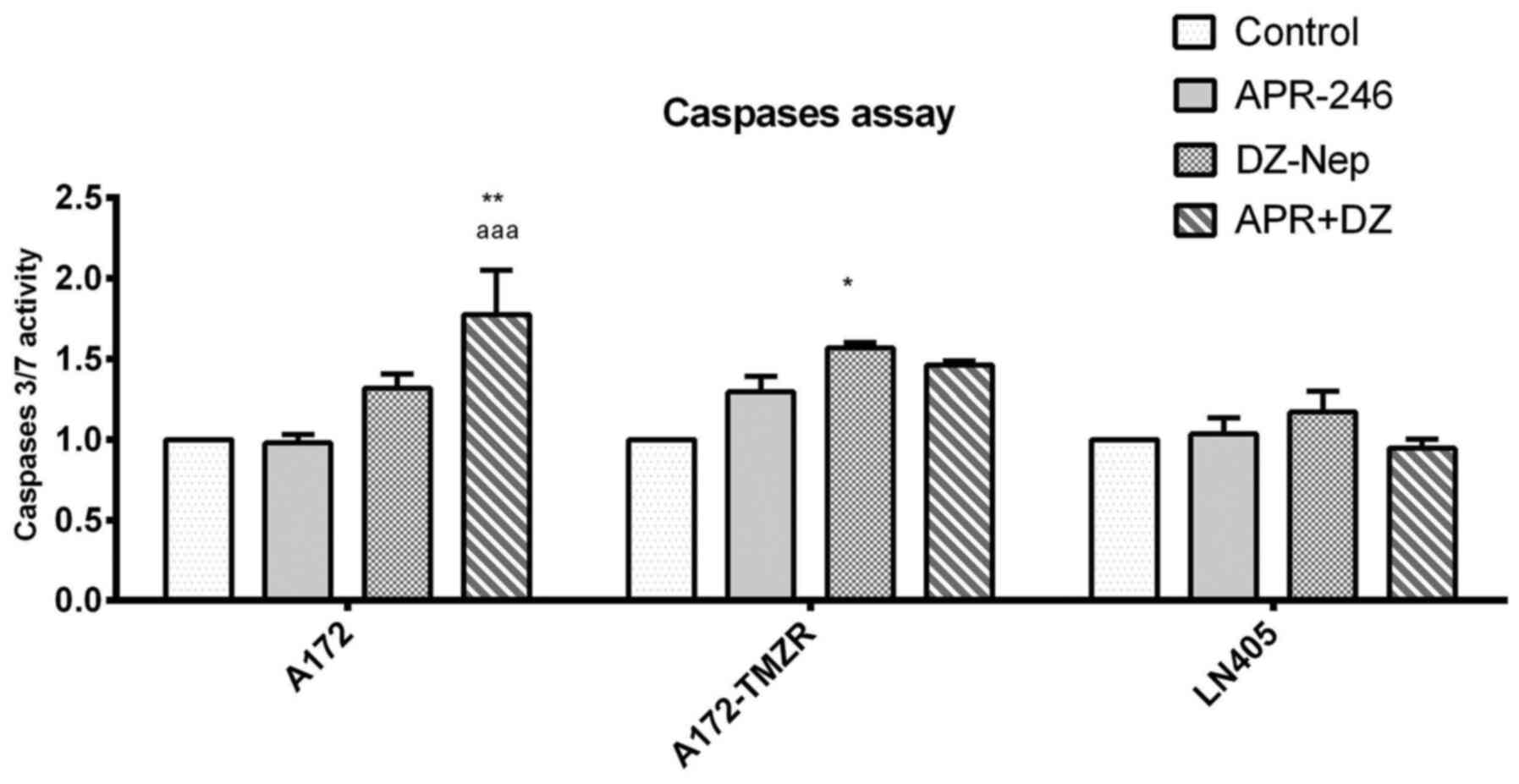
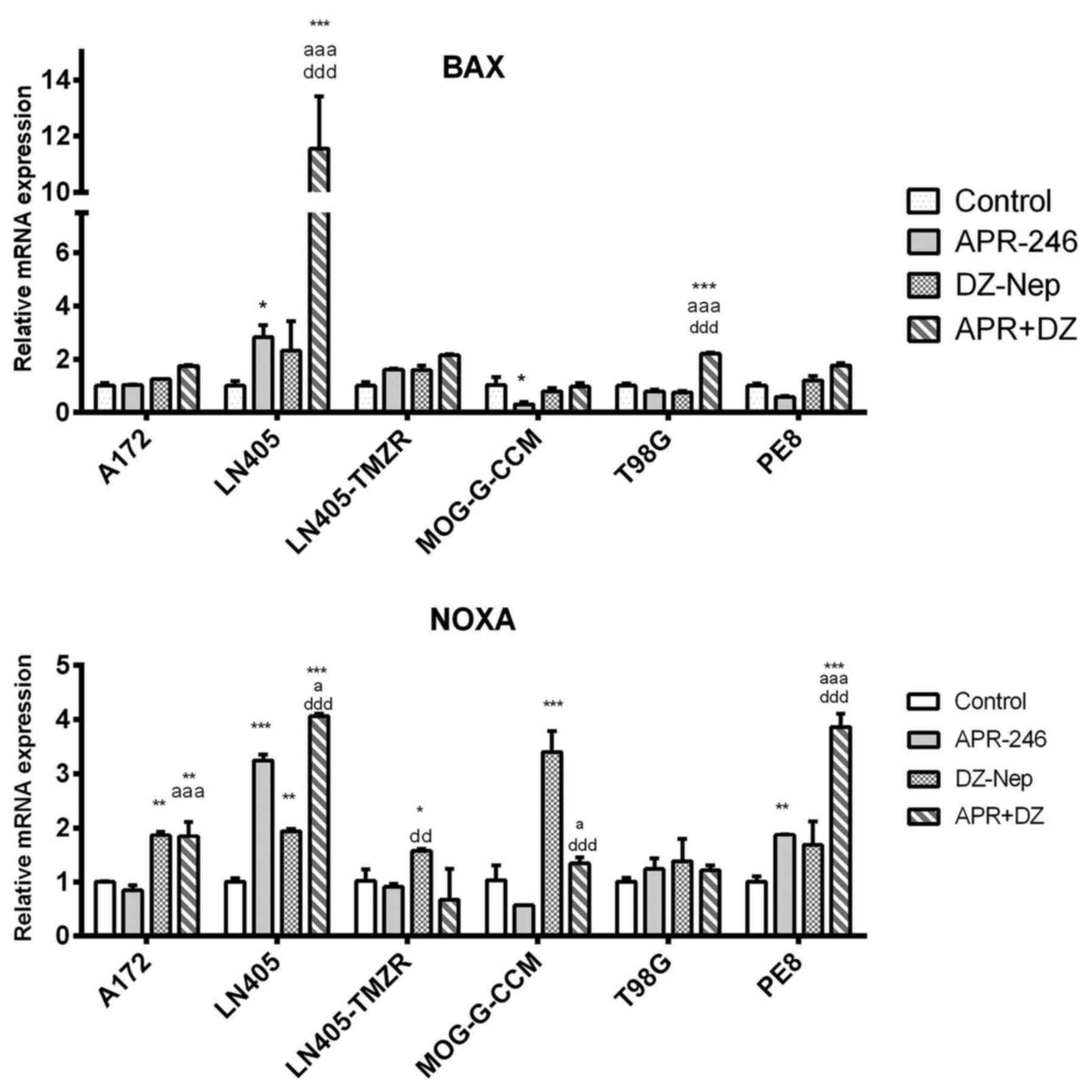
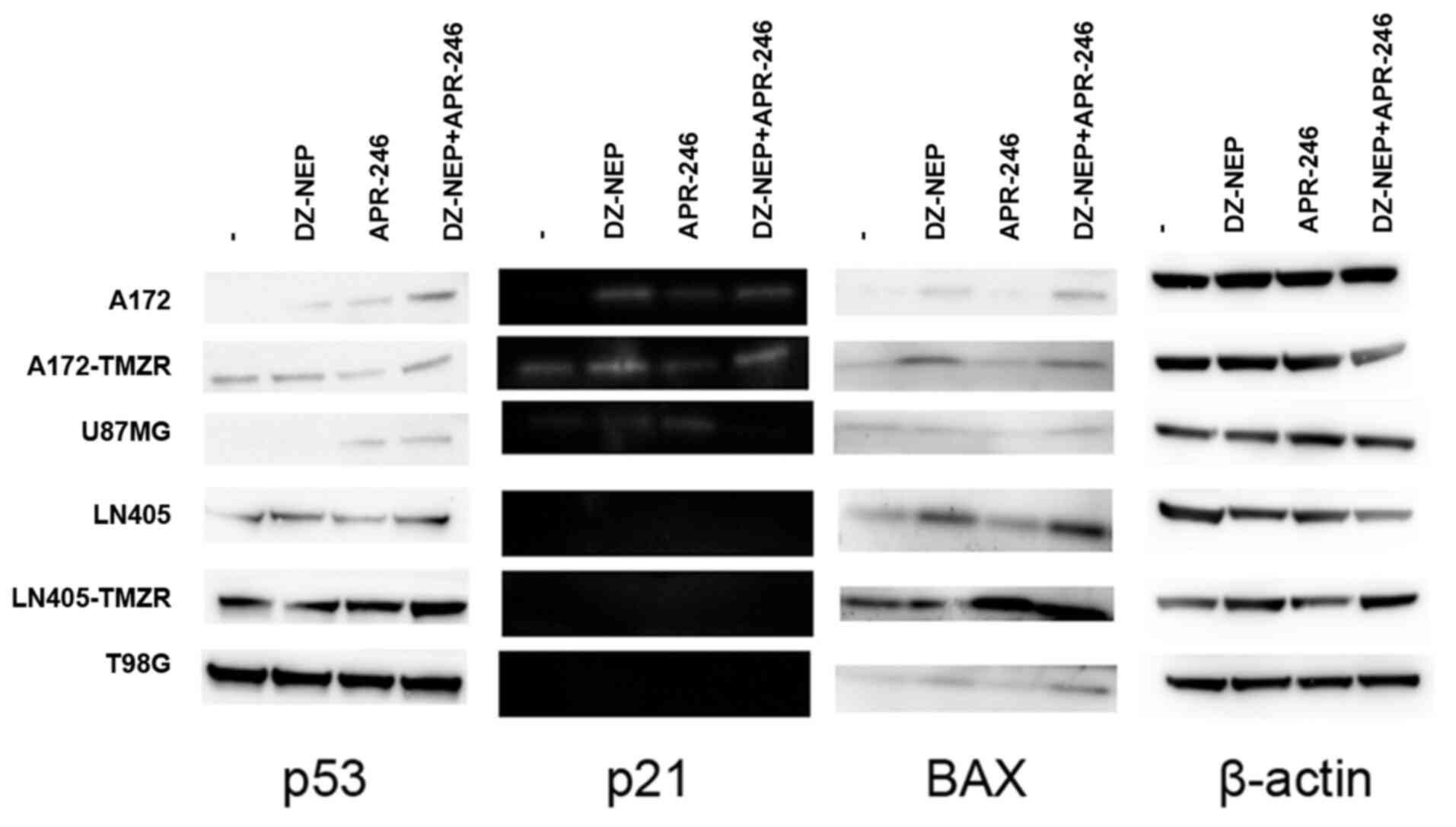
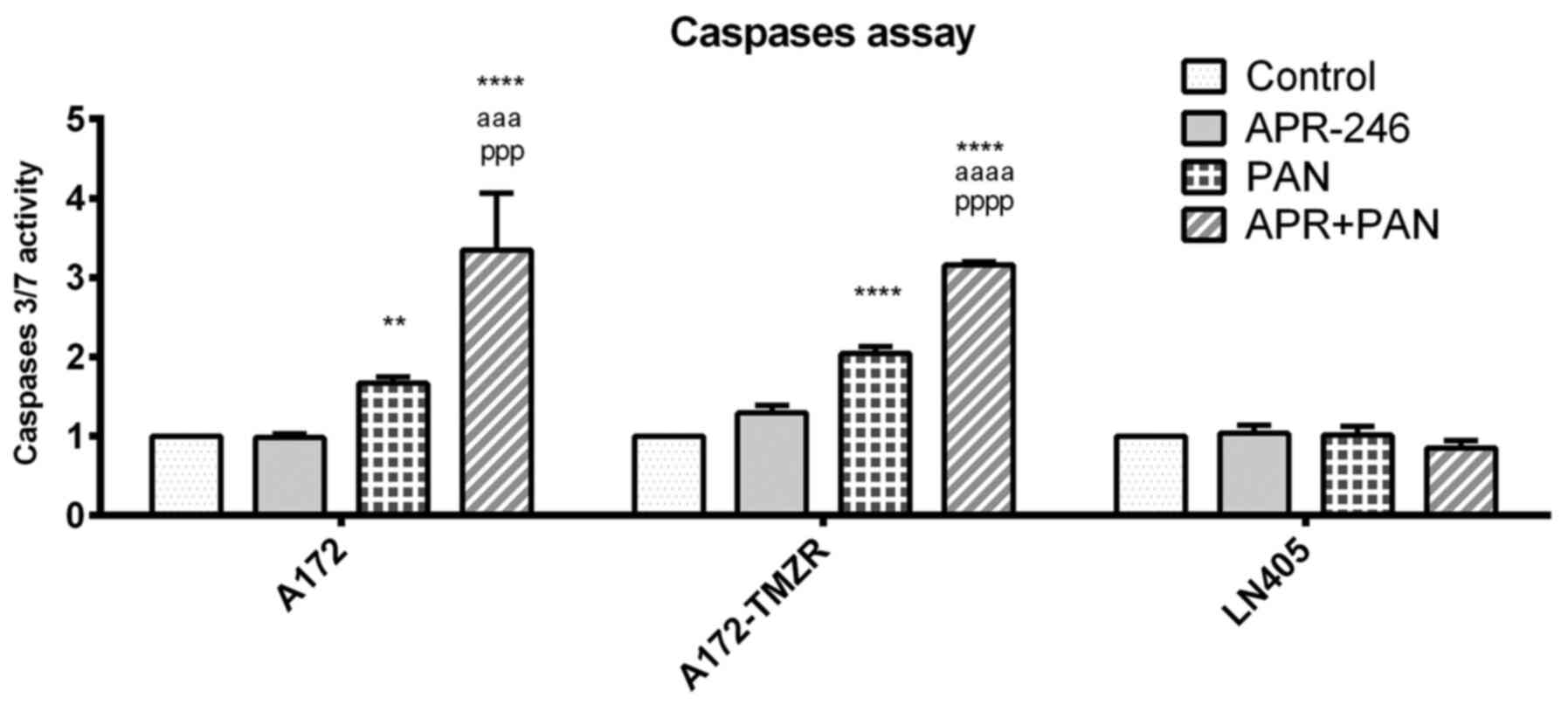
|
1
|
Wirsching HG, Galanis E and Weller M:
Glioblastoma. Handb Clin Neurol. 134:381–397. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Louis DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G, von
Deimling A, Figarella-Branger D, Cavenee WK, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD,
Kleihues P and Ellison DW: The 2016 World Health Organization
Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary.
