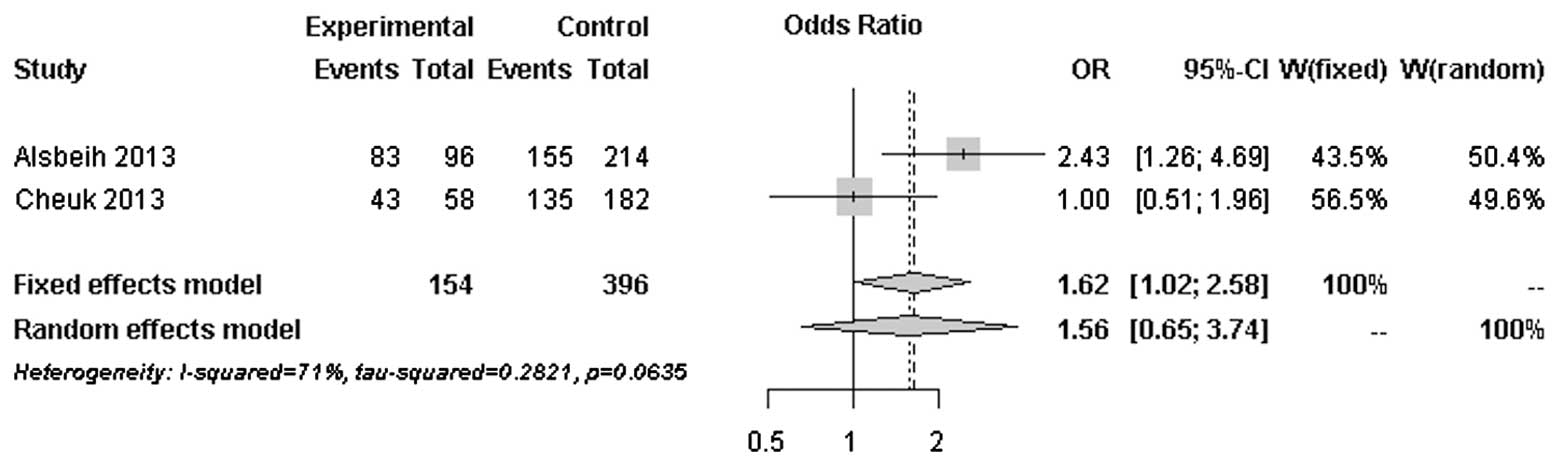
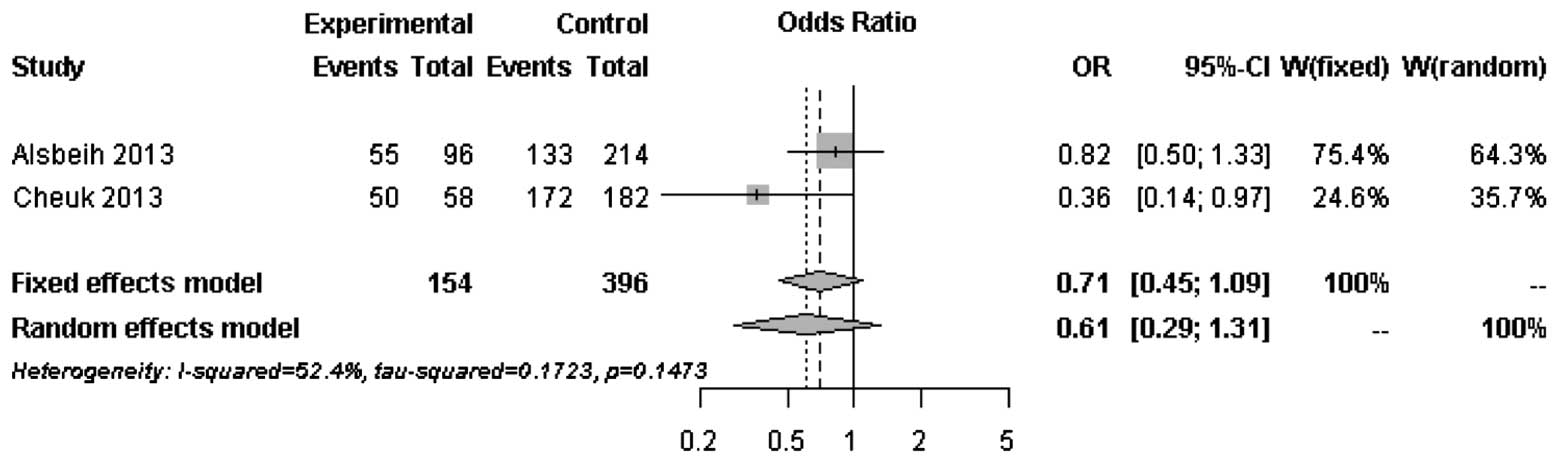
|
1
|
Wei WI and Sham JS: Nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Lancet. 365:2041–2054. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kam MK, Teo PM, Chau RM, et al: Treatment
of nasopharyngeal carcinoma with intensity-modulated radiotherapy:
the Hong Kong experience. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
60:1440–1450. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lee AW, Law SC, Ng SH, et al:
Retrospective analysis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated during
1976–1985 late complications following megavoltage irradiation. Br
J Radiol. 65:918–928. 1992.
|
|
4
|
Alsbeih G, Al-Harbi N, Al-Hadyan K,
El-Sebaie M and Al-Rajhi N: Association between normal tissue
complications after radiotherapy and polymorphic variations in
TGFB1 and XRCC1 genes. Radiat Res. 173:505–511. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Alsbeih GA, El-Sebaie MM, Al-Rajhi NM, et
al: Association between XRCC1 G399A polymorphism and late
complications to radiotherapy in Saudi head and neck cancer
patients. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 20:302–308. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Andreassen CN, Alsner J, Overgaard J, et
al: TGFB1 polymorphisms are associated with risk of late normal
tissue complications in the breast after radiotherapy for early
breast cancer. Radiother Oncol. 75:18–21. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Andreassen CN, Alsner J, Overgaard M and
Overgaard J: Prediction of normal tissue radiosensitivity from
polymorphisms in candidate genes. Radiother Oncol. 69:127–135.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Azria D, Ozsahin M, Kramar A, et al:
Single nucleotide polymorphisms, apoptosis, and the development of
severe late adverse effects after radiotherapy. Clin Cancer Res.
