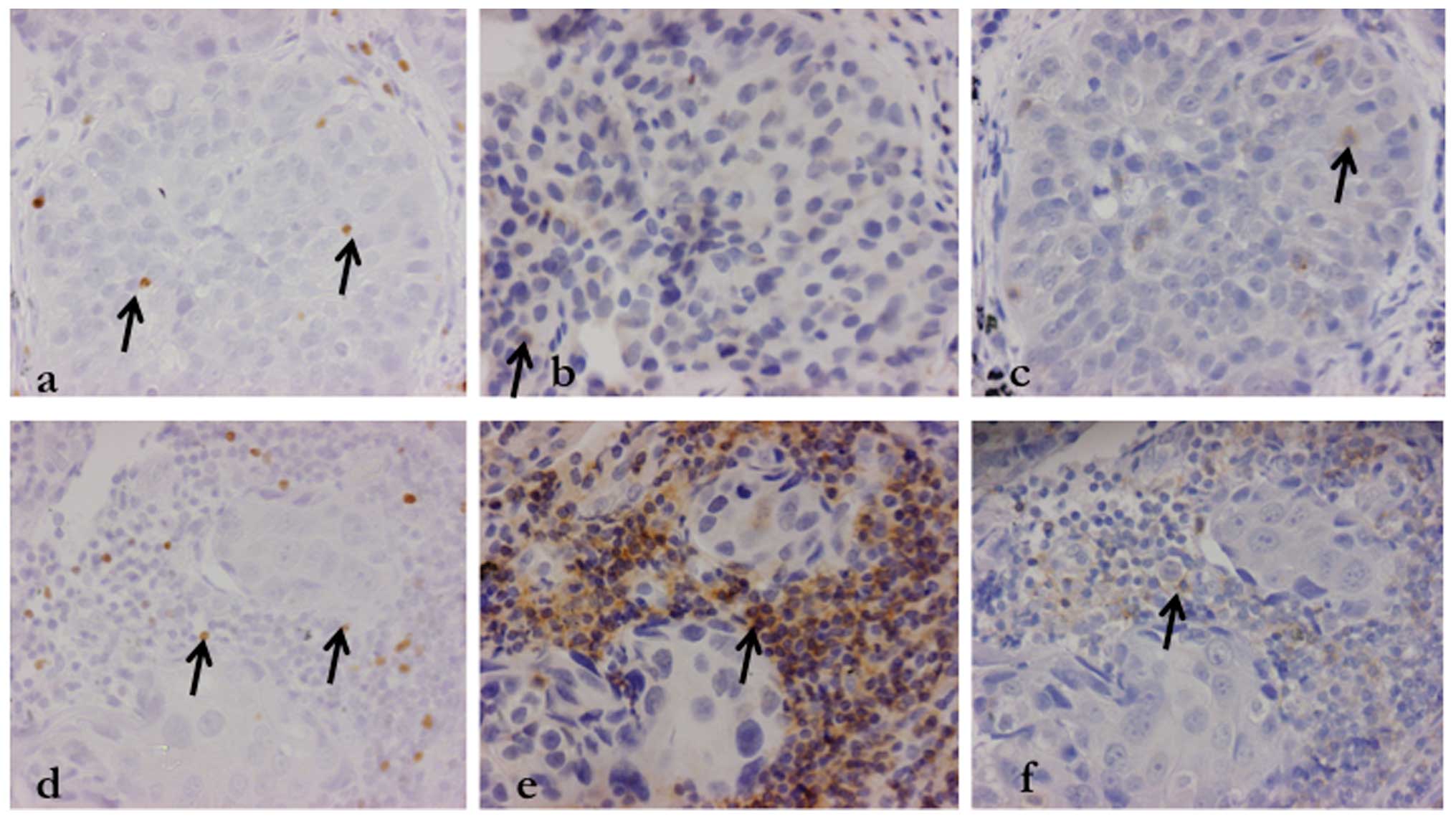
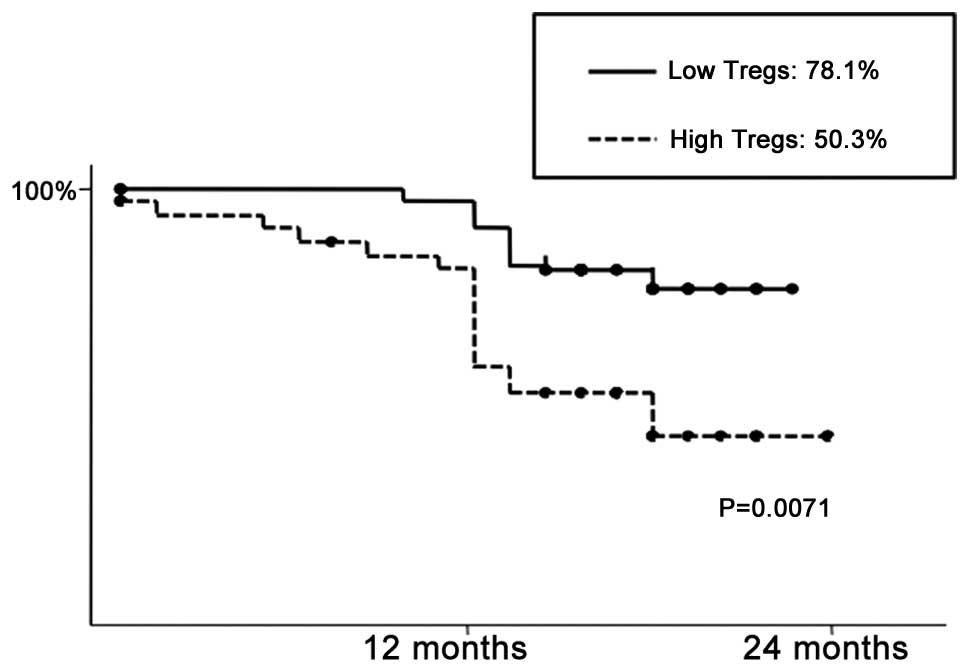
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wang T, Nelson RA, Bogardus A and Grannis
FW Jr: Five-year lung cancer survival: which advanced stage
nonsmall cell lung cancer patients attain long-term survival?
