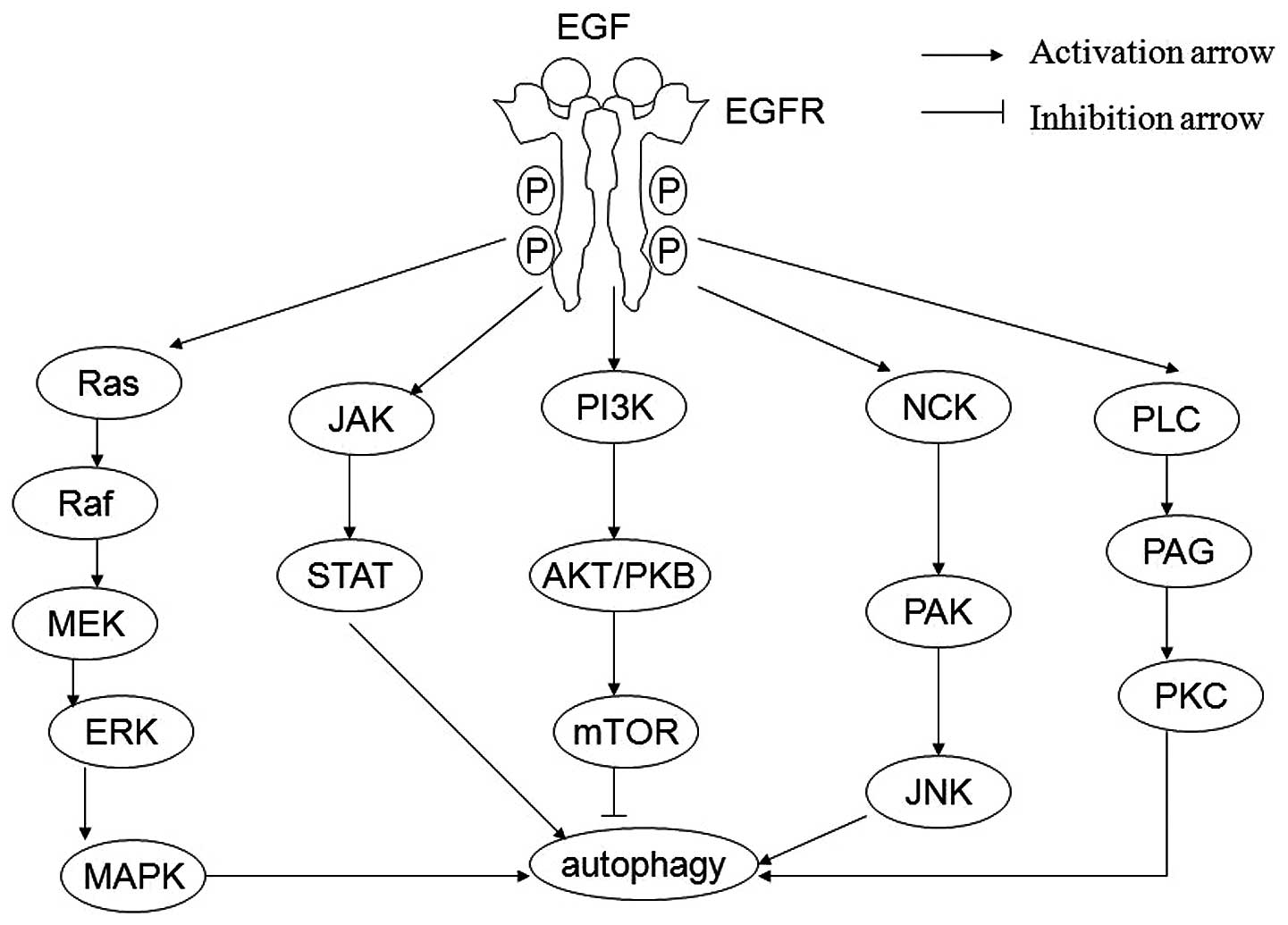
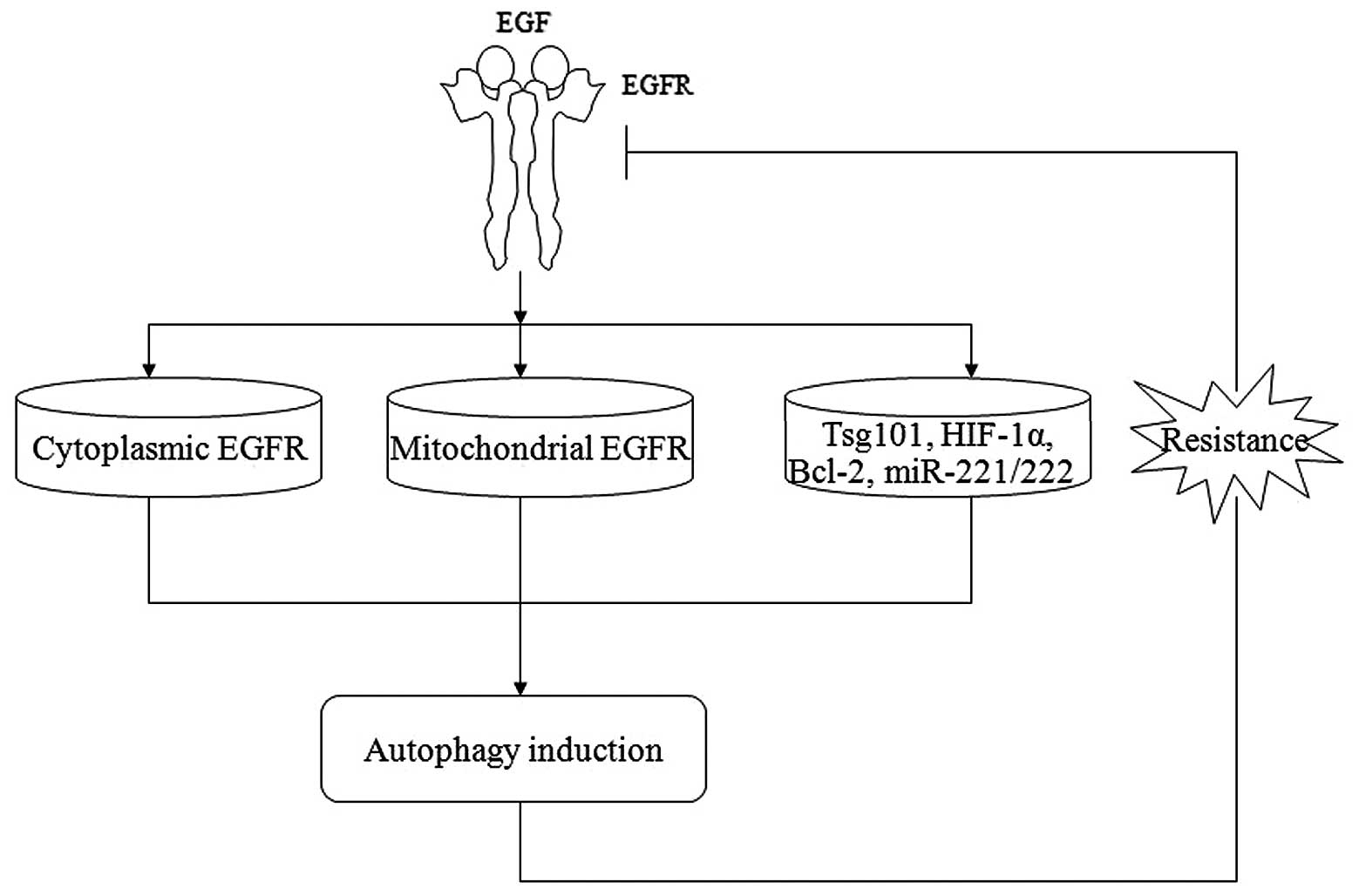
|
1.
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Shigematsu H, Lin L, Takahashi T, Nomura
M, Suzuki M, Wistuba II, Fong KM, Lee H, Toyooka S, Shimizu N, et
al: Clinical and biological features associated with epidermal
growth factor receptor gene mutations in lung cancers. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 97:339–346. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Riely GJ, Politi KA, Miller VA and Pao W:
Update on epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in non-small
cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 12:7232–7241. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Henson ES and Gibson SB: Surviving cell
death through epidermal growth factor (EGF) signal transduction
pathways: implications for cancer therapy. Cell Signal.
