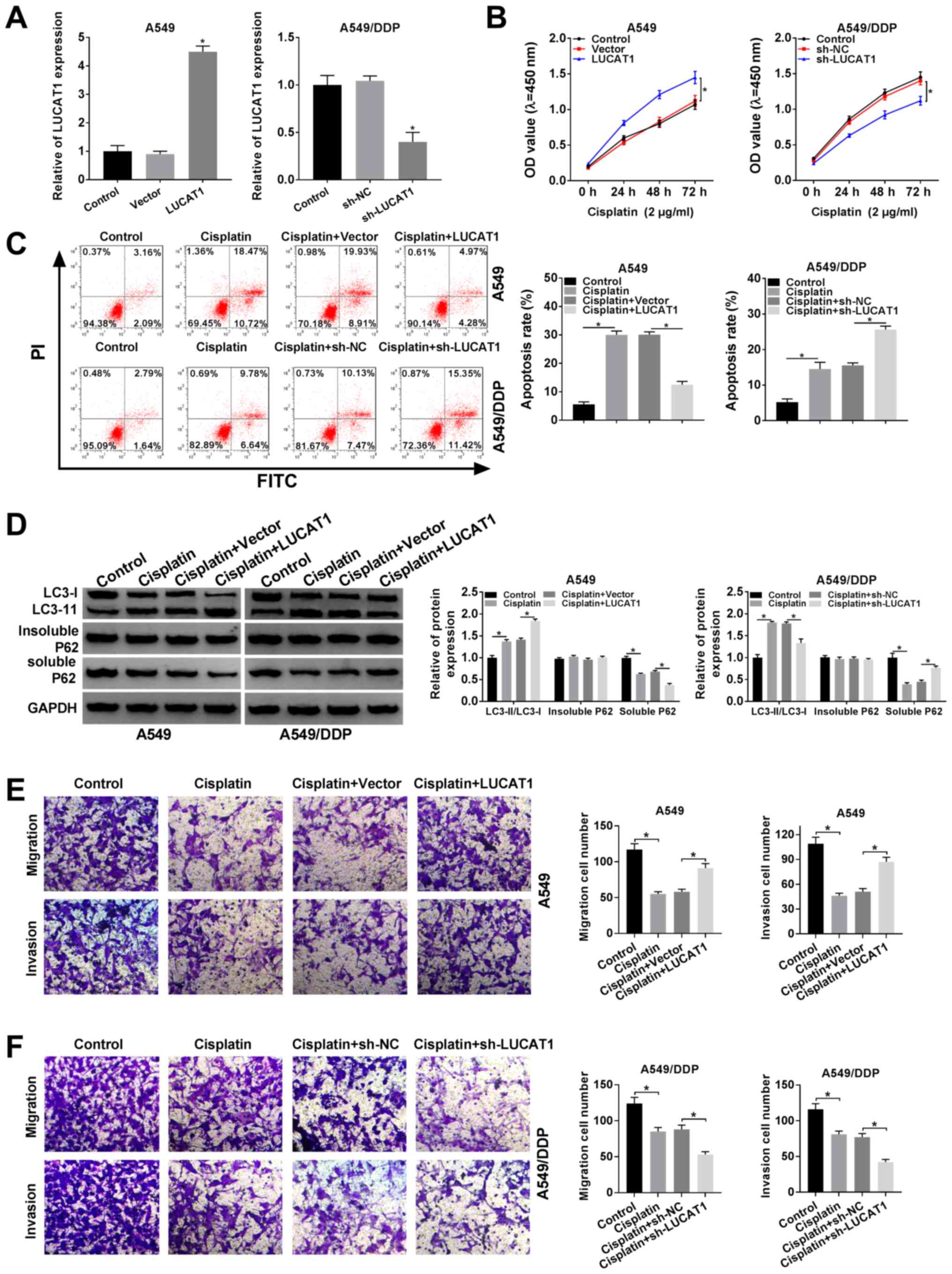
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fitzmaurice C, Akinyemiju TF, Al Lami FH,
Alam T, Alizadeh-Navaei R, Allen C, Alsharif U, Alvis-Guzman N,
Amini E and Anderson BO: Global, regional, and national cancer
incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with
disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 29 cancer
groups, 1990 to 2016: A systematic analysis for the global burden
of disease study. JAMA Oncol. 4:1553–1568. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Heist RS and Engelman JA: SnapShot:
Non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Cell. 21:448.e22012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hirsch FR, Suda K, Wiens J and Bunn PA Jr:
New and emerging targeted treatments in advanced non-small-cell
lung cancer. Lancet. 388:1012–1024. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fennell D, Summers Y, Cadranel J, Benepal
T, Christoph D, Lal R, Das M, Maxwell F, Visseren-Grul C and Ferry
D: Cisplatin in the modern era: The backbone of first-line
chemotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Treat Rev.
44:42–50. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Arriagada R, Bergman B, Dunant A, Le
Chevalier T, Pignon JP and Vansteenkiste J; International Adjuvant
Lung Cancer Trial Collaborative Group: Cisplatin-based adjuvant
chemotherapy in patients with completely resected non-small-cell
lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 350:351–360. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Herbst RS, Morgensztern D and Boshoff C:
The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature.
553:4462018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schmitz SU, Grote P and Herrmann BG:
Mechanisms of long noncoding RNA function in development and
disease. Cell Mol Life Sci. 73:2491–2509. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ge P, Cao L, Yao YJ, Jing RJ, Wang W and
Li HJ: lncRNA FOXD2-AS1 confers cisplatin resistance of
non-small-cell lung cancer via regulation of miR185-5p-SIX1 axis.
