|
1
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chau I, Norman AR, Cunningham D, Waters
JS, Oates J and Ross PJ: Multivariate prognostic factor analysis in
locally advanced and metastatic esophago-gastric cancer - pooled
analysis from three multicenter, randomized, controlled trials
using individual patient data. J Clin Oncol. 22:2395–2403. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yoshida K, Yasui W, Yokozaki H, et al: New
molecular prognostic markers in gastric carcinoma. Gan To Kagaku
Ryoho. 25:2021–2027. 1998.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Leung WK, Kim JJ, Kim JG, Graham DY and
Sepulveda AR: Microsatellite instability in gastric intestinal
metaplasia in patients with and without gastric cancer. Am J
Pathol. 156:537–543. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Arzimanoglou II, Gilbert F and Barber HR:
Microsatellite instability in human solid tumors. Cancer.
82:1808–1820. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
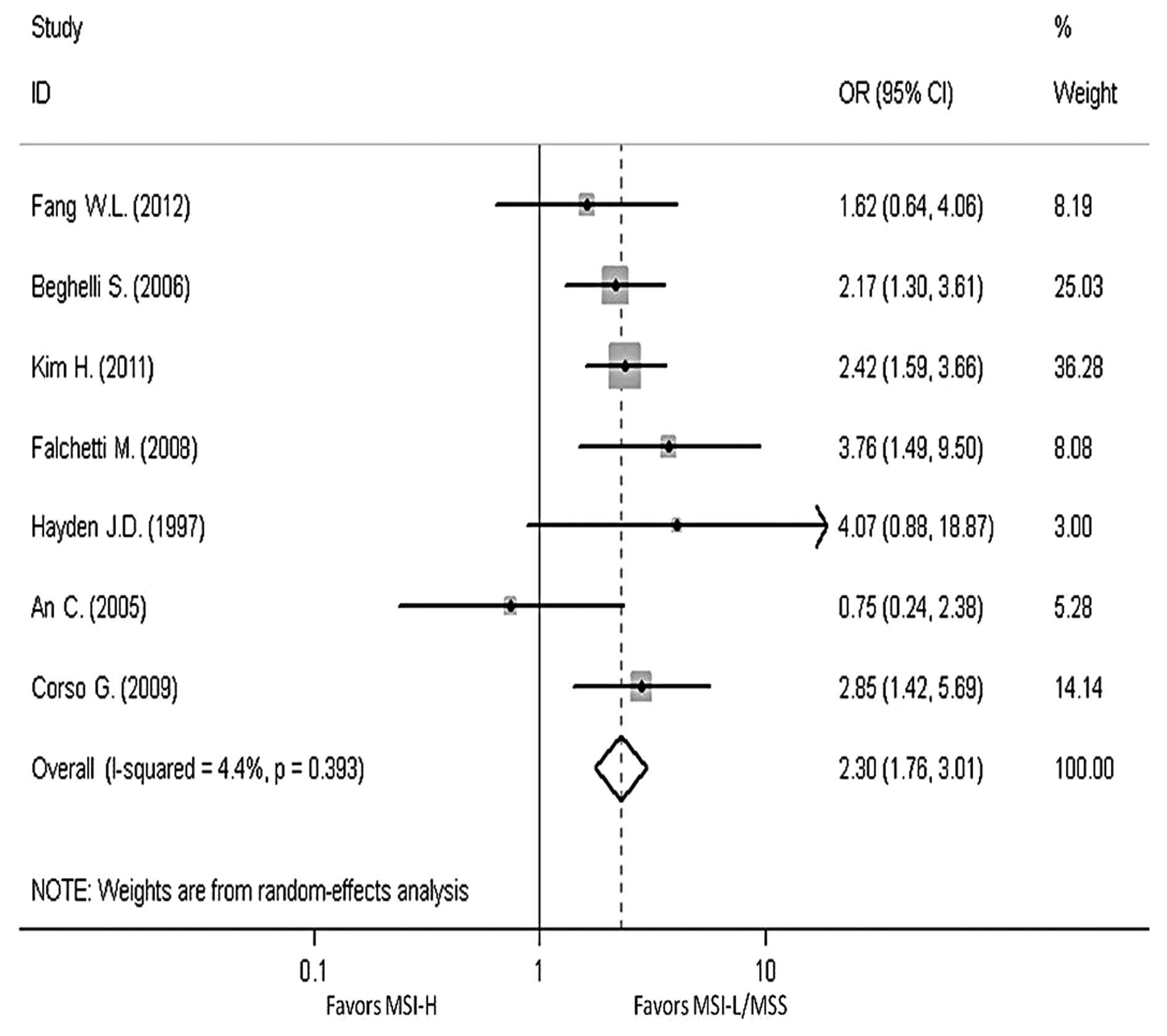
Fang WL, Chang SC, Lan YT, et al:
Microsatellite instability is associated with a better prognosis
for gastric cancer patients after curative surgery. World J Surg.
36:2131–2138. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Boland CR, Thibodeau SN, Hamilton SR, et
al: A National Cancer Institute Workshop on Microsatellite
Instability for cancer detection and familial predisposition:
development of international criteria for the determination of
microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res.
