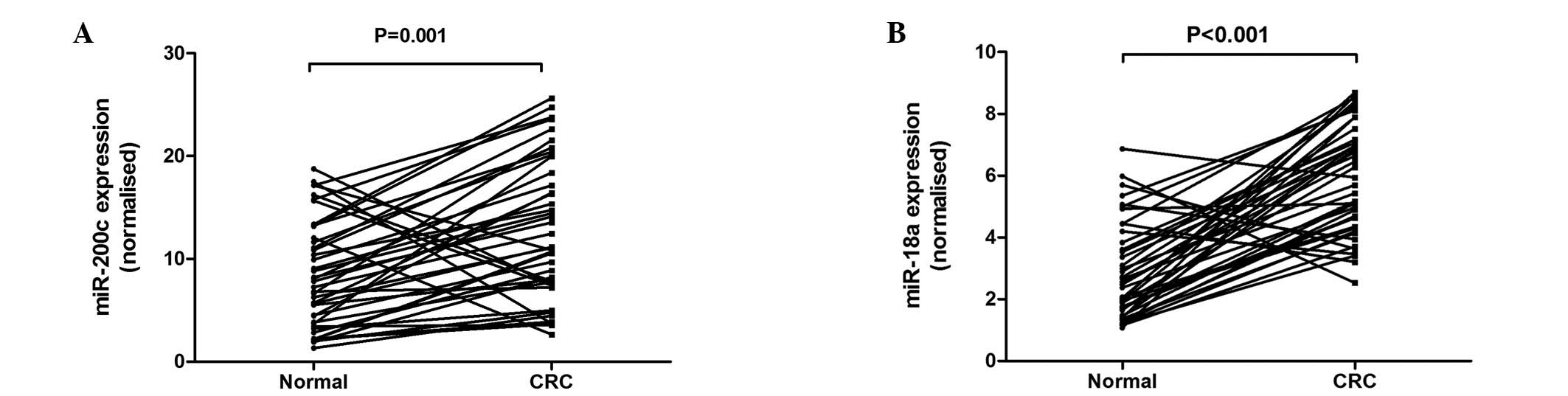
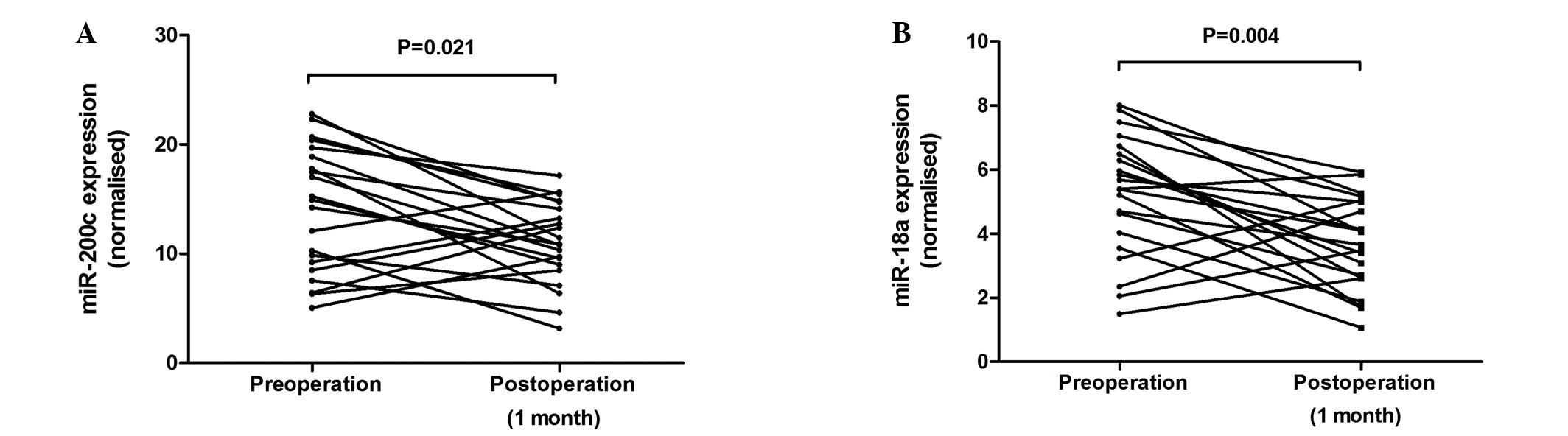
|
1
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Levin B, Lieberman DA, McFarland B, et al:
Screening and surveillance for the early detection of colorectal
cancer and adenomatous polyps, 2008: a joint guideline from the
American Cancer Society, the US Multi-Society Task Force on
Colorectal Cancer, and the American College of Radiology. CA Cancer
J Clin. 58:130–160. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Mandel JS: Screening for colorectal
cancer. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 37:97–115. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, et al:
Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer
detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:10513–10518. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen X, Ba Y, Ma L, et al:
Characterization of microRNAs in serum: a novel class of biomarkers
for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res. 18:997–1006.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang J, Chen J, Chang P, et al: MicroRNAs
in plasma of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients as novel
blood-based biomarkers of disease. Cancer Prev Res (Phila).
