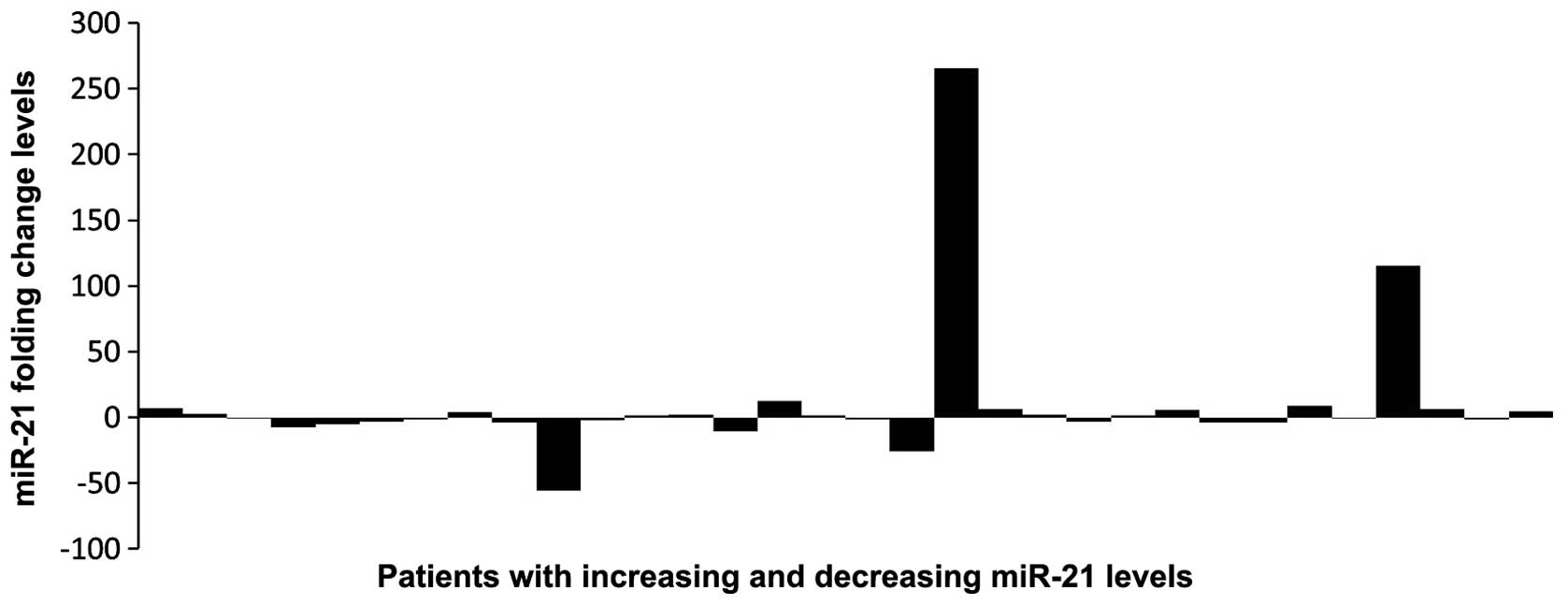
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chuthapisith S, Permsapaya W, Warnnissorn
M, Akewanlop C, Sirivatanauksorn V and Prasarttong Osoth P: Breast
cancer subtypes identified by the ER, PR and HER-2 status in Thai
women. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:459–462. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fu SW, Chen L and Man YG: miRNA biomarkers
in breast cancer detection and management. J Cancer. 2:116–122.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Salter KH, Acharya CR, Walters KS, et al:
An intergrated approach to the prediction of chemotherapeutic
response in patients with breast cancer. PLoS One. 3:e19082008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Miller TE, Ghoshal K, Ramaswamy B, Roy S,
Datta J, Shapiro CL, Jacob S and Majumder S: MicroRNA-221/222
confers tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer by targeting p27Kip1.
J Biol Chem. 283:29897–29903. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cortez MA, Welsh JW and Calin GA:
Circulating microRNAs as noninvasive biomarkers in breast cancer.
Recent Results Cancer Res. 195:151–161. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yan LX, Huang XF, Shao Q, Huang MY, Deng
L, Wu QL, Zeng YX and Shao JY: MicroRNA miR-21 overexpression in
human breast cancer is associated with advanced clinical stage,
lymph node metastasis and patient poor prognosis. RNA.