18:2089–2097. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5.
|
Yarden Y and Shilo BZ: SnapShot: EGFR
signaling pathway. Cell. 131:10182007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Kobayashi S, Boggon TJ, Dayaram T, Janne
PA, Kocher O, Meyerson M, Johnson BE, Eck MJ, Tenen DG and Halmos
B: EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to
gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 352:786–792. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Klionsky DJ, Abdalla FC, Abeliovich H, et
al: Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for
monitoring autophagy. Autophagy. 8:445–544. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8.
|
Yang Z and Klionsky DJ: Eaten alive: a
history of macroautophagy. Nat Cell Biol. 12:814–822. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Kondo Y, Kanzawa T, Sawaya R and Kondo S:
The role of autophagy in cancer development and response to
therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 5:726–734. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Janku F, McConkey DJ, Hong DS and Kurzrock
R: Autophagy as a target for anticancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin
Oncol. 8:528–539. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Maiuri MC, Galluzzi L, Morselli E, Kepp O,
Malik SA and Kroemer G: Autophagy regulation by p53. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 22:181–185. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12.
|
Glick D, Barth S and Macleod KF:
Autophagy: cellular and molecular mechanisms. J Pathol. 221:3–12.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Han W, Pan H, Chen Y, et al: EGFR tyrosine
kinase inhibitors activate autophagy as a cytoprotective response
in human lung cancer cells. PLoS One. 6:e186912011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Sridhar SS, Seymour L and Shepherd FA:
Inhibitors of epidermal-growth-factor receptors: a review of
clinical research with a focus on non-small-cell lung cancer.
Lancet Oncol. 4:397–406. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Galizia G, Lieto E, De Vita F, Orditura M,
Castellano P, Troiani T, Imperatore V and Ciardiello F: Cetuximab,
a chimeric human mouse anti-epidermal growth factor receptor
monoclonal antibody, in the treatment of human colorectal cancer.
Oncogene. 26:3654–3660. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Vecchione L, Jacobs B, Normanno N,
Ciardiello F and Tejpar S: EGFR-targeted therapy. Exp Cell Res.
317:2765–2771. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Lin SY, Makino K, Xia W, Matin A, Wen Y,
Kwong KY, Bourguignon L and Hung MC: Nuclear localization of EGF
receptor and its potential new role as a transcription factor. Nat
Cell Biol. 3:802–808. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Boerner JL, Demory ML, Silva C and Parsons
SJ: Phosphorylation of Y845 on the epidermal growth factor receptor
mediates binding to the mitochondrial protein cytochrome c
oxidase subunit II. Mol Cell Biol. 24:7059–7071. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Han W and Lo HW: Landscape of EGFR
signaling network in human cancers: biology and therapeutic
response in relation to receptor subcellular locations. Cancer
Lett. 318:124–134. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Yue X, Song W, Zhang W, Chen L, Xi Z, Xin
Z and Jiang X: Mitochondrially localized EGFR is subjected to
autophagic regulation and implicated in cell survival. Autophagy.
4:641–649. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Yarden Y and Sliwkowski MX: Untangling the
ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2:127–137. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Ciardiello F and Tortora G: EGFR
antagonists in cancer treatment. N Engl J Med. 358:1160–1174. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Yan J, Yang H, Wang G, Sun L, Zhou Y, Guo
Y, Xi Z and Jiang X: Autophagy augmented by troglitazone is
independent of EGFR transactivation and correlated with
AMP-activated protein kinase signaling. Autophagy. 6:67–73. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Cardone L, Bardelli A and Avvedimento VE:
Activation of β-catenin by oncogenic PIK3CA and EGFR promotes
resistance to glucose deprivation by inducing a strong antioxidant
response. PLoS One. 7:e375262012.
|
|
25.
|
Cao C, Lu S, Jiang Q, et al: EGFR
activation confers protections against UV-induced apoptosis in
cultured mouse skin dendritic cells. Cell Signal. 20:1830–1838.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Ghildiyal R, Dixit D and Sen E: EGFR
inhibitor BIBU induces apoptosis and defective autophagy in glioma
cells. Mol Carcinog. Jun 29–2012.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27.
|
Akhtar S, Yousif MH, Chandrasekhar B and
Benter IF: Activation of EGFR/ERBB2 via pathways involving ERK1/2,
P38 MAPK, AKT and FOXO enhances recovery of diabetic hearts from
ischemia-reperfusion injury. PLoS One. 7:e390662012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28.
|
Chen KL, Chang WS, Cheung CH, et al:
Targeting cathepsin S induces tumor cell autophagy via the EGFR-ERK
signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 317:89–98. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Yu Y, Fan SM, Ye YC, Tashiro S, Onodera S
and Ikejima T: The tyrphostin AG1478 augments oridonin-induced A431
cell apoptosis by blockage of JNK MAPK and enhancement of oxidative
stress. Free Radic Res. 46:1393–1405. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Dreier A, Barth S, Goswami A and Weis J:
Cetuximab induces mitochondrial translocalization of EGFRvIII, but
not EGFR: involvement of mitochondria in tumor drug resistance?
