1860. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
232
|
Kim C, Chung JK, Jeong JM, Chang YS, Lee
YJ, Kim YJ, Lee MC, Koh CS and Kim BK: Uptake of taurine and
taurine chloramine in murine macrophages and their distribution in
mice with experimental inflammation. Adv Exp Med Biol. 442:169–176.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
233
|
Kwaśny-Krochin B, Bobek M, Kontny E,
Gluszko P, Biedroń R, Chain BM, Maśliński W and Marcinkiewicz J:
Effect of taurine chloramine, the product of activated neutrophils,
on the development of collagen-induced arthritis in DBA 1/J mice.
Amino Acids. 23:419–426. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
234
|
Chung Y-L, Wassif WS, Bell JD, Hurley M
and Scott DL: Urinary levels of creatine and other metabolites in
the assessment of polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Rheumatology
(Oxford). 42:298–303. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
235
|
Kim H, Jeon H, Kong H, Yang Y, Choi B, Kim
YM, Neckers L and Jung Y: A molecular mechanism for the
anti-inflammatory effect of taurine-conjugated 5-aminosalicylic
acid in inflamed colon. Mol Pharmacol. 69:1405–1412. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
236
|
Quinn MR, Park E and Schuller-Levis G:
Taurine chloramine inhibits prostaglandin E2 production in
activated raw 264.7 cells by post-transcriptional effects on
inducible cyclooxygenase expression. Immunol Lett. 50:185–188.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
237
|
Park E, Schuller-Levis G and Quinn MR:
Taurine chloramine inhibits production of nitric oxide and
TNF-alpha in activated RAW 264.7 cells by mechanisms that involve
transcriptional and translational events. J Immunol. 154:4778–4784.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
238
|
Kim C, Park E, Quinn MR and Schuller-Levis
G: The production of superoxide anion and nitric oxide by cultured
murine leukocytes and the accumulation of TNF-alpha in the
conditioned media is inhibited by taurine chloramine.
Immunopharmacology. 34:89–95. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
239
|
Barua M, Liu Y and Quinn MR: Taurine
chloramine inhibits inducible nitric oxide synthase and TNF-alpha
gene expression in activated alveolar macrophages: Decreased
NF-kappaB activation and IkappaB kinase activity. J Immunol.
167:2275–2281. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
240
|
Park E, Quinn MR, Wright CE and
Schuller-Levis G: Taurine chloramine inhibits the synthesis of
nitric oxide and the release of tumor necrosis factor in activated
RAW 264.7 cells. J Leukoc Biol. 54:119–124. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
241
|
Sun Jang J, Piao S, Cha YN and Kim C:
Taurine chloramine activates Nrf2, increases HO-1 expression and
protects cells from death caused by hydrogen peroxide. J Clin
Biochem Nutr. 45:37–43. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
242
|
Fazzino F, Obregón F, Morles M, Rojas A,
Arocha L, Mata S and Lima L: Taurine transporter in lymphocytes of
patients with major depression treated with venlafaxine plus
psychotherapy. Adv Exp Med Biol. 643:217–224. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
243
|
Wirleitner B, Neurauter G, Nagl M and
Fuchs D: Down-regulatory effect of N-chlorotaurine on tryptophan
degradation and neopterin production in human PBMC. Immunol Lett.
93:143–149. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
244
|
Kanayama A, Inoue JI, Sugita-Konishi Y,
Shimizu M and Miyamoto Y: Oxidation of Ikappa Balpha at methionine
45 is one cause of taurine chloramine-induced inhibition of
NF-kappa B activation. J Biol Chem. 277:24049–24056. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
245
|
Liu Y and Quinn MR: Chemokine production
by rat alveolar macrophages is inhibited by taurine chloramine.
Immunol Lett. 80:27–32. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
246
|
Cobb MH, Xu S, Hepler JE, Hutchison M,
Frost J and Robbins DJ: Regulation of the MAP kinase cascade. Cell
Mol Biol Res. 40:253–256. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
247
|
Crews CM, Alessandrini A and Erikson RL:
The primary structure of MEK, a protein kinase that phosphorylates
the ERK gene product. Science. 258:478–480. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
248
|
Kim JW and Kim C: Inhibition of
LPS-induced NO production by taurine chloramine in macrophages is
mediated though Ras-ERK-NF-kappaB. Biochem Pharmacol. 70:1352–1360.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
249
|
Bhat NR, Zhang P, Lee JC and Hogan EL:
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase and p38 subgroups of
mitogen-activated protein kinases regulate inducible nitric oxide
synthase and tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene expression in
endotoxin-stimulated primary glial cultures. J Neurosci.
18:1633–1641. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
250
|
Ajizian SJ, English BK and Meals EA:
Specific inhibitors of p38 and extracellular signal-regulated
kinase mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways block inducible
nitric oxide synthase and tumor necrosis factor accumulation in
murine macrophages stimulated with lipopolysaccharide and
interferon-gamma. J Infect Dis. 179:939–944. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
251
|
Chen CC and Wang JK: p38 but not p44/42
mitogen-activated protein kinase is required for nitric oxide
synthase induction mediated by lipopolysaccharide in RAW 264.7
macrophages. Mol Pharmacol. 55:481–488. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
252
|
Kontny E, Szczepańska K, Kowalczewski J,
Kurowska M, Janicka I, Marcinkiewicz J and Maśliński W: The
mechanism of taurine chloramine inhibition of cytokine
(interleukin-6, interleukin-8) production by rheumatoid arthritis
fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 43:2169–2177. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
253
|
Wojtecka-Lukasik E, Gujski M, Roguska K,
Maslinska D and Maslinski S: Taurine chloramine modifies adjuvant
arthritis in rats. Inflamm Res. 54(Suppl 1): S21–S22. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
254
|
Verdrengh M and Tarkowski A: Inhibition of
septic arthritis by local administration of taurine chloramine, a
product of activated neutrophils. J Rheumatol. 32:1513–1517.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
255
|
Kontny E, Plebanczyk M, Lisowska B,
Olszewska M, Maldyk P and Maslinski W: Comparison of rheumatoid
articular adipose and synovial tissue reactivity to proinflammatory
stimuli: Contribution to adipocytokine network. Ann Rheum Dis.