Acta Neuropathol. 131:803–820. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
De La Rosa J, Urdiciain A, Zazpe I, Zelaya
MV, Meléndez B, Rey JA, Idoate MA and Castresana JS: The
synergistic effect of DZ NEP, panobinostat and temozolomide reduces
clonogenicity and induces apoptosis in glioblastoma cells. Int J
Oncol. 56:283–300. 2020.
|
|
4
|
Urdiciain A, Erausquin E, Meléndez B, Rey
JA, Idoate MA and Castresana JS: Tubastatin A, an inhibitor of
HDAC6, enhances temozolomide induced apoptosis and reverses the
malignant phenotype of glioblastoma cells. Int J Oncol.
54:1797–1808. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Campomenosi P, Ottaggio L, Moro F, Urbini
S, Bogliolo M, Zunino A, Camoriano A, Inga A, Gentile SL, Pellegata
NS, et al: Study on aneuploidy and p53 mutations in astrocytomas.
Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 88:95–102. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pedrote MM, Motta MF, Ferretti GD,
Norberto DR, Spohr TC, Lima FR, Gratton E, Silva JL and de Oliveira
GA: Oncogenic gain of function in glioblastoma is linked to mutant
p53 amyloid oligomers. iScience. 23:1008202020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shiraishi S, Tada K, Nakamura H, Makino K,
Kochi M, Saya H, Kuratsu J and Ushio Y: Influence of p53 mutations
on prognosis of patients with glioblastoma. Cancer. 95:249–257.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bykov VJ and Wiman KG: Mutant p53
reactivation by small molecules makes its way to the clinic. FEBS
Lett. 588:2622–2627. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bykov VJ, Zhang Q, Zhang M, Ceder S,
Abrahmsen L and Wiman KG: Targeting of mutant p53 and the cellular
redox balance by APR-246 as a strategy for efficient cancer
therapy. Front Oncol. 6:212016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lambert JM, Gorzov P, Veprintsev DB,
Söderqvist M, Segerbäck D, Bergman J, Fersht AR, Hainaut P, Wiman
KG and Bykov VJ: PRIMA-1 reactivates mutant p53 by covalent binding
to the core domain. Cancer Cell. 15:376–388. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Levine AJ, Wu MC, Chang A, Silver A,
Attiyeh EF, Lin J and Epstein CB: The spectrum of mutations at the
p53 locus. Evidence for tissue-specific mutagenesis, selection of
mutant alleles, and a 'gain of function' phenotype. Ann NY Acad
Sci. 768:111–128. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Strano S, Dell'Orso S, Di Agostino S,
Fontemaggi G, Sacchi A and Blandino G: Mutant p53: An oncogenic
transcription factor. Oncogene. 26:2212–2219. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Soussi T and Wiman KG: TP53: An oncogene
in disguise. Cell Death Differ. 22:1239–1249. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Brosh R and Rotter V: When mutants gain
new powers: News from the mutant p53 field. Nat Rev Cancer.
9:701–713. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Oren M and Rotter V: Mutant p53
gain-of-function in cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
2:a0011072010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chène P: The role of tetramerization in
p53 function. Oncogene. 20:2611–2617. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gencel-Augusto J and Lozano G: p53
tetramerization: At the center of the dominant-negative effect of
mutant p53. Genes Dev. 34:1128–1146. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pitolli C, Wang Y, Mancini M, Shi Y,
Melino G and Amelio I: Do mutations turn p53 into an oncogene? Int
J Mol Sci. 20:202019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Doyle B, Morton JP, Delaney DW, Ridgway
RA, Wilkins JA and Sansom OJ: p53 mutation and loss have different
effects on tumourigenesis in a novel mouse model of pleomorphic
rhabdo-myosarcoma. J Pathol. 222:129–137. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang X, Chen JX, Liu JP, You C, Liu YH and
Mao Q: Gain of function of mutant TP53 in glioblastoma: Prognosis
and response to temozolomide. Ann Surg Oncol. 21:1337–1344. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wang X, Chen JX, Liu YH, You C and Mao Q:
Mutant TP53 enhances the resistance of glioblastoma cells to
temozolomide by up-regulating O(6)-methylguanine
DNA-methyltransferase. Neurol Sci. 34:1421–1428. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Petitjean A, Achatz MI, Borresen-Dale AL,
Hainaut P and Olivier M: TP53 mutations in human cancers:
Functional selection and impact on cancer prognosis and outcomes.
