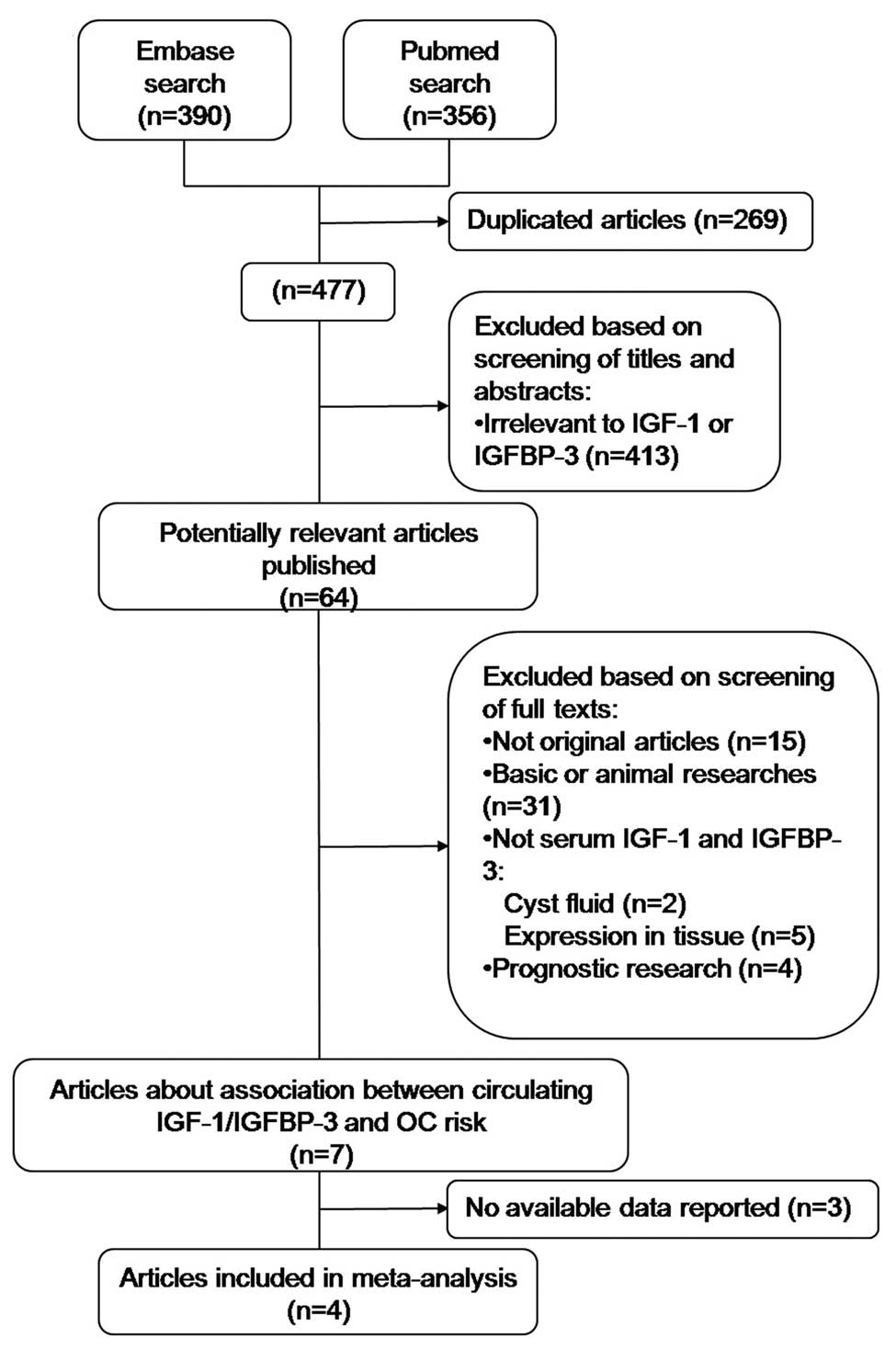
|
1
|
King ER and Wong KK: Insulin-like growth
factor: current concepts and new developments in cancer therapy.
Recent Patents Anticancer Drug Discov. 7:14–30. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Adams TE, Epa VC, Garrett TP and Ward CW:
Structure and function of the type 1 insulin-like growth factor
receptor. Cell Mol Life Sci. 57:1050–1093. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jones JI and Clemmons DR: Insulin-like
growth factors and their binding proteins: biological actions.