71:262–267. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
256
|
Kontny E, Grabowska A, Kowalczewski J,
Kurowska M, Janicka I, Marcinkiewicz J and Maśliński W: Taurine
chlora-mine inhibition of cell proliferation and cytokine
production by rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes.
Arthritis Rheum. 42:2552–2560. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
257
|
Kontny E, Rudnicka W, Kowalczewski J,
Marcinkiewicz J and Maslinski W: Selective inhibition of
cyclooxygenase 2-generated prostaglandin E2 synthesis in rheumatoid
arthritis synoviocytes by taurine chloramine. Arthritis Rheum.
48:1551–1555. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
258
|
Kontny E, Rudnicka W, Chorąży-Massalska M,
Marcinkiewicz J and Maśliński W: Taurine chloramine inhibits
proliferation of rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes by triggering a
p53-dependent pathway. Inflamm Res. 55:446–455. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
259
|
Kim KS, Park EK, Ju SM, Jung HS, Bang JS,
Kim C, Lee YA, Hong SJ, Lee SH, Yang HI and Yoo MC: Taurine
chloramine differentially inhibits matrix metalloproteinase 1 and
13 synthesis in interleukin-1beta stimulated fibroblast-like
synovio-cytes. Arthritis Res Ther. 9:R802007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
260
|
Wang Y, Cha YN, Kim KS and Kim C: Taurine
chloramine inhibits osteoclastogenesis and splenic lymphocyte
proliferation in mice with collagen-induced arthritis. Eur J
Pharmacol. 668:325–330. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
261
|
Davies EV, Williams BD and Campbell AK:
Synovial fluid polymorphonuclear leucocytes from patients with
rheumatoid arthritis have reduced MPO and NADPH-oxidase activity.
Br J Rheumatol. 29:415–421. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
262
|
Kanayama A and Miyamoto Y: Apoptosis
triggered by phago-cytosis-related oxidative stress through
FLIPS downregulation and JNK activation. J Leukoc Biol.
82:1344–1352. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
263
|
Emerson DK, McCormick ML, Schmidt JA and
Knudson CM: Taurine monochloramine activates a cell death pathway
involving Bax and Caspase-9. J Biol Chem. 280:3233–3241. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
264
|
Vile GF, Rothwell LA and Kettle AJ:
Initiation of rapid, P53-dependent growth arrest in cultured human
skin fibroblasts by reactive chlorine species. Arch Biochem
Biophys. 377:122–128. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
265
|
Klamt F and Shacter E: Taurine chloramine,
an oxidant derived from neutrophils, induces apoptosis in human B
lymphoma cells through mitochondrial damage. J Biol Chem.
280:21346–21352. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
266
|
Pilz M, Holinka J, Vavken P, Marian B and
Krepler P: Taurine chloramine induces apoptosis in human
osteosarcoma cell lines. J Orthop Res. 30:2046–2051. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
267
|
Gupta R, Seki Y and Yosida J: Role of
taurine in spinal cord injury. Curr Neurovasc Res. 3:225–235. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
268
|
Kulakowski EC and Maturo J: Hypoglycemic
properties of taurine: Not mediated by enhanced insulin release.
Biochem Pharmacol. 33:2835–2838. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
269
|
McCartney AC and Browne MK: Clinical
studies on administration of taurolin in severe sepsis: A
preliminary study. Prog Clin Biol Res. 272:361–371. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
270
|
Staubach KH: Adjuvant therapy of
peritonitis with taurolidine. Modulation of mediator liberation.
Langenbecks Arch Chir. 382(Suppl 1): S26–S30. 1997.In German.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
271
|
Wesch G, Petermann C and Linder MM: Drug
therapy of peritonitis. 6-year experience with the chemotherapeutic
agent and anti-endotoxin taurolin. Fortschr Med. 101:545–550.
1983.In German. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
272
|
Jurewitsch B and Jeejeebhoy KN:
Taurolidine lock: The key to prevention of recurrent
catheter-related bloodstream infections. Clin Nutr. 24:462–465.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
273
|
Liu Y, Zhang AQ, Cao L, Xia HT and Ma JJ:
Taurolidine lock solutions for the prevention of catheter-related
bloodstream infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis of
random-ized controlled trials. PLoS One. 8:e794172013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
274
|
Hayes KC, Stephan ZF and Sturman JA:
Growth depression in taurine-depleted infant monkeys. J Nutr.
110:2058–2064. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
275
|
Braumann C, Winkler G, Rogalla P,
Menenakos C and Jacobi CA: Prevention of disease progression in a
patient with a gastric cancer-re-recurrence. Outcome after
intravenous treatment with the novel antineoplastic agent
taurolidine. Report of a case. World J Surg Onco. 4:342006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
276
|
Stendel R, Picht T, Schilling A,
Heidenreich J, Loddenkemper C, Jänisch W and Brock M: Treatment of
glioblastoma with intravenous taurolidine. First clinical
experience Anticancer Res. 24:1143–1147. 2004.
|
|
277
|
Teuchner B, Nagl M, Schidlbauer A, Ishiko
H, Dragosits E, Ulmer H, Aoki K, Ohno S, Mizuki N, Gottardi W and
Larcher C: Tolerability and efficacy of N-chlorotaurine in epidemic
kera-toconjunctivitis-A double-blind, randomized, phase-2 clinical
trial. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 21:157–165. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
278
|
Pasich E, Walczewska M, Białecka A, Peruń
A, Kasprowicz A and Marcinkiewicz J: Taurine haloamines and
biofilm: II. Efficacy of taurine bromamine and chlorhexidine
against selected microorganisms of oral biofilm. Adv Exp Med Biol.