Cancer. 116:1518–1525. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tyagi P and Mirakhur B: MAGRIT: the
largest-ever phase III lung cancer trial aims to establish a novel
tumor-specific approach to therapy. Clin Lung Cancer. 10:371–374.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Butts C, Maksymiuk A, Goss G, et al:
Updated survival analysis in patients with stage IIIB or IV
non-small-cell lung cancer receiving BLP25 liposome vaccine
(L-BLP25): phase IIB randomized, multicenter, open-label trial. J
Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 137:1337–1342. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Rosenberg SA, Yang JC and Restifo NP:
Cancer immunotherapy: moving beyond current vaccines. Nat Med.
10:909–915. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Colombo MP and Piconese S:
Regulatory-T-cell inhibition versus depletion: the right choice in
cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:880–887. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rabinovich GA, Gabrilovich D and Sotomayor
EM: Immunosuppressive strategies that are mediated by tumor cells.
Annu Rev Immunol. 25:267–296. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Whiteside TL: The tumor microenvironment
and its role in promoting tumor growth. Oncogene. 27:5904–5912.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Whiteside TL: Inhibiting the inhibitors:
evaluating agents targeting cancer immunosuppression. Expert Opin
Biol Ther. 10:1019–1035. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hori S, Nomura T and Sakaguchi S: Control
of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3.
Science. 299:1057–1061. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Goldstraw P, Crowley J, Chansky K, et al:
International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer
International Staging Committee; Participating Institutions: The
IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: proposals for the revision of
the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (seventh) edition of the
TNM Classification of malignant tumours. J Thorac Oncol. 2:706–714.
2007.
|
|
12
|
Roncador G, Brown PJ, Maestre L, et al:
Analysis of FOXP3 protein expression in human
CD4+CD25+regulatory T cells at the
single-cell level. Eur J Immunol. 35:1681–1691. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wolf D, Wolf AM, Rumpold H, et al: The
expression of the regulatory T cell-specific forkhead box
transcription factor FoxP3 is associated with poor prognosis in
ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 11:8326–8331. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ichihara F, Kono K, Takahashi A, Kawaida
H, Sugai H and Fujii H: Increased populations of regulatory T cells
in peripheral blood and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in patients
with gastric and esophageal cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 9:4404–4408.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liyanage UK, Moore TT, Joo HG, et al:
Prevalence of regulatory T cells is increased in peripheral blood
and tumor microenvironment of patients with pancreas or breast
adenocarcinoma. J Immunol. 169:2756–2761. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wolf AM, Wolf D, Steurer M, Gastl G,
Gunsilius E and Grubeck-Loebenstein B: Increase of regulatory T
cells in the peripheral blood of cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res.
9:606–612. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sakaguchi S, Sakaguchi N, Asano M, Itoh M
and Toda M: Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by activated T
cells expressing IL-2 receptor alpha-chains (CD25). Breakdown of a
single mechanism of self-tolerance causes various autoimmune
diseases. J Immunol. 155:1151–1164. 1995.
|
|
18
|
Fontenot JD, Rasmussen JP, Williams LM,
Dooley JL, Farr AG and Rudensky AY: Regulatory T cell lineage
specification by the forkhead transcription factor foxp3. Immunity.