14:2348–2360. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen J, Wang BC and Tang JH: Clinical
significance of microRNA-155 expression in human breast cancer. J
Surg Oncol. 106:260–266. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ng EK, Li R, Shin VY, et al: Circulating
microRNAs as specific biomarkers for breast cancer detection. PLoS
One. 8:e531412013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Leon SA, Shapiro B, Sklaroff DM and Yaros
MJ: Free DNA in the serum of cancer patients and the effect of
therapy. Cancer Res. 37:646–650. 1977.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sun F, Fu H, Liu Q, Tie Y, Zhu J, Xing R,
Sun Z and Zheng X: Downregulation of CCND1 and CDK6 by miR-34a
induces cell cycle arrest. FEBS Lett. 582:1564–1568. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Welch C, Chen Y and Stallings RL:
MicroRNA-34a functions as a potential tumor suppressor by inducing
apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells. Oncogene. 26:5017–5022. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sachdeva M, Zhu S, Wu F, Wu H, Walia V,
Kumar S, Elble R, Watabe K and Mo YY: p53 represses c-Myc through
induction of the tumor suppressor miR-145. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
106:3207–3212. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lei P, Xie J, Wang L, Yang X, Dai Z and Hu
Y: microRNA-145 inhibits osteosarcoma cell proliferation and
invasion by targeting ROCK1. Mol Med Rep. 10:155–160.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Song B, Wang C, Liu J, Wang X, Lv L, Wei
L, Xie L, Zheng Y and Song X: MicroRNA-21 regulates breast cancer
invasion partly by targeting tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase
3 expression. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 29:292010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nair VS, Maeda LS and Ioannidis JP:
Clinical outcome prediction by microRNAs in human cancer: A
systematic review. J Natl Cancer Inst. 104:528–540. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Frankel LB, Christoffersen NR, Jacobsen A,
Lindow M, Krogh A and Lund AH: Programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) is
an important functional target of the microRNA miR-21 in breast
cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 283:1026–1033. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Qi L, Bart J, Tan LP, Platteel I, Sluis T,
Huitema S, Harms G, Fu L, Hollema H and Berg A: Expression of
miR-21 and its targets (PTEN, PDCD4, TM1) in flat epithelial atypia
of the breast in relation to ductal carcinoma in situ and invasive
carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 9:1632009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhu S, Wu H, Wu F, Nie D, Sheng S and Mo
YY: MicroRNA-21 targets tumor suppressor genes in invasion and
metastasis. Cell Res. 18:350–359. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Le Bot N: MicroRNAs in angiogenesis. Nat
Cell Biol. 14:3422012. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Han X, Yan S, Weijie Z, Feng W, Liuxing W,
Mengquan L and Qingxia F: Critical role of miR-10b in transforming
growth factor-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
breast cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 21:60–67. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J and Weinberg RA:
Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast
cancer. Nature. 449:682–688. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Heneghan HM, Miller N, Lowery AJ, Sweeney
KJ, Newell J and Kerin MJ: Circulating microRNAs as novel minimally
invasive biomarkers for breast cancer. Ann Surg. 251:499–505. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, et al:
MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer.
Cancer Res. 65:7065–7070. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Si ML, Zhu S, Wu H, Lu Z, Wu F and Mo YY:
miR-21-mediated tumor growth. Oncogene. 26:2799–2803. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shibuya H, Iinuma H, Shimada R, Horiuchi A
and Watanabe T: Clinicopathological and prognostic value of
microRNA-21 and microRNA-155 in colorectal cancer. Oncology.
79:313–320. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Akagi I, Miyashita M, Ishibashi O, Mishima
T, Kikuchi K, Makino H, Nomura T, Hagiwara N, Uchida E and Takizawa
T: Relationship between altered expression levels of MIR21, MIR143,
MIR145 and MIR205 and clinicopathologic features of esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Dis Esophagus. 24:523–530. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kliese N, Gobrecht P, Pachow D, et al:
miRNA-145 is downregulated in atypical and anaplastic meningiomas
and negatively regulates motility and proliferation of meningioma
cells. Oncogene. 32:4712–4720. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ren D, Wang M, Guo W, Zhao X, Tu X, Huang
S, Zou X and Peng X: Wild-type p53 suppresses the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stemness in PC-3 prostate
cancer cells by modulating miR-145. Int J Oncol. 42:1473–1481.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|