803:133–143. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
279
|
Kyriakopoulos A, Logotheti S,
Marcinkiewicz J and Nagl M: N-chlorotaurine and N-bromotaurine
combination regimen for the cure of valacyclovir-unresponsive
herpes zoster comorbidity in a multiple sclerosis patient. Int J
Med Pharm Case Rep. 7:1–6. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
280
|
Kyriakopoulos AM, Nagl M, Orth-Höller D,
Marcinkiewicz J, Baliou S and Zoumbourlis V: Successful treatment
of a unique chronic multi-bacterial scalp infection with
N-chlorotaurine, N-bromotaurine and bromamine T. Access Microbiol:
https://doi.org/10.1099/acmi.0.000126.
|
|
281
|
Zhai X, Zhao J, Wang Y, Wei X, Li G, Yang
Y, Chen Z, Bai Y, Wang Q, Chen X and Li M: Bibliometric analysis of
global scientific research on lncRNA: A swiftly expanding trend.
Biomed Res Int. 2018:76250782018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
282
|
Di Gesualdo F, Capaccioli S and Lulli M: A
pathophysi-ological view of the long non-coding RNA world.
Oncotarget. 5:10976–10996. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
283
|
Wapinski O and Chang HY: Long noncoding
RNAs and human disease. Trends Cell Biol. 21:354–361. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
284
|
Thin KZ, Liu X, Feng X, Raveendran S and
Tu JC: LncRNA- DANCR: A valuable cancer related long non-coding RNA
for human cancers. Pathol Res Pract. 214:801–805. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
285
|
Dykes IM and Emanueli C: Transcriptional
and post-transcriptional gene regulation by long non-coding RNA.
Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 15:177–186. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
286
|
Dey BK, Mueller AC and Dutta A: Long
non-coding RNAs as emerging regulators of differentiation,
development, and disease. Transcription. 5:e9440142014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
287
|
Li CH and Chen Y: Targeting long
non-coding RNAs in cancers: Progress and prospects. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 45:1895–1910. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
288
|
Herriges MJ, Swarr DT, Morley MP, Rathi
KS, Peng T, Stewart KM and Morrisey EE: Long noncoding RNAs are
spatially correlated with transcription factors and regulate lung
development. Genes Dev. 28:1363–1379. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
289
|
Kołat D, Hammouz R, Bednarek A and
Płuciennik E: Exosomes as carriers transporting long non-coding
RNAs: Molecular characteristics and their function in cancer
(Review). Mol Med Rep. 20:851–862. 2019.
|
|
290
|
Xiao Y, Zhang J and Deng L: Prediction of
lncRNA-protein interactions using HeteSim scores based on
heterogeneous networks. Sci Rep. 7:36642017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
291
|
Sun B, Liu C, Li H, Zhang L, Luo G, Liang
S and Lü M: Research progress on the interactions between long
non-coding RNAs and microRNAs in human cancer. Oncol Lett.
19:595–605. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
292
|
Cesana M, Cacchiarelli D, Legnini I,
Santini T, Sthandier O, Chinappi M, Tramontano A and Bozzoni I: A
long noncoding RNA controls muscle differentiation by functioning
as a competing endogenous RNA. Cell. 147:358–369. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
293
|
Wang KC and Chang HY: Molecular mechanisms
of long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell. 43:904–914. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
294
|
Mishra K and Kanduri C: Understanding long
noncoding RNA and chromatin interactions: What we know so far.
Noncoding RNA. 5:542019.
|
|
295
|
Tasharrofi B and Ghafouri-Fard S: Long
non-coding RNAs as regulators of the mitogen-activated protein
kinase (MAPK) pathway in cancer. Klin Onkol. 31:95–102. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
296
|
Young TL, Matsuda T and Cepko CL: The
noncoding RNA taurine upregulated gene 1 is required for
differentiation of the murine retina. Curr Biol. 15:501–512. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
297
|
Santoro M, Nociti V, Lucchini M, De Fino
C, Losavio FA and Mirabella M: Expression profile of long
non-coding RNAs in serum of patients with multiple sclerosis. J Mol
Neurosci. 59:18–23. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
298
|
Zang XJ, Li L, Du X, Yang B and Mei CL:
LncRNA TUG1 inhibits the proliferation and fibrosis of mesangial
cells in diabetic nephropathy via inhibiting the PI3K/AKT pathway.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:7519–7525. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
299
|
Li SY and Susztak K: The long noncoding
RNA tug1 connects metabolic changes with kidney disease in
podocytes. J Clin Invest. 126:4072–4075. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
300
|
Gu W, Yuan Y, Wang L, Yang H, Li S, Tang Z
and Li Q: Long non-coding RNA TUG1 promotes airway remodelling by
suppressing the miR-145-5p/DUSP6 axis in cigarette smoke-induced
COPD. J Cell Mol Med. 23:7200–7209. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
301
|
Long J, Badal SS, Ye Z, Wang Y, Ayanga BA,
Galvan DL, Green NH, Chang BH, Overbeek PA and Danesh FR: Long
noncoding RNA Tug1 regulates mitochondrial bioenergetics in
diabetic nephropathy. J Clin Invest. 126:4205–4218. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
302
|
Yin DD, Zhang EB, You LH, Wang N, Wang LT,
Jin FY, Zhu YN, Cao LH, Yuan QX, De W and Tang W: Downregulation of
lncRNA TUG1 affects apoptosis and insulin secretion in mouse
pancreatic β cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 35:1892–1904. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
303
|
Li Z, Shen J, Chan MTV and Wu WKK: TUG1: A
pivotal onco-genic long non-coding RNA of human cancers. Cell
Prolif. 49:471–475. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
304
|
Gutschner T and Diederichs S: The
hallmarks of cancer: A long non-coding RNA point of view. RNA Biol.
9:703–719. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
305
|
Shi X, Sun M, Liu H, Yao Y and Song Y:
Long non-coding RNAs: A new frontier in the study of human
diseases. Cancer Lett. 339:159–166. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
306
|
Li B, Shen S, Zhang W, Qi T, Hu Q and
Cheng Y: Long non-coding RNA TUG1 as a potential novel biomarker
for predicting the clinical outcome of cancer patients: A
meta-analysis. Clin Lab. 64:2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
307
|
van Heesch S, van Iterson M, Jacobi J,
Boymans S, Essers PB, de Bruijn E, Hao W, MacInnes AW, Cuppen E and
Simonis M: Extensive localization of long noncoding RNAs to the
cytosol and mono- and polyribosomal complexes. Genome Biol.
