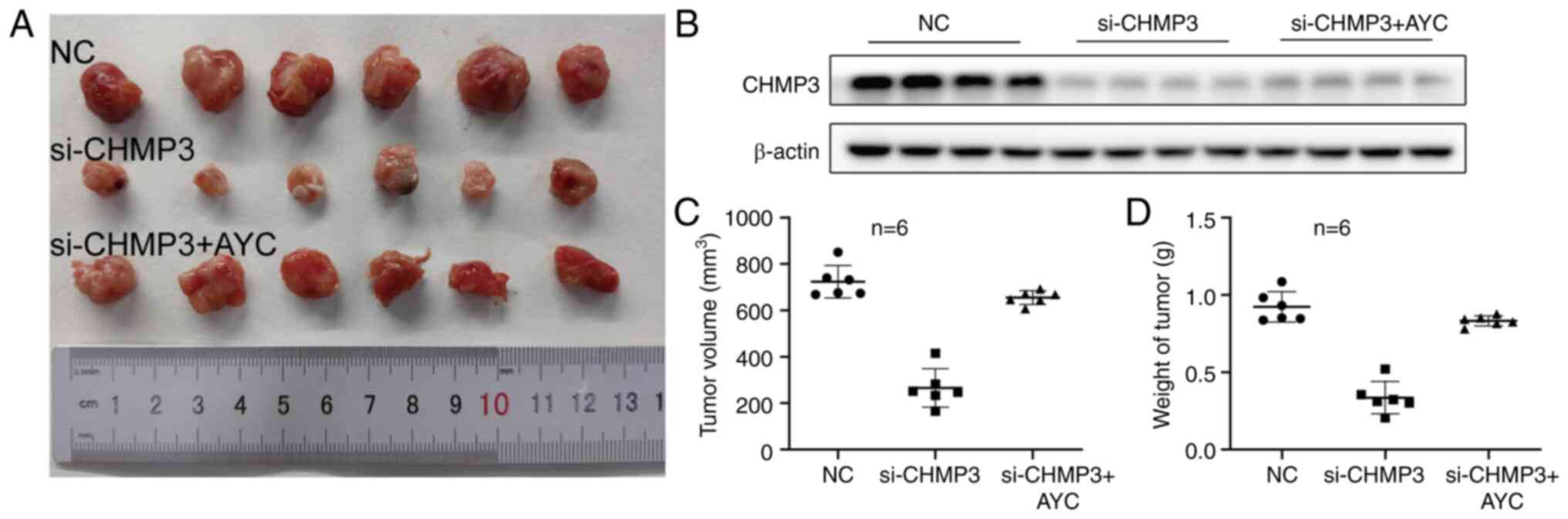
|
1
|
Chapiro J, Wood LD, Lin M, Duran R,
Cornish T, Lesage D, Charu V, Schernthaner R, Wang Z, Tacher V, et
al: Radiologic-pathologic analysis of contrast-enhanced and
diffusion-weighted MR imaging in patients with HCC after TACE:
Diagnostic accuracy of 3D quantitative image analysis. Radiology.
273:746–758. 2014.
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:7–33. 2021.
|
|
3
|
Tao S, Liang S, Zeng T and Yin D:
Epigenetic modification-related mechanisms of hepatocellular
carcinoma resistance to immune checkpoint inhibition. Front
Immunol. 13:10436672023.
|
|
4
|
Glantzounis GK, Paliouras A, Stylianidi
MC, Milionis H, Tzimas P, Roukos D, Pentheroudakis G and Felekouras
E: The role of liver resection in the management of intermediate
and advanced stage hepatocellular carcinoma. A systematic review.
Eur J Surg Oncol. 44:195–208. 2018.
|
|
5
|
Cammarota A, Zanuso V, Manfredi GF, Murphy
R, Pinato DJ and Rimassa L: Immunotherapy in hepatocellular
carcinoma: How will it reshape treatment sequencing? Ther Adv Med
Oncol. 15:175883592211480292023.
|
|
6
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
|
|
7
|
Fang Y, Tian S, Pan Y, Li W, Wang Q, Tang
Y, Yu T, Wu X, Shi Y, Ma P and Shu Y: Pyroptosis: A new frontier in
cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 121:1095952020.
|
|
8
|
Ouyang X, Zhou J, Lin L, Zhang Z, Luo S
and Hu D: Pyroptosis, inflammasome, and gasdermins in tumor
immunity. Innate Immun. 29:3–13. 2023.
|
|
9
|
Shi J, Zhao Y, Wang K, Shi X, Wang Y,
Huang H, Zhuang Y, Cai T, Wang F and Shao F: Cleavage of GSDMD by
inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death. Nature.
