|
1
|
Chung CJ, Huang CY, Pu YS, Shiue HS, Su CT
and Hsueh YM: The effect of cigarette smoke and arsenic exposure on
urothelial carcinoma risk is modified by glutathione S-transferase
M1 gene null genotype. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 266:254–259. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Milenkovic-Petronic D, Milojevic B, Djokic
M, Sipetic-Grujicic S, Milojevic IG, Bumbasirevic U and Dzamic Z:
The impact of tumor size on outcomes in patients with upper urinary
tract urothelial carcinoma. Int Urol Nephrol. 46:563–569. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tanaka N, Kikuchi E, Kanao K, et al: The
predictive value of positive urine cytology for outcomes following
radical nephroureterectomy in patients with primary upper tract
urothelial carcinoma: a multi-institutional study. Urol Oncol.
32(48): e19–26. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Peng Q, Mo C, Tang W, et al: DNA repair
gene XRCC3 polymorphisms and bladder cancer risk: a meta-analysis.
Tumour Biol. 35:1933–1944. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ross JS, Wang K, Al-Rohil RN, et al:
Advanced urothelial carcinoma: next-generation sequencing reveals
diverse genomic alterations and targets of therapy. Mod Pathol.
27:271–280. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Glatt H and Meinl W: Pharmacogenetics of
soluble sulfotransferases (SULTs). Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch
Pharmacol. 369:55–68. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ginsberg G, Guyton K, Johns D, et al:
Genetic polymorphism in metabolism and host defense enzymes:
implications for human health risk assessment. Crit Rev Toxicol.
40:575–619. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang YH, Juang GD, Hwang TI, et al:
Genetic polymorphism of sulfotransferase 1A1, cigarette smoking,
hazardous chemical exposure and urothelial cancer risk in a
Taiwanese population. Int J Urol. 15:1029–1034. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dooley TP, Obermoeller RD, Leiter EH, et
al: Mapping of the phenol sulfotransferase gene (STP) to human
chromosome 16p12.1-p11.2 and to mouse chromosome 7. Genomics.
18:440–443. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pereira WO, Paiva AS, Queiroz JW, et al:
Genetic polymorphism in the sulfotransferase SULT1A1 gene in
cancer. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 160:55–60. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Daniels J and Kadlubar S: Sulfotransferase
genetic variation: from cancer risk to treatment response. Drug
Metab Rev. 45:415–422. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chou HC, Lang NP and Kadlubar FF:
Metabolic activation of the N-hydroxy derivative of the carcinogen
4-aminobiphenyl by human tissue sulfotransferases. Carcinogenesis.
16:413–417. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Davey Smith G and Egger M: Meta-analyses
of randomised controlled trials. Lancet. 350(1182)1997.
|
|
14
|
Mantel N and Haenszel W: Statistical
aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of
disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 22:719–748. 1959.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
DerSimonian R and Laird N: Meta-analysis
in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 7:177–188. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
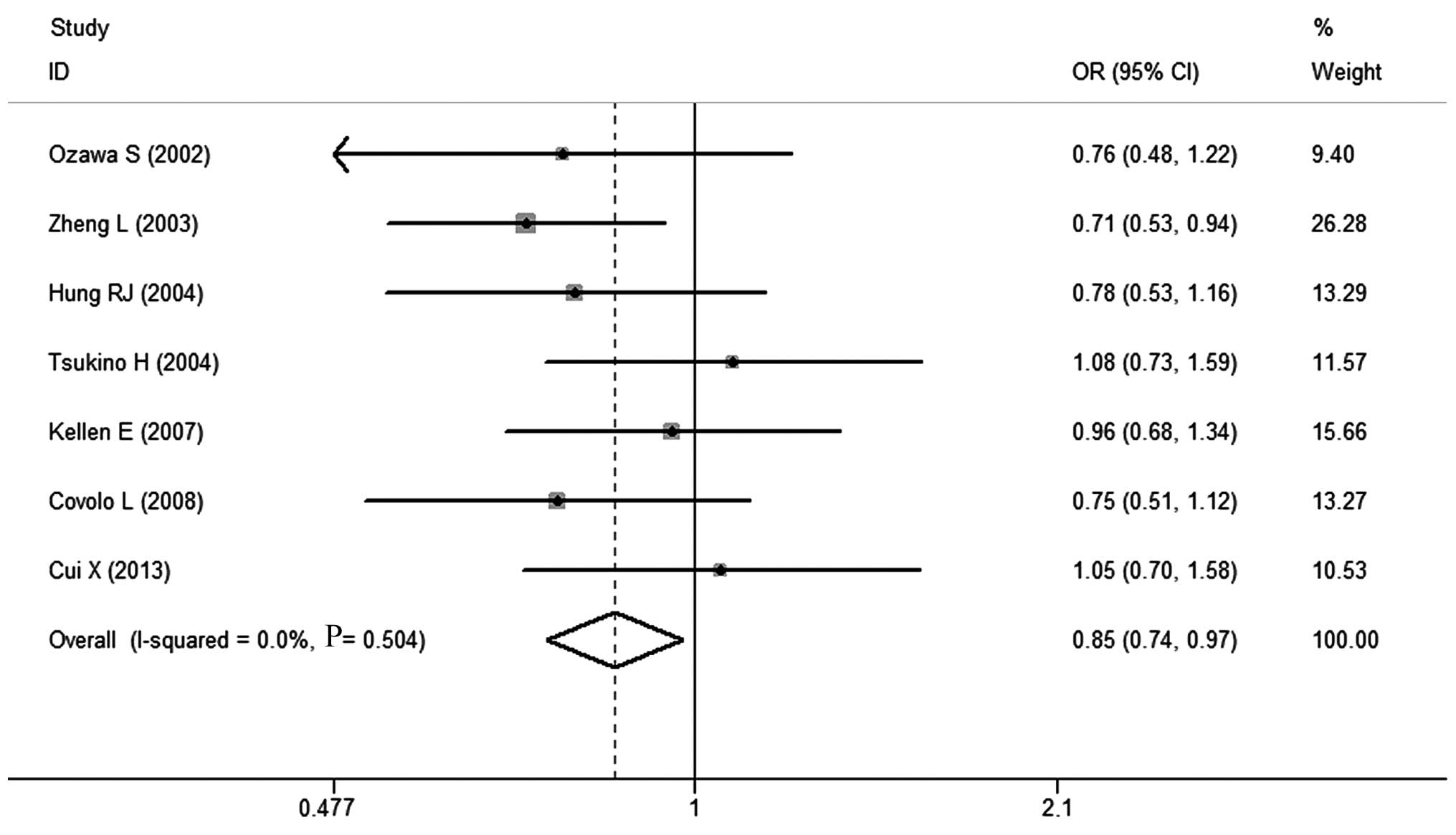
Ozawa S, Katoh T, Inatomi H, et al:
Association of genotypes of carcinogen-activating enzymes, phenol
sulfotransferase SULT1A1 (ST1A3) and arylamine N-acetyltransferase
NAT2, with urothelial cancer in a Japanese population. Int J
Cancer. 102:418–421. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Tsukino H, Kuroda Y, Nakao H, et al:
Cytochrome P450 (CYP) 1A2, sulfotransferase (SULT) 1A1, and
N-acetyltransferase (NAT) 2 polymorphisms and susceptibility to
urothelial cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 130:99–106. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rouprêt M, Cancel-Tassin G, Comperat E, et
al: Phenol sulfotransferase SULT1A1*2 allele and enhanced risk of
upper urinary tract urothelial cell carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 16:2500–2503. 2007.
|
|
19
|
Covolo L, Placidi D, Gelatti U, et al:
Bladder cancer, GSTs, NAT1, NAT2, SULT1A1, XRCC1, XRCC3, XPD
genetic polymorphisms and coffee consumption: a case-control study.
Eur J Epidemiol. 23:355–362. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kellen E, Zeegers M, Paulussen A, et al:
Does occupational exposure to PAHs, diesel and aromatic amines
interact with smoking and metabolic genetic polymorphisms to
increase the risk on bladder cancer?; The Belgian case control
study on bladder cancer risk. Cancer Lett. 245:51–60. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Hung RJ, Boffetta P, Brennan P, et al:
GST, NAT, SULT1A1, CYP1B1 genetic polymorphisms, interactions with
environmental exposures and bladder cancer risk in a high-risk
population. Int J Cancer. 110:598–604. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cui X, Lu X, Hiura M, et al: Association
of genotypes of carcinogen-metabolizing enzymes and smoking status
with bladder cancer in a Japanese population. Environ Health Prev
Med. 18:136–142. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zheng L, Wang Y, Schabath MB, Grossman HB
and Wu X: Sulfotransferase 1A1 (SULT1A1) polymorphism and bladder
cancer risk: a case-control study. Cancer Lett. 202:61–69. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu X, Kubota T, Dhakal I, et al: Copy
number variation in sulfotransferase isoform 1A1 (SULT1A1) is
significantly associated with enzymatic activity in Japanese
subjects. Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 6:19–24. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tengström M, Mannermaa A, Kosma VM,
Hirvonen A and Kataja V: SULT1A1 rs9282861 polymorphism - a
potential modifier of efficacy of the systemic adjuvant therapy in
breast cancer? BMC Cancer. 12:2572012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Coughtrie MW, Gilissen RA, Shek B, et al:
Phenol sulphotransferase SULT1A1 polymorphism: molecular diagnosis
and allele frequencies in Caucasian and African populations.
Biochem J. 337:45–49. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Munafò MR and Flint J: Meta-analysis of
genetic association studies. Trends Genet. 20:439–444.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Patel N, Arya M, Muneer A, et al:
Molecular aspects of upper tract urothelial carcinoma. Urol Oncol.
32(28): e11–20. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Catto JW, Azzouzi AR, Amira N, et al:
Distinct patterns of microsatellite instability are seen in tumours
of the urinary tract. Oncogene. 22:8699–8706. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Catto JW, Azzouzi AR, Rehman I, et al:
Promoter hypermethylation is associated with tumor location, stage,
and subsequent progression in transitional cell carcinoma. J Clin
Oncol. 23:2903–2910. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Roupret M, Catto J, Coulet F, et al:
Microsatellite instability as indicator of MSH2 gene mutation in
patients with upper urinary tract transitional cell carcinoma. J
Med Genet. 41:e912004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bermejo JL, Eng C and Hemminki K: Cancer
characteristics in Swedish families fulfilling criteria for
hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology.
129:1889–1899. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Green DA, Rink M, Xylinas E, et al:
Urothelial carcinoma of the bladder and the upper tract: disparate
twins. J Urol. 189:1214–1221. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liang FX, Bosland MC, Huang H, et al:
Cellular basis of urothelial squamous metaplasia: roles of lineage
heterogeneity and cell replacement. J Cell Biol. 171:835–844. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Klug SJ, Ressing M, Koenig J, et al: TP53
codon 72 polymorphism and cervical cancer: a pooled analysis of
individual data from 49 studies. Lancet Oncol. 10:772–784. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tyler A: Urothelial cancers: ureter, renal
pelvis, and bladder. Semin Oncol Nurs. 28:154–162. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Crivelli JJ, Xylinas E, Kluth LA, et al:
Effect of smoking on outcomes of urothelial carcinoma: a systematic
review of the literature. Eur Urol. 65:742–754. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|