2:807–813. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ng EK, Chong WW, Jin H, et al:
Differential expression of microRNAs in plasma of patients with
colorectal cancer: a potential marker for colorectal cancer
screening. Gut. 58:1375–1381. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Heneghan HM, Miller N, Lowery AJ, et al:
Circulating microRNAs as novel minimally invasive biomarkers for
breast cancer. Ann Surg. 251:499–505. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tsujiura M, Ichikawa D, Komatsu S, et al:
Circulating microRNAs in plasma of patients with gastric cancers.
Br J Cancer. 102:1174–1179. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xi Y, Formentini A, Chien M, et al:
Prognostic values of microRNAs in colorectal cancer. Biomark
Insights. 2:113–121. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Motoyama K, Inoue H, Takatsuno Y, et al:
Over- and under-expressed microRNAs in human colorectal cancer. Int
J Oncol. 34:1069–1075. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Morimura R, Komatsu S, Ichikawa D, et al:
Novel diagnostic value of circulating miR-18a in plasma of patients
with pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer. 105:1733–1740. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
He L, Thomson JM, Hemann MT, et al: A
microRNA polycistron as a potential human oncogene. Nature.
435:828–833. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Voorhoeve PM, le Sage C, Schrier M, et al:
A genetic screen implicates miRNA-372 and miRNA-373 as oncogenes in
testicular germ cell tumors. Cell. 124:1169–1181. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Johnson SM, Grosshans H, Shingara J, et
al: RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family. Cell.
120:635–647. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mattie MD, Benz CC, Bowers J, et al:
Optimized high-throughput microRNA expression profiling provides
novel biomarker assessment of clinical prostate and breast cancer
biopsies. Mol Cancer. 5:242006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, et al:
Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and
prognosis. Cancer Cell. 9:189–198. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huang Z, Huang D, Ni S, et al: Plasma
microRNAs are promising novel biomarkers for early detection of
colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 127:118–126. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Diosdado B, van de Wiel MA, Terhaar Sive,
Droste JS, et al: MiR-17-92 cluster is associated with 13q gain and
c-myc expression during colorectal adenoma to adenocarcinoma
progression. Br J Cancer. 101:707–714. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Connolly E, Melegari M, Landgraf P, et al:
Elevated expression of the miR-17-92 polycistron and miR-21 in
hepadnavirus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma contributes to the
malignant phenotype. Am J Pathol. 173:856–864. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Yao Y, Suo AL, Li ZF, et al: MicroRNA
profiling of human gastric cancer. Mol Med Rep. 2:963–970.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Park SM, Gaur AB, Lengyel E, et al: The
miR-200 family determines the epithelial phenotype of cancer cells
by targeting the E-cadherin repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. Genes
Develop. 22:894–907. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Korpal M, Lee ES, Hu G, et al: The miR-200
family inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer cell
migration by direct targeting of E-cadherin transcriptional
repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. J Biol Chem. 283:14910–14914. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu XG, Zhu WY, Huang YY, et al: High
expression of serum miR-21 and tumor miR-200c associated with poor
prognosis in patients with lung cancer. Med Oncol. 29:618–626.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|