15:R62014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
308
|
Long J, Menggen Q, Wuren Q, Shi Q and Pi
X: Long noncoding RNA taurine-upregulated gene1 (TUG1) promotes
tumor growth and metastasis through
TUG1/Mir-129-5p/astrocyte-elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) axis in malignant
melanoma. Med Sci Monit. 24:1547–1559. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
309
|
Han Y, Liu Y, Gui Y and Cai Z: Long
intergenic non-coding RNA TUG1 is overexpressed in urothelial
carcinoma of the bladder. J Surg Oncol. 107:555–559. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
310
|
Zhang Q, Geng PL, Yin P, Wang XL, Jia JP
and Yao J: Down-regulation of long non-coding RNA TUG1 inhibits
osteo-sarcoma cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis. Asian Pac
J Cancer Prev. 14:2311–2315. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
311
|
Huang MD, Chen WM, Qi FZ, Sun M, Xu TP, Ma
P and Shu YQ: Long non-coding RNA TUG1 is up-regulated in
hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes cell growth and apoptosis by
epigeneti-cally silencing of KLF2. Mol Cancer. 14:1652015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
312
|
Zhai HY, Sui MH, Yu X, Qu Z, Hu JC, Sun
HQ, Zheng HT, Zhou K and Jiang LX: Overexpression of long
non-coding RNA TUG1 promotes colon cancer progression. Med Sci
Monit. 22:3281–3287. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
313
|
Li J, Zhang M, An G and Ma Q: LncRNA TUG1
acts as a tumor suppressor in human glioma by promoting cell
apoptosis. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 241:644–649. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
314
|
Zhang EB, Yin DD, Sun M, Kong R, Liu XH,
You LH, Han L, Xia R, Wang KM, Yang JS, et al: P53-regulated long
non-coding RNA TUG1 affects cell proliferation in human non-small
cell lung cancer, partly through epigenetically regulating HOXB7
expression. Cell Death Dis. 5:e12432014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
315
|
Kondo Y, Shinjo K and Katsushima K: Long
non-coding RNAs as an epigenetic regulator in human cancers. Cancer
Sci. 108:1927–1933. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
316
|
Kim KH and Roberts CWM: Targeting EZH2 in
cancer. Nat Med. 22:128–134. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
317
|
Sun CC, Li SJ, Li G, Hua RX, Zhou XH and
Li DJ: Long intergenic noncoding RNA 00511 acts as an oncogene in
non-small-cell lung cancer by binding to EZH2 and suppressing p57.
Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 5:e3852016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
318
|
Cao R, Wang L, Wang H, Xia L,
Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Jones RS and Zhang Y: Role of
histone H3 lysine 27 methylation in polycomb-group silencing.
Science. 298:1039–1043. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
319
|
Liu H, Zhou G, Fu X, Cui H, Pu G, Xiao Y,
Sun W, Dong X, Zhang L, Cao S, et al: Long noncoding RNA TUG1 is a
diagnostic factor in lung adenocarcinoma and suppresses apoptosis
via epigenetic silencing of BAX. Oncotarget. 8:101899–101910. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
320
|
Zhang E, He X, Yin D, Han L, Qiu M, Xu T,
Xia R, Xu L, Yin R and De W: Increased expression of long noncoding
RNA TUG1 predicts a poor prognosis of gastric cancer and regulates
cell proliferation by epigenetically silencing of p57. Cell Death
Dis. 7:e21092016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
321
|
Ding B, Lou W, Xu L and Fan W: Non-coding
RNA in drug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma. Biosci Rep.
38:BSR201809152018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
322
|
Yang L, Lin C, Liu W, Zhang J, Ohgi KA,
Grinstein JD, Dorrestein PC and Rosenfeld MG: ncRNA- and Pc2
methylation-dependent gene relocation between nuclear structures
mediates gene activation programs. Cell. 147:773–788. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
323
|
Thomson DW and Dinger ME: Endogenous
microRNA sponges: Evidence and controversy. Nat Rev Genet.
17:272–283. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
324
|
Ma L, Bajic VB and Zhang Z: On the
classification of long non-coding RNAs. RNA Biol. 10:925–933. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
325
|
Krol J, Loedige I and Filipowicz W: The
widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay.
Nat Rev Genet. 11:597–610. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
326
|
Tsai KW, Wu CW, Hu LY, Li SC, Liao YL, Lai
CH, Kao HW, Fang WL, Huang KH, Chan WC and Lin WC: Epigenetic
regulation of miR-34b and miR-129 expression in gastric cancer. Int
J Cancer. 129:2600–2610. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
327
|
Ji TT, Huang X, Jin J, Pan SH and Zhuge
XJ: Inhibition of long non-coding RNA TUG1 on gastric cancer cell
transference and invasion through regulating and controlling the
expression of miR-144/c-met axis. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 9:508–512.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
328
|
Zhang M, Huang S and Long D: MiR-381
inhibits migration and invasion in human gastric carcinoma through
downregulating SOX4. Oncol Lett. 14:3760–3766. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
329
|
Li J, Zhang Q, Fan X, Mo W, Dai W, Feng J,
Wu L, Liu T, Li S, Xu S, et al: The long noncoding RNA TUG1 acts as
a competing endogenous RNA to regulate the Hedgehog pathway by
targeting miR-132 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget.
8:65932–65945. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
330
|
Sun J, Hu J, Wang G, Yang Z, Zhao C, Zhang
X and Wang J: LncRNA TUG1 promoted KIAA1199 expression via miR-600
to accelerate cell metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition
in colorectal cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37:1062018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
331
|
Ma F, Wang S, Cai Q, Jin L, Zhou D, Ding J
and Quan ZW: Long non-coding RNA TUG1 promotes cell proliferation
and metastasis by negatively regulating miR-300 in gallbladder
carcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother. 88:863–869. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
332
|
Tan J, Qiu K, Li M and Liang Y:
Double-negative feedback loop between long non-coding RNA TUG1 and
miR-145 promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition and
radioresistance in human bladder cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 589(20 Pt
B): 3175–3181. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
333
|
Cai H, Xue Y, Wang P, Wang Z, Li Z, Hu Y,
Li Z, Shang X and Liu Y: The long noncoding RNA TUG1 regulates
blood-tumor barrier permeability by targeting miR-144. Oncotarget.