526:660–665. 2015.
|
|
10
|
Vande Walle L and Lamkanfi M: Pyroptosis.
Curr Biol. 26:R568–R572. 2016.
|
|
11
|
Yu P, Zhang X, Liu N, Tang L, Peng C and
Chen X: Pyroptosis: Mechanisms and diseases. Signal Transduct
Target Ther. 6:1282021.
|
|
12
|
Kang R, Zeng L, Zhu S, Xie Y, Liu J, Wen
Q, Cao L, Xie M, Ran Q, Kroemer G, et al: Lipid peroxidation drives
gasdermin D-mediated pyroptosis in lethal polymicrobial sepsis.
Cell Host Microbe. 24:97–108.e4. 2018.
|
|
13
|
Pilla DM, Hagar JA, Haldar AK, Mason AK,
Degrandi D, Pfeffer K, Ernst RK, Yamamoto M, Miao EA and Coers J:
Guanylate binding proteins promote caspase-11-dependent pyroptosis
in response to cytoplasmic LPS. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
111:6046–6051. 2014.
|
|
14
|
Wei Q, Guo P, Mu K, Zhang Y, Zhao W, Huai
W, Qiu Y, Li T, Ma X, Liu Y, et al: Estrogen suppresses
hepatocellular carcinoma cells through ERβ-mediated upregulation of
the NLRP3 inflammasome. Lab Invest. 95:804–816. 2015.
|
|
15
|
Lata S, Schoehn G, Solomons J, Pires R,
Göttlinger HG and Weissenhorn W: Structure and function of
ESCRT-III. Biochem Soc Trans. 37:156–160. 2009.
|
|
16
|
Babst M, Katzmann DJ, Estepa-Sabal EJ,
Meerloo T and Emr SD: Escrt-III: An endosome-associated
heterooligomeric protein complex required for mvb sorting. Dev
Cell. 3:271–282. 2002.
|
|
17
|
Babst M, Wendland B, Estepa EJ and Emr SD:
The Vps4p AAA ATPase regulates membrane association of a Vps
protein complex required for normal endosome function. Embo J.
17:2982–2993. 1998.
|
|
18
|
Bishop N and Woodman P: ATPase-defective
mammalian VPS4 localizes to aberrant endosomes and impairs
cholesterol trafficking. Mol Biol Cell. 11:227–239. 2000.
|
|
19
|
Saksena S, Wahlman J, Teis D, Johnson AE
and Emr SD: Functional reconstitution of ESCRT-III assembly and
disassembly. Cell. 136:97–109. 2009.
|
|
20
|
Teis D, Saksena S and Emr SD: Ordered
assembly of the ESCRT-III complex on endosomes is required to
sequester cargo during MVB formation. Dev Cell. 15:578–589.
2008.
|
|
21
|
Wang Z and Wang X: miR-122-5p promotes
aggression and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in triple-negative
breast cancer by suppressing charged multivesicular body protein 3
through mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling. J Cell Physiol.
235:2825–2835. 2020.
|
|
22
|
Zhou Y, Zheng J, Bai M, Gao Y and Lin N:
Effect of pyroptosis-related genes on the prognosis of breast
cancer. Front Oncol. 12:9481692022.
|
|
23
|
Niu D, Chen Y, Mi H, Mo Z and Pang G: The
epiphany derived from T-cell-inflamed profiles: Pan-cancer
characterization of CD8A as a biomarker spanning clinical
relevance, cancer prognosis, immunosuppressive environment, and
treatment responses. Front Genet. 13:9744162022.
|
|
24
|
Li C, Liang H, Bian S, Hou X and Ma Y:
Construction of a prognosis model of the pyroptosis-related gene in
multiple myeloma and screening of core genes. ACS Omega.
