|
1
|
Estey EH: Acute myeloid leukemia: 2012
update on diagnosis, risk stratification, and management. Am J
Hematol. 87:89–99. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shen Y, Zhu YM, Fan X, et al: Gene
mutation patterns and their prognostic impact in a cohort of 1185
patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 118:5593–5603. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mrozek K, Marcucci G, Paschka P, Whitman
SP and Bloomfield CD: Clinical relevance of mutations and
gene-expression changes in adult acute myeloid leukemia with normal
cytogenetics: are we ready for a prognostically prioritized
molecular classification? Blood? Blood. 109:431–448. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Scholl S, Fricke HJ, Sayer HG and Hoffken
K: Clinical implications of molecular genetic aberrations in acute
myeloid leukemia. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 135:491–505. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Baldus CD, Tanner SM, Kusewitt DF, et al:
BAALC, a novel marker of human hematopoietic progenitor cells. Exp
Hematol. 31:1051–1056. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tanner SM, Austin JL, Leone G, et al:
BAALC, the human member of a novel mammalian neuroectoderm gene
lineage, is implicated in hematopoiesis and acute leukemia. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:13901–13906. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tierney JF, Stewart LA, Ghersi D, Burdett
S and Sydes MR: Practical methods for incorporating summary
time-to-event data into meta-analysis. Trials. 8:162007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Weber S, Alpermann T, Dicker F, et al:
