|
1
|
Raza A, Gezer S, Mundle S, et al:
Apoptosis in bone marrow biopsy samples involving stromal and
hematopoietic cells in 50 patients with myelodysplastic syndromes.
Blood. 86:268–276. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cogle CR, Craig BM, Rollison DE and List
AF: Incidence of the myelodysplastic syndromes using a novel
claims-based algorithm: high number of uncaptured cases by cancer
registries. Blood. 117:7121–7125. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Tong H, Hu C, Yin X, Yu M, Yang J and Jin
J: A meta-analysis of the relationship between cigarette smoking
and incidence of myelodysplastic syndromes. PLoS One. 8:e675372013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ma X: Epidemiology of myelodysplastic
syndromes. Am J Med. 125(Suppl 7): S2–S5. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Boffetta P and Hashibe M: Alcohol and
cancer. Lancet Oncol. 7:149–156. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Danaei G, Vander Hoorn S, Lopez AD, Murray
CJ and Ezzati M; Comparative Risk Assessment collaborating group
(Cancers). Causes of cancer in the world: comparative risk
assessment of nine behavioural and environmental risk factors.
Lancet. 366:1784–1793. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
de Menezes RF, Bergmann A and Thuler LC:
Alcohol consumption and risk of cancer: a systematic literature
review. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:4965–4972. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pekmezovic T, Suvajdzic Vukovic N, Kisic
D, et al: A case-control study of myelodysplastic syndromes in
Belgrade (Serbia Montenegro). Ann Hematol. 85:514–519. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ido M, Nagata C, Kawakami N, et al: A
case-control study of myelodysplastic syndromes among Japanese men
and women. Leuk Res. 20:727–731. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lv L, Lin G, Gao X, et al: Case-control
study of risk factors of myelodysplastic syndromes according to
World Health Organization classification in a Chinese population.
Am J Hematol. 86:163–169. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Strom SS, Gu Y, Gruschkus SK, Pierce SA
and Estey EH: Risk factors of myelodysplastic syndromes: a
case-control study. Leukemia. 19:1912–1918. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dalamaga M, Petridou E, Cook FE and
Trichopoulos D: Risk factors for myelodysplastic syndromes: a
case-control study in Greece. Cancer Causes Control. 13:603–608.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nagata C, Shimizu H, Hirashima K, et al:
Hair dye use and occupational exposure to organic solvents as risk
factors for myelodysplastic syndrome. Leuk Res. 23:57–62. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Brown LM, Gibson R, Burmeister LF, Schuman
LM, Everett GD and Blair A: Alcohol consumption and risk of
leukemia, non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, and multiple myeloma. Leuk Res.
16:979–984. 1992.
|
|
15
|
Crane MM and Keating MJ: Exposure
histories in acute nonlymphocytic leukemia patients with a prior
preleukemic condition. Cancer. 67:2211–2214. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ma X, Lim U, Park Y, et al: Obesity,
lifestyle factors, and risk of myelodysplastic syndromes in a large
US cohort. Am J Epidemiol. 169:1492–1499. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang J and Yu KF: What’s the relative
risk? A method of correcting the odds ratio in cohort studies of
common outcomes. JAMA. 280:1690–1691. 1998.
|
|
18
|
Hu ZH, Lin YW, Xu X, et al: No association
between tea consumption and risk of renal cell carcinoma: a
meta-analysis of epidemiological studies. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
14:1691–1695. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wells GA, Shea B, O’Connell D, et al: The
Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of
nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp.