58:5248–5257. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shemirani AI, Haghighi MM, Zadeh SM, et
al: Simplified MSI marker panel for diagnosis of colorectal cancer.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 12:2101–2104. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Brennetot C, Buhard O, Jourdan F, Flejou
JF, Duval A and Hamelin R: Mononucleotide repeats BAT-26 and BAT-25
accurately detect MSI-H tumors and predict tumor content:
implications for population screening. Int J Cancer. 113:446–450.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Umar A, Boland CR, Terdiman JP, et al:
Revised Bethesda Guidelines for hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal
cancer (Lynch syndrome) and microsatellite instability. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 96:261–268. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Baudhuin LM, Burgart LJ, Leontovich O and
Thibodeau SN: Use of microsatellite instability and
immunohistochemistry testing for the identification of individuals
at risk for Lynch syndrome. Fam Cancer. 4:255–265. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Aaltonen LA, Peltomaki P, Leach FS, et al:
Clues to the pathogenesis of familial colorectal cancer. Science.
260:812–816. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Guastadisegni C, Colafranceschi M, Ottini
L and Dogliotti E: Microsatellite instability as a marker of
prognosis and response to therapy: a meta-analysis of colorectal
cancer survival data. Eur J Cancer. 46:2788–2798. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Paulson TG, Wright FA, Parker BA, Russack
V and Wahl GM: Microsatellite instability correlates with reduced
survival and poor disease prognosis in breast cancer. Cancer Res.
56:4021–4026. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Diaz-Padilla I, Romero N, Amir E, et al:
Mismatch repair status and clinical outcome in endometrial cancer:
a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
88:154–167. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Oki E, Kakeji Y, Zhao Y, et al:
Chemosensitivity and survival in gastric cancer patients with
microsatellite instability. Ann Surg Oncol. 16:2510–2515. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Seo HM, Chang YS, Joo SH, et al:
Clinicopathologic characteristics and outcomes of gastric cancers
with the MSI-H phenotype. J Surg Oncol. 99:143–147. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Corso G, Pedrazzani C, Marrelli D, Pascale
V, Pinto E and Roviello F: Correlation of microsatellite
instability at multiple loci with long-term survival in advanced
gastric carcinoma. Arch Surg. 144:722–727. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Falchetti M, Saieva C, Lupi R, et al:
Gastric cancer with high-level microsatellite instability: target
gene mutations, clinicopathologic features, and long-term survival.
Hum Pathol. 39:925–932. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim H, An JY, Noh SH, Shin SK, Lee YC and
Kim H: High microsatellite instability predicts good prognosis in
intestinal-type gastric cancers. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
26:585–592. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Beghelli S, de Manzoni G, Barbi S, et al:
Microsatellite instability in gastric cancer is associated with
better prognosis in only stage II cancers. Surgery. 139:347–356.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
An JY, Kim H, Cheong JH, Hyung WJ, Kim H
and Noh SH: Microsatellite instability in sporadic gastric cancer:
its prognostic role and guidance for 5-FU based chemotherapy after
R0 resection. Int J Cancer. 131:505–511. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
dos Santos NR, Seruca R, Constancia M,
Seixas M and Sobrinho-Simoes M: Microsatellite instability at
multiple loci in gastric carcinoma: clinicopathologic implications
and prognosis. Gastroenterology. 110:38–44. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hayden JD, Cawkwell L, Quirke P, et al:
Prognostic significance of microsatellite instability in patients
with gastric carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 33:2342–2346. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chiaravalli AM, Feltri M, Bertolini V, et
al: Intratumour T cells, their activation status and survival in
gastric carcinomas characterised for microsatellite instability and
Epstein-Barr virus infection. Virchows Arch. 448:344–353. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Perez RO, Jacob CE, D'Ottaviano FL, et al:
Microsatellite instability in solitary and sporadic gastric cancer.
Rev Hosp Clin Fac Med Sao Paulo. 59:279–285. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wirtz HC, Muller W, Noguchi T, et al:
Prognostic value and clinicopathological profile of microsatellite
instability in gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 4:1749–1754.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
An C, Choi IS, Yao JC, et al: Prognostic
significance of CpG island methylator phenotype and microsatellite
instability in gastric carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 11:656–663.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Stang A: Critical evaluation of the
Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of
nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol.
25:603–605. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Parmar MK, Torri V and Stewart L:
Extracting summary statistics to perform meta-analyses of the
published literature for survival endpoints. Stat Med.
17:2815–2834. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chiaravalli AM, Cornaggia M, Furlan D, et
al: The role of histological investigation in prognostic evaluation
of advanced gastric cancer. Analysis of histological structure and
molecular changes compared with invasive pattern and stage.
Virchows Arch. 439:158–169. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Carethers JM, Smith EJ, Behling CA, et al:
Use of 5-fluorouracil and survival in patients with
microsatellite-unstable colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology.
126:394–401. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Grogg KL, Lohse CM, Pankratz VS, Halling
KC and Smyrk TC: Lymphocyte-rich gastric cancer: associations with
Epstein-Barr virus, microsatellite instability, histology, and
survival. Mod Pathol. 16:641–651. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fang WL, Chang SC, Lan YT, et al:
Molecular and survival differences between familial and sporadic
gastric cancers. Biomed Res Int. 2013:3962722013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|