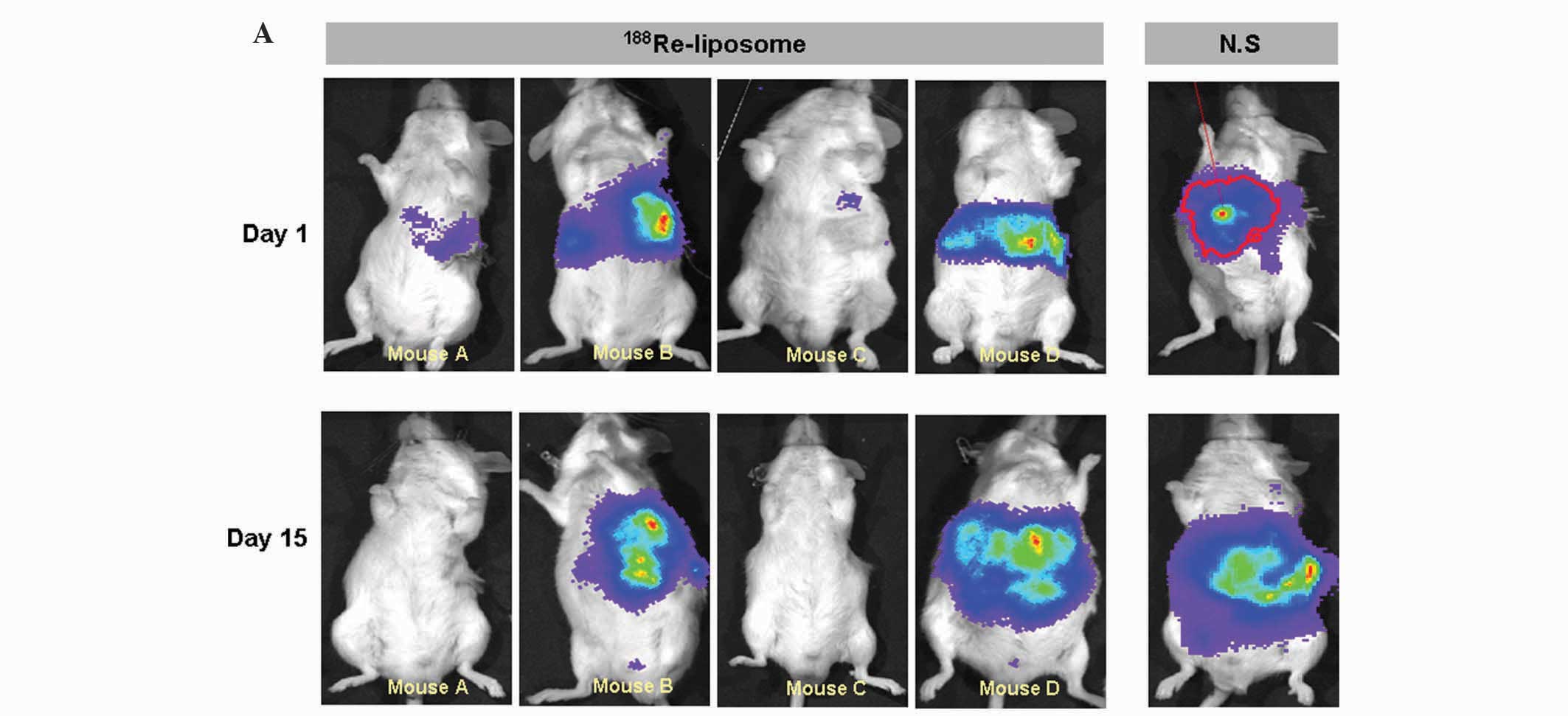
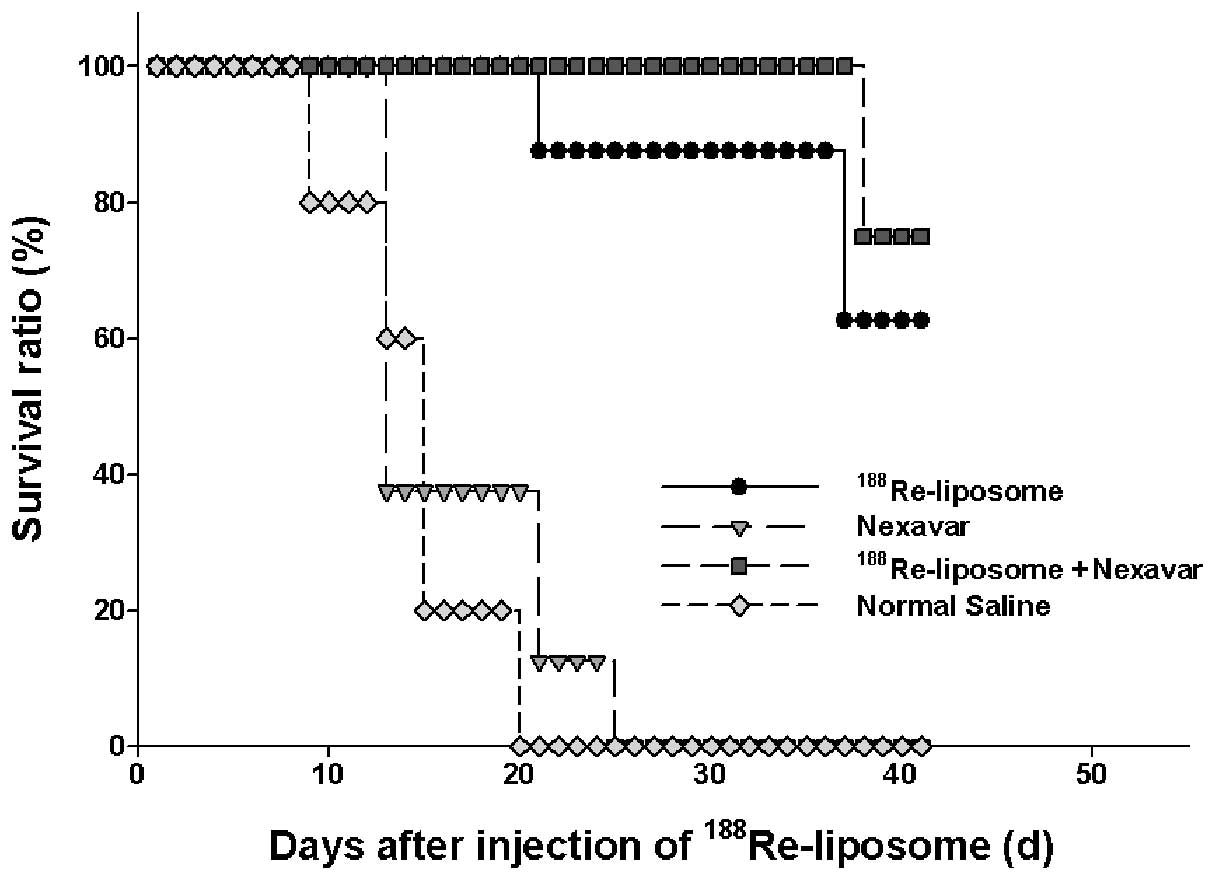
|
1.
|
Reissfelder C, Timke C, Schmitz-Winnenthal
H, et al: A randomized controlled trial to investigate the
influence of low dose radiotherapy on immune stimulatory effects in
liver metastases of colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer. 11:4192011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Reissfelder C, Rahbari NN, Koch M, Ulrich
A, Pfeilschifter I, Waltert A, Muller SA, Schemmer P, Buchler MW
and Weitz J: Validation of prognostic scoring systems for patients
undergoing resection of colorectal cancer liver metastases. Ann
Surg Oncol. 16:3279–3288. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4.
|
Cummings LC, Payes JD and Cooper GS:
Survival after hepatic resection in metastatic colorectal cancer: a
population-based study. Cancer. 109:718–726. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Vavrova J and Rezacova M: The importance
of senescence in ionizing radiation-induced tumour suppression.
Folia Biol. 57:41–46. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Bakkenist CJ and Kastan MB: DNA damage
activates ATM through intermolecular autophosphorylation and dimer
dissociation. Nature. 421:499–506. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Jeggo PA, Geuting V and Lobrich M: The
role of homologous recombination in radiation-induced double-strand
break repair. Radiother Oncol. 101:7–12. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Lobrich M and Jeggo PA: The impact of a
negligent G2/M checkpoint on genomic instability and cancer
induction. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:861–869. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Jeggo PA and Löbrich M: DNA double-strand
breaks: their cellular and clinical impact? Oncogene. 26:7717–7719.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Davis ME, Chen ZG and Shin DM:
Nanoparticle therapeutics: an emerging treatment modality for
cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 7:771–782. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Cho K, Wang X, Nie S, Chen ZG and Shin DM:
Therapeutic nanoparticles for drug delivery in cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 14:1310–1316. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Wolpin BM, Meyerhardt JA, Mamon HJ and
Mayer RJ: Adjuvant treatment of colorectal cancer. CA Cancer J
Clin. 57:168–185. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13.