6:19759–19779. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
334
|
Xie CH, Cao YM, Huang Y, Shi QW, Guo JH,
Fan ZW, Li JG, Chen BW and Wu BY: Long non-coding RNA TUG1
contributes to tumorigenesis of human osteosarcoma by sponging
miR-9-5p and regulating POU2F1 expression. Tumor Biol.
37:15031–15041. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
335
|
Dong R, Liu GB, Liu BH, Chen G, Li K,
Zheng S and Dong KR: Targeting long non-coding RNA-TUG1 inhibits
tumor growth and angiogenesis in hepatoblastoma. Cell Death Dis.
7:e22782016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
336
|
Cai H, Liu X, Zheng J, Xue Y, Ma J, Li Z,
Xi Z, Li Z, Bao M and Liu Y: Long non-coding RNA taurine
upregulated 1 enhances tumor-induced angiogenesis through
inhibiting microRNA-299 in human glioblastoma. Oncogene.
36:318–331. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
337
|
Hu Y, Sun X, Mao C, Guo G, Ye S, Xu J, Zou
R, Chen J, Wang L, Duan P and Xue X: Upregulation of long noncoding
RNA TUG1 promotes cervical cancer cell proliferation and migration.
Cancer Med. 6:471–482. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
338
|
Katsushima K, Natsume A, Ohka F, Shinjo K,
Hatanaka A, Ichimura N, Sato S, Takahashi S, Kimura H, Totoki Y, et
al: Targeting the Notch-regulated non-coding RNA TUG1 for glioma
treatment. Nat Commun. 7:136162016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
339
|
Yun-Bo F, Xiao-Po L, Xiao-Li L, Guo-Long
C, Pei Z and Fa-Ming T: LncRNA TUG1 is upregulated and promotes
cell proliferation in osteosarcoma. Open Med (Wars). 11:163–167.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
340
|
Liang S, Zhang S, Wang P, Yang C, Shang C,
Yang J and Wang J: LncRNA, TUG1 regulates the oral squamous cell
carcinoma progression possibly via interacting with Wnt/β-catenin
signaling. Gene. 608:49–57. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
341
|
Tang T, Cheng Y, She Q, Jiang Y, Chen Y,
Yang W and Li Y: Long non-coding RNA TUG1 sponges miR-197 to
enhance cisplatin sensitivity in triple negative breast cancer.
Biomed Pharmacother. 107:338–346. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
342
|
Xiao CH, Yu HZ, Guo CY, Wu ZM, Cao HY, Li
WB and Yuan JF: Long non-coding RNA TUG1 promotes the proliferation
of colorectal cancer cells through regulating Wnt/β-catenin
pathway. Oncol Lett. 16:5317–5324. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
343
|
Qin CF and Zhao FL: Long non-coding RNA
TUG1 can promote proliferation and migration of pancreatic cancer
via EMT pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:2377–2384.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
344
|
Zhang CG, Yin DD, Sun SY and Han L: The
use of lncRNA analysis for stratification management of prognostic
risk in patients with NSCLC. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:115–119.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
345
|
Lin PC, Huang HD, Chang CC, Chang YS, Yen
JC, Lee CC, Chang WH, Liu TC and Chang JG: Long noncoding RNA TUG1
is downregulated in non-small cell lung cancer and can regulate
CELF1 on binding to PRC2. BMC Cancer. 16:5832016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
346
|
Baratieh Z, Khalaj Z, Honardoost MA,
Emadi-Baygi M, Khanahmad H, Salehi M and Nikpour P: Aberrant
expression of PlncRNA-1 and TUG1: Potential biomarkers for gastric
cancer diagnosis and clinically monitoring cancer progression.
Biomark Med. 11:1077–1090. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
347
|
Ren K, Li Z, Li Y, Zhang W and Han X: Long
noncoding RNA taurine-upregulated gene 1 promotes cell
proliferation and invasion in gastric cancer via negatively
modulating miRNA-145-5p. Oncol Res. 25:789–798. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
348
|
Lin YH, Wu MH, Huang YH, Yeh CT and Lin
KH: TUG1 is a regulator of AFP and serves as prognostic marker in
non-hepatitis B non-hepatitis C hepatocellular carcinoma. Cells.
9:2622020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
349
|
Dai Q, Deng J, Zhou J, Wang Z, Yuan X, Pan
S and Zhang HB: Long non-coding RNA TUG1 promotes cell progression
in hepatocellular carcinoma via regulating miR-216b-5p/DLX2 axis.
Cancer Cell Int. 20:82020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
350
|
Fang T, Fang Y, Xu X, He M, Zhao Z, Huang
P, Yuan F, Guo M, Yang B and Xia J: Actinidia chinensis planch root
extract attenuates proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular
carcinoma by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J
Ethnopharmacol. 231:474–485. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
351
|
Huang J, Lu D, Xiang T, Wu X, Ge S, Wang
Y, Wang J and Cheng N: MicroRNA-132-3p regulates cell
proliferation, apop-tosis, migration and invasion of liver cancer
by targeting Sox4. Oncol Lett. 19:3173–3180. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
352
|
Lv J, Kong Y, Gao Z, Liu Y, Zhu P and Yu
Z: LncRNA TUG1 interacting with miR-144 contributes to
proliferation, migration and tumorigenesis through activating the
JAK2/STAT3 pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 101:19–28. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
353
|
He C, Liu Z, Jin L, Zhang F, Peng X, Xiao
Y, Wang X, Lyu Q and Cai XJ: lncRNA TUG1-mediated mir-142-3p
downregulation contributes to metastasis and the
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma by
targeting ZEB1. Cell Physiol Biochem. 48:1928–1941. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
354
|
Xie F, Zhang L, Yao Q, Shan L, Liu J, Dong
N and Liang J: TUG1 promoted tumor progression by sponging
miR-335-5p and regulating CXCR4-mediated infiltration of pro-tumor
immunocytes in CTNNB1-mutated hepatoblastoma. Onco Targets Ther.