BAALC expression: a suitable marker for prognostic risk
stratification and detection of residual disease in cytogenetically
normal acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Cancer J. 4:e1732014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
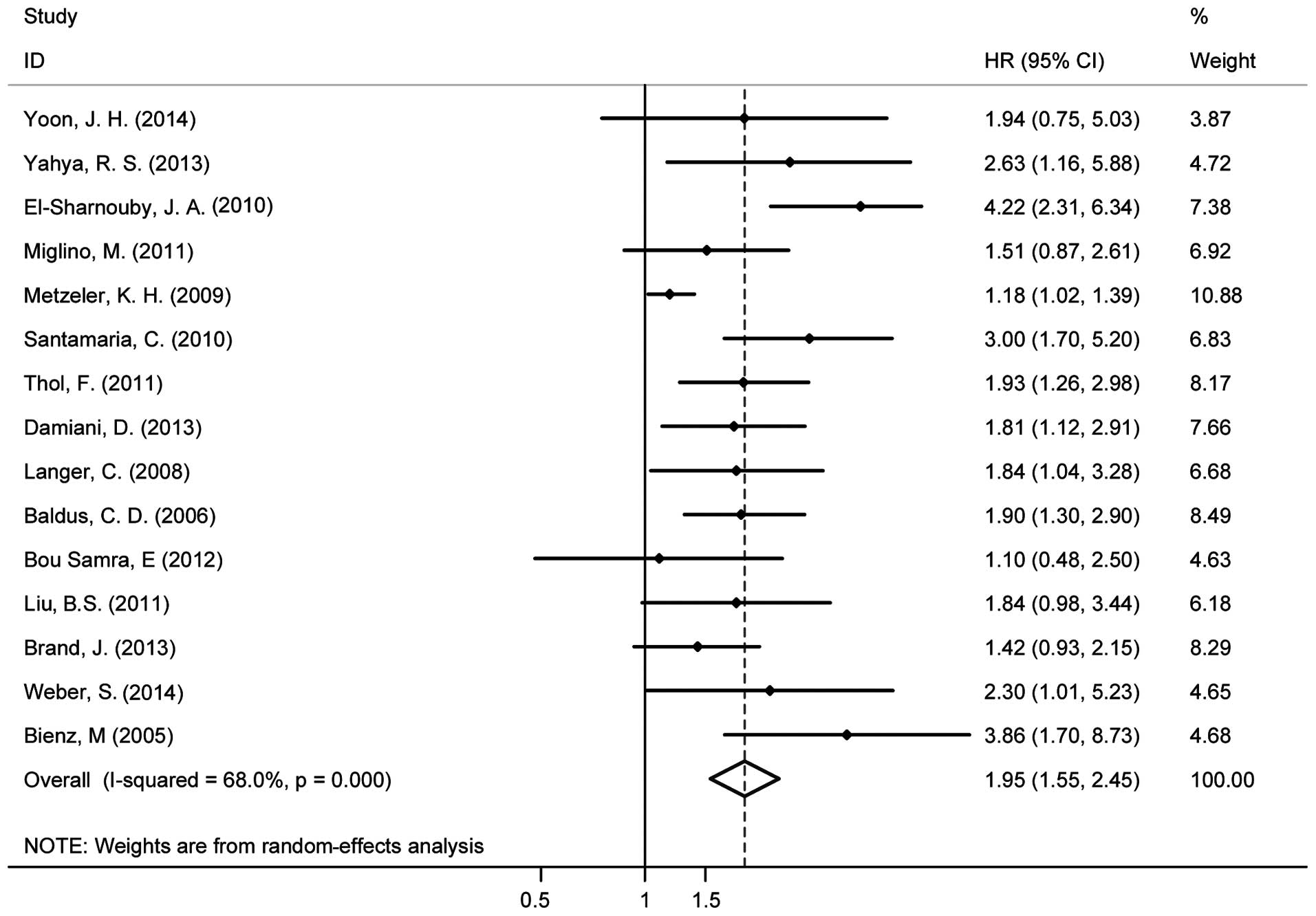
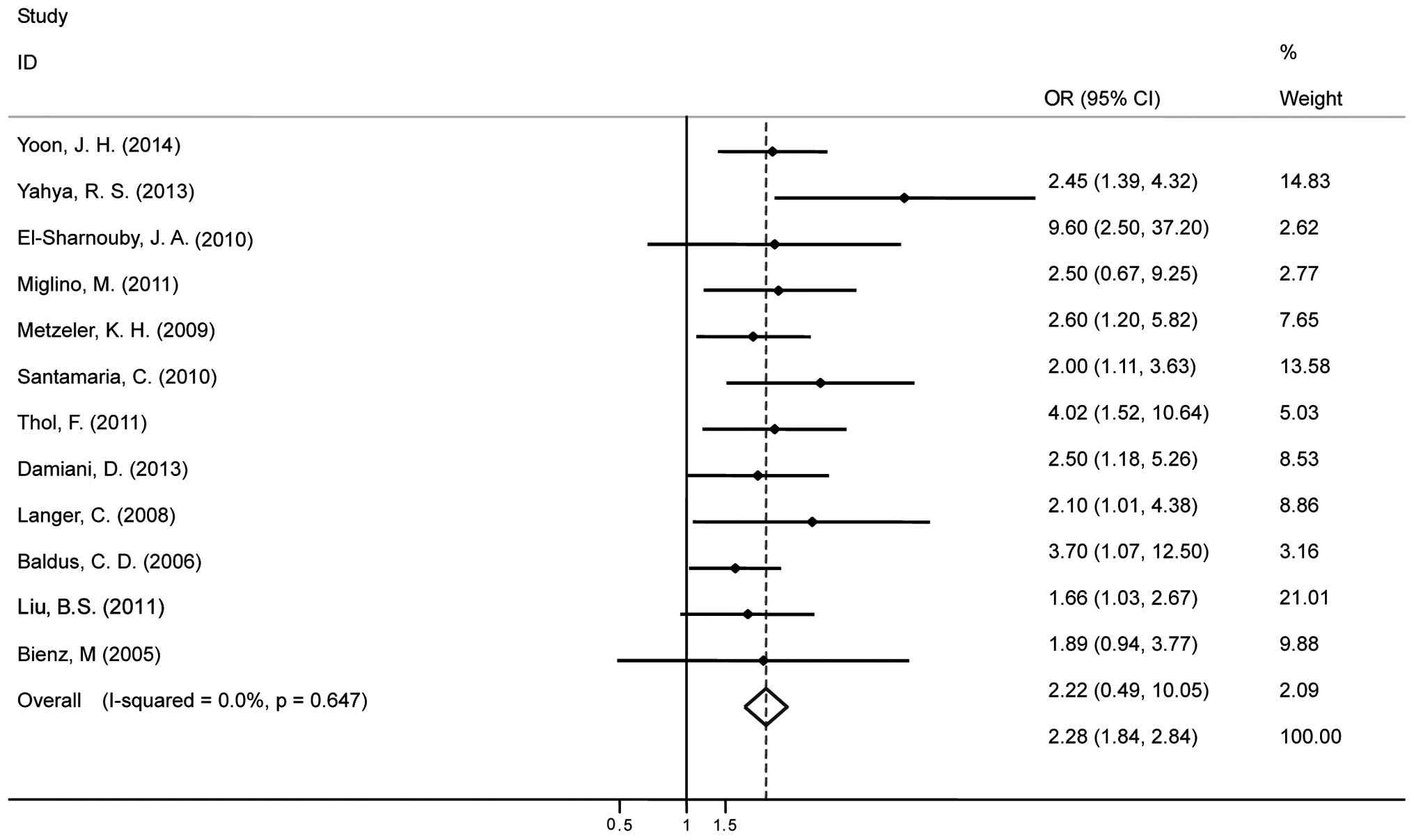
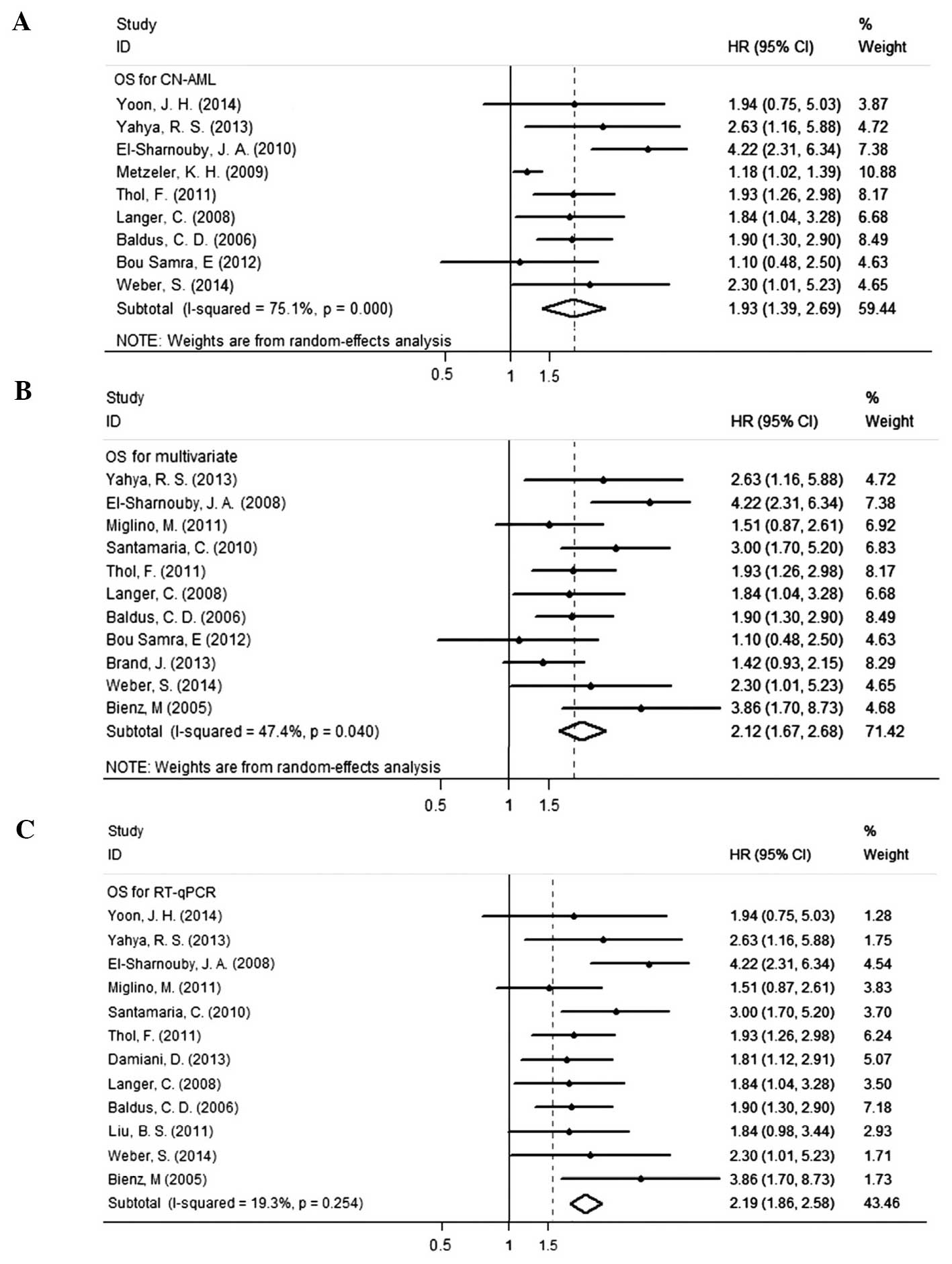
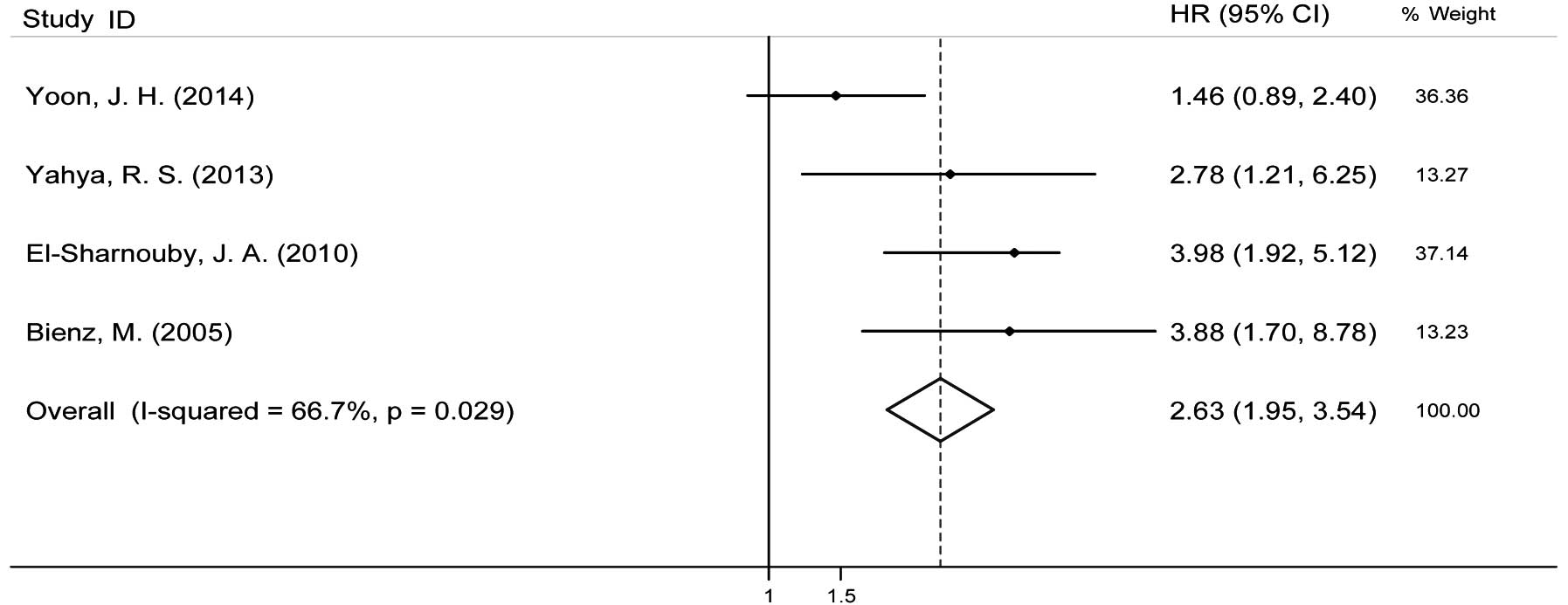
Yoon JH, Kim HJ, Shin SH, et al:
Implication of higher BAALC expression in combination with other
gene mutations in adult cytogenetically normal acute myeloid
leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 55:110–120. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yahya RS, Sofan MA, Abdelmasseih HM, Saudy
N and Sharaf-Eldein MA: Prognostic implication of BAALC gene
expression in adult acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Lab. 59:621–628.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Damiani D, Tiribelli M, Franzoni A, et al:
BAALC overexpression retains its negative prognostic role across
all cytogenetic risk groups in acute myeloid leukemia patients. Am
J Hematol. 88:848–852. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Brand J, van Vliet MH, de Best L, et al: A
standardized microarray assay for the independent gene expression
markers in AML: EVI1 and BAALC. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2:72013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bou Samra E, Klein B, Commes T and Moreaux
J: Development of gene expression-based risk score in
cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia patients. Oncotarget.