14:6284–6288. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Brem R, Cox DG, Chapot B, et al: The XRCC1
-77T->C variant: haplotypes, breast cancer risk, response to
radiotherapy and the cellular response to DNA damage.
Carcinogenesis. 27:2469–2474. 2006.
|
|
10
|
Burri RJ, Stock RG, Cesaretti JA, et al:
Association of single nucleotide polymorphisms in SOD2, XRCC1 and
XRCC3 with susceptibility for the development of adverse effects
resulting from radiotherapy for prostate cancer. Radiat Res.
170:49–59. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Damaraju S, Murray D, Dufour J, et al:
Association of DNA repair and steroid metabolism gene polymorphisms
with clinical late toxicity in patients treated with conformal
radiotherapy for prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 12:2545–2554.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Giotopoulos G, Symonds RP, Foweraker K, et
al: The late radiotherapy normal tissue injury phenotypes of
telangiectasia, fibrosis and atrophy in breast cancer patients have
distinct genotype-dependent causes. Br J Cancer. 96:1001–1007.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Moullan N, Cox DG, Angèle S, Romestaing P,
Gerard JP and Hall J: Polymorphisms in the DNA repair gene XRCC1,
breast cancer risk, and response to radiotherapy. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 12:1168–1174. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Suga T, Iwakawa M, Tsuji H, et al:
Influence of multiple genetic polymorphisms on genitourinary
morbidity after carbon ion radiotherapy for prostate cancer. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 72:808–813. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zschenker O, Raabe A, Boeckelmann IK, et
al: Association of single nucleotide polymorphisms in ATM, GSTP1,
SOD2, TGFB1, XPD and XRCC1 with clinical and cellular
radiosensitivity. Radiother Oncol. 97:26–32. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chang-Claude J, Ambrosone CB, Lilla C, et
al: Genetic polymorphisms in DNA repair and damage response genes
and late normal tissue complications of radiotherapy for breast
cancer. Br J Cancer. 100:1680–1686. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Popanda O, Marquardt JU, Chang-Claude J
and Schmezer P: Genetic variation in normal tissue toxicity induced
by ionizing radiation. Mutat Res. 667:58–69. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Alsbeih G, El-Sebaie M, Al-Harbi N,
Al-Hadyan K, Shoukri M and Al-Rajhi N: SNPs in genes implicated in
radiation response are associated with radiotoxicity and evoke
roles as predictive and prognostic biomarkers. Radiat Oncol.
8:1252013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
de Bakker PI, Yelensky R, Pe’er I, Gabriel
SB, Daly MJ and Altshuler D: Efficiency and power in genetic
association studies. Nat Genet. 37:1217–1223. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
International HapMap Consortium. The
International HapMap Project. Nature. 426:789–796. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, et al:
PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based
linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet. 81:pp. 559–575. 2007, http://pngu.mgh.harvard.edu/~purcell/plink.
Accessed, July 19, 2013
|
|
22
|
Schwarzer G: Meta: An R package for
meta-analysis. R News. 7:pp. 40–45. 2007, http://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/meta/index.html.
Accessed, September 8, 2013
|
|
23
|
Higgins JPT and Green S: Cochrane Handbook
for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, version 5.10. The Cochrane
Collaboration; 2011, http://handbook.cochrane.org.
Accessed July 27, 2013
|
|
24
|
Bentzen SM: Preventing or reducing late
side effects of radiation therapy: radiobiology meets molecular
pathology. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:702–713. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Andreassen CN and Alsner J: Genetic
variants and normal tissue toxicity after radiotherapy: a
systematic review. Radiother Oncol. 92:299–309. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Barnett GC, Coles CE, Elliott RM, et al:
Independent validation of genes and polymorphisms reported to be
associated with radiation toxicity: a prospective analysis study.
Lancet Oncol. 13:65–77. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
West CM, Dunning AM and Rosenstein BS:
Genome-wide association studies and prediction of normal tissue
toxicity. Semin Radiat Oncol. 22:91–99. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Talbot CJ, Tanteles GA, Barnett GC, et al:
A replicated association between polymorphisms near TNFα and risk
for adverse reactions to radiotherapy. Br J Cancer. 107:748–753.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kerns SL, Ostrer H, Stock R, et al:
Genome-wide association study to identify single nucleotide
polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with the development of erectile
dysfunction in African-American men after radiotherapy for prostate
cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 78:1292–1300. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Lorimore SA, Coates PJ and Wright EG:
Radiation-induced genomic instability and bystander effects:
inter-related nontargeted effects of exposure to ionizing
radiation. Oncogene. 22:7058–7069. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Barnett GC, West CM, Coles CE, et al:
Standardized total average toxicity score: a scale- and
grade-independent measure of late radiotherapy toxicity to
facilitate pooling of data from different studies. Int J Radiat
Oncol Biol Phys. 82:1065–1074. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|