|
Brannon-Peppas L and Blanchette JO:
Nanoparticle and targeted systems for cancer therapy. Adv Drug
Deliv Rev. 56:1649–1659. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Chang YJ, Chang CH, Chang TJ, Yu CY, Chen
LC, Jan ML, Luo TY, Lee TW and Ting G: Biodistribution,
pharmacokinetics and microSPECT/CT imaging of
188Re-bMEDA-liposome in a C26 murine colon carcinoma
solid tumor animal model. Anticancer Res. 27:2217–2225.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Chen LC, Chang CH, Yu CY, Chang YJ, Hsu
WC, Ho CL, Yeh CH, Luo TY, Lee TW and Ting G: Biodistribution,
pharmacokinetics and imaging of 188Re-BMEDA-labeled
pegylated liposomes after intraperitoneal injection in a C26 colon
carcinoma ascites mouse model. Nucl Med Biol. 34:415–423. 2007.
|
|
16.
|
Ibrahim N, Yu Y, Walsh WR and Yang JL:
Molecular targeted therapies for cancer: Sorafenib mono-therapy and
its combination with other therapies (Review). Oncol Rep.
27:1303–1311. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Dal Lago L, D′Hondt V and Awada A:
Selected combination therapy with sorafenib: a review of clinical
data and perspectives in advanced solid tumors. Oncologist.
13:845–858. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Wilhelm SM, Adnane L, Newell P, Villanueva
A, Llovet JM and Lynch M: Preclinical overview of sorafenib, a
multikinase inhibitor that targets both Raf and VEGF and PDGF
receptor tyrosine kinase signaling. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:3129–3140.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L, et al: BAY
43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and targets
the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases involved in
tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 64:7099–7109. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Escudier B, Eisen T, Stadler WM, et al
TARGET Study Group: Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal-cell
carcinoma. New Engl J Med. 356:125–134. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, et al
SHARP Investigators Study Group: Sorafenib in advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma. New Engl J Med. 359:378–390. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Suen AW, Galoforo S, Marples B, McGonagle
M, Downing L, Martinez AA, Robertson JM and Wilson GD: Sorafenib
and radiation: a promising combination in colorectal cancer. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 78:213–220. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Kim YB, Jeung HC, Jeong I, Lee K, Rha SY,
Chung HC and Kim GE: Mechanism of enhancement of radiation-induced
cytotoxicity by sorafenib in colorectal cancer. J Radiat Res.
54:52–60. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Di Nicolantonio F, Martini M, Molinari F,
Sartore-Bianchi A, Arena S, Saletti P, De Dosso S, Mazzucchelli L,
Frattini M, Siena S and Bardelli A: Wild-type BRAF is required for
response to panitumumab or cetuximab in metastatic colorectal
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 26:5705–5712. 2008.
|
|
25.
|
Ratain MJ, Eisen T, Stadler WM, et al:
Phase II placebo-controlled randomized discontinuation trial of
sorafenib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin
Oncol. 24:2505–2512. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26.
|
Wehler TC, Hamdi S, Maderer A, et al:
Single-agent therapy with sorafenib or 5-FU is equally effective in
human colorectal cancer xenograft - no benefit of combination
therapy. Int J Colorect Dis. 28:385–398. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Kuo YC, Lin WC, Chiang IT, Chang YF, Chen
CW, Su SH, Chen CL and Hwang JJ: Sorafenib sensitizes human
colorectal carcinoma to radiation via suppression of NF-kappaB
expression in vitro and in vivo. Biomed Pharmacother. 66:12–20.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Martinelli E, Troiani T, Morgillo F, et
al: Synergistic antitumor activity of sorafenib in combination with
epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors in colorectal and lung
cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res. 16:4990–5001. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Galal KM, Khaled Z and Mourad AM: Role of
cetuximab and sorafenib in treatment of metastatic colorectal
cancer. Indian J Cancer. 48:47–54. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Plastaras JP, Kim SH, Liu YY, et al: Cell
cycle dependent and schedule-dependent antitumor effects of
sorafenib combined with radiation. Cancer Res. 67:9443–9454. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Amundson SA, Bittner M and Fornace AJ Jr:
Functional genomics as a window on radiation stress signaling.
Oncogene. 22:5828–5833. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Abraham RT: Checkpoint signaling:
epigenetic events sound the DNA strand-breaks alarm to the ATM
protein kinase. Bioessays. 25:627–630. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Valerie K, Yacoub A, Hagan MP, Curiel DT,
Fisher PB, Grant S and Dent P: Radiation-induced cell signaling:
inside-out and outside-in. Mol Cancer Ther. 6:789–801. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Dent P, Yacoub A, Fisher PB, Hagan MP and
Grant S: MAPK pathways in radiation responses. Oncogene.
22:5885–5896. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Deshpande A, Sicinski P and Hinds PW:
Cyclins and cdks in development and cancer: a perspective.
Oncogene. 24:2909–2915. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Jirawatnotai S, Hu Y, Michowski W, et al:
A function for cyclin D1 in DNA repair uncovered by protein
interactome analyses in human cancers. Nature. 474:230–234. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|