13:3105–3115. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
355
|
An N and Cheng D: The long noncoding RNA
HOST2 promotes gemcitabine resistance in human pancreatic cancer
cells. Pathol Oncol Res. 26:425–431. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
356
|
Zhao L, Sun H, Kong H, Chen Z, Chen B and
Zhou M: The lncrna-TUG1/EZH2 axis promotes pancreatic cancer cell
proliferation, migration and EMT phenotype formation through
sponging mir-382. Cell Physiol Biochem. 42:2145–2158. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
357
|
Xu K and Zhang L: Inhibition of
TUG1/miRNA-299-3p axis represses pancreatic cancer malignant
progression via suppression of the notch1 pathway. Dig Dis Sci.
65:1748–1760. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
358
|
Yang F and Li X, Zhang L, Cheng L and Li
X: LncRNA TUG1 promoted viability and associated with gemcitabine
resistant in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J Pharmacol Sci.
137:116–121. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
359
|
Burris HA III, Moore MJ, Andersen J, Green
MR, Rothenberg ML, Modiano MR, Cripps MC, Portenoy RK, Storniolo
AM, Tarassoff P, et al: Improvements in survival and clinical
benefit with gemcitabine as first-line therapy for patients with
advanced pancreas cancer: A randomized trial. J Clin Oncol.
15:2403–2413. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
360
|
Lu Y, Tang L, Zhang Z, Li S, Liang S, Ji
L, Yang B, Liu Y and Wei W: Long noncoding RNA TUG1/miR-29c axis
affects cell proliferation, invasion, and migration in human
pancreatic cancer. Dis Markers. 2018:68570422018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
361
|
Miyamoto Y, Maitra A, Ghosh B, Zechner U,
Argani P, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA, Sriuranpong V, Iso T, Meszoely IM,
Wolfe MS, et al: Notch mediates TGFα-induced changes in epithelial
differentiation during pancreatic tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell.
3:565–576. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
362
|
Hu H, Zhou L, Awadallah A and Xin W:
Significance of Notch1-signaling pathway in human pancreatic
development and carcinogenesis. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol.
21:242–247. 2013.
|
|
363
|
Chen X, Qi M, Yang Q and Li JY: MiR-299-3p
functions as a tumor suppressor in thyroid cancer by regulating
SHOC2. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:232–240. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
364
|
Dang S, Zhou J, Wang Z, Wang K, Dai S and
He S: MiR-299-3p functions as a tumor suppressor via targeting
Sirtuin 5 in hepato-cellular carcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother.
106:966–975. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
365
|
Wang JY, Jiang JB, Li Y, Wang YL and Dai
Y: MicroRNA-299-3p suppresses proliferation and invasion by
targeting VEGFA in human colon carcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother.
93:1047–1054. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
366
|
Hui B, Xu Y, Zhao B, Ji H, Ma Z, Xu S, He
ZY, Wang K and Lu J: Overexpressed long noncoding RNA TUG1 affects
the cell cycle, proliferation, and apoptosis of pancreatic cancer
partly through suppressing RND3 and MT2A. Onco Targets Ther.
12:1043–1057. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
367
|
Zhu Y, Zhou J, Xia H, Chen X, Qiu M, Huang
J, Liu S, Tang Q, Lang N, Liu Z, et al: The Rho GTPase RhoE is a
p53-regulated candidate tumor suppressor in cancer cells. Int J
Oncol. 44:896–904. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
368
|
Poch E, Miñambres R, Mocholí E, Ivorra C,
Pérez-Aragó A, Guerri C, Pérez-Roger I and Guasch RM: RhoE
interferes with Rb inactivation and regulates the proliferation and
survival of the U87 human glioblastoma cell line. Exp Cell Res.
313:719–731. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
369
|
Wang L, Zhao Z, Feng W, Ye Z, Dai W, Zhang
C, Peng J and Wu K: Long non-coding RNA TUG1 promotes colorectal
cancer metastasis via EMT pathway. Oncotarget. 7:51713–51719. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
370
|
Shen X, Hu X, Mao J, Wu Y, Liu H, Shen J,
Yu J and Chen W: The long noncoding RNA TUG1 is required for
TGF-β/TWIST1/EMT-mediated metastasis in colorectal cancer cells.
Cell Death Dis. 11:652020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
371
|
Sun J, Ding C, Yang Z, Liu T, Zhang X,
Zhao C and Wang J: The long non-coding RNA TUG1 indicates a poor
prognosis for colorectal cancer and promotes metastasis by
affecting epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Transl Med.
14:422016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
372
|
Fan S, Yang Z, Ke Z, Huang K, Liu N, Fang
X and Wang K: Downregulation of the long non-coding RNA TUG1 is
associated with cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in
breast cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 95:1636–1643. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
373
|
Caldon CE, Daly RJ, Sutherland RL and
Musgrove EA: Cell cycle control in breast cancer cells. J Cell
Biochem. 97:261–274. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
374
|
Zhao X and Ren G: LncRNA
taurine-upregulated gene 1 promotes cell proliferation by
inhibiting microRNA-9 in MCF-7 cells. J Breast Cancer. 19:349–357.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
375
|
Gradia DF, Mathias C, Coutinho R, Cavalli
IJ, Ribeiro EMSF and de Oliveira JC: Long non-coding RNA TUG1
expression is associated with different subtypes in human breast
cancer. Noncoding RNA. 3:262017.
|
|
376
|
Neuwelt EA, Barnett PA, Bigner DD and
Frenkel EP: Effects of adrenal cortical steroids and osmotic
blood-brain barrier opening on methotrexate delivery to gliomas in
the rodent: The factor of the blood-brain barrier. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 79:4420–4423. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
377
|
Li TH, Zhang JJ, Liu SX and Chen Y: Long
non-coding RNA taurine-upregulated gene 1 predicts unfavorable
prognosis, promotes cells proliferation, and inhibits cells
apoptosis in epithelial ovarian cancer. Medicine (Baltimore).