22:329–341. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sakaguchi S: The origin of
FOXP3-expressing CD4+regulatory T cells: thymus or
periphery. J Clin Invest. 112:1310–1312. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cools N, Ponsaerts P, Van Tendeloo VF and
Berneman ZN: Regulatory T cells and human disease. Clin Dev
Immunol. 2007:891952007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yokokawa J, Cereda V, Remondo C, et al:
Enhanced functionality of
CD4+CD25(high)Foxp3+regulatory T cells in the
peripheral blood of patients with prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
14:1032–1040. 2008.
|
|
22
|
Heimberger AB, Abou-Ghazal M, Reina-Ortiz
C, et al: Incidence and prognostic impact of
Foxp3+regulatory T cells in human gliomas. Clin Cancer
Res. 14:5166–5172. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Grabenbauer GG, Lahmer G, Distel L and
Niedobitek G: Tumor-infiltrating cytotoxic T cells but not
regulatory T cells predict outcome in anal squamous cell carcinoma.
Clin Cancer Res. 12:3355–3360. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hiraoka N, Onozato K, Kosuge T and
Hirohashi S: Prevalence of Foxp3+regulatory T cells
increases during the progression of pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma and its premalignant lesions. Clin Cancer Res.
12:5423–5434. 2006.
|
|
25
|
Kobayashi N, Hiraoka N, Yamagami W, et al:
Foxp3+regulatory T cells affect the development and
progression of hepatocarcinogenesis. Clin Cancer Res. 13:902–911.
2007.
|
|
26
|
Siddiqui SA, Frigola X, Bonne-Annee S, et
al: Tumor-infiltrating Foxp3-CD4+CD25+T cells
predict poor survival in renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
13:2075–2081. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Badoual C, Hans S, Rodriguez J, et al:
Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating CD4+T-cell
subpopulations in head and neck cancers. Clin Cancer Res.
12:465–472. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Petersen RP, Campa MJ, Sperlazza J, et al:
Tumor infiltrating Foxp3+regulatory T-cells are
associated with recurrence in pathologic stage I NSCLC patients.
Cancer. 107:2866–2872. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ishibashi Y, Tanaka S, Tajima K, Yoshida T
and Kuwano H: Expression of Foxp3 in non-small cell lung cancer
patients is significantly higher in tumor tissues than in normal
tissues, especially in tumors smaller than 30 mm. Oncol Rep.
15:1315–1319. 2006.
|
|
30
|
Schneider T, Kimpfler S, Warth A, et al:
Foxp3+regulatory T cells and natural killer cells
distinctly infiltrate primary tumors and draining lymph nodes in
pulmonary adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol. 6:432–438. 2011.
|
|
31
|
Hiraoka K, Miyamoto M, Cho Y, et al:
Concurrent infiltration by CD8+T cells and
CD4+T cells is a favourable prognostic factor in
non-small-cell lung carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 94:275–280.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang L, Conejo-Garcia JR, Katsaros D, et
al: Intratumoral T cells, recurrence, and survival in epithelial
ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med. 348:203–213. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cho Y, Miyamoto M, Kato K, et al:
CD4+and CD8+T cells cooperate to improve
prognosis of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Cancer Res. 63:1555–1559. 2003.
|
|
34
|
Fukunaga A, Miyamoto M, Cho Y, et al:
CD8+tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes together with
CD4+tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and dendritic cells
improve the prognosis of patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma.
Pancreas. 28:e26–e31. 2004.
|
|
35
|
Gallimore A and Sakaguchi S: Regulation of
tumour immunity by CD25+T cells. Immunology. 107:5–9.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Morse MA, Hobeika AC, Osada T, et al:
Depletion of human regulatory T cells specifically enhances
antigen-specific immune responses to cancer vaccines. Blood.
112:610–618. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Onizuka S, Tawara I, Shimizu J, Sakaguchi
S, Fujita T and Nakayama E: Tumor rejection by in vivo
administration of anti-CD25 (interleukin-2 receptor alpha)
monoclonal antibody. Cancer Res. 59:3128–3133. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sutmuller RP, van Duivenvoorde LM, van
Elsas A, et al: Synergism of cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated
antigen 4 blockade and depletion of CD25+regulatory T
cells in antitumor therapy reveals alternative pathways for
suppression of autoreactive cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses. J Exp
Med. 194:823–832. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ko K, Yamazaki S, Nakamura K, et al:
Treatment of advanced tumors with agonistic anti-GITR mAb and its
effects on tumor-infiltrating
Foxp3+CD25+CD4+regulatory T cells.
J Exp Med. 202:885–891. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yamaguchi T, Hirota K, Nagahama K, et al:
Control of immune responses by antigen-specific regulatory T cells
expressing the folate receptor. Immunity. 27:145–159. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Nair S, Boczkowski D, Fassnacht M,
Pisetsky D and Gilboa E: Vaccination against the forkhead family
transcription factor Foxp3 enhances tumor immunity. Cancer
research. 67:371–380. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|