Oncogene. 26:2157–2165. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Langerød A, Zhao H, Borgan Ø, Nesland JM,
Bukholm IR, Ikdahl T, Kåresen R, Børresen-Dale AL and Jeffrey SS:
TP53 mutation status and gene expression profiles are powerful
prognostic markers of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 9:R302007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Leroy B, Fournier JL, Ishioka C, Monti P,
Inga A, Fronza G and Soussi T: The TP53 website: An integrative
resource centre for the TP53 mutation database and TP53 mutant
analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 41:D962–D969. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Dumay A, Feugeas JP, Wittmer E,
Lehmann-Che J, Bertheau P, Espié M, Plassa LF, Cottu P, Marty M,
André F, et al: Distinct tumor protein p53 mutants in breast cancer
subgroups. Int J Cancer. 132:1227–1231. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Lehmann S, Bykov VJ, Ali D, Andrén O,
Cherif H, Tidefelt U, Uggla B, Yachnin J, Juliusson G, Moshfegh A,
et al: Targeting p53 in vivo: A first-in-human study with
p53-targeting compound APR-246 in refractory hematologic
malignancies and prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 30:3633–3639. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Omar SI and Tuszynski J: The molecular
mechanism of action of methylene quinuclidinone and its effects on
the structure of p53 mutants. Oncotarget. 9:37137–37156. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Weinmann L, Wischhusen J, Demma MJ,
Naumann U, Roth P, Dasmahapatra B and Weller M: A novel p53 rescue
compound induces p53-dependent growth arrest and sensitises glioma
cells to Apo2L/TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Differ.
15:718–729. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Patyka M, Sharifi Z, Petrecca K, Mansure
J, Jean-Claude B and Sabri S: Sensitivity to PRIMA-1MET is
associated with decreased MGMT in human glioblastoma cells and
glioblastoma stem cells irrespective of p53 status. Oncotarget.
7:60245–60269. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Momparler RL and Côté S: Targeting of
cancer stem cells by inhibitors of DNA and histone methylation.
Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 24:1031–1043. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Srinivas NR: Clinical pharmacokinetics of
panobinostat, a novel histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor: Review
and perspectives. Xenobiotica. 47:354–368. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Chou TC: Drug combination studies and
their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method. Cancer
Res. 70:440–446. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chou T and Martin N: CompuSyn Software for
Drug Combinations and for General Dose Effect Analysis, and user's
guide. ComboSyn, Inc; Paramus, NJ: 2005
|
|
34
|
Dulić V, Kaufmann WK, Wilson SJ, Tlsty TD,
Lees E, Harper JW, Elledge SJ and Reed SI: p53-dependent inhibition
of cyclin-dependent kinase activities in human fibroblasts during
radiation-induced G1 arrest. Cell. 76:1013–1023. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Liu X, Shi Y, Guan R, Donawho C, Luo Y,
Palma J, Zhu GD, Johnson EF, Rodriguez LE, Ghoreishi-Haack N, et
al: Potentiation of temozolomide cytotoxicity by poly(ADP)ribose
polymerase inhibitor ABT-888 requires a conversion of
single-stranded DNA damages to double-stranded DNA breaks. Mol
Cancer Res. 6:1621–1629. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller
M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn
U, et al European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer
Brain Tumor and Radiotherapy Groups; National Cancer Institute of
Canada Clinical Trials Group: Radiotherapy plus concomitant and
adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 352:987–996.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Komotar RJ, Otten ML, Moise G and Connolly
ES Jr: Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for
glioblastoma-a critical review. Clin Med Oncol. 2:421–422.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Maslah N, Salomao N, Drevon L, Verger E,
Partouche N, Ly P, Aubin P, Naoui N, Schlageter MH, Bally C, et al:
Synergistic effects of PRIMA-1Met (APR-246) and 5-azacitidine in
TP53-mutated myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia.