7:34608–34620. 2022.
|
|
25
|
Li Y, Li Y, Zhang X, Duan X, Feng H, Yu Z
and Gao Y: A novel association of pyroptosis-related gene signature
with the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Oncol.
12:9868272022.
|
|
26
|
Man SM and Kanneganti TD: Regulation of
inflammasome activation. Immunol Rev. 265:6–21. 2015.
|
|
27
|
Kovacs SB and Miao EA: Gasdermins:
Effectors of pyroptosis. Trends Cell Biol. 27:673–684. 2017.
|
|
28
|
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C and
Zhang Z: GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression
profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 45:W98–W102.
2017.
|
|
29
|
Liu L, Li Y, Cao D, Qiu S, Li Y, Jiang C,
Bian R, Yang Y, Li L, Li X, et al: SIRT3 inhibits gallbladder
cancer by induction of AKT-dependent ferroptosis and blockade of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Lett. 510:93–104.
2021.
|
|
30
|
Jia C, Chen H, Zhang J, Zhou K, Zhuge Y,
Niu C, Qiu J, Rong X, Shi Z, Xiao J, et al: Role of pyroptosis in
cardiovascular diseases. Int Immunopharmacol. 67:311–318. 2019.
|
|
31
|
Wei Q, Mu K, Li T, Zhang Y, Yang Z, Jia X,
Zhao W, Huai W, Guo P and Han L: Deregulation of the NLRP3
inflammasome in hepatic parenchymal cells during liver cancer
progression. Lab Invest. 94:52–62. 2014.
|
|
32
|
Yan Z, Da Q, Li Z, Lin Q, Yi J, Su Y, Yu
G, Ren Q, Liu X, Lin Z, et al: Inhibition of NEK7 suppressed
hepatocellular carcinoma progression by mediating cancer cell
pyroptosis. Front Oncol. 12:8126552022.
|
|
33
|
Chen W, Quan Y, Fan S, Wang H, Liang J,
Huang L, Chen L, Liu Q, He P and Ye Y: Exosome-transmitted circular
RNA hsa_circ_0051443 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma
progression. Cancer Lett. 475:119–128. 2020.
|
|
34
|
Zhang Q, Chen L, Gao M, Wang S, Meng L and
Guo L: Molecular docking and in vitro experiments verified that
kaempferol induced apoptosis and inhibited human HepG2 cell
proliferation by targeting BAX, CDK1, and JUN. Mol Cell Biochem.
478:767–780. 2023.
|
|
35
|
Sun X, Zhong X, Ma W, Feng W, Huang Q, Ma
M, Lv M, Hu R, Han Z, Li J and Zhou X: Germacrone induces
caspase-3/GSDME activation and enhances ROS production, causing
HepG2 pyroptosis. Exp Ther Med. 24:4562022.
|
|
36
|
Hou J, Zhao R, Xia W, Chang CW, You Y, Hsu
JM, Nie L, Chen Y, Wang YC, Liu C, et al: PD-L1-mediated gasdermin
C expression switches apoptosis to pyroptosis in cancer cells and
facilitates tumour necrosis. Nat Cell Biol. 22:1264–1275. 2020.
|
|
37
|
Zhang T, Li Y, Zhu R, Song P, Wei Y, Liang
T and Xu G: Transcription factor p53 suppresses tumor growth by
prompting pyroptosis in non-small-cell lung cancer. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2019:87468952019.
|
|
38
|
Tan Y, Chen Q, Li X, Zeng Z, Xiong W, Li
G, Li X, Yang J, Xiang B and Yi M: Pyroptosis: A new paradigm of
cell death for fighting against cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
40:1532021.
|
|
39
|
Hsu SK, Li CY, Lin IL, Syue WJ, Chen YF,
Cheng KC, Teng YN, Lin YH, Yen CH and Chiu CC: Inflammation-related
pyroptosis, a novel programmed cell death pathway, and its
crosstalk with immune therapy in cancer treatment. Theranostics.
11:8813–8835. 2021.
|
|
40
|
Cui J, Zhou Z, Yang H, Jiao F, Li N, Gao
Y, Wang L, Chen J and Quan M: MST1 suppresses pancreatic cancer
progression via ROS-induced pyroptosis. Mol Cancer Res.
