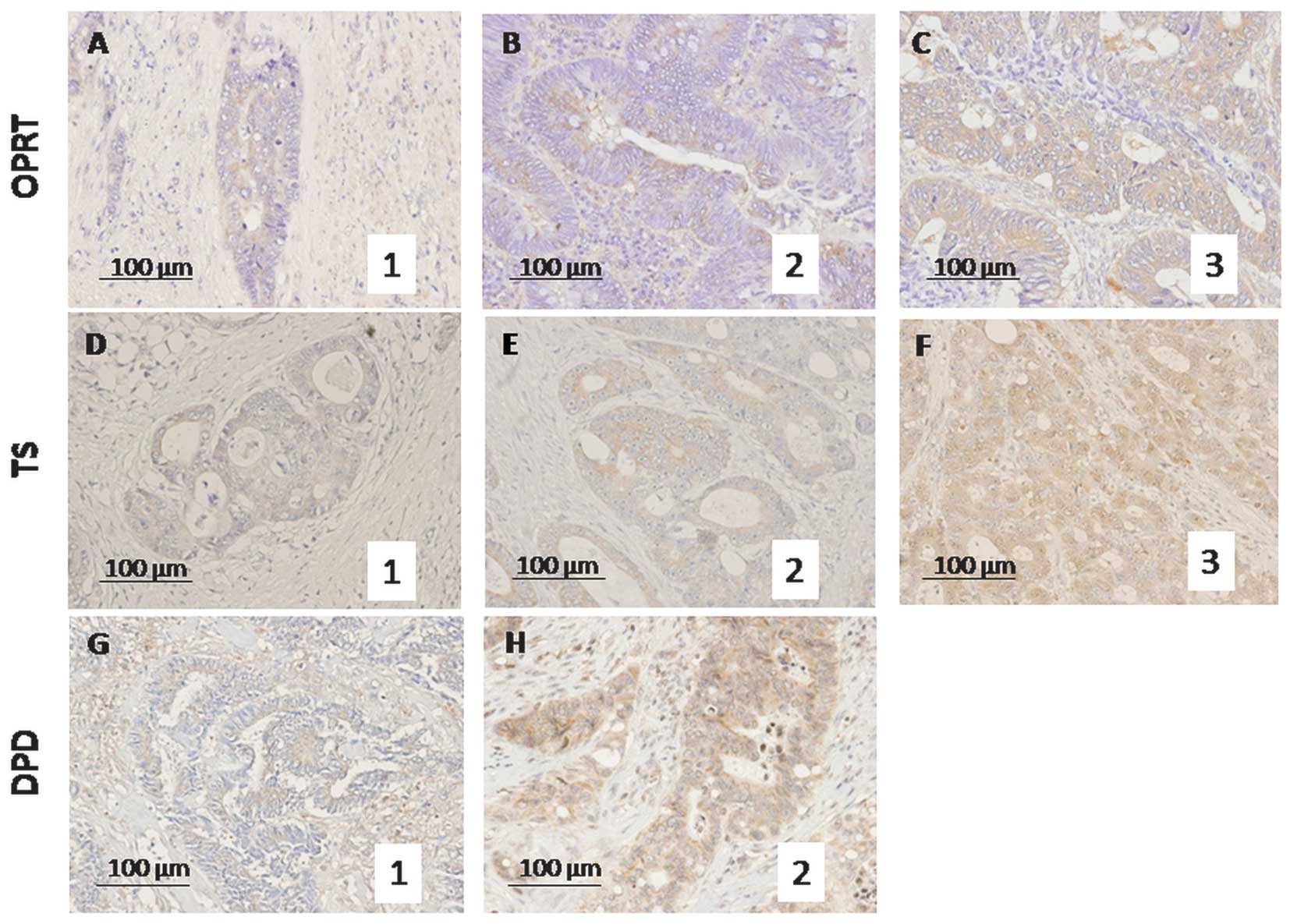
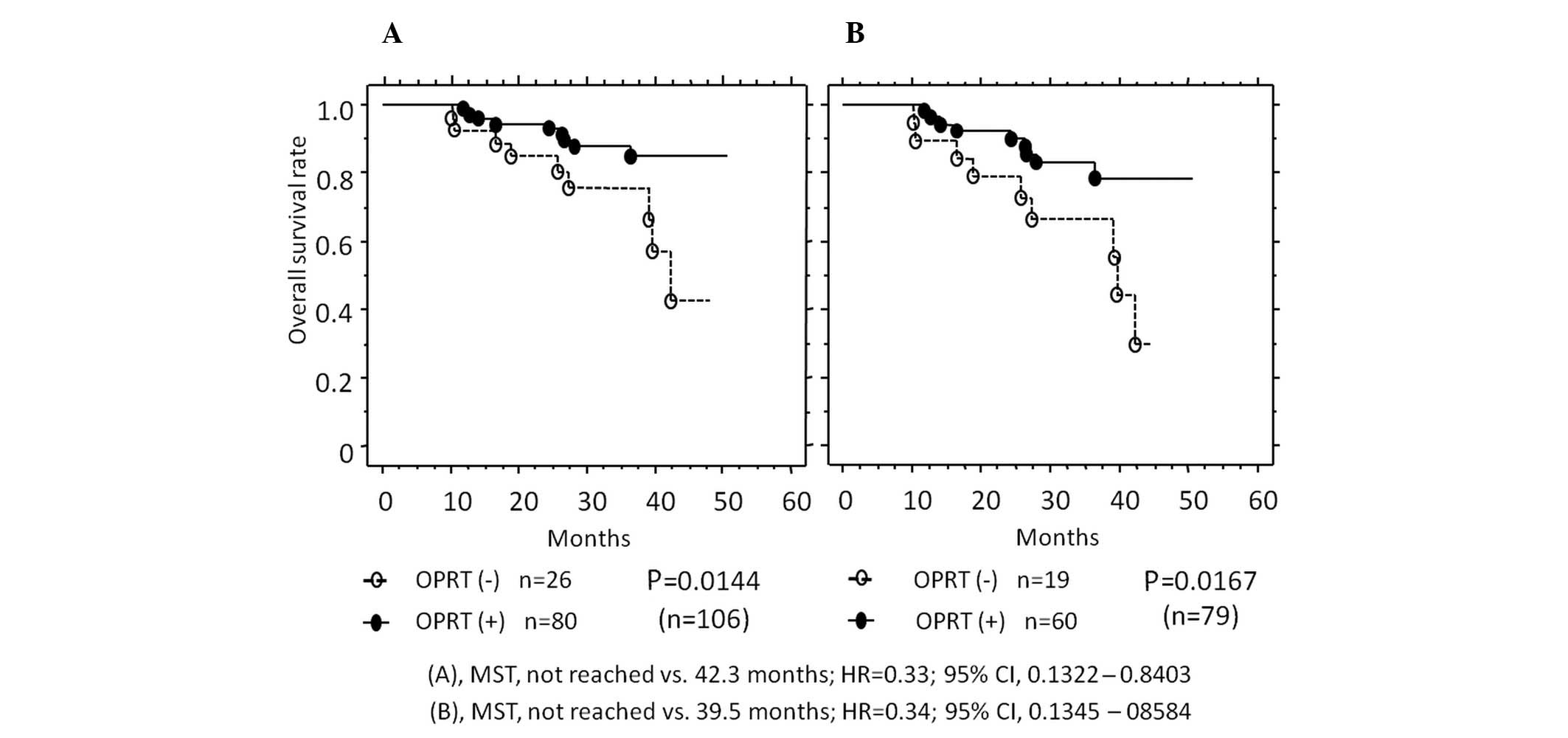
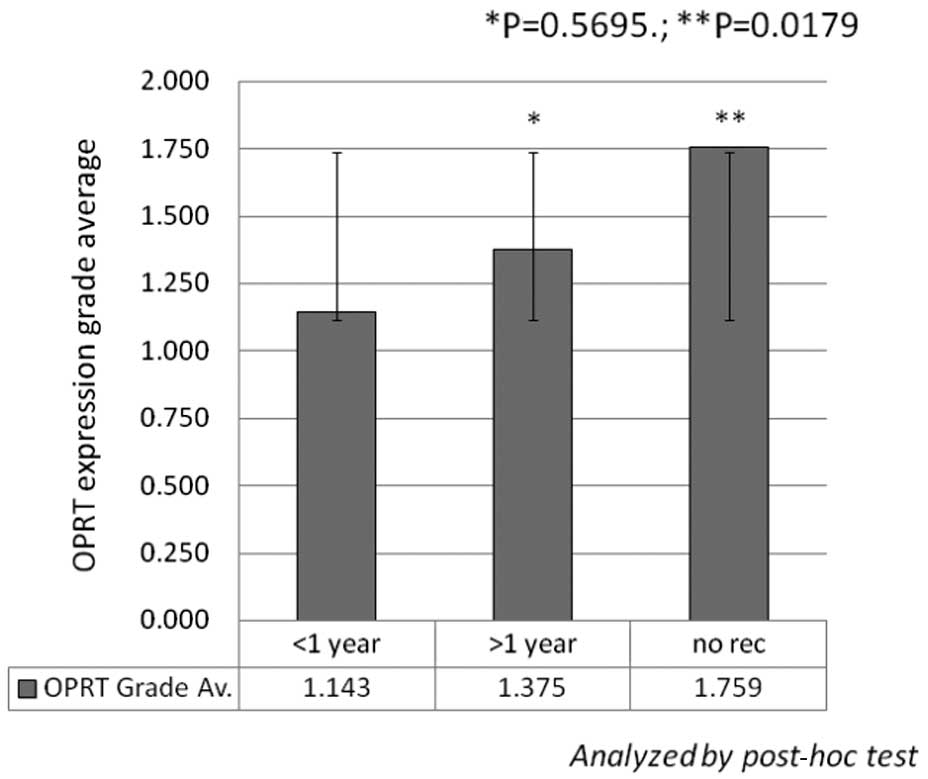
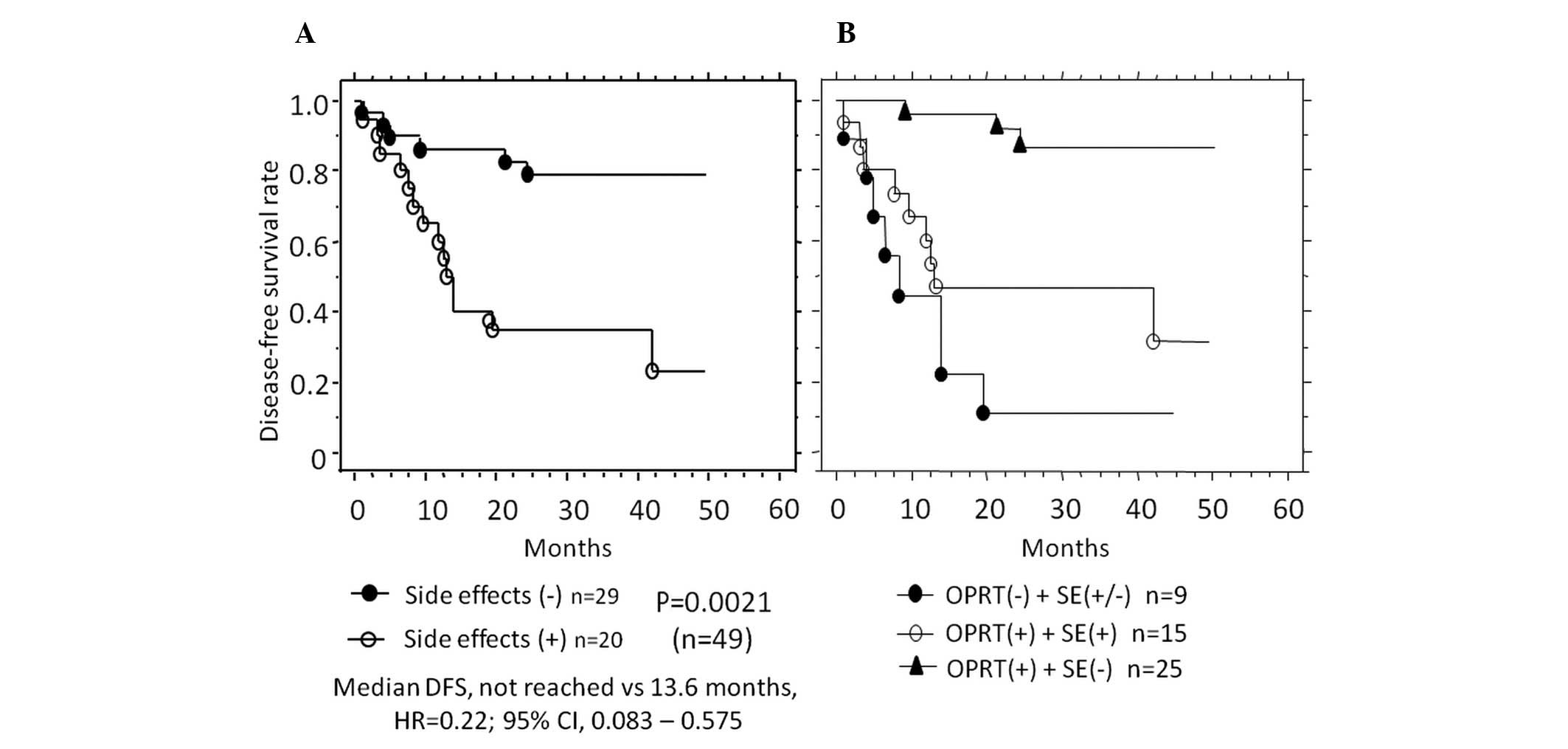
|
1.
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012.
|
|
2.
|
Osada S, Imai H, Sasaki Y, et al: Strategy
for synchronous and multiple liver metastasis.
Hepatogastroenterology. 59:198–203. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
de Gramont A, Figer A, Seymour M, et al:
Leucovorin and fluorouracil with or without oxaliplatin as
first-line treatment in advanced colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol.
18:2938–2947. 2000.
|
|
4.
|
Giantonio BJ, Catalano PJ, Meropol NJ, et
al: Bevacizumab in combination with oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and
leucovorin (FOLFOX4) for previously treated metastatic colorectal