Tumour Biol. 33:85–94. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Cao X, Zhu H, Ali-Osman F and Lo HW: EGFR
and EGFRvIII undergo stress- and EGFR kinase inhibitor-induced
mitochondrial translocalization: a potential mechanism of
EGFR-driven antagonism of apoptosis. Mol Cancer. 10:262011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32.
|
Morris CR, Stanton MJ, Manthey KC, Oh KB
and Wagner KU: A knockout of the Tsg101 gene leads to decreased
expression of ErbB receptor tyrosine kinases and induction of
autophagy prior to cell death. PLoS One. 7:e343082012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Li X and Fan Z: The epidermal growth
factor receptor antibody cetuximab induces autophagy in cancer
cells by downregulating HIF-α and Bcl-2 and activating the beclin
1/hVps34 complex. Cancer Res. 70:5942–5952. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Teixeira AL, Gomes M and Medeiros R: EGFR
signaling pathway and related-miRNAs in age-related diseases: the
example of miR-221 and miR-222. Front Genet. 3:2862012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Hu YL, Jahangiri A, Delay M and Aghi MK:
Tumor cell autophagy as an adaptive response mediating resistance
to treatments such as antiangiogenic therapy. Cancer Res.
72:4294–4299. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Zou Z, Yuan Z, Zhang Q, et al: Aurora
kinase A inhibition-induced autophagy triggers drug resistance in
breast cancer cells. Autophagy. 8:1798–1810. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Regales L, Balak MN, Gong Y, Politi K,
Sawai A, Le C, Koutcher JA, Solit DB, Rosen N, Zakowski MF and Pao
W: Development of new mouse lung tumor models expressing EGFR T790M
mutants associated with clinical resistance to kinase inhibitors.
PLoS One. 2:e8102007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38.
|
Nguyen KS, Kobayashi S and Costa DB:
Acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine
kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancers dependent on the
epidermal growth factor receptor pathway. Clin Lung Cancer.
10:281–289. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Moreira-Leite FF, Harrison LR, Mironov A,
Roberts RA and Dive C: Inducible EGFR T790M-mediated gefitinib
resistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells does not modulate
sensitivity to PI103 provoked autophagy. J Thorac Oncol. 5:765–777.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Eimer S, Belaud-Rotureau MA, Airiau K,
Jeanneteau M, Laharanne E, Veron N, Vital A, Loiseau H, Merlio JP
and Belloc F: Autophagy inhibition cooperates with erlotinib to
induce glioblastoma cell death. Cancer Biol Ther. 11:1017–1027.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Guo GF, Jiang WQ, Zhang B, Cai YC, Xu RH,
Chen XX, Wang F and Xia LP: Autophagy-related proteins Beclin-1 and
LC3 predict cetuximab efficacy in advanced colorectal cancer. World
J Gastroenterol. 17:4779–4786. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Nilsson JR: Does chloroquine, an
antimalarial drug, affect autophagy in Tetrahymena
pyriformis? J Protozool. 39:9–16. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Gunja N, Roberts D, McCoubrie D, Lamberth
P, Jan A, Simes DC, Hackett P and Buckley NA: Survival after
massive hydroxychloroquine overdose. Anaesth Intensive Care.
37:130–133. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Sasaki K, Tsuno NH, Sunami E, et al:
Chloroquine potentiates the anti-cancer effect of 5-fluorouracil on
colon cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 10:3702010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Sasaki K, Tsuno NH, Sunami E, et al:
Resistance of colon cancer to 5-fluorouracil may be overcome by
combination with chloroquine, an in vivo study. Anticancer Drugs.
23:675–682. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Goldberg SB, Supko JG, Neal JW, et al: A
phase I study of erlotinib and hydroxychloroquine in advanced
non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 7:1602–1608. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47.
|
Hu YL, Jahangiri A, Delay M and Aghi MK:
Tumor cell autophagy as an adaptive response mediating resistance
to treatments such as antiangiogenic therapy. Cancer Res.
72:4294–4299. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48.
|
Li X, Lu Y, Pan T and Fan Z: Roles of
autophagy in cetuximab-mediated cancer therapy against EGFR.
Autophagy. 6:1066–1077. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49.
|
Buchser WJ, Laskow TC, Pavlik PJ, Lin HM
and Lotze MT: Cell-mediated autophagy promotes cancer cell
survival. Cancer Res. 72:2970–2979. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|