3:824–832. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Thol F, Damm F, Ludeking A, et al:
Incidence and prognostic influence of DNMT3A mutations in acute
myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 29:2889–2896. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu BS, Guo XT, Zha J, et al: Simultaneous
detection of MDR1 and BAALC gene expression in acute myeloid
leukemias and its clinical implication. Chin J Cancer Prev Treat.
18:1691–1695. 2011.
|
|
16
|
Rockova V, Abbas S, Wouters BJ, et al:
Risk stratification of intermediate-risk acute myeloid leukemia:
integrative analysis of a multitude of gene mutation and gene
expression markers. Blood. 118:1069–1076. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Miglino M, Colombo N, Pica G, et al: WT1
overexpression at diagnosis may predict favorable outcome in
patients with de novo non-M3 acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma.
52:1961–1969. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Santamaria C, Chillon MC, Garcia-Sanz R,
et al: BAALC is an important predictor of refractoriness to
chemotherapy and poor survival in intermediate-risk acute myeloid
leukemia (AML). Ann Hematol. 89:453–458. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
El-Sharnouby JA, Ahmed LM, Taha AM and
Kamal O: Prognostic significance of CEBPA mutations and BAALC
expression in acute myeloid leukemia Egyptian patients with normal
karyotype. Egypt J Immunol. 15:131–143. 2010.
|
|
20
|
Metzeler KH, Dufour A, Benthaus T, et al:
ERG expression is an independent prognostic factor and allows
refined risk stratification in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid
leukemia: a comprehensive analysis of ERG, MN1, and BAALC
transcript levels using oligonucleotide microarrays. J Clin Oncol.
27:5031–5038. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Langer C, Radmacher MD, Ruppert AS, et al:
High BAALC expression associates with other molecular prognostic
markers, poor outcome, and a distinct gene-expression signature in
cytogenetically normal patients younger than 60 years with acute
myeloid leukemia: a Cancer and Leukemia Group B (CALGB) study.
Blood. 111:5371–5379. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Baldus CD, Thiede C, Soucek S, Bloomfield
CD, Thiel E and Ehninger G: BAALC expression and FLT3 internal
tandem duplication mutations in acute myeloid leukemia patients
with normal cytogenetics: prognostic implications. J Clin Oncol.
24:790–797. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bienz M, Ludwig M, Leibundgut EO, et al:
Risk assessment in patients with acute myeloid leukemia and a
normal karyotype. Clin Cancer Res. 11:1416–1424. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sabattini E, Bacci F, Sagramoso C and
Pileri SA: WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and
lymphoid tissues in 2008: an overview. Pathologica. 102:83–87.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dohner H, Estey EH, Amadori S, et al:
Diagnosis and management of acute myeloid leukemia in adults:
recommendations from an international expert panel, on behalf of
the European LeukemiaNet. Blood. 115:453–474. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schlenk RF, Dohner K, Krauter J, et al:
Mutations and treatment outcome in cytogenetically normal acute
myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 358:1909–1918. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Patel JP, Gonen M, Figueroa ME, et al:
Prognostic relevance of integrated genetic profiling in acute
myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 366:1079–1089. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Port M, Bottcher M, Thol F, et al:
Prognostic significance of FLT3 internal tandem duplication,
nucleophosmin 1 and CEBPA gene mutations for acute myeloid leukemia
patients with normal karyotype, and younger than 60 years: a
systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Hematol. 93:1279–1286.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Damm F, Heuser M, Morgan M, et al:
Integrative prognostic risk score in acute myeloid leukemia with
normal karyotype. Blood. 117:4561–4568. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xu B, Chen G, Shi P, et al: shRNA-mediated
BAALC knockdown affects proliferation and apoptosis in human acute
myeloid leukemia cells. Hematology. 17:35–40. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Heuser M, Berg T, Kuchenbauer F, et al:
Functional role of BAALC in leukemogenesis. Leukemia. 26:532–536.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Franzoni A, Passon N, Fabbro D, Tiribelli
M, Damiani D and Damante G: Histone post-translational
modifications associated to BAALC expression in leukemic cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 417:721–725. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Heesch S, Bartram I, Neumann M, et al:
Expression of IGFBP7 in acute leukemia is regulated by DNA
methylation. Cancer Sci. 102:253–259. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Eisfeld AK, Marcucci G, Liyanarachchi S,
et al: Heritable polymorphism predisposes to high BAALC expression
in acute myeloid leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:6668–6673.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|