cancer: results from the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Study
E3200. J Clin Oncol. 25:1539–1544. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5.
|
Hamilton SR: Targeted therapy of cancer:
new roles for pathologists in colorectal cancer. Mod Pathol.
21:S23–S30. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Yamada H, Iinuma H and Watanabe T:
Prognostic value of 5-fluorouracil metabolic enzyme genes in Dukes’
stage B and C colorectal cancer patients treated with oral
5-fluorouracil-based adjuvant chemotherapy. Oncol Rep. 19:729–735.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Komori S, Osada S, Mori R, et al:
Contribution of thymidylate synthase to gemcitabine therapy for
advanced pancreatic cancer. Pancreas. 39:1284–1292. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Komori S, Osada S and Yoshida K: Novel
strategy with gemcitabine for advanced pancreatic cancer. ISRN
Oncol. 2011:9368932011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Tomita H, Yamada Y, Oyama T, et al:
Development of gastric tumors in Apc(Min/+) mice by the activation
of the beta-catenin/Tcf signaling pathway. Cancer Res.
67:4079–4087. 2007.
|
|
10.
|
Osada S, Saji S and Kuno T: Clinical
significance of combination study of apoptotic factors and
proliferating cell nuclear antigen in estimating the prognosis of
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 85:48–54. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Osada S, Saji S and Takahashi T: A case
report of papilla Vater carcinoma showing positive expression of
thymidine phosphorylase. Hepatogastroenterology. 51:375–377.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Kawahara A, Akagi Y, Hattori S, et al:
Higher expression of deoxyuridine triphosphatase (dUTPase) may
predict the metastasis potential of colorectal cancer. J Clin
Pathol. 62:364–369. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Van Cutsem EJ and Oliveira J: Colon
cancer: ESMO clinical recommendations for diagnosis, adjuvant
treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 19:ii29–ii30. 2008.
|
|
14.
|
Tokunaga Y, Sasaki H and Saito T: Clinical
role of orotate phosphoribosyl transferase and dihydropyrimidine
dehydrogenase in colorectal cancer treated with postoperative
fluoropyrimidine. Surgery. 141:346–353. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15.
|
Ochiai T, Sugitani M, Nishimura K, et al:
Impact of orotate phosphoribosyl transferase activity as a
predictor of lymph node metastasis in gastric cancer. Oncol Rep.