97:e05752018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
378
|
Iliev R, Kleinova R, Juracek J, Dolezel J,
Ozanova Z, Fedorko M, Pacik D, Svoboda M, Stanik M and Slaby O:
Overexpression of long non-coding RNA TUG1 predicts poor prognosis
and promotes cancer cell proliferation and migration in high-grade
muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Tumour Biol. 37:13385–13390. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
379
|
Guo P, Zhang G, Meng J, He Q, Li Z and
Guan Y: Upregulation of long noncoding RNA TUG1 promotes bladder
cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by inhibiting
miR-29c. Oncol Res. 26:1083–1091. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
380
|
Liu Q, Liu H, Cheng H, Li Y, Li X and Zhu
C: Downregulation of long noncoding RNA TUG1 inhibits proliferation
and induces apoptosis through the TUG1/miR-142/ZEB2 axis in bladder
cancer cells. Onco Targets Ther. 10:2461–2471. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
381
|
Jiang H, Hu X, Zhang H and Li W:
Down-regulation of LncRNA TUG1 enhances radiosensitivity in bladder
cancer via suppressing HMGB1 expression. Radiat Oncol. 12:652017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
382
|
Zhu J, Shi H, Liu H, Wang X and Li F: Long
non-coding RNA TUG1 promotes cervical cancer progression by
regulating the miR-138-5p-SIRT1 axis. Oncotarget. 8:65253–65264.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
383
|
Fan M, Li C, He P, Fu Y, Li M and Zhao X:
Knockdown of long noncoding RNA-taurine-upregulated gene 1 inhibits
tumor angiogenesis in ovarian cancer by regulating leucine-rich
α-2-glycoprotein-1. Anticancer Drugs. 30:562–570. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
384
|
Wang X, Abraham S, McKenzie JAG, Jeffs N,
Swire M, Tripathi VB, Luhmann UFO, Lange CAK, Zhai Z, Arthur HM, et
al: LRG1 promotes angiogenesis by modulating endothelial TGF-β
signalling. Nature. 499:306–311. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
385
|
Goel S, Duda DG, Xu L, Munn LL, Boucher Y,
Fukumura D and Jain RK: Normalization of the vasculature for
treatment of cancer and other diseases. Physiol Rev. 91:1071–1121.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
386
|
Meng H, Song Y, Zhu J, Liu Q, Lu P, Ye N,
Zhang Z, Pang Y, Qi J and Wu H: LRG1 promotes angiogenesis through
upregulating the TGF-β1 pathway in ischemic rat brain. Mol Med Rep.
14:5535–5543. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
387
|
Zhang J, Zhu L, Fang J, Ge Z and Li X:
LRG1 modulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and angiogenesis
in colorectal cancer via HIF-1α activation. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
35:292016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
388
|
Baek YY, Cho DH, Choe J, Lee H, Jeoung D,
Ha KS, Won MH, Kwon YG and Kim YM: Extracellular taurine induces
angio-genesis by activating ERK-, Akt-, and FAK-dependent signal
pathways. Eur J Pharmacol. 674:188–199. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
389
|
Xu T, Liu CL, Li T, Zhang YH and Zhao YH:
LncRNA TUG1 aggravates the progression of prostate cancer and
predicts the poor prognosis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
23:4698–4705. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
390
|
Hao SD, Ma JX, Liu Y, Liu PJ and Qin Y:
Long non-coding TUG1 accelerates prostate cancer progression
through regulating miR-128-3p/YES1 axis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
24:619–632. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
391
|
Jiang L, Wang W, Li G, Sun C, Ren Z, Sheng
H, Gao H, Wang C and Yu H: High TUG1 expression is associated with
chemotherapy resistance and poor prognosis in esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 78:333–339. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
392
|
Xu Y, Wang J, Qiu M and Xu L, Li M, Jiang
F, Yin R and Xu L: Upregulation of the long noncoding RNA TUG1
promotes proliferation and migration of esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 36:1643–1651. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
393
|
Tang Y, Yang P, Zhu Y and Su Y: LncRNA
TUG1 contributes to ESCC progression via regulating miR-148a-3p/
MCL-1/Wnt/β-catenin axis in vitro. Thorac Cancer. 11:82–94. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
394
|
Ma B, Li M, Zhang L, Huang M, Lei JB, Fu
GH, Liu CX, Lai QW, Chen QQ and Wang YL: Upregulation of long
non-coding RNA TUG1 correlates with poor prognosis and disease
status in osteosarcoma. Tumor Biol. 37:4445–4455. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
395
|
Wang H, Yu Y, Fan S and Luo L: Knockdown
of Long noncoding RNA TUG1 inhibits the proliferation and cellular
invasion of osteosarcoma cells by sponging miR-153. Oncol Res.
26:665–673. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
396
|
Xie C, Chen B, Wu B, Guo J and Cao Y:
LncRNA TUG1 promotes cell proliferation and suppresses apoptosis in
osteosarcoma by regulating miR-212-3p/FOXA1 axis. Biomed
Pharmacother. 97:1645–1653. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
397
|
Li G, Liu K and Du X: Long Non-Coding RNA
TUG1 promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of osteosarcoma
cells by sponging miR-132-3p and upregulating SOX4 expression.
Yonsei Med J. 59:226–235. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
398
|
Liu Y, Li Y, Liu J, Wu Y and Zhu Q:
MicroRNA-132 inhibits cell growth and metastasis in osteosarcoma
cell lines possibly by targeting Sox4. Int J Oncol. 47:1672–1684.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
399
|
Wang Y, Yang T, Zhang Z, Lu M, Zhao W,
Zeng X and Zhang W: Long non-coding RNA TUG1 promotes migration and
invasion by acting as a ceRNA of miR-335-5p in osteosarcoma cells.