Haematologica. 105:1539–1551. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
39
|
Fransson Å, Glaessgen D, Alfredsson J,
Wiman KG, Bajalica-Lagercrantz S and Mohell N: Strong synergy with
APR-246 and DNA-damaging drugs in primary cancer cells from
patients with TP53 mutant High-Grade Serous ovarian cancer. J
Ovarian Res. 9:272016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Peng X, Zhang MQ, Conserva F, Hosny G,
Selivanova G, Bykov VJ, Arnér ES and Wiman KG: APR-246/PRIMA-1MET
inhibits thioredoxin reductase 1 and converts the enzyme to a
dedicated NADPH oxidase. Cell Death Dis. 4:e8812013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Aryee DN, Niedan S, Ban J, Schwentner R,
Muehlbacher K, Kauer M, Kofler R and Kovar H: Variability in
functional p53 reactivation by PRIMA-1(Met)/APR-246 in Ewing
sarcoma. Br J Cancer. 109:2696–2704. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Robles AI, Jen J and Harris CC: Clinical
outcomes of TP53 mutations in cancers. Cold Spring Harb Perspect
Med. 6:a0262942016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Walerych D, Lisek K and Del Sal G: Mutant
p53: One, no one, and one hundred thousand. Front Oncol. 5:2892015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Pflaum J, Schlosser S and Müller M: p53
Family and cellular stress responses in cancer. Front Oncol.
4:2852014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Osanai T, Takagi Y, Toriya Y, Nakagawa T,
Aruga T, Iida S, Uetake H and Sugihara K: Inverse correlation
between the expression of O6-methylguanine-DNA methyl transferase
(MGMT) and p53 in breast cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 35:121–125.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cabrini G, Fabbri E, Lo Nigro C, Dechecchi
MC and Gambari R: Regulation of expression of O6-methylguanine-DNA
methyl-transferase and the treatment of glioblastoma (Review). Int
J Oncol. 47:417–428. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Oldrini B, Vaquero-Siguero N, Mu Q, Kroon
P, Zhang Y, Galán-Ganga M, Bao Z, Wang Z, Liu H, Sa JK, et al: MGMT
genomic rearrangements contribute to chemotherapy resistance in
gliomas. Nat Commun. 11:38832020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Barciszewska AM, Gurda D, Głodowicz P,
Nowak S and Naskręt-Barciszewska MZ: A new epigenetic mechanism of
temozolomide action in glioma cells. PLoS One. 10:e01366692015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lo Dico A, Salvatore D, Martelli C, Ronchi
D, Diceglie C, Lucignani G and Ottobrini L: Intracellular
redox-balance involvement in temozolomide resistance-related
molecular mechanisms in glioblastoma. Cells. 8:82019.
|
|
50
|
Rabé M, Dumont S, Álvarez-Arenas A, Janati
H, Belmonte-Beitia J, Calvo GF, Thibault-Carpentier C, Séry Q,
Chauvin C, Joalland N, et al: Identification of a transient state
during the acquisition of temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma.