14:987–992. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Sanada Y, Yoshida K, Hihara J and Okada M:
Expression of orotate phosphoribosyltransferase in colorectal
carcinoma: An immunohistochemical analysis in several components of
neoplastic lesions. Oncol Rep. 20:1005–1011. 2008.
|
|
17.
|
Tsutani Y, Yoshida K, Sanada Y, et al:
Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase and orotate
phosphoribosyltransferase in esophageal cancer patients:
Correlation with clinicopathological factors and prognosis. Mol Med
Rep. 1:713–719. 2008.
|
|
18.
|
Ichikawa W, Uetake H, Shirota Y, et al:
Combination of dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase and thymidylate
synthase gene expressions in primary tumors as predictive
parameters for the efficacy of fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy
for metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 9:786–791.
2003.
|
|
19.
|
Ichikawa W, Uetake H, Shirota Y, et al:
Both gene expression for orotate phosphoribosyltransferase and its
ratio to dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase influence outcome
following fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy for metastatic
colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 89:1486–1492. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20.
|
Hosono Y, Osada S, Nawa M, et al:
Combination therapy of 5-fluorouracil with rapamycin for hormone
receptor-negative human breast cancer. Anticancer Res.
30:2625–2630. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Ochiai T, Nishimura K, Noguchi H, et al:
Prognostic impact of orotate phosphoribosyl transferase among
5-fluorouracil metabolic enzymes in resectable colorectal cancers
treated by oral 5-fluorouracil-based adjuvant chemotherapy. Int J
Cancer. 118:3084–3088. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22.
|
Lecomte T, Ferraz JM, Zinzindohoue F, et
al: Thymidylate synthase gene polymorphism predicts toxicity in
colorectal cancer patients receiving 5-fluorouracil-based
chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 10:5880–5888. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23.
|
Ichikawa W, Takahashi T, Suto K, Sasaki Y
and Hirayama R: Orotate phosphoribosyltransferase gene polymorphism
predicts toxicity in patients treated with bolus 5-fluorouracil
regimen. Clin Cancer Res. 12:3928–3934. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
van Kuilenburg AB: Dihydropyrimidine
dehydrogenase and the efficacy and toxicity of 5-fluorouracil. Eur
J Cancer. 40:939–950. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Tsuchida M, Yamato Y, Hashimoto T, et al:
Expression of 5-fluorouracil-related enzymes in lung cancer: ELISA
characterizes enzyme activity and messenger RNA expression. Oncol
Rep. 21:1037–1043. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Arellano M, Malet-Martino M, Martino R and
Spector T: 5-Ethynyluracil (GW776): effects on the formation of the
toxic catabolites of 5-fluorouracil, fluoroacetate and
fluorohydroxypropionic acid in the isolated perfused rat liver
model. Br J Cancer. 76:1170–1180. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Yoshisue K, Hironaga K, Yamaguchi S,
Yamamoto A, Nagayama S and Kawaguchi Y: Reduction of 5-fluorouracil
(5-FU) gastrointestinal (GI) toxicity resulting from the protection
of thymidylate synthase (TS) in GI tissue by repeated simultaneous
administration of potassium oxonate (Oxo) in rats. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 46:51–56. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28.
|
Kato T, Shimamoto Y, Uchida J, et al:
Possible regulation of 5-fluorouracil-induced neuro- and oral
toxicities by two biochemical modulators consisting of S-1, a new
oral formulation of 5-fluorouracil. Anticancer Res. 21:1705–1712.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|