Accessed October, 19, 2009
|
|
20
|
Mantel N and Haenszel W: Statistical
aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of
disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 22:719–748. 1959.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
DerSimonian R and Laird N: Meta-analysis
in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 7:177–188. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
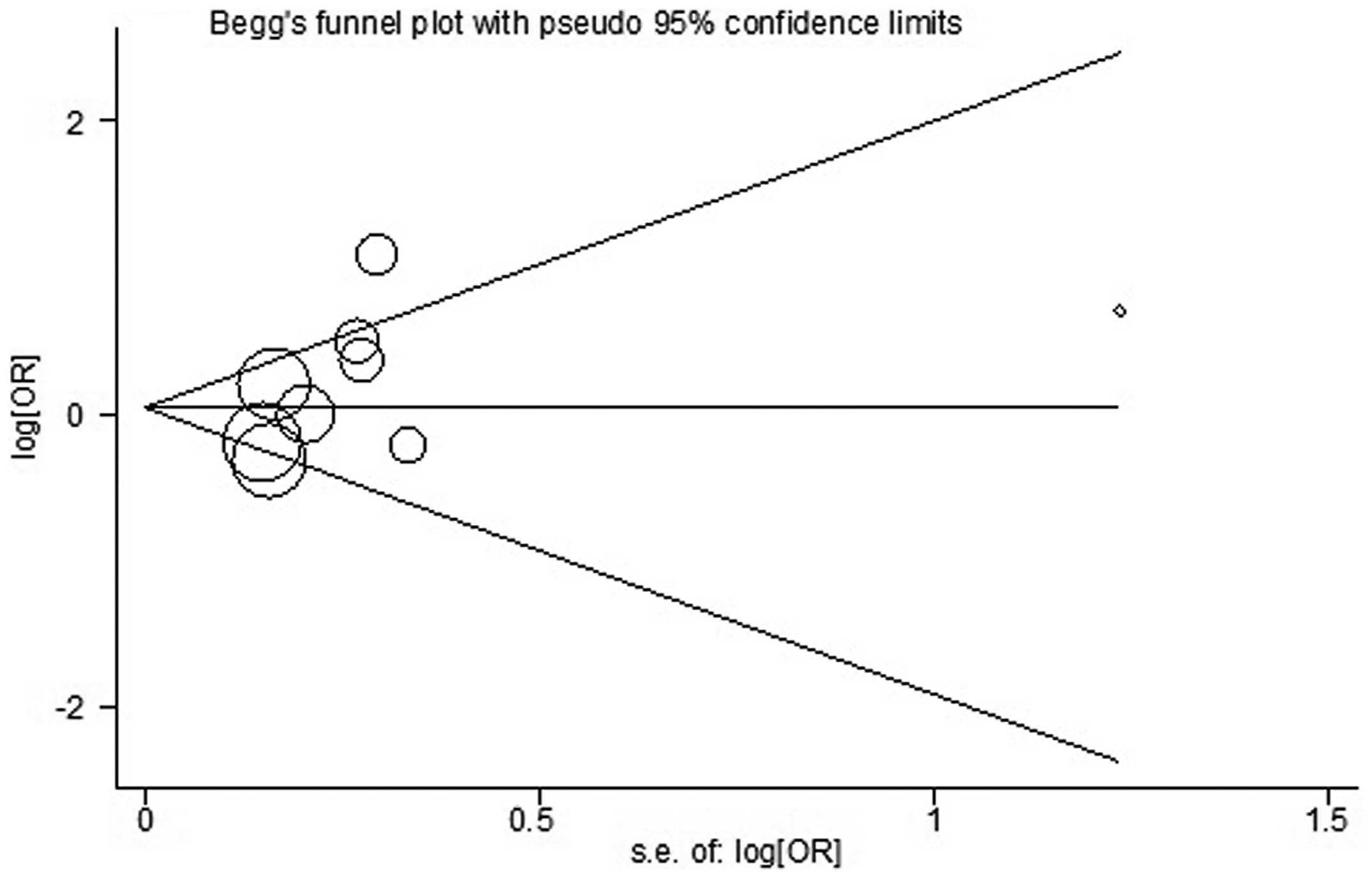
Begg CB and Mazumdar M: Operating
characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias.
Biometrics. 50:1088–1101. 1994. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M and
Minder C: Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical
test. BMJ. 315:629–634. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Newman K, Maness-Harris L, El-Hemaidi I
and Akhtari M: Revisiting use of growth factors in myelodysplastic
syndromes. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:1081–1091. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Casagrande G and Michot F: Alcohol-induced
bone marrow damage: status before and after a 4-week period of
abstinence from alcohol with or without disulfiram. A randomized
bone marrow study in alcohol-dependent individuals. Blut.
59:231–236. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Sunil Kumar KB, Ankathil R and Devi KS:
Chromosomal aberrations induced by methyl parathion in human
peripheral lymphocytes of alcoholics and smokers. Hum Exp Toxicol.
12:285–288. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Diaz LE, Montero A, Gonzalez-Gross M,
Vallejo AI, Romeo J and Marcos A: Influence of alcohol consumption
on immunological status: a review. Eur J Clin Nutr. 56(Suppl 3):
S50–S53. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gerhauser C: Beer constituents as
potential cancer chemopreventive agents. Eur J Cancer.
41:1941–1954. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tsan MF, White JE, Maheshwari JG and
Chikkappa G: Anti-leukemia effect of resveratrol. Leuk Lymphoma.
43:983–987. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Surh YJ, Hurh YJ, Kang JY, Lee E, Kong G
and Lee SJ: Resveratrol, an antioxidant present in red wine,
induces apoptosis in human promyelocytic leukemia (HL-60) cells.
Cancer Lett. 140:1–10. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Steensma DP: Are myelodysplastic syndromes
‘cancer’? Unexpected adverse consequences of linguistic ambiguity.
Leuk Res. 30:1227–1233. 2006.
|