Cell Death Dis. 11:192020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Cheng LL, Itahana Y, Lei ZD, Chia NY, Wu
Y, Yu Y, Zhang SL, Thike AA, Pandey A, Rozen S, et al: TP53 genomic
status regulates sensitivity of gastric cancer cells to the histone
meth-ylation inhibitor 3-deazaneplanocin A (DZNep). Clin Cancer
Res. 18:4201–4212. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Cui B, Yang Q, Guan H, Shi B, Hou P and Ji
M: PRIMA-1, a mutant p53 reactivator, restores the sensitivity of
TP53 mutant-type thyroid cancer cells to the histone methylation
inhibitor 3-Deazaneplanocin A. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
99:E962–E970. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhou J, Bi C, Cheong LL, Mahara S, Liu SC,
Tay KG, Koh TL, Yu Q and Chng WJ: The histone methyltransferase
inhibitor, DZNep, up-regulates TXNIP, increases ROS production, and
targets leukemia cells in AML. Blood. 118:2830–2839. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Juan LJ, Shia WJ, Chen MH, Yang WM, Seto
E, Lin YS and Wu CW: Histone deacetylases specifically
down-regulate p53-dependent gene activation. J Biol Chem.
275:20436–20443. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Cai Y, Yan X, Zhang G, Zhao W and Jiao S:
The predictive value of ERCC1 and p53 for the effect of
panobinostat and cisplatin combination treatment in NSCLC.
Oncotarget. 6:18997–19005. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Greve G, Schiffmann I, Pfeifer D, Pantic
M, Schüler J and Lübbert M: The pan-HDAC inhibitor panobinostat
acts as a sensitizer for erlotinib activity in EGFR-mutated and
-wildtype non-small cell lung cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 15:9472015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Chan D, Zheng Y, Tyner JW, Chng WJ, Chien
WW, Gery S, Leong G, Braunstein GD and Koeffler HP: Belinostat and
pano-binostat (HDACI): In vitro and in vivo studies in thyroid
cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 139:1507–1514. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Andreu-Vieyra CV and Berenson JR: The
potential of panobinostat as a treatment option in patients with
relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma. Ther Adv Hematol.
5:197–210. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Anne M, Sammartino D, Barginear MF and
Budman D: Profile of panobinostat and its potential for treatment
in solid tumors: An update. OncoTargets Ther. 6:1613–1624. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Gao L, Gao M, Yang G, Tao Y, Kong Y, Yang
R, Meng X, Ai G, Wei R, Wu H, et al: Synergistic activity of
carfilzomib and panobinostat in multiple myeloma cells via
modulation of ROS generation and ERK1/2. BioMed Res Int.
2015:4590522015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Yung WK: Temozolomide in malignant
gliomas. Semin Oncol. 27(Suppl 6): 27–34. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Johannessen TC and Bjerkvig R: Molecular
mechanisms of temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma multiforme.
Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 12:635–642. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Grogan PT, Sarkaria JN, Timmermann BN and
Cohen MS: Oxidative cytotoxic agent withaferin A resensitizes
temo-zolomide-resistant glioblastomas via MGMT depletion and
induces apoptosis through Akt/mTOR pathway inhibitory modulation.
Invest New Drugs. 32:604–617. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Günther W, Pawlak E, Damasceno R, Arnold H
and Terzis AJ: Temozolomide induces apoptosis and senescence in
glioma cells cultured as multicellular spheroids. Br J Cancer.
88:463–469. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Kohsaka S, Takahashi K, Wang L, Tanino M,
Kimura T, Nishihara H and Tanaka S: Inhibition of GSH synthesis
potentiates temozolomide-induced bystander effect in glioblastoma.
Cancer Lett. 331:68–75. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Haffo L, Lu J, Bykov VJ, Martin SS, Ren X,
Coppo L, Wiman KG and Holmgren A: Inhibition of the glutaredoxin
and thioredoxin systems and ribonucleotide reductase by mutant
p53-targeting compound APR-246. Sci Rep. 8:126712018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|