Endocr Rev. 16:3–34. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Khandwala HM, McCutcheon IE, Flyvbjerg A
and Friend KE: The effects of insulin-like growth factors on
tumorigenesis and neoplastic growth. Endocr Rev. 21:215–244. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Renehan AG, Zwahlen M, Minder C, O'Dwyer
ST, Shalet SM and Egger M: Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF
binding protein-3 and cancer risk: systematic review, and
meta-regression analysis. Lancet. 363:1346–1353. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Toniolo P, Bruning PF, Akhmedkhanov A, et
al: Serum insulin-like growth factor-I and breast cancer. Int J
Cancer. 88:828–832. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Stattin P, Bylund A, Rinaldi S, et al:
Plasma insulin-like growth factor-I, insulin-like growth
factor-binding proteins, and prostate cancer risk: a prospective
study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 92:1910–1917. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chan JM, Stampfer MJ, Giovannucci E, et
al: Plasma insulin-like growth factor-I and prostate cancer risk: a
prospective study. Science. 279:563–566. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Palmqvist R, Hallmans G, Rinaldi S, et al:
Plasma insulin-like growth factor 1, insulin-like growth factor
binding protein 3, and risk of colorectal cancer: a prospective
study in northern Sweden. Gut. 50:642–646. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Peeters PH, Lukanova A, Allen N, et al:
Serum IGF-I, its major binding protein (IGFBP-3) and epithelial
ovarian cancer risk: the European Prospective Investigation into
Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC). Endocr Relat Cancer. 14:81–90. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lukanova A, Lundin E, Toniolo P, et al:
Circulating levels of insulin-like growth factor-I and risk of
ovarian cancer. Int J Cancer. 101:549–554. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tworoger SS, Lee IM, Buring JE, Pollak MN
and Hankinson SE: Insulin-like growth factors and ovarian cancer
risk: a nested case-control study in three cohorts. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 16:1691–1695. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, et al:
Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal
for reporting. Meta-analysis Of Observational Studies in
Epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA. 283:2008–2012. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Stang A: Critical evaluation of the
Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of
nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol.
25:603–605. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
DerSimonian R and Laird N: Meta-analysis
in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 7:177–188. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Greenland S and Longnecker MP: Methods for
trend estimation from summarized dose-response data, with
applications to meta-analysis. Am J Epidemiol. 135:1301–1309.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Thompson SG and Sharp SJ: Explaining
heterogeneity in meta-analysis: a comparison of methods. Stat Med.
18:2693–2708. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M and
Minder C: Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical
test. BMJ. 315:629–634. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dal Maso L, Augustin LS, Franceschi S, et
al: Association between components of the insulin-like growth
factor system and epithelial ovarian cancer risk. Oncology.
67:225–230. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fox EM, Miller TW, Balko JM, et al: A
kinome-wide screen identifies the insulin/IGF-I receptor pathway as
a mechanism of escape from hormone dependence in breast cancer.
Cancer Res. 71:6773–6784. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Suikkari AM, Tiitinen A, Stenman UH,
Seppala M and Laatikainen T: Oral contraceptives increase
insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 concentration in women
with polycystic ovarian disease. Fertil Steril. 55:895–899.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tas F, Karabulut S, Serilmez M, Ciftci R
and Duranyildiz D: Clinical significance of serum insulin-like
growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and insulin-like growth factor binding
protein-3 (IGFBP-3) in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer.
Tumour Biol. 35:3125–3132. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dursun P, Gultekin M and Esin S:
Preoperative serum IGF-1 and IGFBP-3 levels in patients with
ovarian carcinoma: preliminary results. Int J Gynecol Cancer.
14:105–106. 2004.
|
|
24
|
Serin IS, Tanriverdi F, Yilmaz MO, Ozcelik
B and Unluhizarci K: Serum insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF
binding protein (IGFBP)-3, leptin concentrations and insulin
resistance in benign and malignant epithelial ovarian tumors in
postmenopausal women. Gynecol Endocrinol. 24:117–121. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
El-Roeiy A, Chen X, Roberts VJ, et al:
Expression of the genes encoding the insulin-like growth factors
(IGF-I and II), the IGF and insulin receptors, and IGF-binding
proteins-1–6 and the localization of their gene products in normal
and polycystic ovary syndrome ovaries. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
78:1488–1496. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Flyvbjerg A, Mogensen O, Mogensen B and
Nielsen OS: Elevated serum insulin-like growth factor-binding
protein 2 (IGFBP-2) and decreased IGFBP-3 in epithelial ovarian
cancer: correlation with cancer antigen 125 and tumor-associated
trypsin inhibitor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 82:2308–2313. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|