Cancer Sci. 108:859–867. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
400
|
Li Y, Zhang T, Zhang Y, Zhao X and Wang W:
Targeting the FOXM1-regulated long noncoding RNA TUG1 in
osteosar-coma. Cancer Sci. 109:3093–3104. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
401
|
Cao J, Han X, Qi X, Jin X and Li X: TUG1
promotes osteo-sarcoma tumorigenesis by upregulating EZH2
expression via miR-144-3p. Int J Oncol. 51:1115–1123. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
402
|
Yu X, Hu L, Li S, Shen J, Wang D, Xu R and
Yang H: Long non-coding RNA Taurine upregulated gene 1 promotes
osteo-sarcoma cell metastasis by mediating HIF-1α via miR-143-5p.
Cell Death Dis. 10:2802019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
403
|
Li Q, Song W and Wang J: TUG1 confers
Adriamycin resistance in acute myeloid leukemia by epigenetically
suppressing miR-34a expression via EZH2. Biomed Pharmacother.
109:1793–1801. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
404
|
Isin M, Ozgur E, Cetin G, Erten N, Aktan
M, Gezer U and Dalay N: Investigation of circulating lncRNAs in
B-cell neoplasms. Clin Chim Acta. 431:255–259. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
405
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
406
|
Yang L, Moss T, Mangala LS, Marini J, Zhao
H, Wahlig S, Armaiz-Pena G, Jiang D, Achreja A, Win J, et al:
Metabolic shifts toward glutamine regulate tumor growth, invasion
and bioenergetics in ovarian cancer. Mol Syst Biol. 10:7282014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
407
|
Wang J, Xie H, Ling Q, Lu D, Lv Z, Zhuang
R, Liu Z, Wei X, Zhou L, Xu X and Zheng S: Coding-noncoding gene
expression in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Transl Res.
168:107–121. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
408
|
Zeng B, Ye H, Chen J, Cheng D, Cai C, Chen
G, Chen X, Xin H, Tang C and Zeng J: LncRNA TUG1 sponges miR-145 to
promote cancer progression and regulate glutamine metabolism via
Sirt3/GDH axis. Oncotarget. 8:113650–113661. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
409
|
Han X and Yang Y, Sun Y, Qin L and Yang Y:
LncRNA TUG1 affects cell viability by regulating glycolysis in
osteosarcoma cells. Gene. 674:87–92. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
410
|
Kunej T, Obsteter J, Pogacar Z, Horvat S
and Calin GA: The decalog of long non-coding RNA involvement in
cancer diagnosis and monitoring. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 51:344–357.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
411
|
Dutour A, Leclers D, Monteil J, Paraf F,
Charissoux JL, Rousseau R and Rigaud M: Non-invasive imaging
correlates with histological and molecular characteristics of an
osteosar-coma model: Application for early detection and follow-up
of MDR phenotype. Anticancer Res. 27(6B): 4171–4178. 2007.
|
|
412
|
Fidler IJ: The biology of brain
metastasis: Challenges for therapy. Cancer J. 21:284–293. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
413
|
La Porta CA: Drug resistance in melanoma:
New perspectives. Curr Med Chem. 14:387–391. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
414
|
Liu YY, Han TY, Giuliano AE and Cabot MC:
Ceramide glyco-sylation potentiates cellular multidrug resistance.
FASEB J. 15:719–730. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
415
|
Synold TW, Dussault I and Forman BM: The
orphan nuclear receptor SXR coordinately regulates drug metabolism
and efflux. Nat Med. 7:584–590. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
416
|
Gottesman MM: Mechanisms of cancer drug
resistance. Annu Rev Med. 53:615–627. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
417
|
Liu Z and Zhang H: LncRNA plasmacytoma
variant trans-location 1 is an oncogene in bladder urothelial
carcinoma. Oncotarget. 8:64273–64282. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
418
|
Xie D, Zhang H, Hu X and Shang C:
Knockdown of long non-coding RNA Taurine Up-Regulated 1 inhibited
doxorubicin resistance of bladder urothelial carcinoma via
Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Oncotarget. 8:88689–88696. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
419
|
Li C, Gao Y, Li Y and Ding D: TUG1
mediates methotrexate resistance in colorectal cancer via
miR-186/CPEB2 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 491:552–557. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
420
|
Gu L, Li Q, Liu H, Lu X and Zhu M: Long
noncoding RNA TUG1 promotes autophagy-associated paclitaxel
resistance by sponging miR-29b-3p in ovarian cancer cells.
OncoTargets Ther. 13:2007–2019. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
421
|
Xi G, Hu X, Wu B, Jiang H, Young CY, Pang
Y and Yuan H: Autophagy inhibition promotes paclitaxel-induced
apoptosis in cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 307:141–148. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
422
|
Wei X, Zhou Y, Qiu J, Wang X, Xia Y and
Sui L: Low expression of TUG1 promotes cisplatin sensitivity in
cervical cancer by activating the MAPK pathway. J BUON.
24:1020–1026. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
423
|
Köberle B, Tomicic MT, Usanova S and Kaina
B: Cisplatin resistance: Preclinical findings and clinical
implications. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1806:172–182. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
424
|
Niu Y, Ma F, Huang W, Fang S, Li M, Wei T
and Guo L: Long non-coding RNA TUG1 is involved in cell growth and
chemo-resistance of small cell lung cancer by regulating LIMK2b via
EZH2. Mol Cancer. 16:52017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
425
|
Xu C, Guo Y, Liu H, Chen G, Yan Y and Liu
T: TUG1 confers cisplatin resistance in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma by epigenetically suppressing PDCD4 expression via EZH2.
Cell Biosci. 8:612018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
426
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
427
|
Liu Q, Sun S, Yu W, Jiang J, Zhuo F, Qiu
G, Xu S and Jiang X: Altered expression of long non-coding RNAs
during genotoxic stress-induced cell death in human glioma cells. J
Neurooncol. 122:283–292. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
428
|
Wang X, Chen X, Zhang D, Yang G, Yang Z,
Yin Z and Zhao S: Prognostic and clinicopathological role of long
non-coding RNA taurine upregulated 1 in various human malignancies:
A systemic review and meta-analysis. Tumor Biol.
39:10104283177143612017. View Article : Google Scholar
|