17:1316–1325. 2019.
|
|
41
|
Teng JF, Mei QB, Zhou XG, Tang Y, Xiong R,
Qiu WQ, Pan R, Law BY, Wong VK, Yu CL, et al: Polyphyllin VI
induces caspase-1-mediated pyroptosis via the induction of
ROS/NF-κB/NLRP3/GSDMD signal axis in non-small cell lung cancer.
Cancers (Basel). 12:1932020.
|
|
42
|
Rébé C and Ghiringhelli F: Interleukin-1β
and cancer. Cancers (Basel). 12:17912020.
|
|
43
|
Yan W, Chang Y, Liang X, Cardinal JS,
Huang H, Thorne SH, Monga SP, Geller DA, Lotze MT and Tsung A:
High-mobility group box 1 activates caspase-1 and promotes
hepatocellular carcinoma invasiveness and metastases. Hepatology.
55:1863–1875. 2012.
|
|
44
|
Lopez-Pastrana J, Ferrer LM, Li YF, Xiong
X, Xi H, Cueto R, Nelson J, Sha X, Li X, Cannella AL, et al:
Inhibition of caspase-1 activation in endothelial cells improves
angiogenesis: A NOVEL THERAPEUTIC POTENTIAL FOR ISCHEMIA. J Biol
Chem. 290:17485–17494. 2015.
|
|
45
|
He Q, Liu M, Huang W, Chen X, Zhang B,
Zhang T, Wang Y, Liu D, Xie M, Ji X, et al: IL-1β-induced elevation
of solute carrier family 7 member 11 promotes hepatocellular
carcinoma metastasis through up-regulating programmed death ligand
1 and colony-stimulating factor 1. Hepatology. 74:3174–3193.
2021.
|
|
46
|
Dang Y, Chen J, Feng W, Qiao C, Han W, Nie
Y, Wu K, Fan D and Xia L: Interleukin 1β-mediated HOXC10
overexpression promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by
upregulating PDPK1 and VASP. Theranostics. 10:3833–3848. 2020.
|
|
47
|
Hage C, Hoves S, Strauss L, Bissinger S,
Prinz Y, Pöschinger T, Kiessling F and Ries CH: Sorafenib induces
pyroptosis in macrophages and triggers natural killer cell-mediated
cytotoxicity against hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology.
70:1280–1297. 2019.
|
|
48
|
Shen Z, Zhou H, Li A, Wu T, Ji X, Guo L,
Zhu X, Zhang D and He X: Metformin inhibits hepatocellular
carcinoma development by inducing apoptosis and pyroptosis through
regulating FOXO3. Aging (Albany NY). 13:22120–22133. 2021.
|
|
49
|
Rühl S, Shkarina K, Demarco B, Heilig R,
Santos JC and Broz P: ESCRT-dependent membrane repair negatively
regulates pyroptosis downstream of GSDMD activation. Science.
362:956–960. 2018.
|
|
50
|
Tang Q, Li W, Zheng X, Ren L, Liu J, Li S,
Wang J and Du G: MELK is an oncogenic kinase essential for
metastasis, mitotic progression, and programmed death in lung
carcinoma. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 5:2792020.
|
|
51
|
Bruix J, Gores GJ and Mazzaferro V:
Hepatocellular carcinoma: Clinical frontiers and perspectives. Gut.
63:844–855. 2014.
|
|
52
|
Kuphal S and Bosserhoff AK: Influence of
the cytoplasmic domain of E-cadherin on endogenous N-cadherin
expression in malignant melanoma. Oncogene. 25:248–259. 2006.
|
|
53
|
Mondal S, Adhikari N, Banerjee S, Amin SA
and Jha T: Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and its inhibitors in
cancer: A minireview. Eur J Med Chem. 194:1122602020.
|
|
54
|
Satelli A and Li S: Vimentin in cancer and
its potential as a molecular target for cancer therapy. Cell Mol
Life Sci. 68:3033–3046. 2011.
|
|
55
|
Walker A, Frei R and Lawson KR: The
cytoplasmic domain of N-cadherin modulates MMP-9 induction in oral
squamous carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 45:1699–1706. 2014.
|
|
56
|
Cao ZQ, Wang Z and Leng P: Aberrant
N-cadherin expression in cancer. Biomed Pharmacother.
118:1093202019.
|