Onco Targets Ther. 12:6105–6117. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
10
|
Liu MY, Li XQ, Gao TH, Cui Y, Ma N, Zhou Y
and Zhang GJ: Elevated HOTAIR expression associated with cisplatin
resistance in non-small cell lung cancer patients. J Thorac Dis.
8:3314–3322. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wang P, Chen D, Ma H and Li Y: LncRNA MEG3
enhances cisplatin sensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer by
regulating miR-21-5p/SOX7 axis. Onco Targets Ther. 10:5137–5149.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dragomir MP, Knutsen E and Calin GA:
SnapShot: Unconventional miRNA functions. Cell. 174:1038–1038.e1.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fujita Y, Yagishita S, Hagiwara K,
Yoshioka Y, Kosaka N, Takeshita F, Fujiwara T, Tsuta K, Nokihara H,
Tamura T, et al: The clinical relevance of the
miR-197/CKS1B/STAT3-mediated PD-L1 network in chemoresistant
non-small-cell lung cancer. Mol The. 23:717–727. 2015.
|
|
14
|
Bian B, Pan X, Yang JS, Wang ZX and De W:
Upregulation of microRNA-451 increases cisplatin sensitivity of
non-small cell lung cancer cell line (A549). J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
30:202011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gao Y, Fan X, Li W, Ping W, Deng Y and Fu
X: miR-138-5p reverses gefitinib resistance in non-small cell lung
cancer cells via negatively regulating G protein-coupled receptor
124. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 446:179–186. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jin F, Wang Y, Li M, Zhu Y, Liang H, Wang
C, Wang F, Zhang CY, Zen K and Li L: MiR-26 enhances
chemosensitivity and promotes apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma
cells through inhibiting autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 8:e25402017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu Z, Shi A, Song D, Han B, Zhang Z, Ma
L, Liu D and Fan Z: Resistin confers resistance to
doxorubicin-induced apoptosis in human breast cancer cells through
autophagy induction. Am J Cancer Res. 7:574–583. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang X, Lan Z, He J, Lai Q, Yao X, Li Q,
Liu Y, Lai H, Gu C and Yan Q: LncRNA SNHG6 promotes chemoresistance
through ULK1-induced autophagy by sponging miR-26a-5p in colorectal
cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int. 19:2342019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhao Z, Li J, Jiang Y, Xu W, Li X and Jing
W: CLDN1 increases drug resistance of non-small cell lung cancer by
activating autophagy via up-regulation of ULK1 phosphorylation. Med
Sci Monit. 23:2906–2916. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Du Z, Sun T, Hacisuleyman E, Fei T, Wang
X, Brown M, Rinn JL, Lee MG, Chen Y, Kantoff PW and Liu XS:
Integrative analyses reveal a long noncoding RNA-mediated sponge
regulatory network in prostate cancer. Nat Commun. 7:109822016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kartha RV and Subramanian S: Competing
endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs): New entrants to the intricacies of gene
regulation. Front Genet. 5:82014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Deng H, Zhang J, Shi J, Guo Z, He C, Ding
L, Tang JH and Hou Y: Role of long non-coding RNA in tumor drug
resistance. Tumor Biol. 37:11623–11631. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Majidinia M and Yousefi B: Long non-coding
RNAs in cancer drug resistance development. DNA Repair (Amst).
45:25–33. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zheng ZG, Xu H, Suo SS, Xu XL, Ni MW, Gu
LH, Chen W, Wang LY, Zhao Y and Tian B: The essential role of H19
contributing to cisplatin resistance by regulating glutathione
metabolism in high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Sci Rep.
6:260932016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Han Z and Shi L: Long non-coding RNA
LUCAT1 modulates methotrexate resistance in osteosarcoma via
miR-200c/ABCB1 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 495:947–953. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wang W, Dong M, Zhang W and Liu T: Long
noncoding LUCAT1 promotes cisplatin resistance of non-small cell
lung cancer by promoting IGF-2. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
23:5229–5234. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Galluzzi L, Pietrocola F, Bravo-San Pedro
JM, Amaravadi RK, Baehrecke EH, Cecconi F, Codogno P, Debnath J,
Gewirtz DA, Karantza V, et al: Autophagy in malignant
transformation and cancer progression. EMBO J. 34:856–880. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang Y, Jiang C, Yang Y, Guo L, Huang J,
Liu X, Wu C and Zou J: Silencing of LncRNA-HOTAIR decreases drug
resistance of Non-small cell lung cancer cells by inactivating
autophagy via suppressing the phosphorylation of ULK1. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 497:1003–1010. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xiong H, Ni Z, He J, Jiang S, Li X, Gong
W, Zheng L, Chen S, Li B and Zhang N: LncRNA HULC triggers
autophagy via stabilizing Sirt1 and attenuates the chemosensitivity
of HCC cells. Oncogene. 36:35282017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jin L, Li Y, Zhang Z, He T, Hu J, Liu J,
Chen M, Gui Y, Yang S and Mao X: miR-514a-3p functions as a tumor
suppressor in renal cell carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 14:5624–5630.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim J, Kundu M, Viollet B and Guan KL:
AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of
Ulk1. Nat Cell Biol. 13:1322011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tang F, Hu P, Yang Z, Xue C, Gong J, Sun
S, Shi L, Zhang S, Li Z and Yang C: SBI0206965, a novel inhibitor
of Ulk1, suppresses non-small cell lung cancer cell growth by
modulating both autophagy and apoptosis pathways. Oncol Rep.
37:3449–3458. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|