Spandidos Publications style
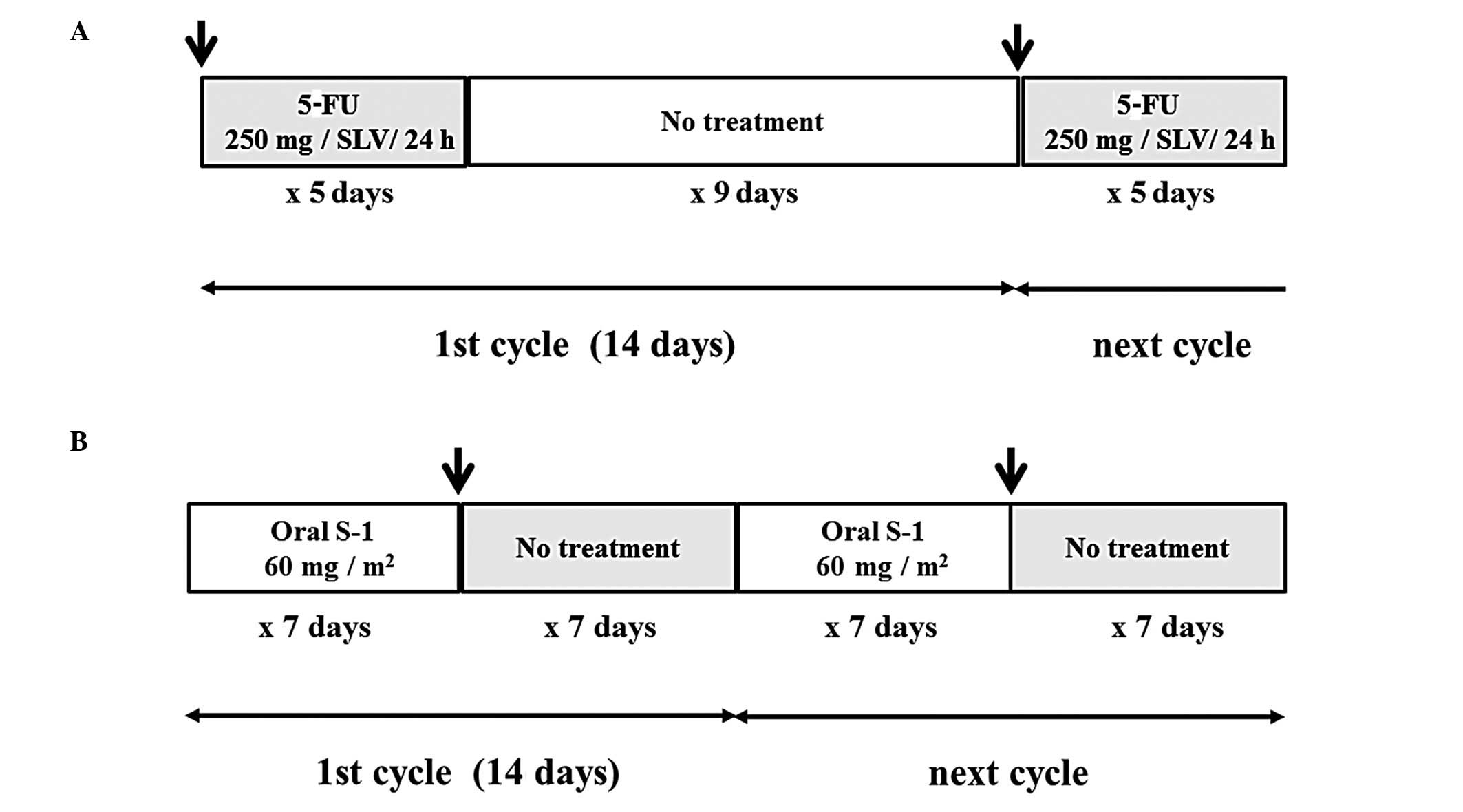
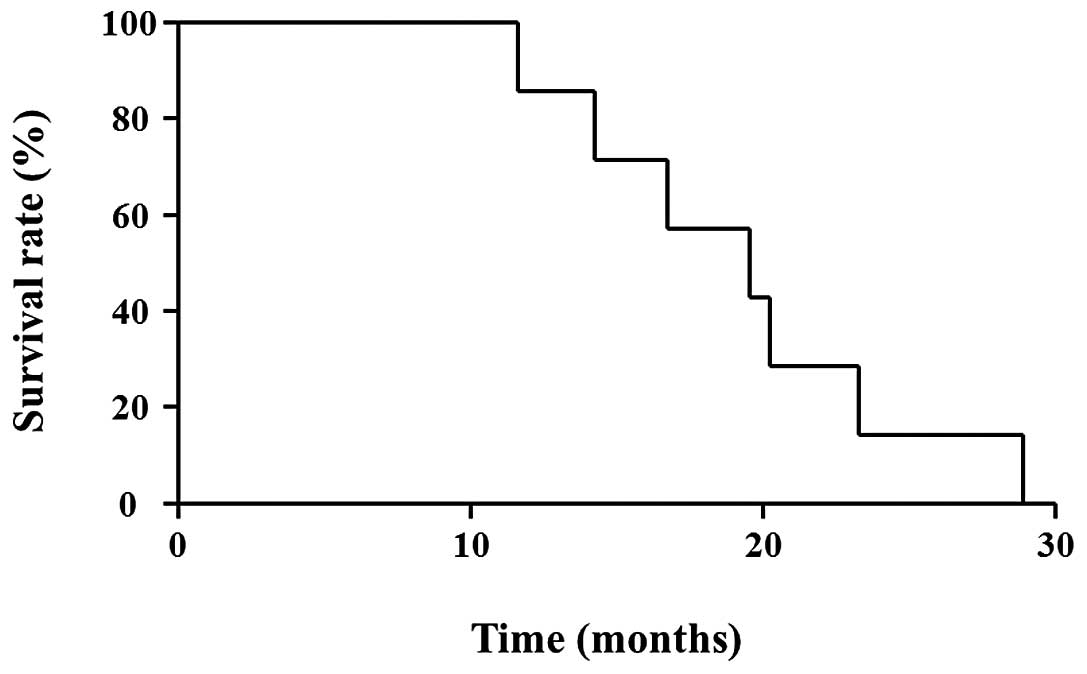
Tajima H, Kitagawa H, Tsukada T, Okamoto K, Nakanuma SI, Sakai S, Makino I, Furukawa H, Hayashi H, Oyama K, Oyama K, et al: Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy with gemcitabine and 5‑fluorouracil or oral S‑1 improves the prognosis of patients with postoperative liver metastases from pancreatic cancer. Mol Clin Oncol 1: 869-874, 2013.
APA
Tajima, H., Kitagawa, H., Tsukada, T., Okamoto, K., Nakanuma, S., Sakai, S. ... Sai, Y. (2013). Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy with gemcitabine and 5‑fluorouracil or oral S‑1 improves the prognosis of patients with postoperative liver metastases from pancreatic cancer. Molecular and Clinical Oncology, 1, 869-874. https://doi.org/10.3892/mco.2013.152
MLA
Tajima, H., Kitagawa, H., Tsukada, T., Okamoto, K., Nakanuma, S., Sakai, S., Makino, I., Furukawa, H., Hayashi, H., Oyama, K., Inokuchi, M., Nakagawara, H., Miyashita, T., Itoh, H., Fujita, H., Takamura, H., Ninomiya, I., Fushida, S., Fujimura, T., Ohta, T., Koda, W., Minami, T., Ryu, Y., Sanada, J., Gabata, T., Matsui, O., Sai, Y."Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy with gemcitabine and 5‑fluorouracil or oral S‑1 improves the prognosis of patients with postoperative liver metastases from pancreatic cancer". Molecular and Clinical Oncology 1.5 (2013): 869-874.
Chicago
Tajima, H., Kitagawa, H., Tsukada, T., Okamoto, K., Nakanuma, S., Sakai, S., Makino, I., Furukawa, H., Hayashi, H., Oyama, K., Inokuchi, M., Nakagawara, H., Miyashita, T., Itoh, H., Fujita, H., Takamura, H., Ninomiya, I., Fushida, S., Fujimura, T., Ohta, T., Koda, W., Minami, T., Ryu, Y., Sanada, J., Gabata, T., Matsui, O., Sai, Y."Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy with gemcitabine and 5‑fluorouracil or oral S‑1 improves the prognosis of patients with postoperative liver metastases from pancreatic cancer". Molecular and Clinical Oncology 1, no. 5 (2013): 869-874. https://doi.org/10.3892/mco.2013.152